
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use Battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with Battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
- The 9V battery is a compact, portable energy storage device that provides a nominal voltage of 9 volts. It is commonly used to power small electronic devices, such as smoke detectors, remote controls, portable radios, and various DIY electronics projects.
- Its rectangular shape and snap-style connectors make it easy to integrate into circuits, especially for prototyping and low-power applications. The 9V battery is a reliable power source for devices requiring moderate energy consumption.
Explore Projects Built with Battery
Solar-Powered Battery Charger with LED Indicator and Motor Control
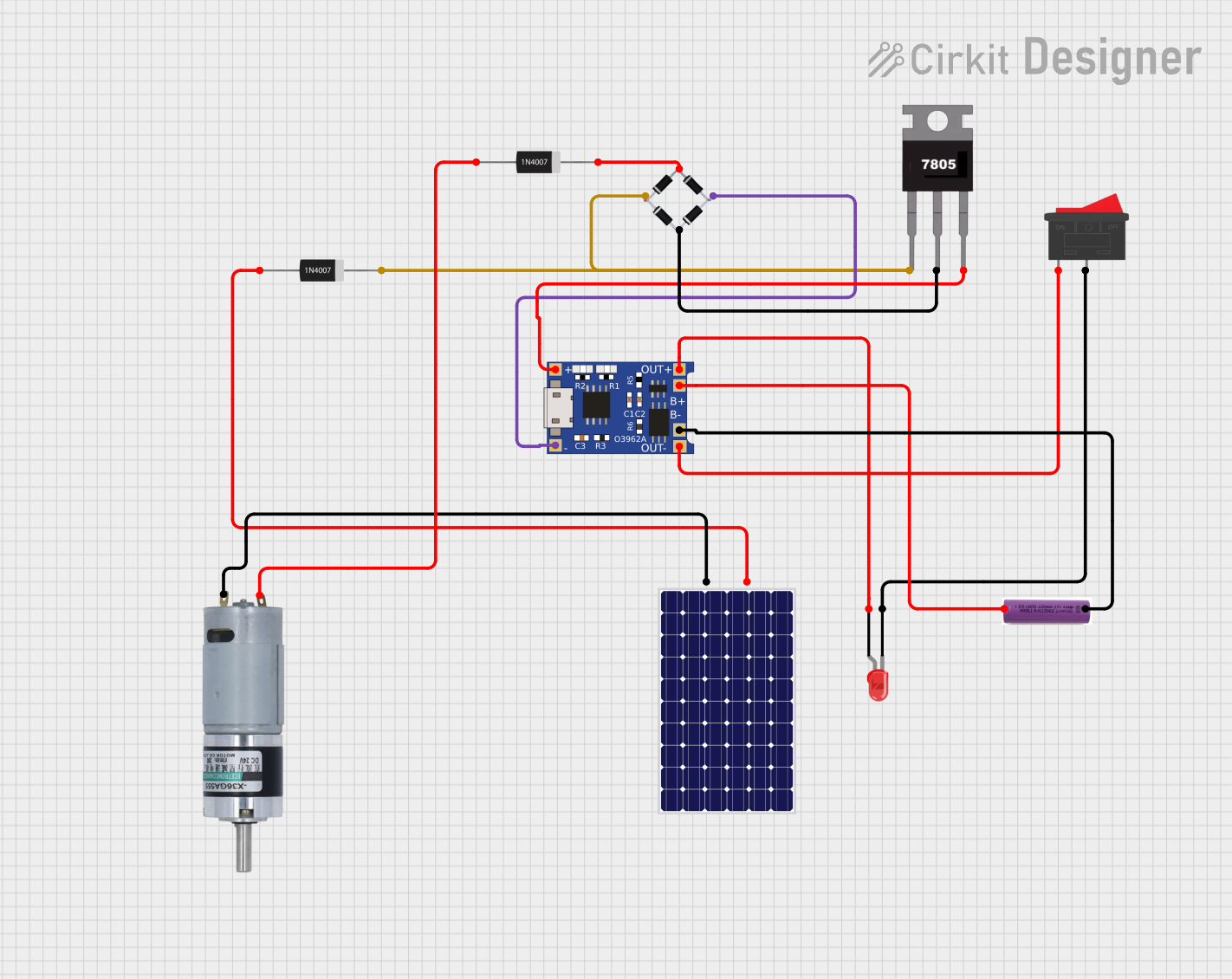
This circuit is a solar-powered battery charging and motor control system. The solar panel charges a 3.7V battery through a TP4056 charging module, which also powers an LED indicator via a rocker switch. Additionally, the circuit includes a motor driven by the battery, with a 7805 voltage regulator and bridge rectifier ensuring stable power delivery.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerSolar-Powered Battery Charging System with Voltage Display and Regulation
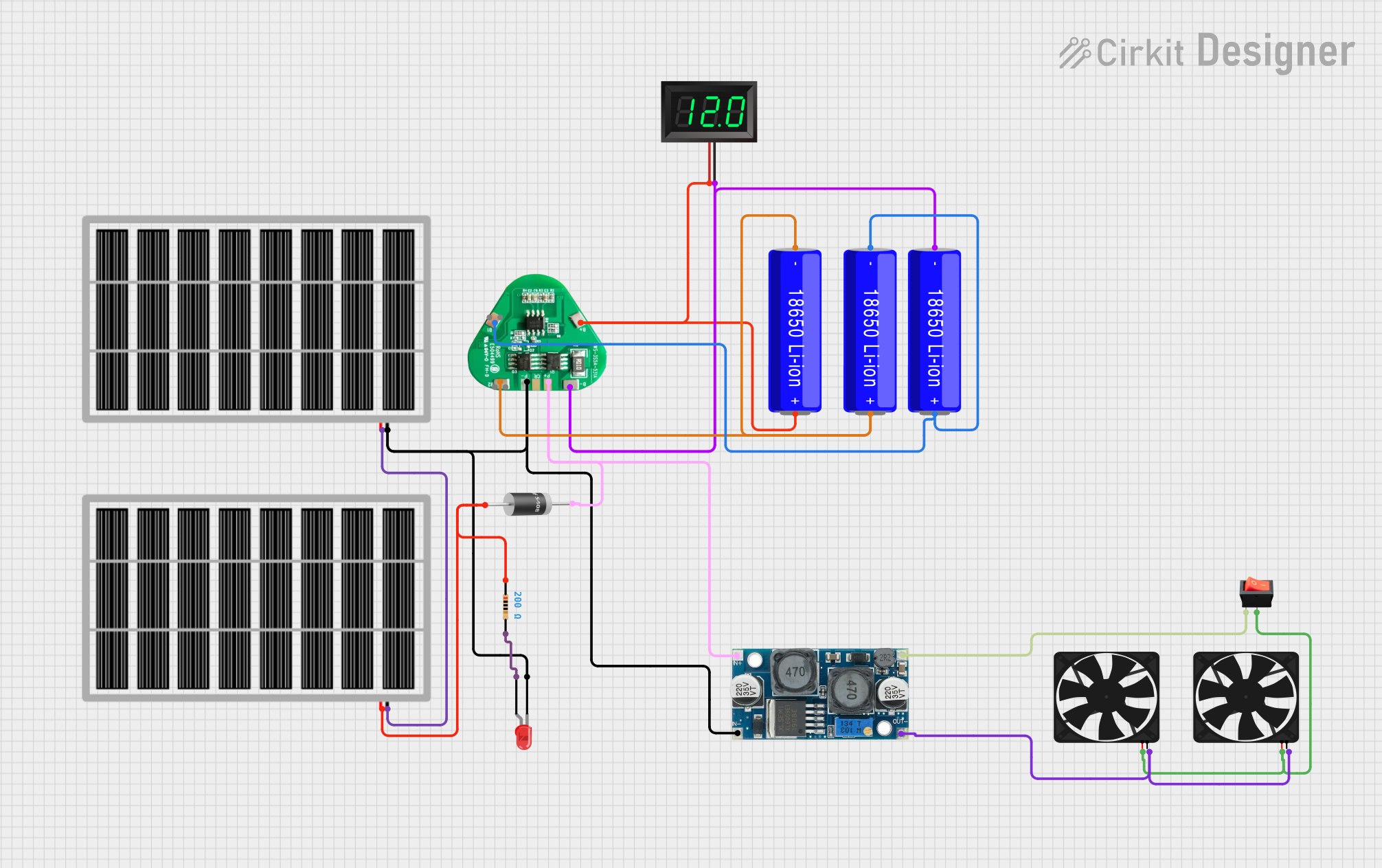
This is a solar-powered battery charging and power supply circuit with a battery management system for 18650 Li-ion batteries. It includes a voltage regulator for stable power delivery to fans, a visual power indicator LED with a current-limiting resistor, and a voltmeter to monitor battery voltage. A rocker switch controls the fans, and diodes are used to prevent reverse current flow.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerBattery-Powered DC Motor Control with USB Charging and LED Indicator

This circuit is designed to charge a Li-ion battery and power a DC motor and a 12V LED. The TP4056 module manages the battery charging process, while the PowerBoost 1000 and MT3608 boost converters step up the voltage to drive the motor and LED, respectively. Two rocker switches control the power flow to the LED and the charging circuit.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerSolar-Powered Battery Charging Circuit with LED Indicator
