
How to Use Motor Driver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
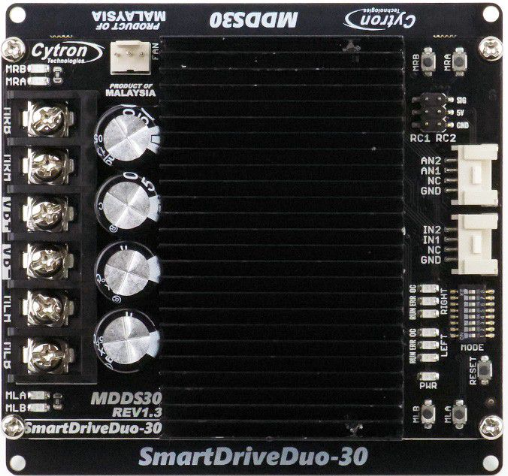
 Design with Motor Driver in Cirkit Designer
Design with Motor Driver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A motor driver is an electronic circuit designed to control the operation of a motor by providing the necessary voltage and current. It acts as an interface between a microcontroller or control system and the motor, enabling precise control of motor speed, direction, and torque. Motor drivers are essential in applications where motors are used, such as robotics, automation systems, electric vehicles, and industrial machinery.
Explore Projects Built with Motor Driver
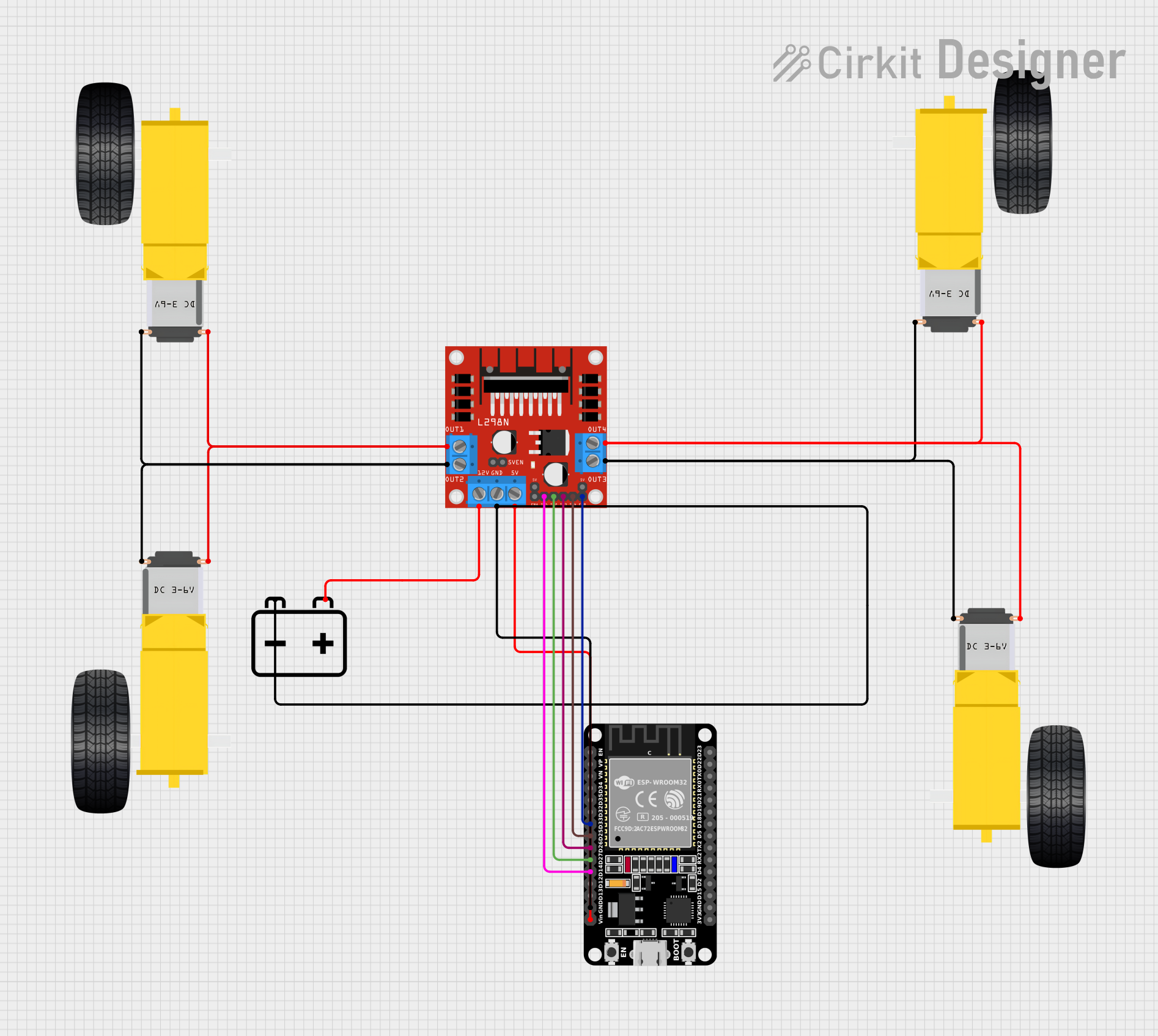
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer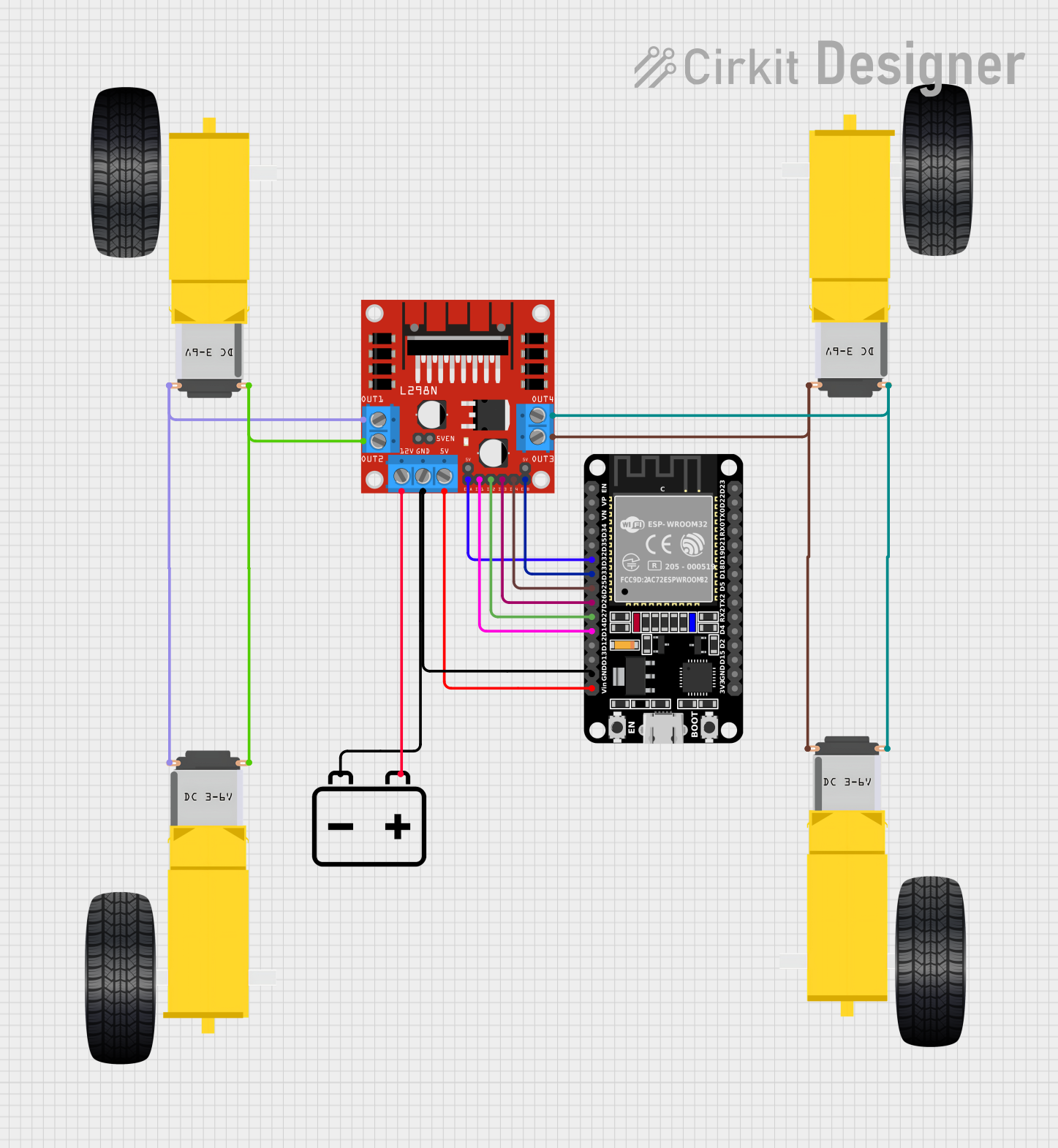
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer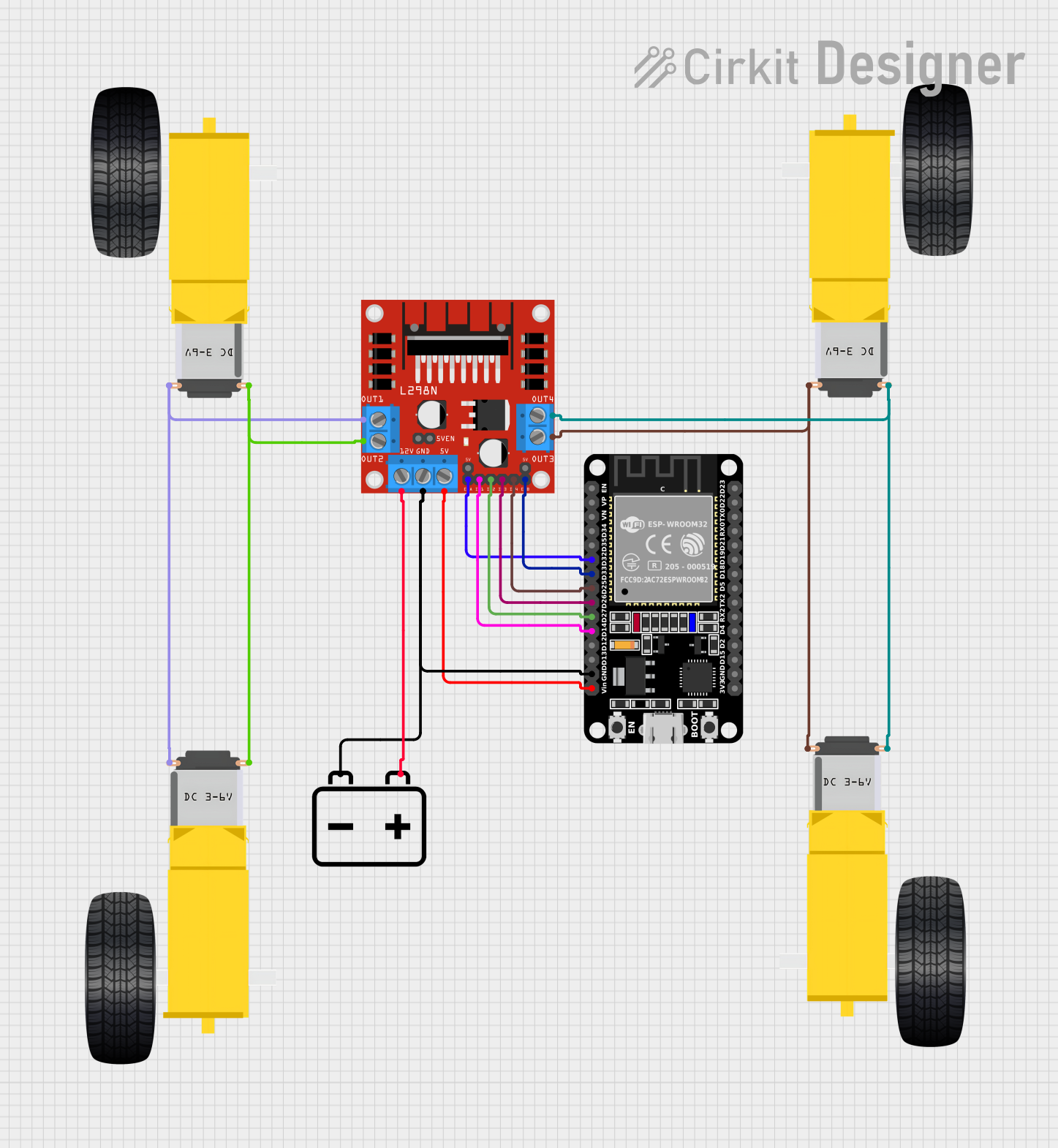
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer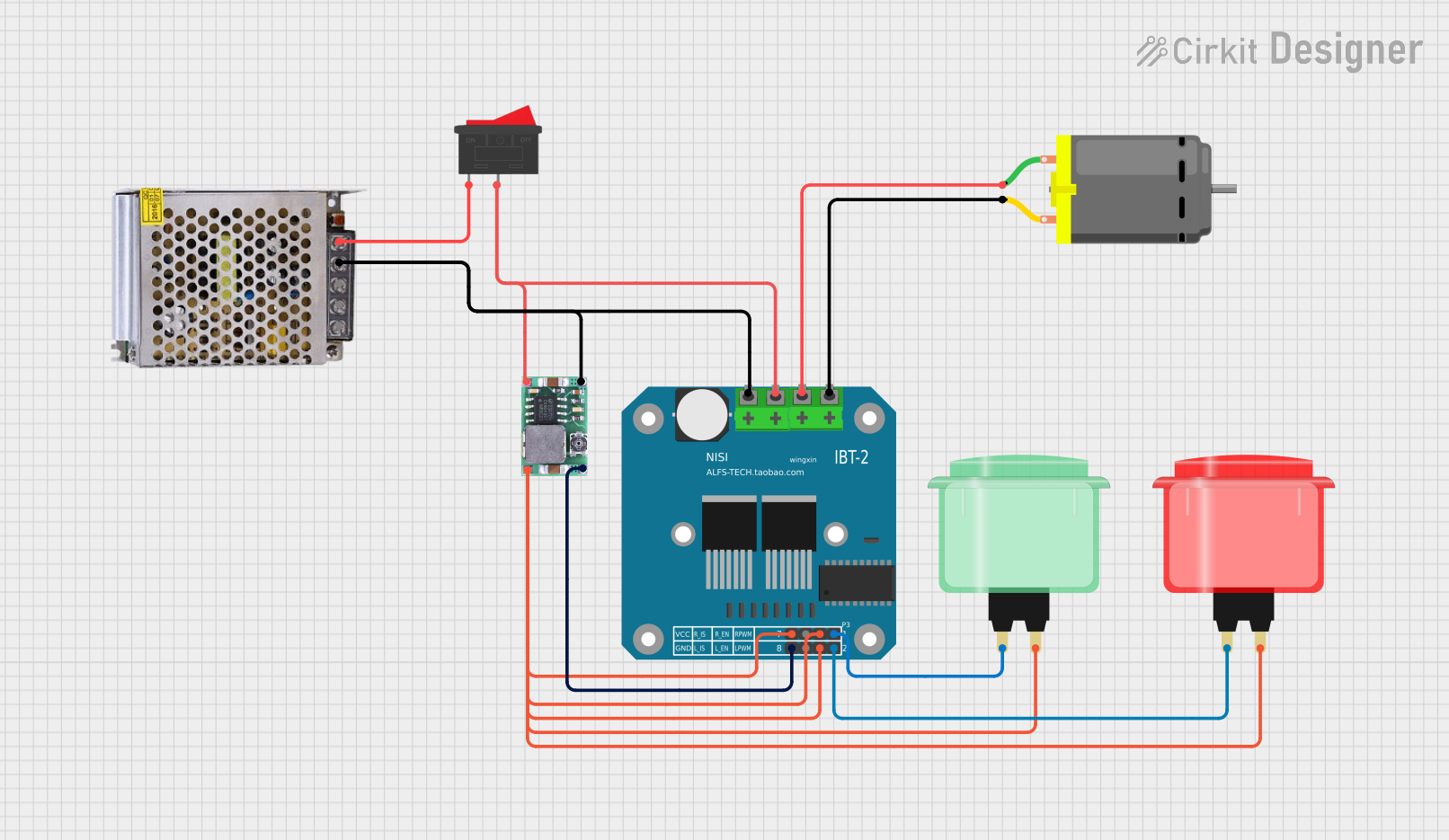
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Motor Driver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Controlling the movement of robotic arms, wheels, or actuators.
- Automation: Driving conveyor belts, pumps, or other automated systems.
- Electric vehicles: Managing the operation of DC or stepper motors in EVs.
- Industrial machinery: Powering and controlling motors in manufacturing equipment.
