
How to Use Water Tank: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
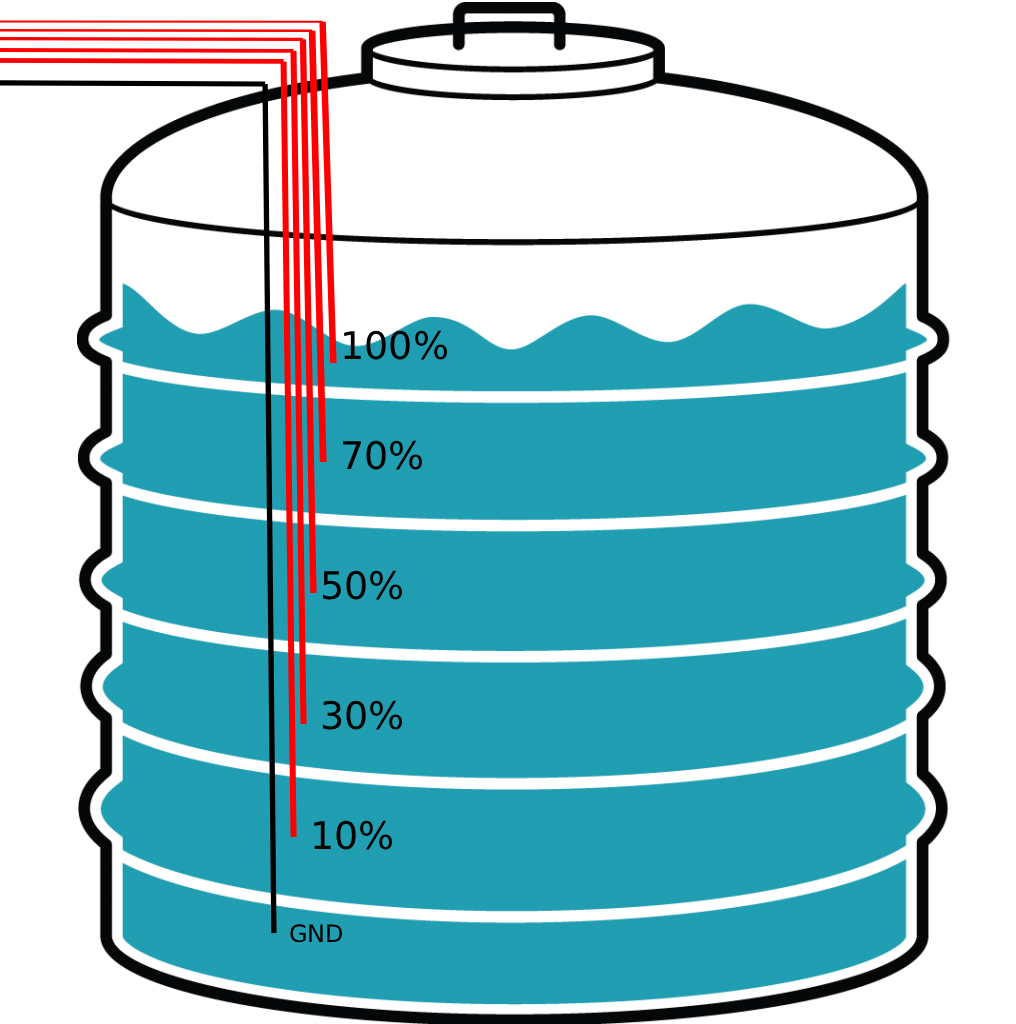
 Design with Water Tank in Cirkit Designer
Design with Water Tank in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A water tank is a container designed to store water for a variety of applications, including irrigation, plumbing, industrial processes, and emergency water supply. Water tanks are available in different shapes, sizes, and materials, such as plastic, metal, or concrete, to suit specific needs. They play a critical role in water management systems by ensuring a steady and reliable supply of water.
Common applications of water tanks include:
- Residential water storage for daily use.
