
How to Use MPPT 48V/70-80A: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
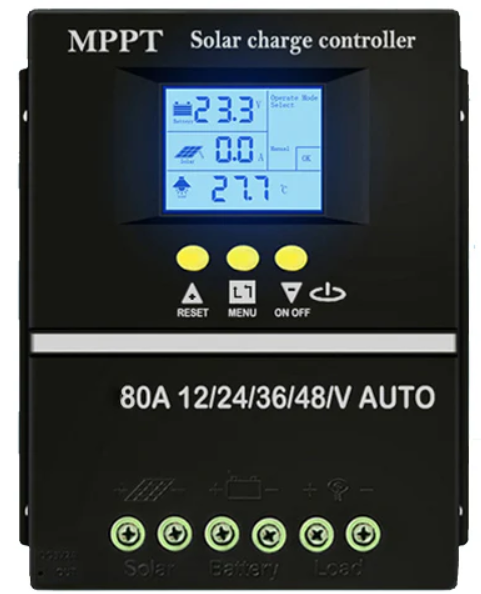

 Design with MPPT 48V/70-80A in Cirkit Designer
Design with MPPT 48V/70-80A in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MPPT 48V/70-80A is a high-performance Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) charge controller designed for solar energy systems. It is specifically engineered to optimize energy harvest from solar panels by dynamically adjusting the operating point of the panels to their maximum power point. This component is ideal for 48V systems and can handle a current range of 70-80A, making it suitable for medium to large-scale solar installations.
