
How to Use boost converter MT3608: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
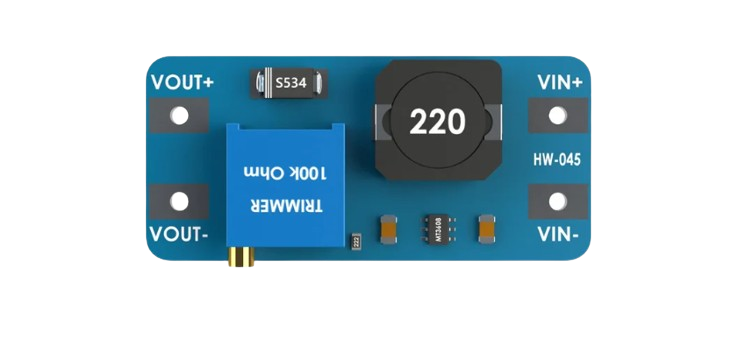
 Design with boost converter MT3608 in Cirkit Designer
Design with boost converter MT3608 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MT3608 is a highly efficient, fixed frequency, step-up (boost) converter designed for a wide range of applications. It is capable of driving a 1.2A load with excellent line and load regulation. The device is suitable for battery-powered devices, portable electronics, and any system requiring a higher voltage output from a lower voltage source.
Explore Projects Built with boost converter MT3608
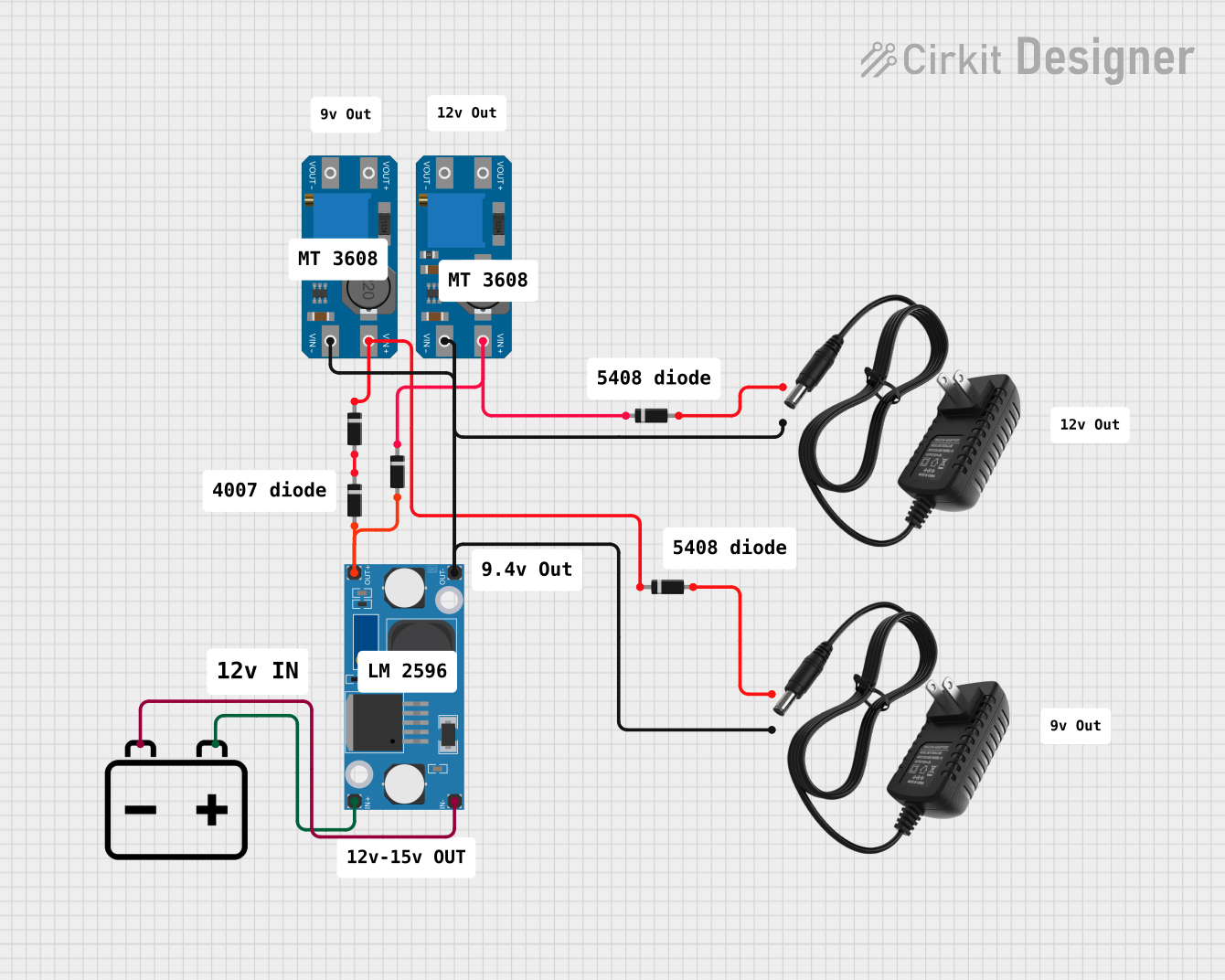
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer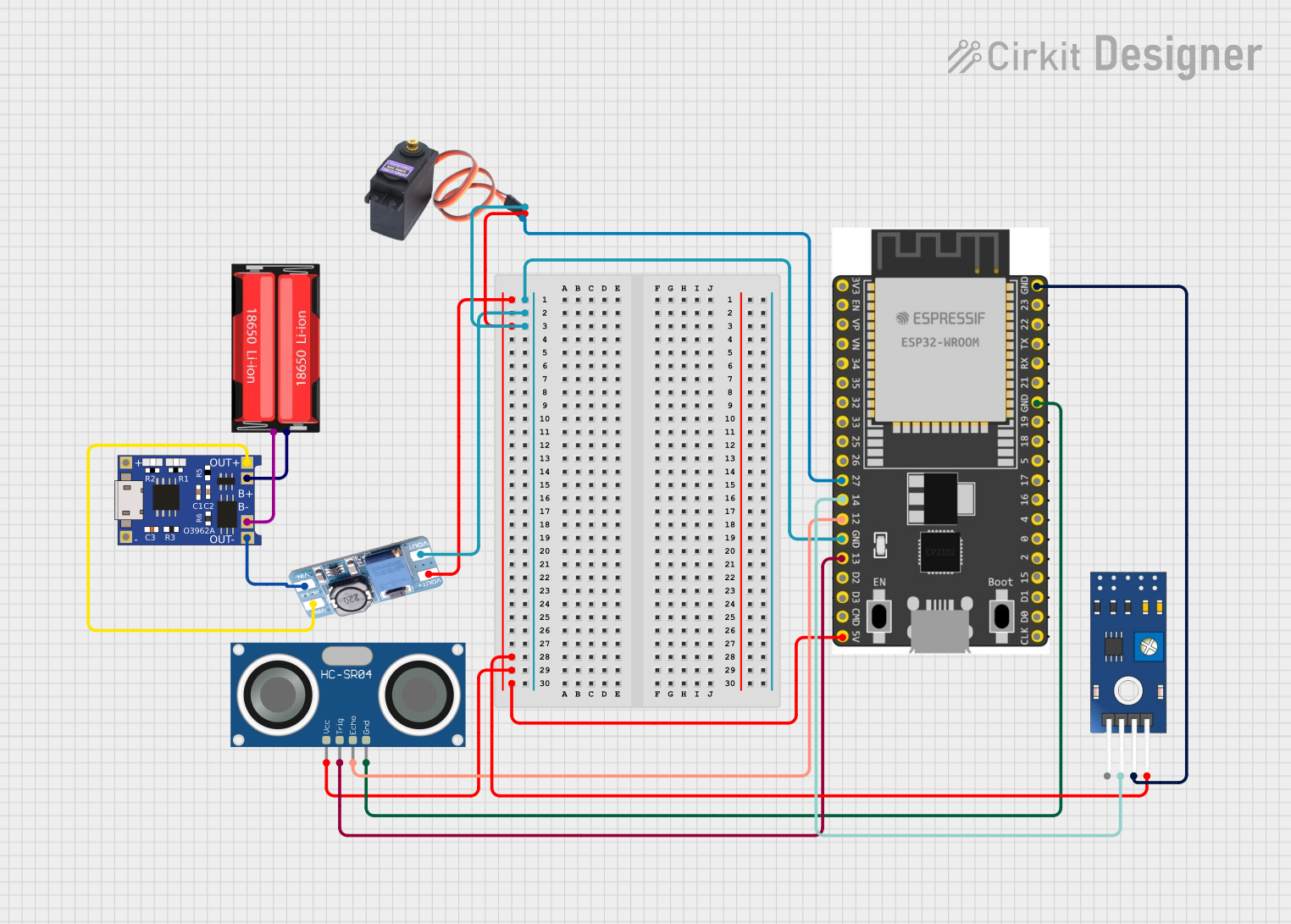
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with boost converter MT3608

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Powering 5V or 12V devices from a single-cell lithium-ion battery
- Supplying power to LED strings
- Portable power banks
- USB-powered devices requiring higher voltages
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: 2V to 24V
- Maximum Output Voltage: 28V
- Switch Current Limit: 4A (typical)
- Quiescent Current: 200µA
- Efficiency: Up to 93%
- Switching Frequency: 1.2MHz
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection. Connect to the system ground plane. |
| 2 | EN | Enable pin. Drive high to enable the converter, low to disable. |
| 3 | VIN | Input voltage. Connect to the source of the DC voltage to be boosted. |
| 4 | SW | Switch pin. Connects to the inductor, carrying the switching current. |
| 5 | FB | Feedback pin. Connects to the voltage divider for output voltage regulation. |
