
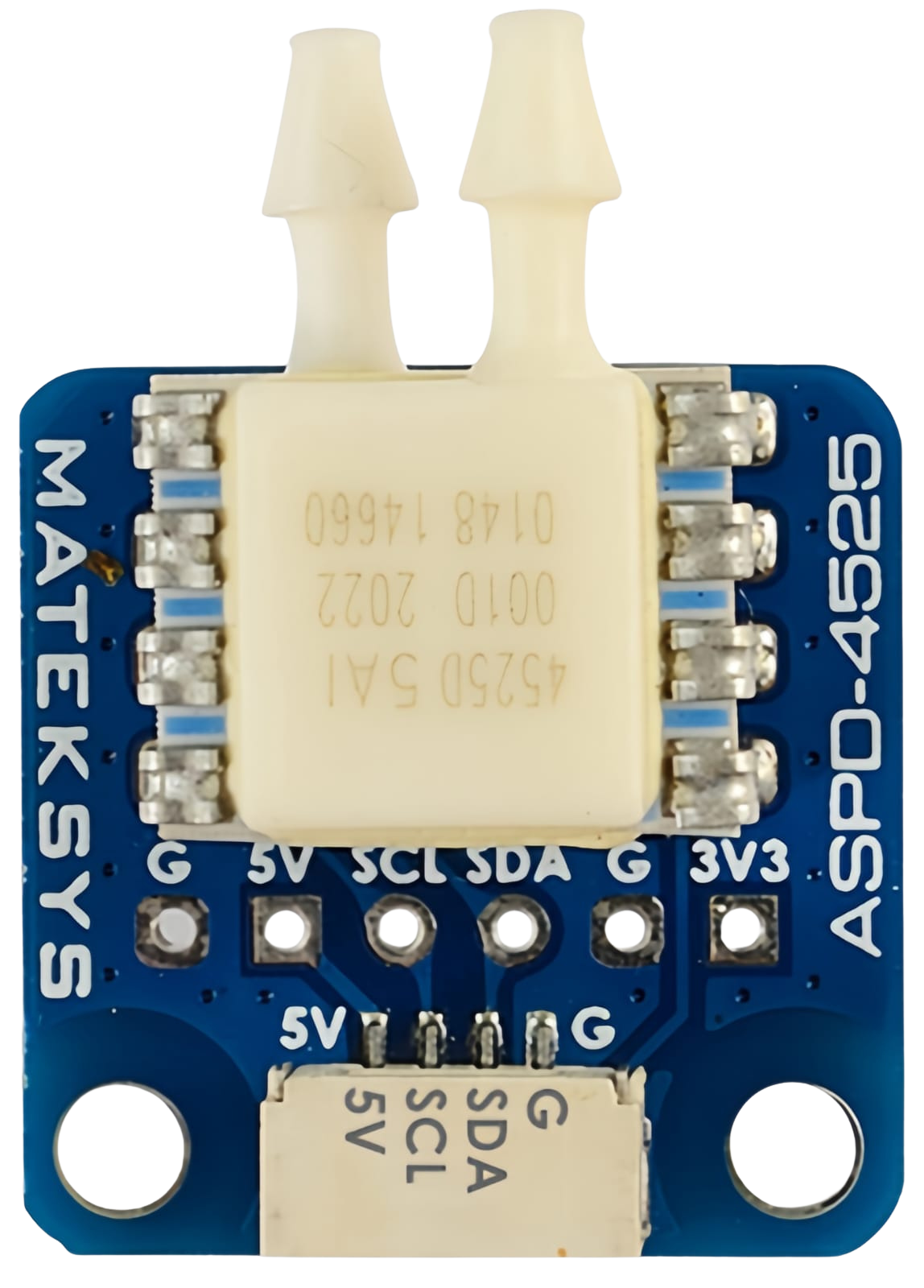
How to Use Airspeed Sensor Matek ASPD-4525: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Airspeed Sensor Matek ASPD-4525 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Airspeed Sensor Matek ASPD-4525 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Matek ASPD-4525 is a high-performance airspeed sensor designed for use in drones and other UAVs. It measures airspeed by detecting differential pressure and provides accurate readings for flight control and navigation. This sensor is ideal for applications requiring precise airspeed data, such as autopilot systems, flight stabilization, and advanced navigation.