- DIY projects: Enabling motor control in hobbyist and educational projects.
Technical Specifications
Motor drivers come in various types, such as H-bridge drivers, stepper motor drivers, and servo motor drivers. Below are the general technical specifications for a typical DC motor driver (e.g., L298N):
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 5V to 46V (varies by model)
- Output Current: Up to 2A per channel (continuous)
- Peak Current: Up to 3A per channel (short duration)
- Number of Channels: Dual-channel (can control two motors independently)
- Control Logic Voltage: 3.3V or 5V (compatible with most microcontrollers)
- PWM Frequency: Up to 25 kHz
- Thermal Protection: Built-in over-temperature shutdown
- Dimensions: Typically compact, e.g., 43mm x 43mm for L298N modules
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Below is the pin configuration for a common motor driver module (e.g., L298N):
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
IN1 |
Input pin to control motor 1 direction (logic HIGH or LOW). |
IN2 |
Input pin to control motor 1 direction (logic HIGH or LOW). |
IN3 |
Input pin to control motor 2 direction (logic HIGH or LOW). |
IN4 |
Input pin to control motor 2 direction (logic HIGH or LOW). |
ENA |
Enable pin for motor 1 (connect to PWM signal for speed control). |
ENB |
Enable pin for motor 2 (connect to PWM signal for speed control). |
VCC |
Power supply for the motors (e.g., 12V or 24V, depending on motor requirements). |
GND |
Ground connection. |
5V |
Logic voltage output (can power a microcontroller in some modules). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Motor Driver: Connect the
VCCpin to the motor power supply (e.g., 12V) and theGNDpin to the ground of the power supply. - Connect the Motors: Attach the motor terminals to the output pins of the motor driver (e.g.,
OUT1andOUT2for motor 1,OUT3andOUT4for motor 2). - Connect Control Pins: Link the
IN1,IN2,IN3, andIN4pins to the microcontroller's GPIO pins for direction control. - Enable Speed Control: Connect the
ENAandENBpins to PWM-capable GPIO pins on the microcontroller for speed control. - Logic Voltage: If required, connect the
5Vpin to the microcontroller's logic voltage input.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the motor power supply voltage matches the motor's specifications.
- Heat Dissipation: Use a heat sink or cooling fan if the motor driver operates at high currents for extended periods.
- Current Limits: Do not exceed the motor driver's maximum current rating to avoid damage.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Add capacitors near the motor driver to reduce noise and voltage spikes.
- Wiring: Use thick wires for motor connections to handle high currents.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a DC motor using an L298N motor driver and an Arduino UNO:
// Define motor control pins
const int IN1 = 9; // Motor 1 direction pin 1
const int IN2 = 8; // Motor 1 direction pin 2
const int ENA = 10; // Motor 1 speed control (PWM)
// Setup function
void setup() {
// Set motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT);
}
// Loop function
void loop() {
// Rotate motor clockwise
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH); // Set IN1 HIGH
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 LOW
analogWrite(ENA, 128); // Set speed to 50% (PWM value: 128 out of 255)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop motor
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 LOW
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 LOW
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Rotate motor counterclockwise
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 LOW
digitalWrite(IN2, HIGH); // Set IN2 HIGH
analogWrite(ENA, 200); // Set speed to ~78% (PWM value: 200 out of 255)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop motor
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW); // Set IN1 LOW
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 LOW
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Running:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, especially power and control pins.
Motor Running in the Wrong Direction:
- Cause: Control pins (
IN1,IN2, etc.) are set incorrectly. - Solution: Swap the logic levels of the control pins or reverse the motor wires.
- Cause: Control pins (
Motor Driver Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the current rating or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Use a heat sink or fan, and ensure the motor's current is within the driver's limits.
PWM Not Controlling Speed:
- Cause: Incorrect PWM pin or frequency.
- Solution: Verify the PWM pin and ensure the frequency is within the motor driver's range.
FAQs
Can I use the motor driver with a 3.3V microcontroller?
- Yes, most motor drivers are compatible with 3.3V logic, but check the datasheet to confirm.
What type of motors can I control with this driver?
- DC motors, stepper motors (with additional control logic), and small brushed motors.
Can I power the motor driver and microcontroller from the same power source?
- Yes, but ensure the power source can handle the combined current draw of the motor and microcontroller.