- Agricultural irrigation systems.
- Industrial processes requiring large volumes of water.
- Rainwater harvesting and storage.
- Emergency water supply during shortages or disasters.
Explore Projects Built with Water Tank
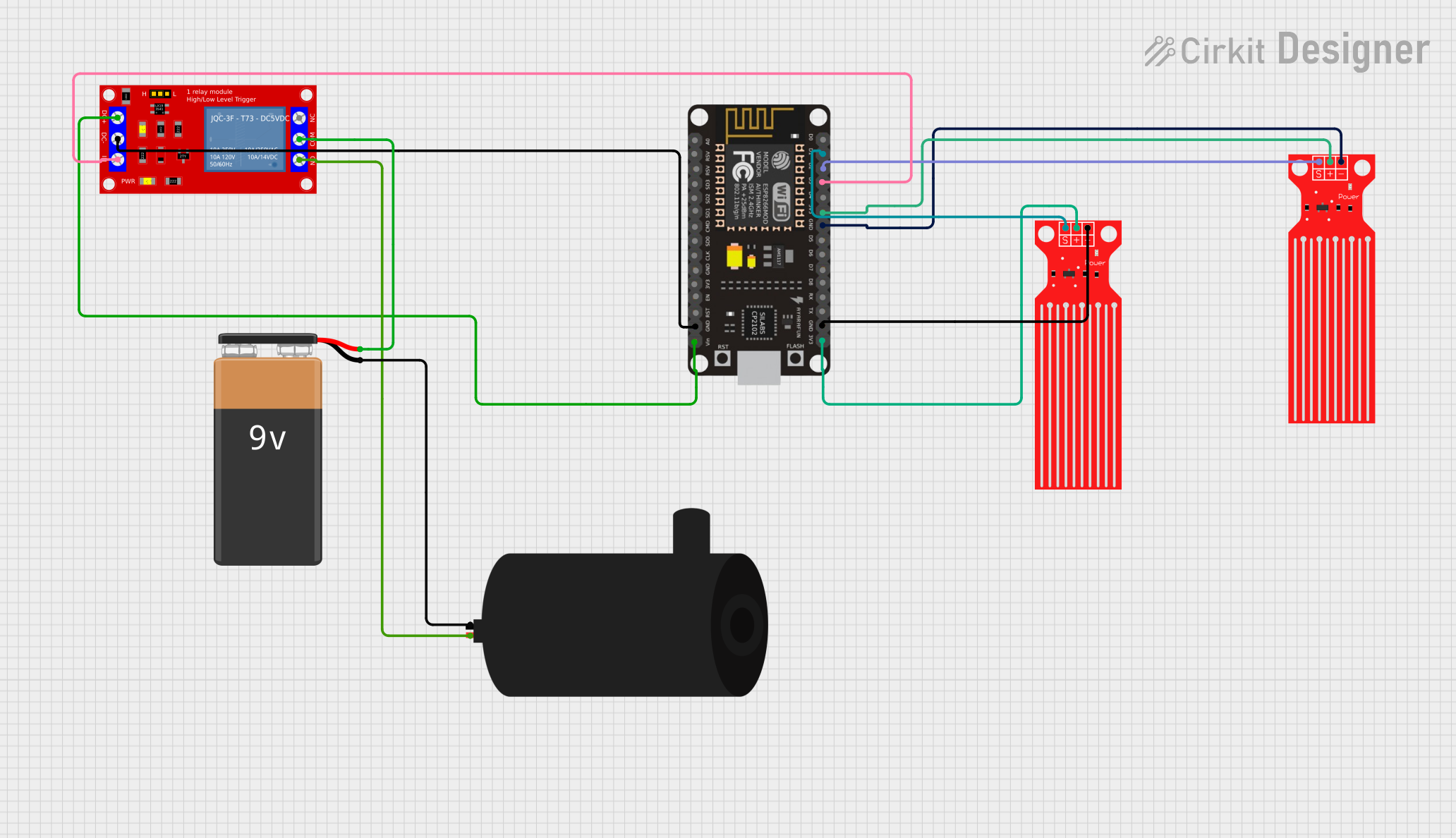
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer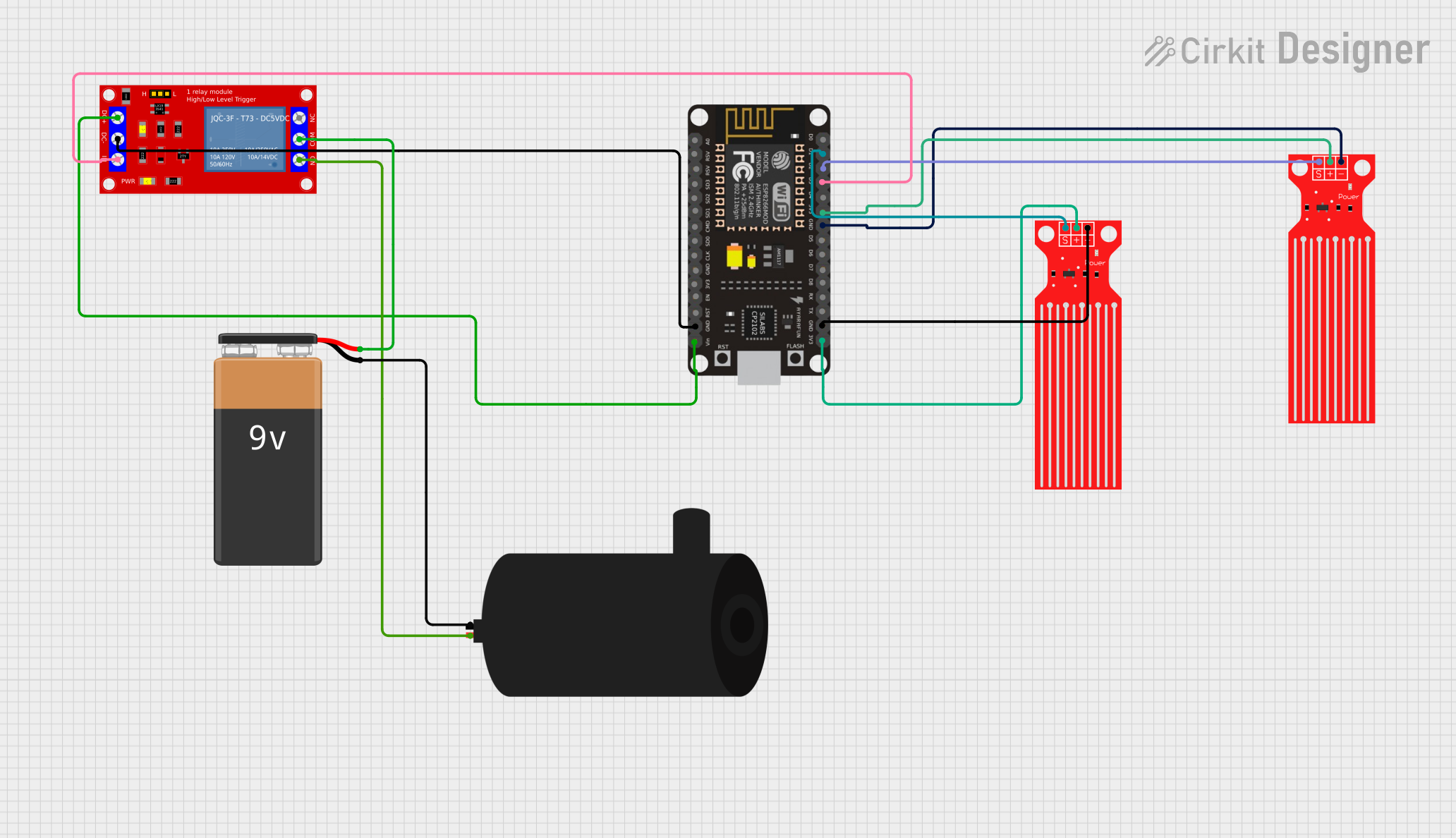
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer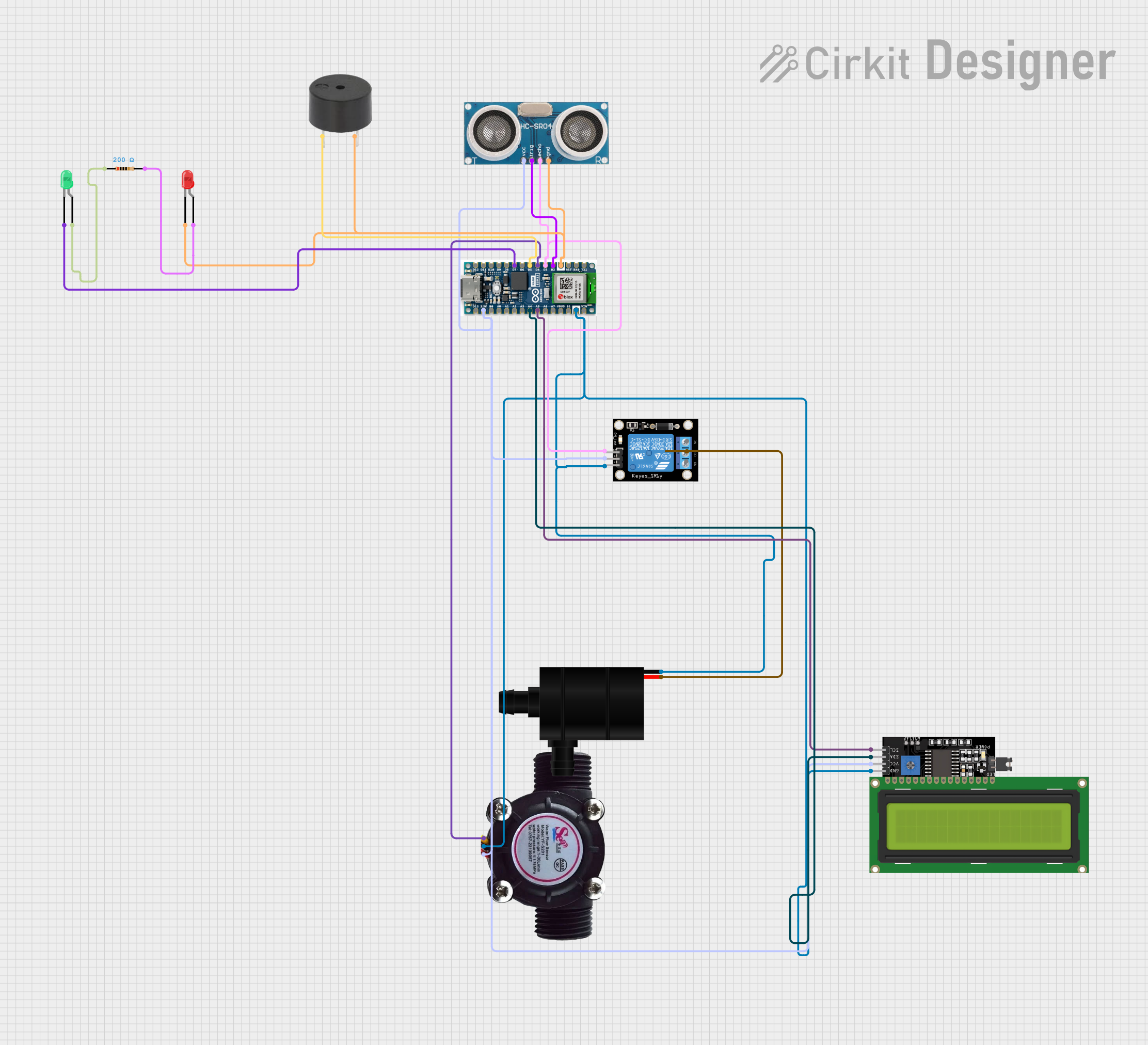
