
How to Use KY-022: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
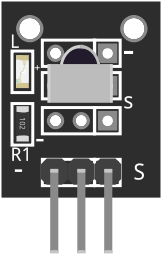
 Design with KY-022 in Cirkit Designer
Design with KY-022 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The KY-022 is an infrared (IR) receiver module designed to detect and process infrared signals, typically from remote controls. It is a compact and reliable component that enables wireless communication between a remote control and a device. The module is widely used in projects involving home automation, robotics, and consumer electronics, where remote control functionality is required.
Explore Projects Built with KY-022
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer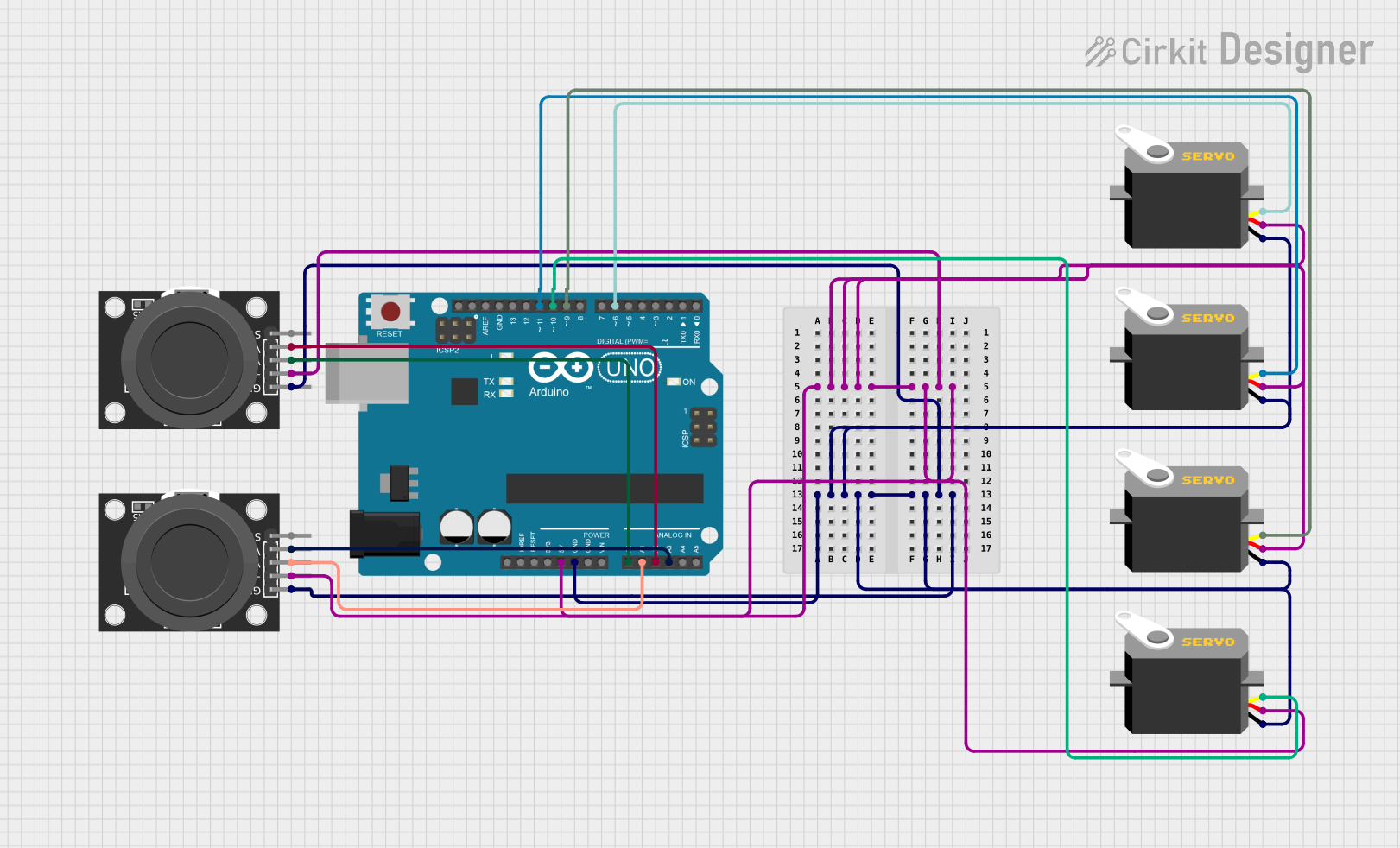
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with KY-022

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Remote-controlled robots and vehicles
- Home automation systems
- Media player control
- Wireless communication in IoT devices
- Learning and prototyping with Arduino and other microcontrollers
Technical Specifications
The KY-022 module is built around a 38 kHz IR receiver, which is tuned to detect signals from most standard remote controls. Below are the key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.0V to 5.5V |
| Operating Current | 0.4mA to 1.5mA |
| Carrier Frequency | 38 kHz |
| Reception Distance | Up to 18 meters (line of sight) |
| Viewing Angle | ±45° |
| Output Signal | Digital (active low) |
| Dimensions | 18.5mm x 15mm x 10mm |
Pin Configuration:
The KY-022 module has three pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Signal | Digital output pin that transmits the received IR signal (active low) |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply pin (3.0V to 5.5V) |
| 3 | GND | Ground pin for the module |
Usage Instructions
The KY-022 module is straightforward to use and can be easily interfaced with microcontrollers like Arduino. Below are the steps to use the module in a circuit:
Connecting the KY-022:
- Power the Module: Connect the
VCCpin to a 5V power source and theGNDpin to the ground. - Signal Output: Connect the
Signalpin to a digital input pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino). - Place the Module: Ensure the module's IR receiver is facing the remote control for optimal signal reception.
Arduino Example Code:
The following example demonstrates how to use the KY-022 with an Arduino UNO to decode IR signals from a remote control. This code uses the IRremote library, which must be installed in the Arduino IDE.