Explore Projects Built with MPPT 48V/70-80A
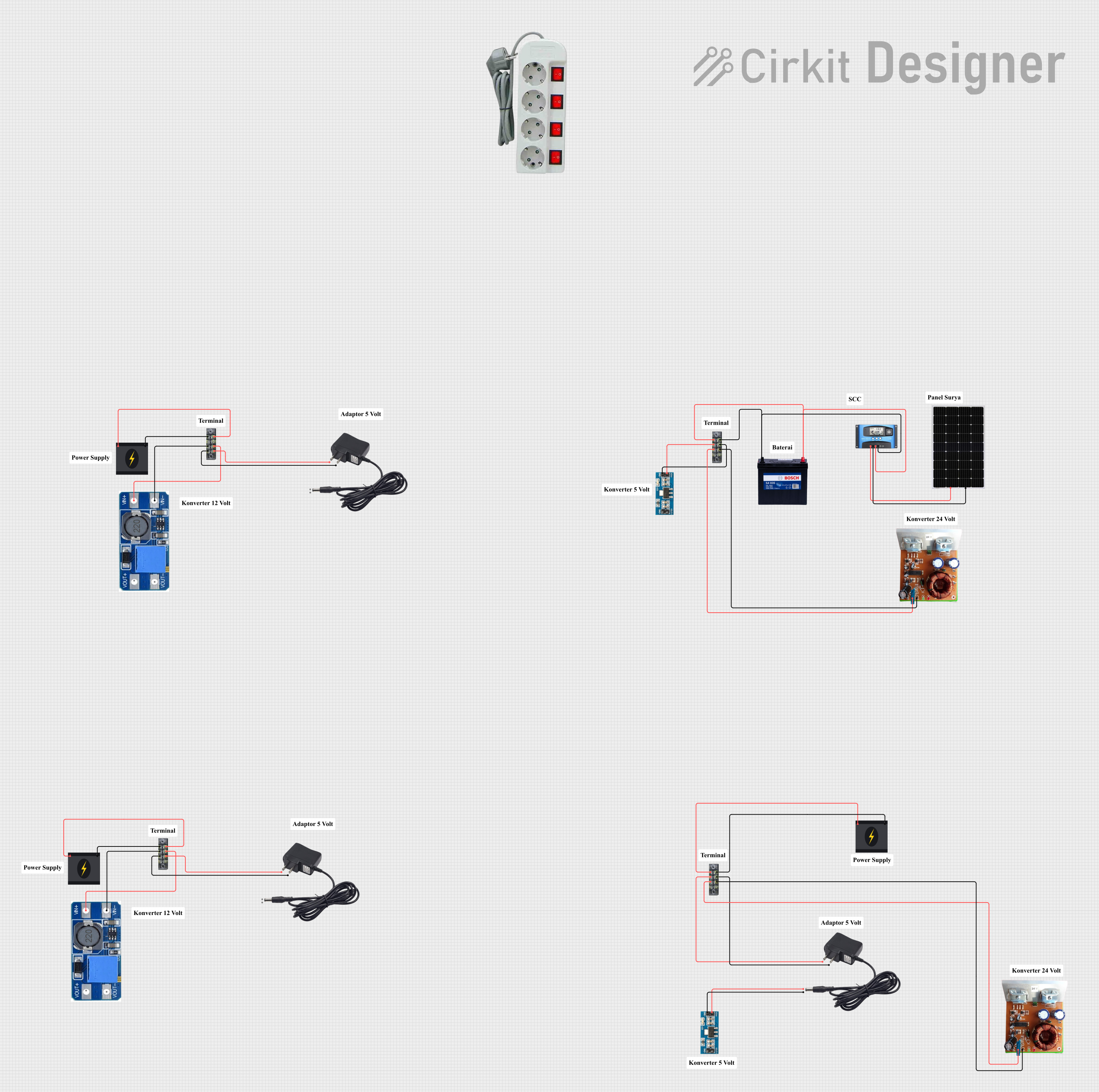
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer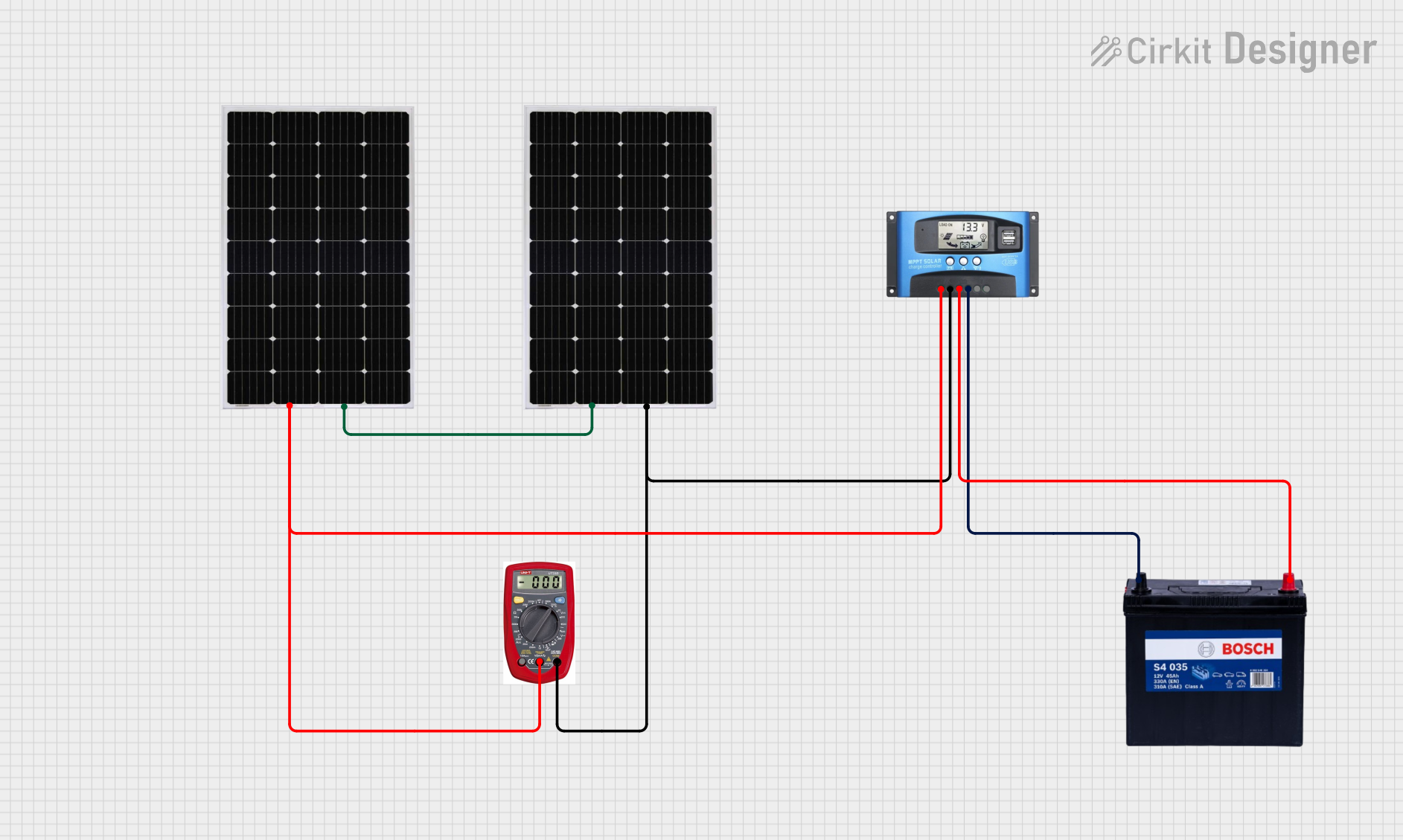
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer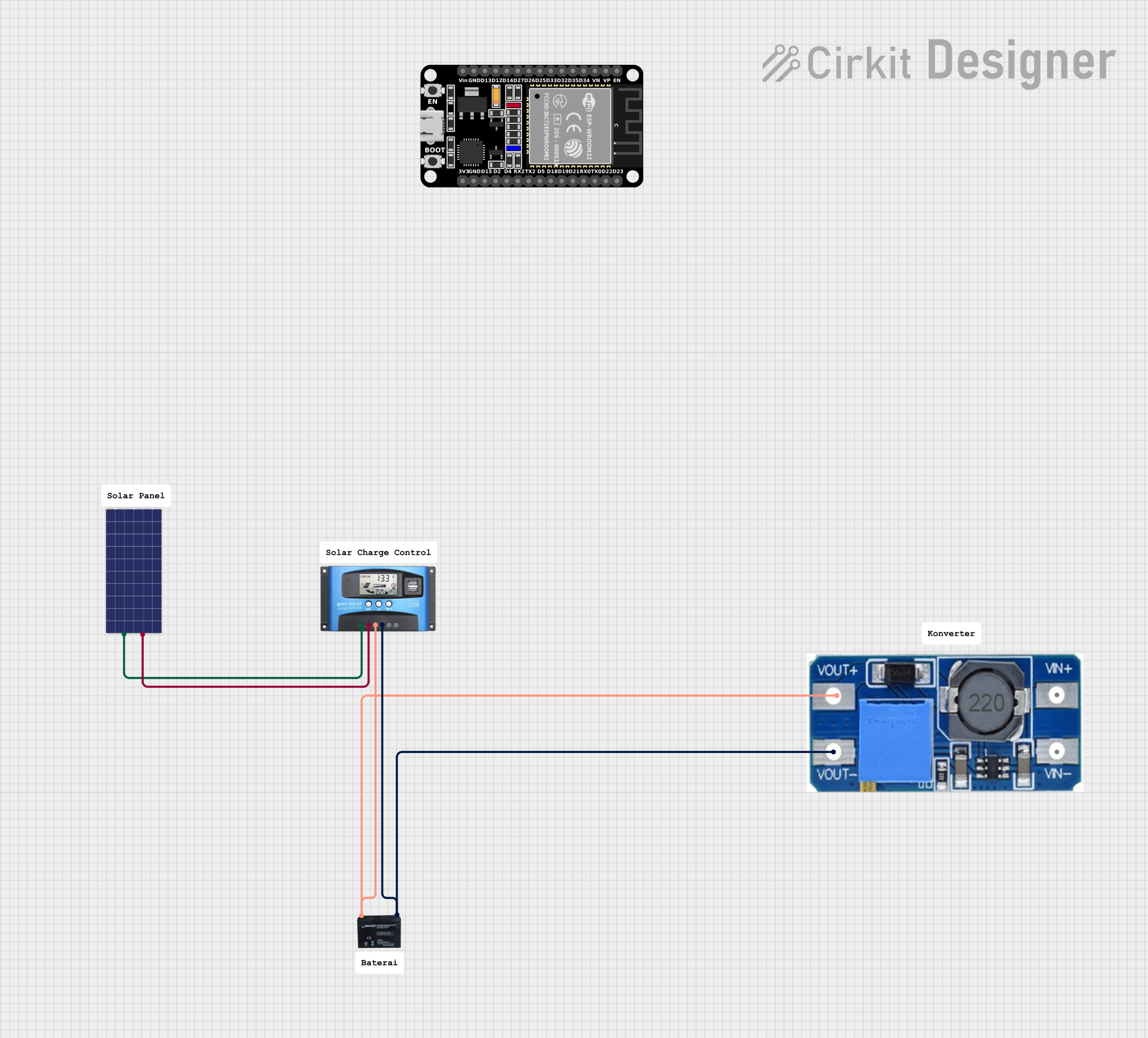
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer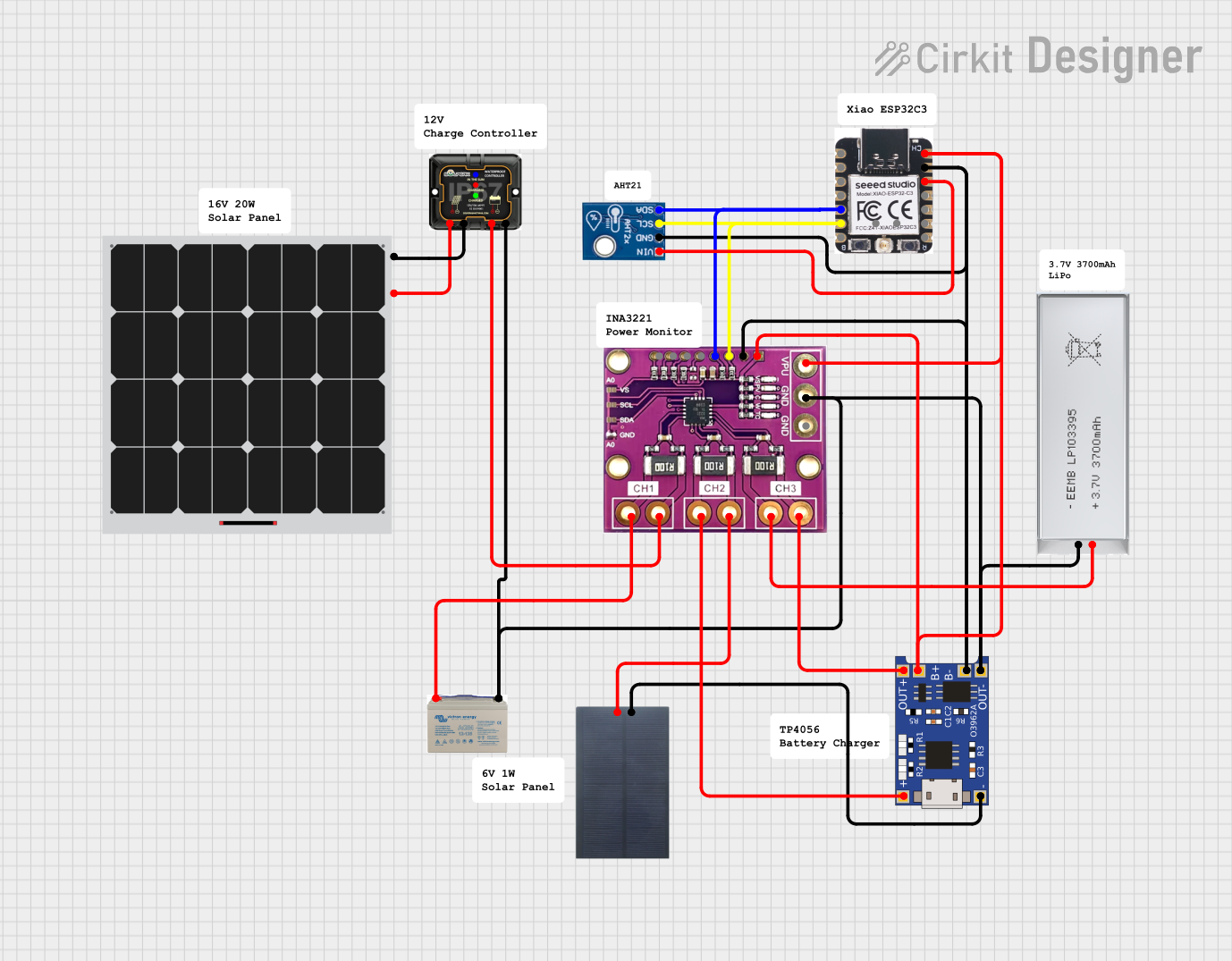
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MPPT 48V/70-80A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Solar power systems for residential, commercial, and industrial applications
- Off-grid and hybrid solar energy systems
- Battery charging and energy storage systems
- Renewable energy projects requiring high-efficiency power management
Technical Specifications
The MPPT 48V/70-80A charge controller is built to deliver reliable and efficient performance. Below are its key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| System Voltage | 48V |
| Maximum Current | 70-80A |
| Maximum Input Voltage | 150V DC |
| Efficiency | Up to 98% |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +60°C |
| Cooling Method | Active cooling (fan-based) |
| Communication Interface | RS485, CAN, or Bluetooth |
| Protection Features | Overvoltage, overcurrent, |
| short circuit, reverse polarity |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin/Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PV+ | Positive input terminal for solar panel array |
| PV- | Negative input terminal for solar panel array |
| BAT+ | Positive output terminal for battery connection |
| BAT- | Negative output terminal for battery connection |
| COM | Communication port for monitoring and control |
| GND | Ground terminal for communication interface |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MPPT 48V/70-80A in a Circuit
Connect the Solar Panels:
- Ensure the solar panel array's voltage does not exceed the maximum input voltage (150V DC).
