
How to Use STEP-UP CONVERTER: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
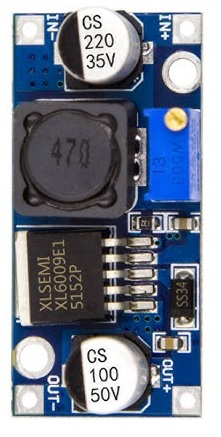
 Design with STEP-UP CONVERTER in Cirkit Designer
Design with STEP-UP CONVERTER in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A step-up converter, also known as a boost converter, is a type of DC-DC converter that increases the input voltage to a higher output voltage. This component is widely used in applications where a higher voltage is required than what is available from the power source. It is commonly employed in battery-powered devices, renewable energy systems, and LED drivers.
Explore Projects Built with STEP-UP CONVERTER
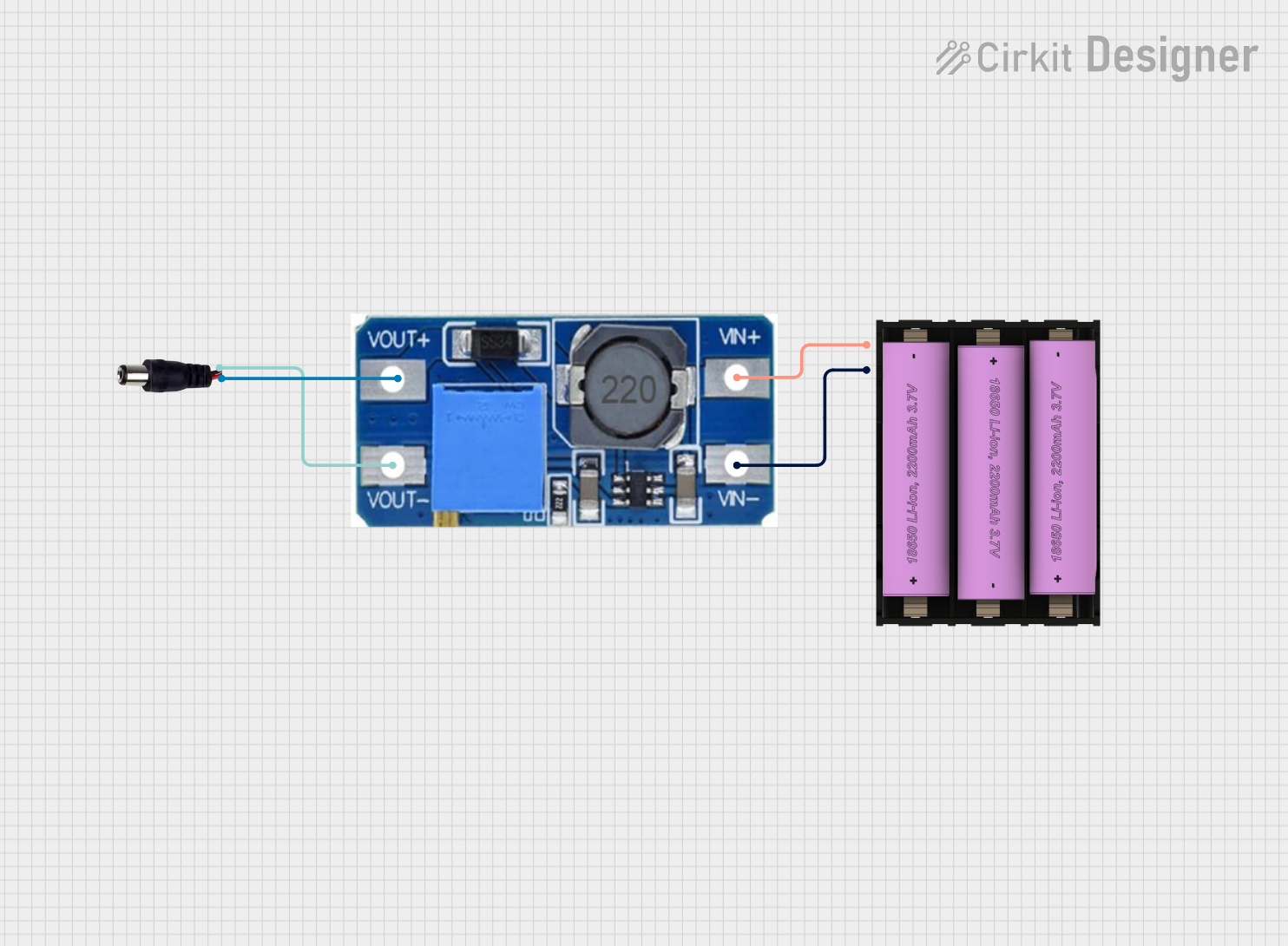
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer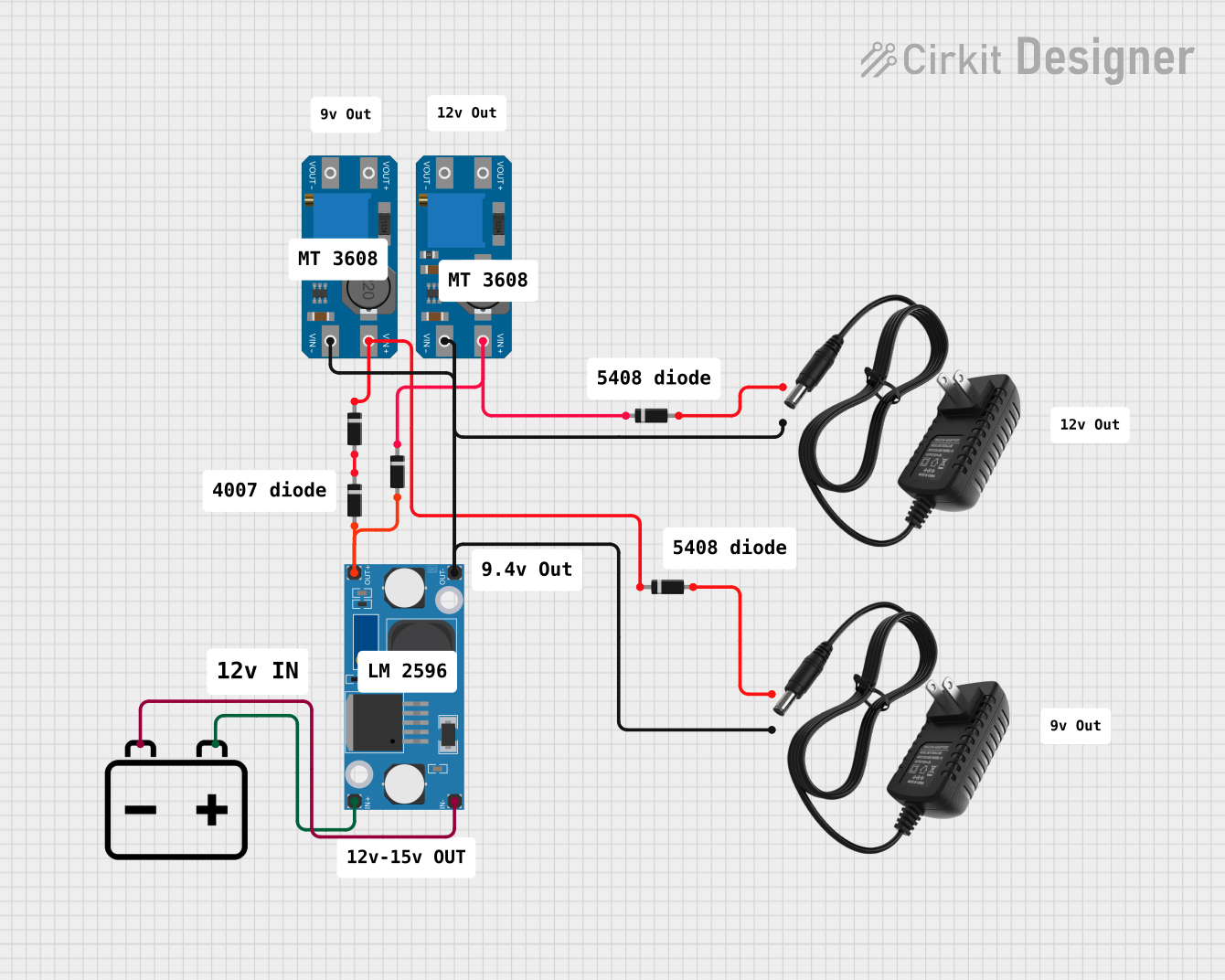
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with STEP-UP CONVERTER

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering devices requiring higher voltage from a low-voltage source (e.g., 5V to 12V).