Explore Projects Built with Airspeed Sensor Matek ASPD-4525
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer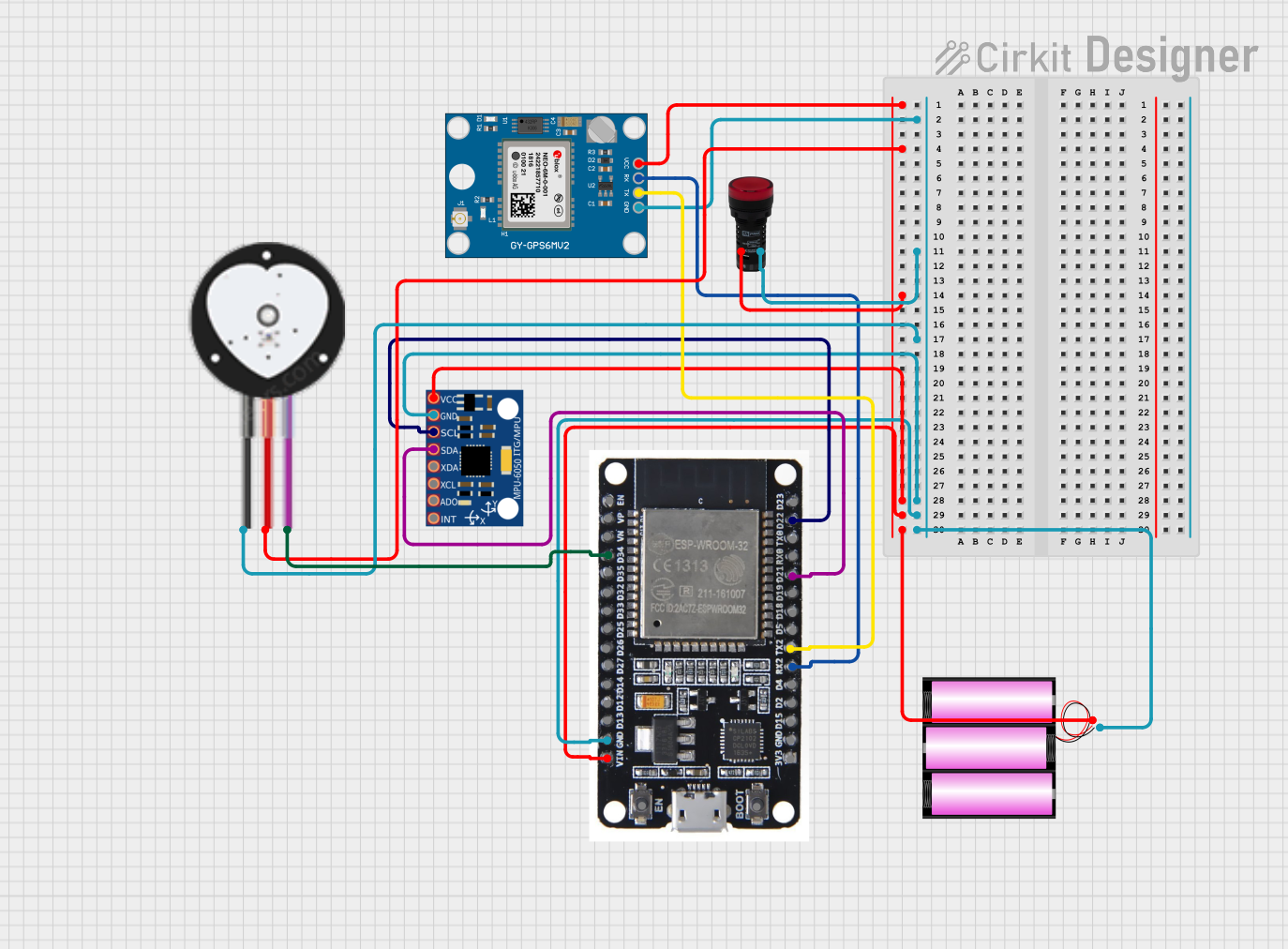
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Airspeed Sensor Matek ASPD-4525

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Autopilot systems for drones and UAVs
- Flight stabilization and control
- Navigation in fixed-wing aircraft
- Wind speed measurement in research and development
- Enhancing flight efficiency and safety
Technical Specifications
The Matek ASPD-4525 is built for reliability and precision. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 4.5V to 5.5V |
| Operating Current | 5mA (typical) |
| Pressure Range | ±1 psi |
| Measurement Resolution | 14-bit |
| Communication Interface | I²C |
| I²C Address | 0x28 (default) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 21mm x 15mm x 6mm |
| Weight | 2 grams |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Matek ASPD-4525 has a 4-pin JST-GH connector for interfacing. Below is the pinout:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (4.5V to 5.5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | SDA | I²C data line |
| 4 | SCL | I²C clock line |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 5V power source and the GND pin to the ground.
