
How to Use sound card: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with sound card in Cirkit Designer
Design with sound card in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A sound card is an internal hardware component that enables a computer to process audio data. It serves as the interface between the computer and audio devices, such as speakers, headphones, and microphones. The sound card converts digital audio signals into analog signals for playback and can also capture analog audio signals from microphones, converting them into digital data for processing or storage.
Explore Projects Built with sound card
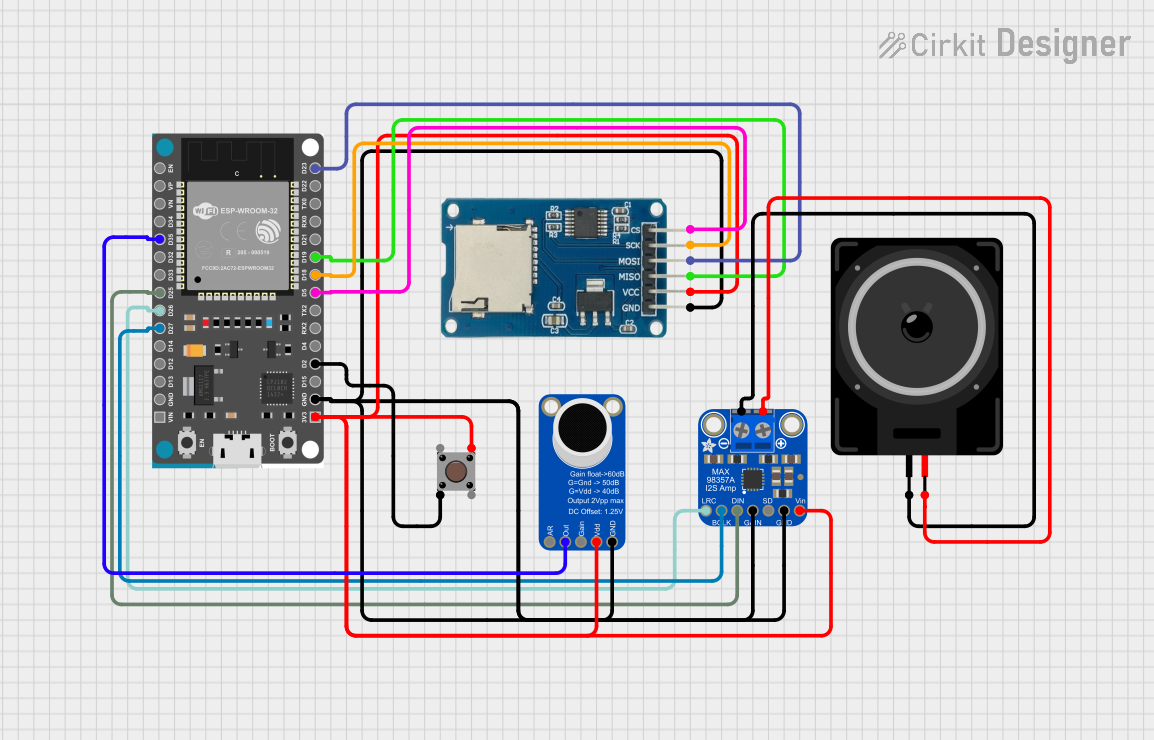
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer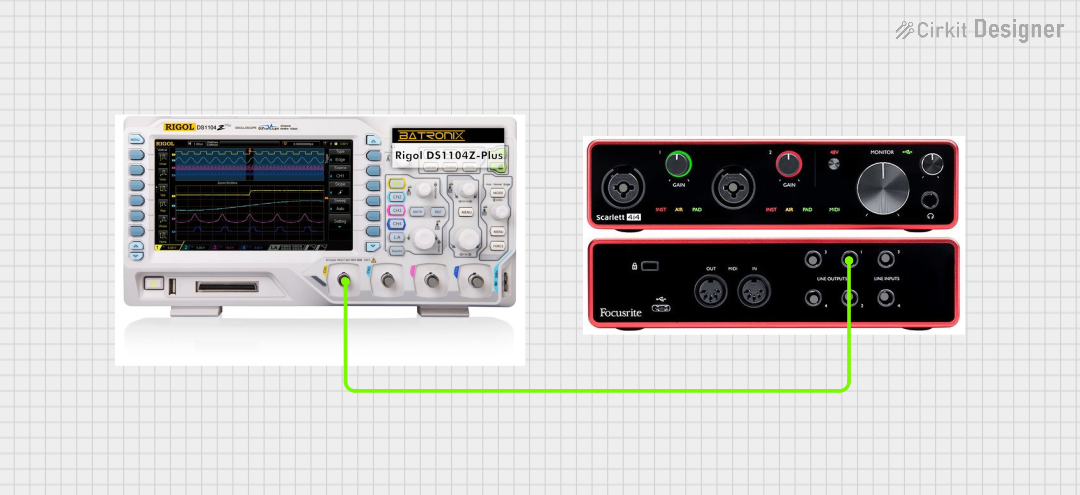
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer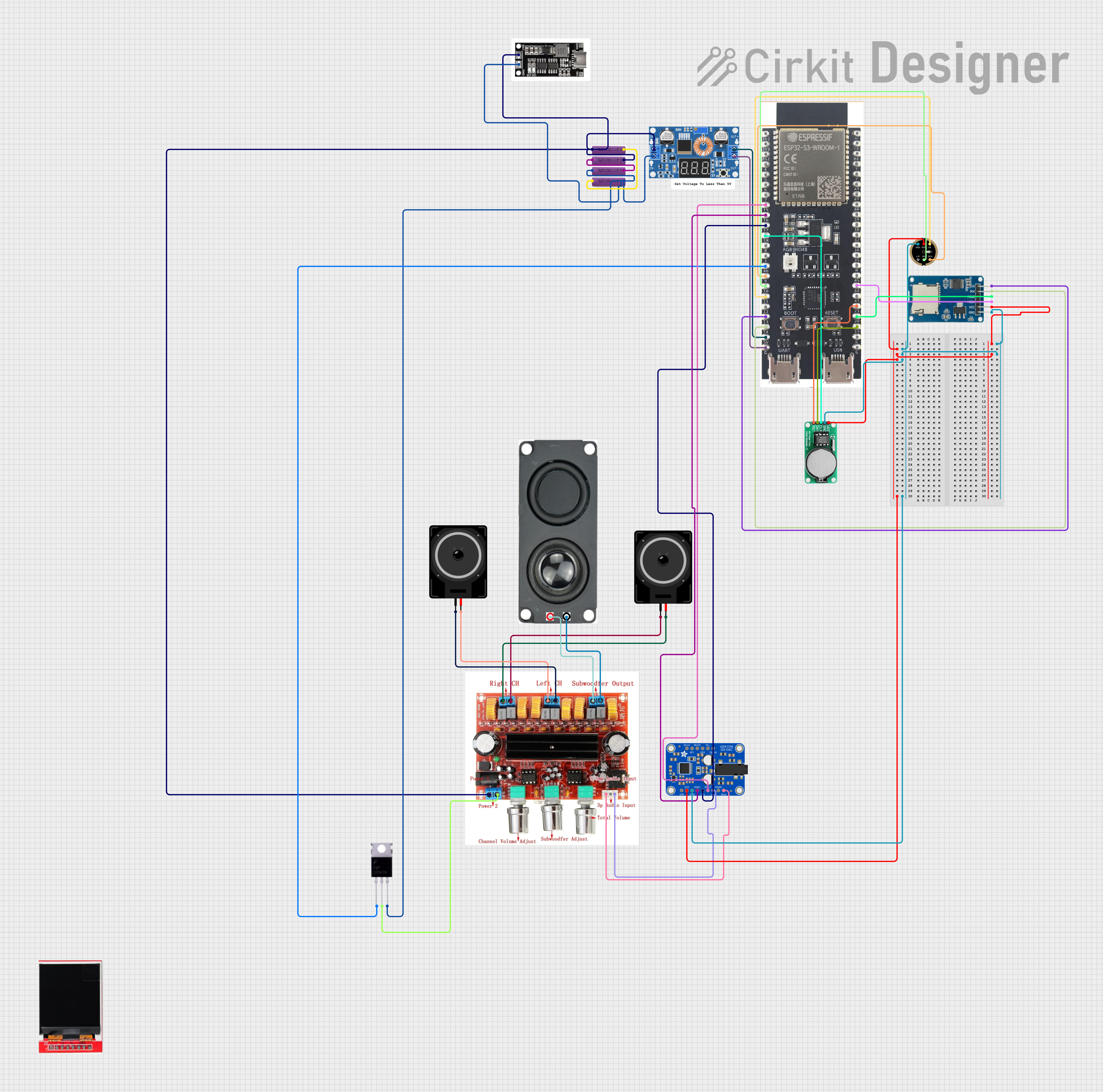
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer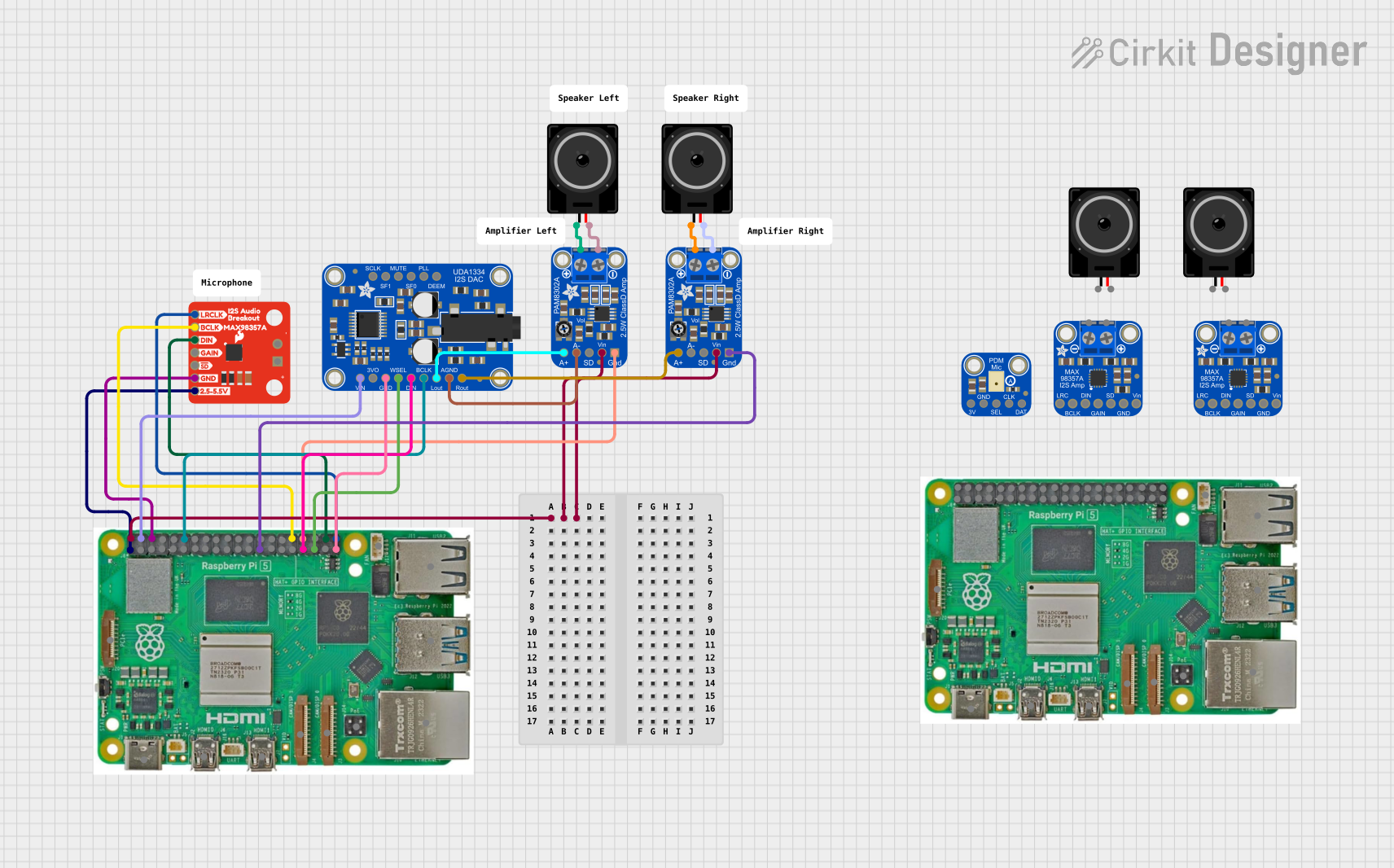
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with sound card

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Audio Playback: Enhances the quality of sound output for music, movies, and games.
- Audio Recording: Captures high-quality audio from microphones for podcasts, voiceovers, or music production.
- Gaming: Provides immersive audio experiences with surround sound and 3D audio effects.
- Professional Audio Production: Used in studios for mixing, mastering, and editing audio tracks.
- Video Conferencing: Ensures clear audio input and output for online meetings and calls.