- Connect the positive terminal of the solar panel array to the
PV+terminal and the negative terminal to thePV-terminal.
Connect the Battery:
- Verify that the battery system is compatible with a 48V charge controller.
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the
BAT+terminal and the negative terminal to theBAT-terminal.
Communication Setup (Optional):
- If monitoring or remote control is required, connect the communication interface (e.g., RS485 or Bluetooth) to the
COMandGNDterminals.
- If monitoring or remote control is required, connect the communication interface (e.g., RS485 or Bluetooth) to the
Power On:
- Once all connections are secure, power on the system. The MPPT controller will automatically detect the maximum power point of the solar panels and begin charging the battery.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- System Compatibility: Ensure the solar panel array and battery system are compatible with the MPPT controller's voltage and current ratings.
- Wiring: Use appropriately rated cables to handle the high current (70-80A) and minimize voltage drops.
- Cooling: Install the MPPT controller in a well-ventilated area to ensure proper cooling and prevent overheating.
- Safety: Always disconnect the battery and solar panels before performing maintenance or making adjustments to the system.
Arduino Integration Example
While the MPPT 48V/70-80A is not directly controlled by an Arduino, it can be monitored using its communication interface (e.g., RS485). Below is an example of how to read data from the MPPT controller using an Arduino UNO and an RS485 module:
#include <ModbusMaster.h>
// Instantiate ModbusMaster object
ModbusMaster node;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
node.begin(1, Serial); // Set Modbus slave ID to 1 and use Serial for RS485
}
void loop() {
uint8_t result;
uint16_t data;
// Read battery voltage (example register address: 0x3100)
result = node.readInputRegisters(0x3100, 1);
if (result == node.ku8MBSuccess) {
data = node.getResponseBuffer(0);
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(data / 100.0); // Convert to volts
Serial.println(" V");
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to read data from MPPT controller.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before next read
}
Notes:
- Replace
0x3100with the actual register address for the desired data, as specified in the MPPT controller's communication protocol. - Use an RS485-to-TTL module to connect the Arduino to the MPPT controller.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No power output from the controller | Incorrect wiring or loose connections | Verify all connections and wiring. |
| Overheating | Poor ventilation or high ambient temp. | Ensure proper cooling and ventilation. |
| Communication failure | Incorrect baud rate or wiring issues | Check communication settings and cables. |
| Battery not charging | Battery voltage mismatch or fault | Verify battery compatibility and health. |
FAQs
Can I use this MPPT controller with a 24V system?
- No, this controller is specifically designed for 48V systems.
What happens if the input voltage exceeds 150V?
- The controller has overvoltage protection and will shut down to prevent damage.
Can I monitor the MPPT controller remotely?
- Yes, the controller supports communication interfaces like RS485, CAN, or Bluetooth for remote monitoring and control.
What type of batteries can I use with this controller?
- The MPPT 48V/70-80A is compatible with lead-acid, lithium-ion, and other 48V battery systems. Always check the battery manufacturer's specifications for compatibility.