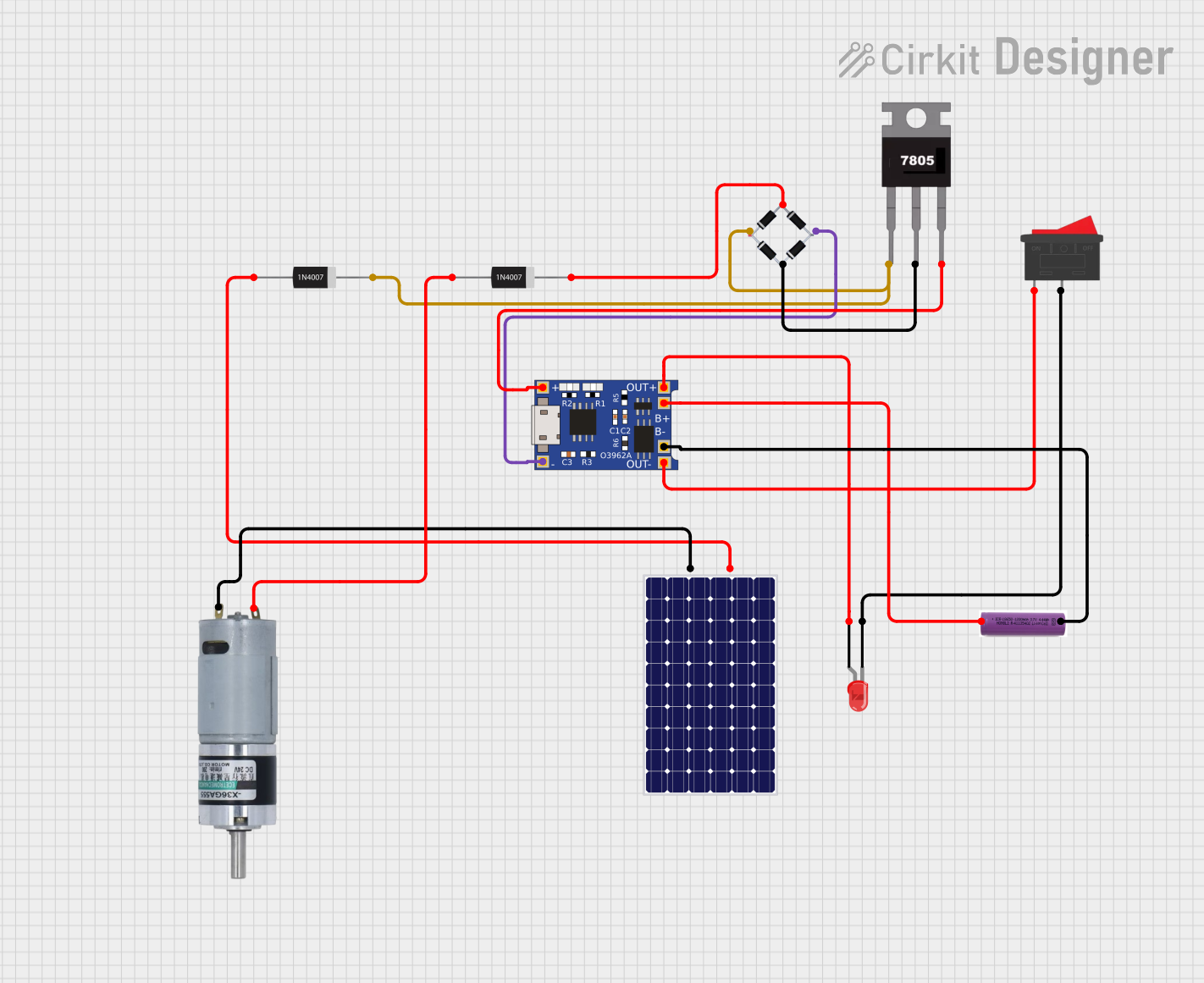
This circuit appears to be a solar-powered charging and power supply system with a battery backup. A TP4056 module is used for charging the 3.7V battery from the solar panel via a bridge rectifier, ensuring proper battery management. The system can power an LED and a motor, with a rocker switch to control the LED, and diodes are used to provide correct polarity and prevent backflow of current.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Battery

Solar-Powered Battery Charger with LED Indicator and Motor Control
This circuit is a solar-powered battery charging and motor control system. The solar panel charges a 3.7V battery through a TP4056 charging module, which also powers an LED indicator via a rocker switch. Additionally, the circuit includes a motor driven by the battery, with a 7805 voltage regulator and bridge rectifier ensuring stable power delivery.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Solar-Powered Battery Charging System with Voltage Display and Regulation
This is a solar-powered battery charging and power supply circuit with a battery management system for 18650 Li-ion batteries. It includes a voltage regulator for stable power delivery to fans, a visual power indicator LED with a current-limiting resistor, and a voltmeter to monitor battery voltage. A rocker switch controls the fans, and diodes are used to prevent reverse current flow.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Battery-Powered DC Motor Control with USB Charging and LED Indicator
This circuit is designed to charge a Li-ion battery and power a DC motor and a 12V LED. The TP4056 module manages the battery charging process, while the PowerBoost 1000 and MT3608 boost converters step up the voltage to drive the motor and LED, respectively. Two rocker switches control the power flow to the LED and the charging circuit.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Solar-Powered Battery Charging Circuit with LED Indicator