- I²C Communication: Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I²C pins on your microcontroller or flight controller.
- Tubing Connection: Attach the provided silicone tubing to the sensor's pressure ports. Ensure the tubing is securely connected to avoid leaks.
- The "P+" port is for the dynamic pressure (facing airflow).
- The "P-" port is for the static pressure (ambient air).
- Software Configuration: Configure your flight controller or microcontroller to read data from the sensor's I²C address (default: 0x28).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Calibration: Perform airspeed sensor calibration before each flight to ensure accurate readings.
- Tubing Placement: Ensure the tubing is free from kinks or obstructions and is properly aligned with the airflow.
- I²C Pull-Up Resistors: If your microcontroller does not have built-in pull-up resistors on the I²C lines, add external resistors (4.7kΩ recommended) between SDA/SCL and VCC.
- Avoid Moisture: Protect the sensor from water or moisture, as it can affect pressure readings.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the Matek ASPD-4525 with an Arduino UNO using the Wire library:
#include <Wire.h>
#define AIRSPEED_SENSOR_ADDR 0x28 // Default I²C address of ASPD-4525
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I²C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication for debugging
Serial.println("Matek ASPD-4525 Airspeed Sensor Test");
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(AIRSPEED_SENSOR_ADDR); // Start communication
Wire.write(0x00); // Request data from the sensor
Wire.endTransmission(false); // Send stop condition
Wire.requestFrom(AIRSPEED_SENSOR_ADDR, 4); // Request 4 bytes of data
if (Wire.available() == 4) {
uint16_t pressure = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Read pressure
uint16_t temperature = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Read temp
// Convert pressure to airspeed (example calculation, adjust as needed)
float airspeed = (pressure - 8192) / 16384.0 * 1.0; // Example scaling
Serial.print("Pressure: ");
Serial.print(pressure);
Serial.print(" | Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.print(" | Airspeed: ");
Serial.print(airspeed);
Serial.println(" m/s");
} else {
Serial.println("Error: No data received from sensor");
}
delay(500); // Wait before next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Data Received from Sensor
- Cause: Incorrect I²C wiring or address mismatch.
- Solution: Verify the SDA and SCL connections. Ensure the I²C address matches the sensor's default (0x28) or configured address.
Inaccurate Airspeed Readings
- Cause: Calibration not performed or tubing misaligned.
- Solution: Perform a proper calibration before use. Check the tubing for leaks or obstructions.
Sensor Not Detected
- Cause: Missing pull-up resistors on I²C lines.
- Solution: Add 4.7kΩ pull-up resistors between SDA/SCL and VCC.
Moisture Damage
- Cause: Exposure to water or high humidity.
- Solution: Protect the sensor with a waterproof enclosure or avoid flying in wet conditions.
FAQs
Q: Can the ASPD-4525 be used with flight controllers like Pixhawk?
A: Yes, the Matek ASPD-4525 is compatible with Pixhawk and other flight controllers that support I²C airspeed sensors.
Q: How do I calibrate the airspeed sensor?
A: Calibration is typically done through your flight controller's software (e.g., Mission Planner for Pixhawk). Follow the software's instructions to zero the sensor before flight.
Q: What is the maximum airspeed the sensor can measure?
A: The sensor can measure airspeeds up to approximately 100 m/s, depending on the calibration and setup.
Q: Can I extend the tubing for remote placement?
A: Yes, but ensure the tubing is of high quality and free from leaks or kinks to maintain accuracy.