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications of a typical sound card. Note that specific models may vary in their features and performance.
Key Technical Details
- Audio Channels: 2.0 (stereo), 5.1, 7.1 surround sound support
- Sampling Rate: Up to 192 kHz
- Bit Depth: 16-bit, 24-bit, or 32-bit
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): Typically 90 dB to 120 dB
- Input/Output Ports:
- 3.5mm jacks for headphones, microphones, and line-in/line-out
- Optical (TOSLINK) or coaxial digital audio output
- MIDI input/output (on some models)
- Interface: PCI, PCIe, or USB (for external sound cards)
- Power Supply: Typically powered through the PCI/PCIe slot or USB connection
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
For internal sound cards, the pin configuration is typically associated with the PCI or PCIe interface. Below is a table describing the common input/output ports found on sound cards:
| Port | Description |
|---|---|
| Line-Out (Green) | Outputs analog audio to speakers or headphones. |
| Line-In (Blue) | Accepts analog audio input from external devices (e.g., CD players). |
| Mic-In (Pink) | Connects to a microphone for audio input. |
| Digital Out | Outputs digital audio via optical (TOSLINK) or coaxial connections. |
| MIDI In/Out | Connects to MIDI devices for music production (available on some sound cards). |
| USB (External) | Provides power and data transfer for external sound cards. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Sound Card in a System
Installation:
- For internal sound cards:
- Power off the computer and unplug it from the power source.
- Open the computer case and locate an available PCI or PCIe slot.
- Insert the sound card into the slot and secure it with a screw.
- Close the case, reconnect the power, and boot the computer.
- For external sound cards:
- Connect the sound card to a USB port on the computer.
- Install any required drivers or software provided by the manufacturer.
- For internal sound cards:
Driver Installation:
- Download and install the latest drivers from the sound card manufacturer's website.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Connecting Audio Devices:
- Plug speakers or headphones into the Line-Out port.
- Connect a microphone to the Mic-In port if needed.
- Use the Line-In port for external audio sources.
Configuration:
- Open the computer's sound settings to select the sound card as the default playback and recording device.
- Adjust volume levels and other settings as needed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the sound card is compatible with your computer's operating system and hardware.
- Use high-quality cables and connectors to minimize signal loss and interference.
- Regularly update the sound card drivers to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
- Avoid placing the sound card near components that generate electromagnetic interference, such as power supplies.
Example: Using a Sound Card with Arduino UNO
While sound cards are not typically used directly with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO, you can interface an external USB sound card with a computer and control audio playback or recording via the Arduino. Below is an example of controlling audio playback using an Arduino and a computer:
// Example: Controlling audio playback on a computer using Arduino
// This code sends serial commands to the computer to control audio playback.
// Requires a serial communication program on the computer to interpret commands.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
// Send a command to play audio
Serial.println("PLAY_AUDIO");
delay(5000); // Wait for 5 seconds before sending the next command
// Send a command to stop audio
Serial.println("STOP_AUDIO");
delay(5000); // Wait for 5 seconds before repeating
}
Note: The above code requires a custom program on the computer to interpret the "PLAY_AUDIO" and "STOP_AUDIO" commands and control the sound card accordingly.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Sound Output:
- Cause: Incorrect audio device selected in the operating system.
- Solution: Open the sound settings and select the sound card as the default playback device.
Distorted or Low-Quality Audio:
- Cause: Outdated drivers or poor-quality cables.
- Solution: Update the sound card drivers and use high-quality cables.
Microphone Not Working:
- Cause: Incorrect input port or muted microphone.
- Solution: Ensure the microphone is connected to the correct port and unmuted in the sound settings.
Sound Card Not Detected:
- Cause: Improper installation or hardware conflict.
- Solution: Reseat the sound card in the PCI/PCIe slot or try a different USB port for external sound cards.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a sound card with a laptop?
- A: Yes, external USB sound cards are compatible with laptops and provide enhanced audio capabilities.
Q: Do I need a sound card for gaming?
- A: While most modern motherboards have built-in audio, a dedicated sound card can improve audio quality and support advanced features like surround sound.
Q: How do I know if my sound card supports 7.1 surround sound?
- A: Check the specifications on the manufacturer's website or the product manual for details on supported audio channels.
Q: Can I use a sound card for professional audio production?
- A: Yes, many high-end sound cards are designed for studio use and offer features like low-latency recording and high-resolution audio support.