- Boosting voltage in solar power systems.
- Driving high-power LEDs.
- Battery-powered systems where efficient voltage conversion is critical.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the DC-DC Step-Up Converter 12V:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 3V to 10V |
| Output Voltage | 12V (fixed) |
| Maximum Output Current | 2A |
| Efficiency | Up to 90% |
| Switching Frequency | 150 kHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 22mm x 17mm x 6mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Positive input voltage (3V to 10V). |
| GND | Ground connection for input and output. |
| VOUT | Positive output voltage (12V). |
| EN | Enable pin (optional, active high). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage:
- Connect the positive terminal of the power source to the
VINpin. - Connect the negative terminal of the power source to the
GNDpin.
- Connect the positive terminal of the power source to the
Connect the Load:
- Connect the positive terminal of the load to the
VOUTpin. - Connect the negative terminal of the load to the
GNDpin.
- Connect the positive terminal of the load to the
Enable the Converter (if applicable):
- If the converter has an
EN(enable) pin, ensure it is connected to a high logic level (e.g., 3.3V or 5V) to activate the converter.
- If the converter has an
Power On:
- Turn on the power source. The converter will boost the input voltage to the specified output voltage (12V).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (3V to 10V). Exceeding this range may damage the converter.
- Load Current: Do not exceed the maximum output current of 2A to avoid overheating or failure.
- Heat Dissipation: If operating at high currents, consider adding a heatsink or ensuring proper ventilation to manage heat.
- Ripple and Noise: Use appropriate capacitors at the input and output to minimize voltage ripple and noise.
- Polarity: Double-check the polarity of connections to avoid damage to the converter or connected devices.
Example: Using with an Arduino UNO
The step-up converter can be used to power an Arduino UNO from a low-voltage source (e.g., 5V battery) by boosting the voltage to 12V. Below is an example code to control the EN pin of the converter using the Arduino:
// Example code to control the EN pin of a step-up converter
// Connect the EN pin of the converter to Arduino pin 7
const int enablePin = 7; // Pin connected to the EN pin of the converter
void setup() {
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT); // Set the enable pin as an output
digitalWrite(enablePin, HIGH); // Enable the step-up converter
}
void loop() {
// The converter remains enabled in this example
// Add your application code here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Input voltage is below the minimum required value.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (3V to 10V).
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive load current or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the load current or improve heat dissipation with a heatsink or fan.
High Output Ripple:
- Cause: Insufficient filtering at the input or output.
- Solution: Add low-ESR capacitors (e.g., 100µF) at the input and output.
Converter Not Turning On:
- Cause:
ENpin is not connected or is at a low logic level. - Solution: Connect the
ENpin to a high logic level (e.g., 3.3V or 5V).
- Cause:
FAQs
Q: Can I adjust the output voltage of this converter?
A: No, this model has a fixed output voltage of 12V. For adjustable output, consider using a different step-up converter.
Q: What happens if I exceed the maximum input voltage?
A: Exceeding the input voltage range may permanently damage the converter. Always stay within the specified range.
Q: Can I use this converter with a solar panel?
A: Yes, as long as the solar panel's output voltage is within the input range (3V to 10V) and provides sufficient current.
Q: Is reverse polarity protection included?
A: No, this converter does not have built-in reverse polarity protection. Use a diode to protect against reverse polarity.