#include <IRremote.h> // Include the IRremote library
const int RECV_PIN = 2; // Define the pin connected to the KY-022 Signal pin
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN); // Create an IR receiver object
decode_results results; // Variable to store decoded IR data
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the IR receiver
Serial.println("KY-022 IR Receiver is ready to decode signals.");
}
void loop() {
if (irrecv.decode(&results)) { // Check if an IR signal is received
Serial.print("Received IR code: ");
Serial.println(results.value, HEX); // Print the received code in hexadecimal
irrecv.resume(); // Prepare to receive the next signal
}
}
Important Considerations:
- Line of Sight: Ensure there is a clear line of sight between the remote control and the KY-022 for reliable signal reception.
- Ambient Light: Avoid using the module in environments with strong IR interference, such as direct sunlight or near incandescent bulbs.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to prevent erratic behavior.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions:
No Signal Detected:
- Ensure the remote control is functional and emits IR signals.
- Verify the connections (VCC, GND, and Signal) are correct and secure.
- Check that the module is powered within the specified voltage range.
Unstable or Incorrect Signal:
- Reduce ambient IR interference by shielding the module from strong light sources.
- Ensure the remote control is within the module's reception range and angle.
Arduino Not Receiving Data:
- Confirm that the
IRremotelibrary is installed and properly included in the code. - Verify that the correct digital pin is defined in the code (
RECV_PIN).
- Confirm that the
FAQs:
Q: Can the KY-022 receive signals from any remote control?
A: The KY-022 is designed to work with most remote controls that use a 38 kHz carrier frequency, which is standard for many consumer devices.
Q: How can I test if the KY-022 is working?
A: Use a smartphone camera to check if the remote control emits IR light when a button is pressed. Then, connect the KY-022 to an Arduino and run the example code to verify signal reception.
Q: Can I use the KY-022 with a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, the KY-022 can be used with a Raspberry Pi. You will need to use an appropriate library, such as lirc, to decode the IR signals.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the KY-022 into your projects and troubleshoot any issues that arise.