| 6 | VOUT | Output voltage. The boosted voltage is available at this pin. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MT3608 in a Circuit
Connecting Input Power:
- Connect the source voltage to the VIN pin.
- Connect the ground of the power source to the GND pin.
Output Voltage Setup:
- Attach a resistor divider from VOUT to FB to GND to set the desired output voltage.
- The output voltage can be calculated using the formula:
Vout = 0.6V * (1 + R1/R2), where 0.6V is the reference voltage.
Inductor Selection:
- Choose an inductor with a current rating above the maximum load current and a saturation current above the switch current limit.
Capacitor Selection:
- Use a good quality ceramic capacitor at the input and output for stability.
- The input capacitor should be rated for at least the maximum input voltage.
- The output capacitor should be rated for at least the maximum output voltage.
Enable Pin:
- To turn on the MT3608, apply a high logic level to the EN pin.
- To turn off the MT3608, apply a low logic level to the EN pin.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure that the input voltage does not exceed the maximum rating of 24V.
- Do not exceed the maximum output voltage of 28V.
- The layout of the PCB should minimize the loop area formed by the input capacitor, the MT3608, and the inductor to reduce EMI.
- Keep the feedback trace away from noisy components to avoid interference.
- Use a heat sink if the converter is expected to handle loads near the upper limit of its capability.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Output Voltage Not Regulated:
- Check the resistor divider values connected to the FB pin.
- Ensure that the feedback trace is not picking up noise.
Converter Not Starting:
- Verify that the EN pin is being driven high.
