
How to Use VCC 3.3V: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with VCC 3.3V in Cirkit Designer
Design with VCC 3.3V in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The VCC 3.3V is a voltage supply that provides a constant output of 3.3 volts. It is widely used in digital circuits to power microcontrollers, sensors, and other low-voltage components. This regulated voltage source is essential for devices that operate at 3.3V logic levels, ensuring stable and reliable performance in a variety of applications.
Explore Projects Built with VCC 3.3V

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer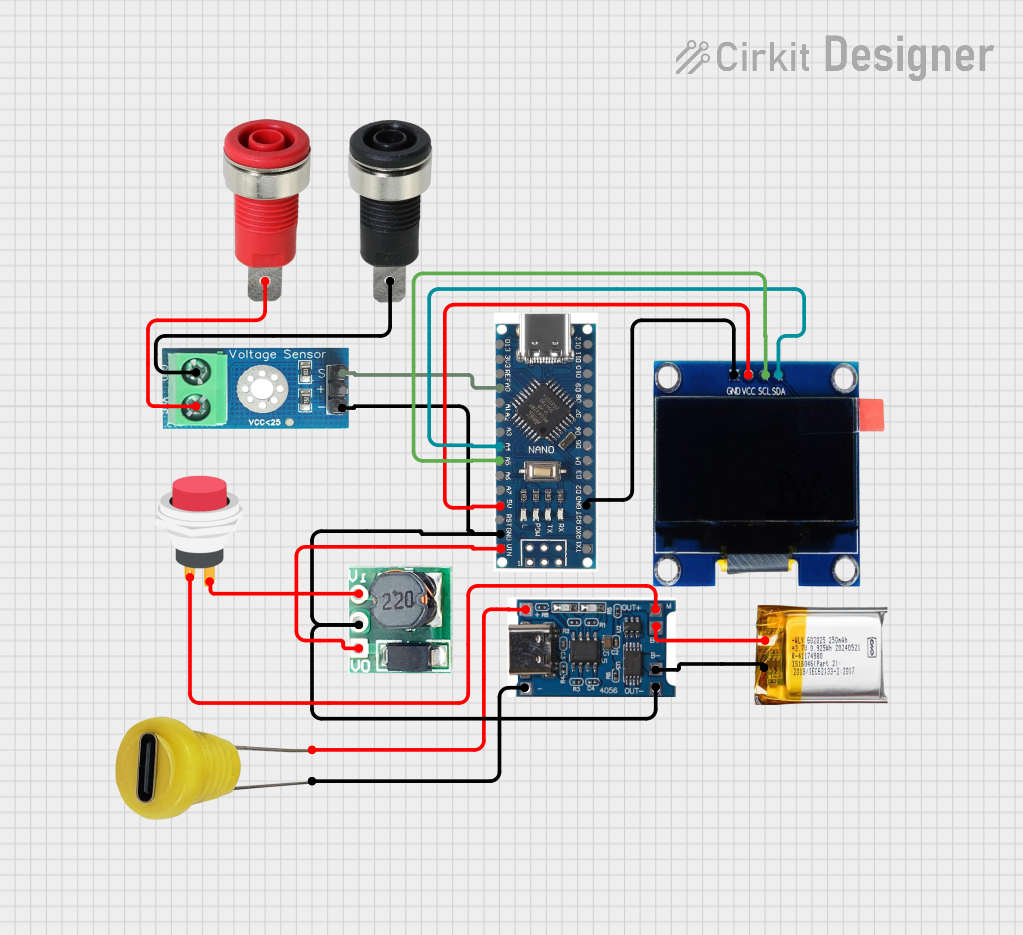
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with VCC 3.3V

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering microcontrollers such as ESP32, ESP8266, and STM32.
- Supplying voltage to low-power sensors like temperature, humidity, and pressure sensors.
- Driving communication modules such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LoRa.
- Providing power to 3.3V logic-level integrated circuits (ICs).
Technical Specifications
The VCC 3.3V supply is typically derived from a voltage regulator or a dedicated power supply circuit. Below are the key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Output Voltage | 3.3V ± 5% |
| Maximum Output Current | Depends on the regulator (e.g., 500mA, 1A, etc.) |
| Input Voltage Range | Typically 5V to 12V (for regulators) |
| Ripple Voltage | < 50mV |
| Efficiency | Up to 90% (for switching regulators) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The VCC 3.3V supply is often available as part of a voltage regulator module or integrated into development boards. Below is a typical pinout for a 3.3V voltage regulator module:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage (e.g., 5V or higher) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| VOUT | Regulated 3.3V output |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the VCC 3.3V in a Circuit
- Connect the Input Voltage (VIN): Provide a suitable input voltage to the VIN pin. For example, if using an LM1117-3.3 regulator, supply 5V to 12V at the input.
- Connect the Ground (GND): Ensure the GND pin is connected to the ground of your circuit.
- Obtain the 3.3V Output (VOUT): Use the VOUT pin to power your 3.3V devices.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range of the regulator or power supply.
- Current Requirements: Verify that the VCC 3.3V source can supply sufficient current for all connected devices.
- Bypass Capacitors: Place decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF and 10µF) near the VOUT pin to reduce noise and improve stability.
- Heat Dissipation: If using a linear regulator, ensure proper heat dissipation, especially for high input voltages and currents.
- Polarity Protection: Use a diode at the input to prevent damage from reverse polarity connections.
Example: Using VCC 3.3V with an Arduino UNO
Although the Arduino UNO operates at 5V logic levels, it can interface with 3.3V devices using level shifters or directly if the device tolerates 5V inputs. Below is an example of connecting a 3.3V sensor to an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the sensor's VCC pin to the 3.3V output of a voltage regulator.
- Connect the sensor's GND pin to the Arduino's GND.
- Connect the sensor's data pin to an appropriate Arduino input pin (use a level shifter if needed).
Example Code
// Example code to read data from a 3.3V sensor connected to Arduino UNO
// Ensure proper level shifting if the sensor cannot tolerate 5V signals.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor's output
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert to voltage (5V reference)
// Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Sensor Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Check the input voltage to ensure it is within the specified range.
- Verify all connections, especially the GND and VIN pins.
- Inspect the regulator for overheating or damage.
Output Voltage is Unstable:
- Add decoupling capacitors near the VOUT pin.
- Ensure the input voltage is stable and free from excessive noise.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating of the regulator.
Device Not Powering On:
- Confirm that the device's current requirements do not exceed the regulator's capacity.
- Check for loose or incorrect connections.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the VCC 3.3V to power a 5V device?
A: No, 5V devices typically require a higher voltage and may not function correctly at 3.3V. Use a step-up converter if needed.
Q: What happens if I exceed the maximum current rating?
A: Exceeding the current rating can cause the regulator to overheat, shut down, or become permanently damaged.
Q: Do I need a heatsink for the regulator?
A: For linear regulators, a heatsink is recommended if the input voltage is significantly higher than 3.3V or if the current draw is high.
Q: Can I connect multiple devices to the same VCC 3.3V source?
A: Yes, as long as the total current draw of all devices does not exceed the regulator's maximum output current.