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer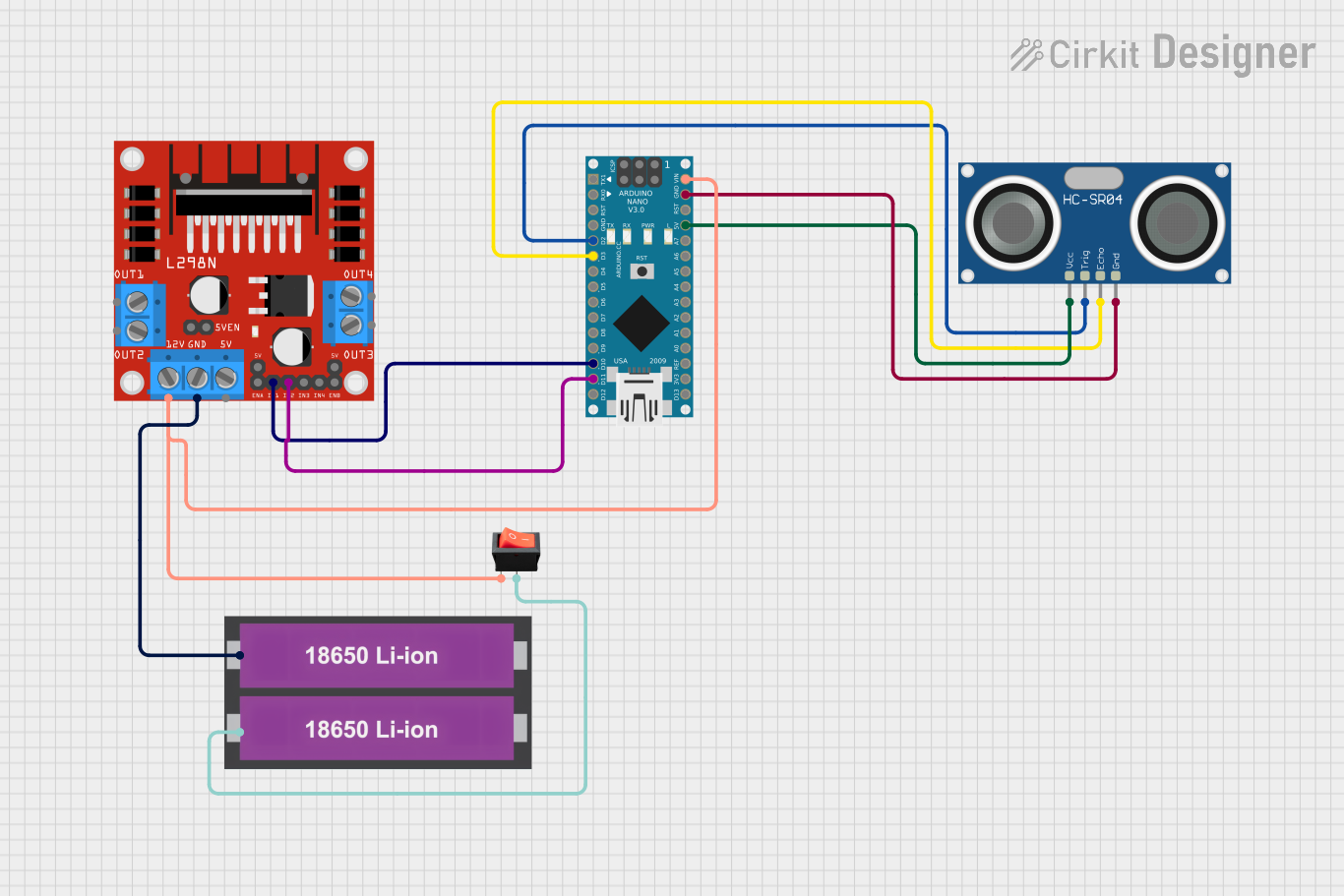
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Water Tank

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The technical specifications of a water tank depend on its material, size, and intended use. Below are general specifications for a typical plastic water tank:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | High-density polyethylene (HDPE), metal, or concrete |
| Capacity | 100 liters to 50,000 liters (varies by model) |
| Shape | Cylindrical, rectangular, or spherical |
| Installation Type | Overhead, underground, or ground-level |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 50°C (varies by material) |
| UV Resistance | Yes (for outdoor plastic tanks) |
| Inlet/Outlet Diameter | 1/2 inch to 4 inches (varies by model) |
Example Pin Configuration (for tanks with electronic level sensors)
If the water tank is equipped with an electronic water level sensor, the pin configuration for the sensor may look like this:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply for the sensor (e.g., 5V or 3.3V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | Signal Output | Outputs the water level signal (analog or digital) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use a Water Tank in a System
Installation:
- Choose a suitable location for the tank based on its type (overhead, underground, or ground-level).