This circuit appears to be a solar-powered charging and power supply system with a battery backup. A TP4056 module is used for charging the 3.7V battery from the solar panel via a bridge rectifier, ensuring proper battery management. The system can power an LED and a motor, with a rocker switch to control the LED, and diodes are used to provide correct polarity and prevent backflow of current.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Nominal Voltage: 9V
- Capacity: Typically ranges from 400mAh to 600mAh (varies by brand and type)
- Chemistry: Alkaline, Lithium, or Rechargeable (NiMH or Li-ion)
- Dimensions: 48.5mm x 26.5mm x 17.5mm (standard size)
- Weight: Approximately 45g (varies by type)
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 55°C (varies by chemistry)
- Connector Type: Snap-style terminals (positive and negative)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Terminal | Description | Polarity |
|---|---|---|
| Snap 1 | Positive terminal | +9V |
| Snap 2 | Negative terminal (ground) | 0V |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 9V Battery in a Circuit
Connecting the Battery:
- Use a 9V battery snap connector to securely attach the battery to your circuit. Ensure the red wire connects to the positive terminal and the black wire to the negative terminal.
- Double-check the polarity before connecting to avoid damaging your components.
Powering a Circuit:
- The 9V battery can directly power low-current devices or circuits. For higher current applications, ensure the battery's capacity and chemistry are suitable.
- If using the battery with a voltage regulator (e.g., 7805 for 5V output), ensure proper heat dissipation for the regulator.
Using with Arduino UNO:
- The 9V battery can power an Arduino UNO via the DC barrel jack or the VIN pin.
- Example connection:
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the Arduino's VIN pin or DC barrel jack center pin.
- Connect the negative terminal to the Arduino's GND pin.
Arduino UNO Example Code
// Example: Blink an LED using a 9V battery to power the Arduino UNO
// Ensure the 9V battery is connected to the Arduino's VIN and GND pins.