- Check for proper input voltage and connections.
Excessive Noise or Ripple:
- Ensure that the input and output capacitors are of adequate value and quality.
- Check the PCB layout for large loop areas that could be causing EMI.
FAQs
Q: Can the MT3608 be used to charge batteries? A: Yes, but an additional charge controller circuit is required to safely charge batteries.
Q: What is the maximum current the MT3608 can output? A: The MT3608 can drive a 1.2A load, but the actual current capability depends on input voltage, output voltage, and thermal conditions.
Q: How do I adjust the output voltage? A: The output voltage is set by a resistor divider connected to the FB pin. Adjust the resistor values according to the formula provided in the Usage Instructions.
Q: Is the MT3608 suitable for automotive applications? A: The MT3608 can be used in automotive applications, provided the input voltage range is within specification and proper thermal management is in place.
Example Arduino Connection
// Example code to control the MT3608 Boost Converter with an Arduino UNO
const int enablePin = 9; // Connect to the EN pin of the MT3608
void setup() {
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW); // Start with the converter disabled
}
void loop() {
// Enable the MT3608 for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(enablePin, HIGH);
delay(5000);
// Disable the MT3608 for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW);
delay(5000);
}
Note: This code example simply turns the MT3608 on and off. For applications requiring variable output voltage control via the Arduino, additional circuitry and code would be necessary to adjust the feedback resistors or to use a digital potentiometer connected to the FB pin.