- Ensure the base is level and strong enough to support the tank's weight when full.
- Connect the inlet pipe to the water source and the outlet pipe to the distribution system.
Water Level Monitoring:
- If the tank includes a water level sensor, connect the sensor to a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) or a monitoring system.
- Use the sensor's signal to automate water pumps or alert users when the tank is full or empty.
Maintenance:
- Regularly clean the tank to prevent algae and sediment buildup.
- Inspect the tank and its fittings for leaks or damage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use UV-resistant tanks for outdoor installations to prevent material degradation.
- Ensure proper ventilation for underground tanks to avoid pressure buildup.
- Avoid overfilling the tank to prevent overflow and structural damage.
- Use a first-flush diverter in rainwater harvesting systems to filter out debris.
Example Code for Water Level Monitoring with Arduino UNO
If the water tank is equipped with an ultrasonic water level sensor (e.g., HC-SR04), the following code can be used to monitor the water level:
// Include necessary libraries
#define TRIG_PIN 9 // Pin connected to the sensor's TRIG pin
#define ECHO_PIN 10 // Pin connected to the sensor's ECHO pin
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(TRIG_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set TRIG pin as output
pinMode(ECHO_PIN, INPUT); // Set ECHO pin as input
}
void loop() {
long duration;
float distance;
// Send a 10-microsecond pulse to the TRIG pin
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(TRIG_PIN, LOW);
// Measure the time it takes for the echo to return
duration = pulseIn(ECHO_PIN, HIGH);
// Calculate the distance in centimeters
distance = (duration * 0.034) / 2;
// Print the distance to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Water Level Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(" cm");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Water Overflow:
- Cause: Faulty float valve or pump automation system.
- Solution: Inspect and replace the float valve or recalibrate the automation system.
Low Water Pressure:
- Cause: Clogged outlet pipe or insufficient tank height.
- Solution: Clean the outlet pipe or raise the tank to increase gravity-fed pressure.
Sensor Not Working:
- Cause: Loose connections or damaged sensor.
- Solution: Check all connections and replace the sensor if necessary.
Algae Growth in Tank:
- Cause: Exposure to sunlight.
- Solution: Use a UV-resistant tank or cover the tank to block sunlight.
FAQs
Q1: How often should I clean my water tank?
A1: It is recommended to clean the tank every 6 months to prevent sediment and algae buildup.
Q2: Can I use a water tank for drinking water storage?
A2: Yes, but ensure the tank is made of food-grade material and is properly cleaned and maintained.
Q3: What is the ideal height for an overhead water tank?
A3: The height depends on the required water pressure, but typically 10-15 feet above ground level is sufficient for most residential applications.
Q4: Can I connect multiple tanks together?
A4: Yes, you can connect multiple tanks in series or parallel to increase storage capacity or improve water distribution.