int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED pin on Arduino UNO
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Life: Monitor the battery's voltage regularly. Replace or recharge the battery when the voltage drops below 7V to avoid circuit instability.
- Storage: Store the battery in a cool, dry place when not in use. Avoid exposing it to extreme temperatures or moisture.
- Disposal: Dispose of used batteries responsibly. Follow local regulations for recycling or disposal of alkaline or rechargeable batteries.
- Short Circuits: Avoid shorting the terminals, as this can cause overheating, leakage, or damage to the battery.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Battery Drains Quickly:
- Cause: High current draw from the circuit or a partially discharged battery.
- Solution: Use a fresh or fully charged battery. Check the circuit's current requirements and ensure they match the battery's capacity.
Device Does Not Power On:
- Cause: Incorrect polarity or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify the battery's polarity and ensure all connections are secure.
Battery Overheats:
- Cause: Short circuit or excessive current draw.
- Solution: Disconnect the battery immediately. Inspect the circuit for shorts or reduce the load.
Voltage Drops Below 9V:
- Cause: Natural discharge or nearing end of battery life.
- Solution: Replace or recharge the battery as needed.
FAQs
Can I use a rechargeable 9V battery in place of an alkaline one?
- Yes, but ensure the rechargeable battery's voltage and capacity are compatible with your circuit.
How long does a 9V battery last?
- Battery life depends on the load. For example, a 500mAh battery powering a 10mA circuit can last approximately 50 hours.
Can I connect two 9V batteries in series?
- Yes, connecting two 9V batteries in series will provide 18V. Ensure your circuit can handle the increased voltage.
What happens if I reverse the polarity?
- Reversing the polarity can damage your circuit. Always double-check connections before powering on.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use a 9V battery in your electronic projects while ensuring safety and optimal performance.