
How to Use Servo SG90: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Servo SG90 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Servo SG90 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Servo SG90 is a small, lightweight servo motor widely used in hobby projects, robotics, and remote-controlled devices. It is designed to provide precise control of angular position, making it ideal for applications such as steering mechanisms, robotic arms, and pan-tilt camera systems. Its compact size, affordability, and ease of use make it a popular choice for beginners and experienced makers alike.
Explore Projects Built with Servo SG90
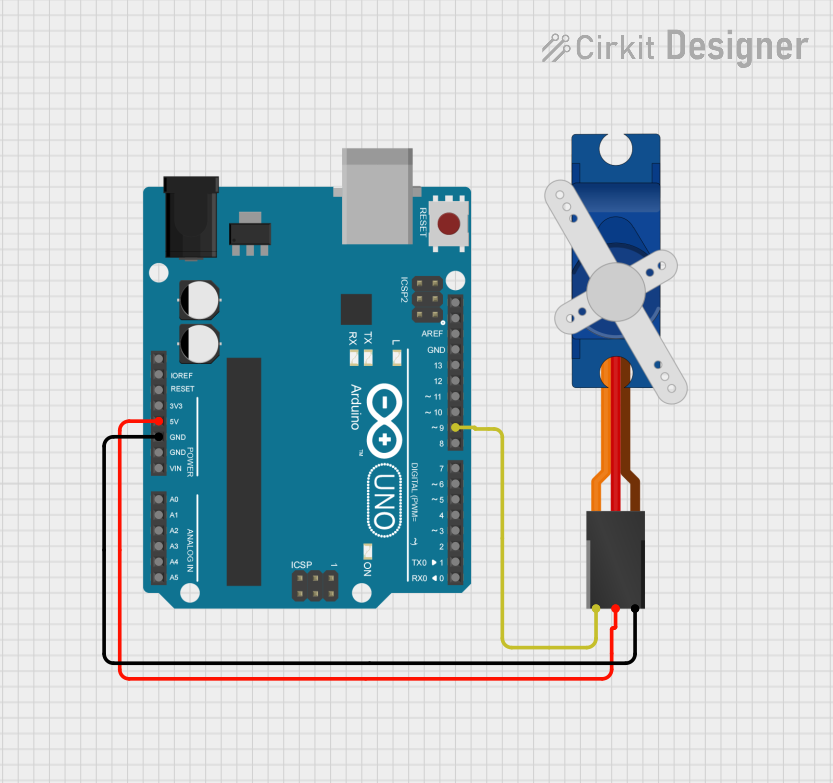
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer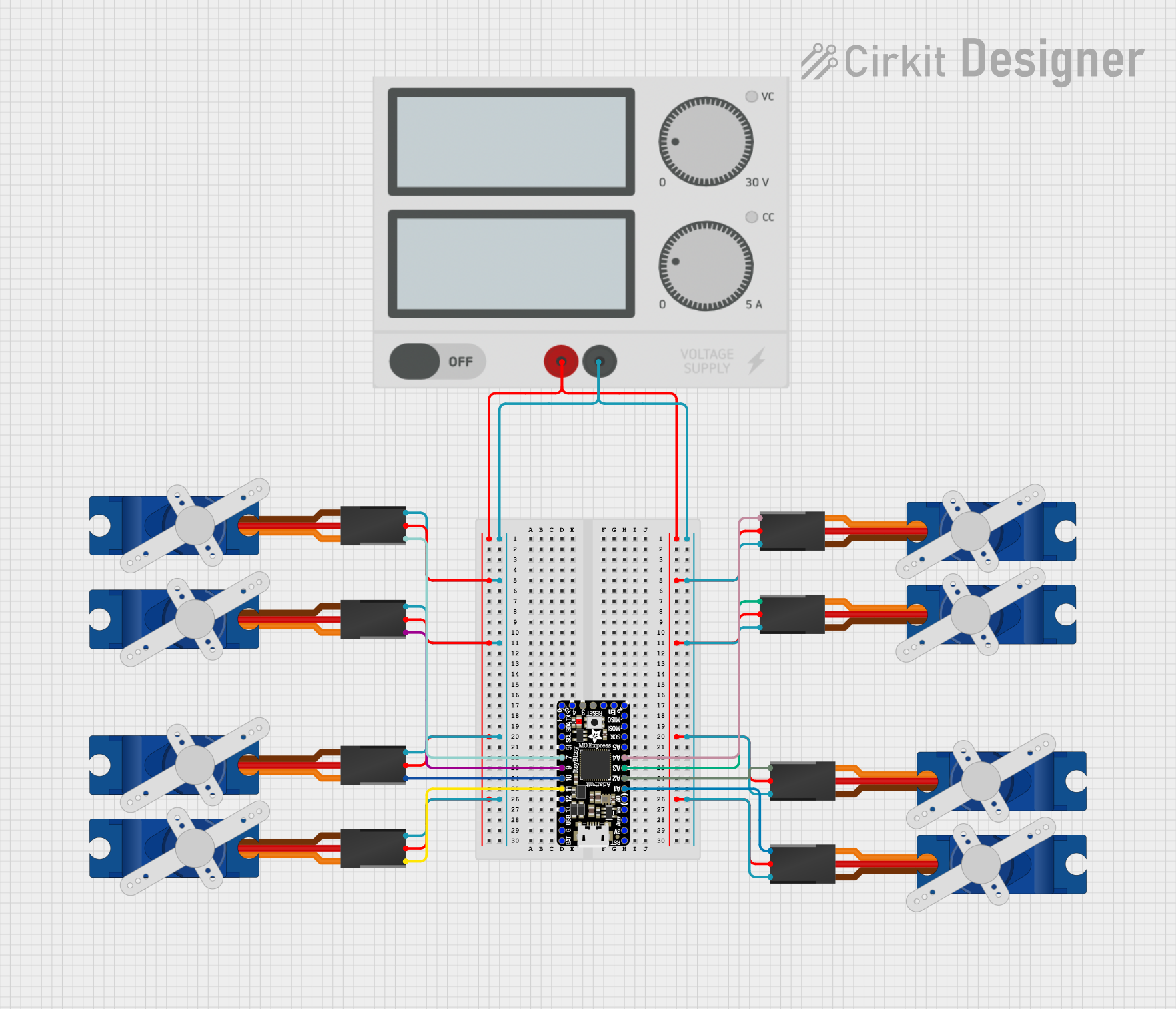
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer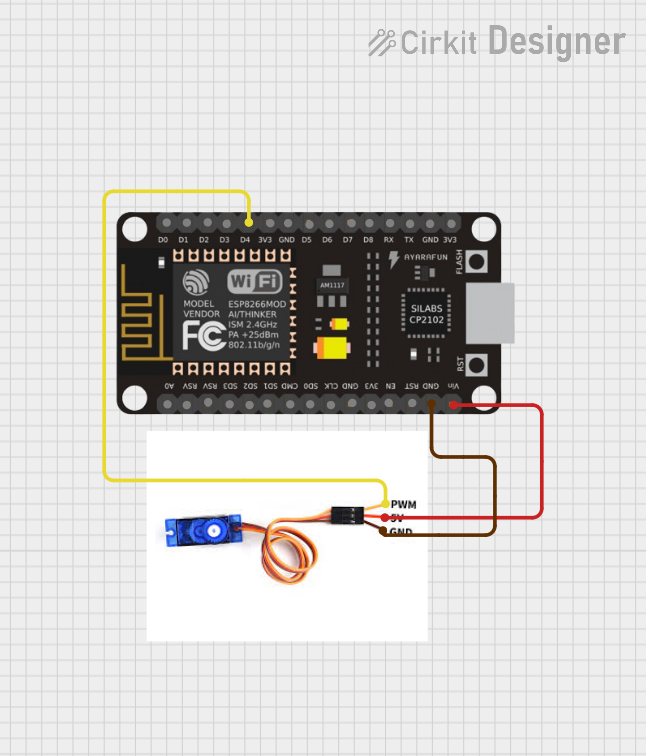
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer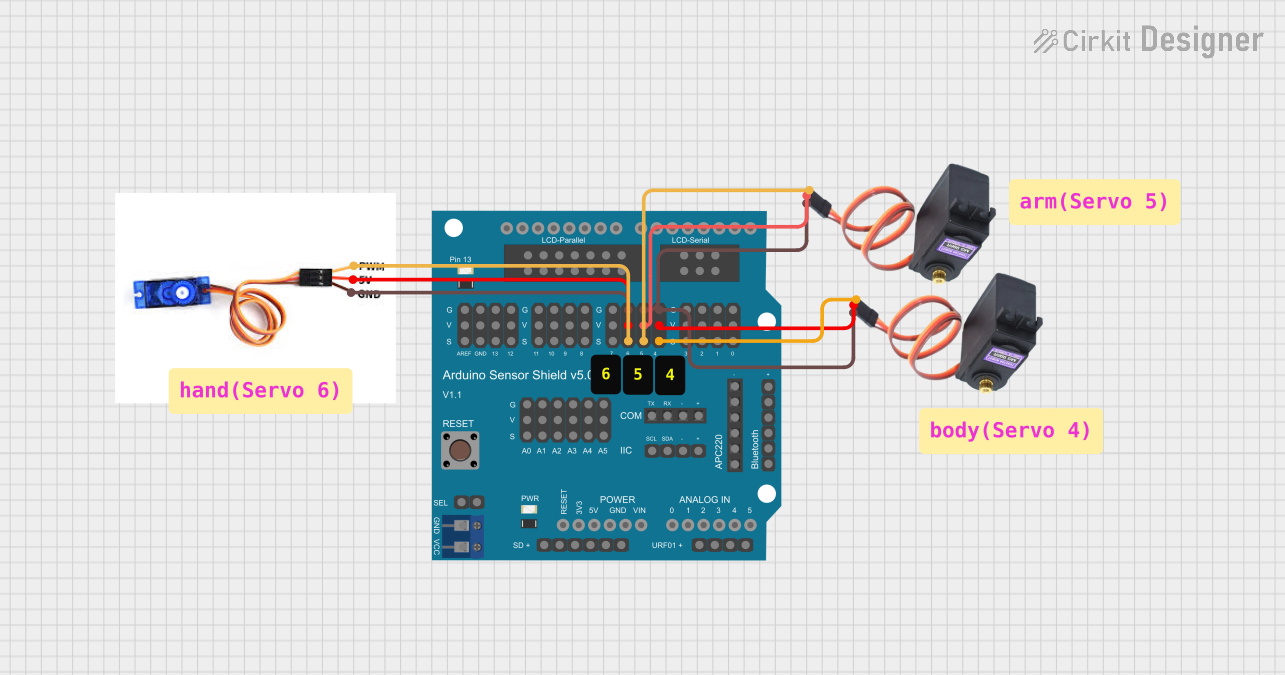
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Servo SG90

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Model: SG90
- Type: Analog Servo Motor
- Operating Voltage: 4.8V to 6.0V
- Operating Speed: 0.1 seconds/60° at 4.8V, 0.09 seconds/60° at 6.0V
- Torque: 1.8 kg·cm at 4.8V, 2.2 kg·cm at 6.0V
- Weight: 9 grams
- Angle Range: 0° to 180°
- Control Signal: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- Connector Type: 3-pin female header (compatible with standard servo connectors)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Servo SG90 has a 3-pin connector with the following pinout:
| Pin Number | Wire Color | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brown | Ground (GND) | Connect to the ground of the power supply |
| 2 | Red | Power (VCC) | Connect to a 4.8V-6.0V power source |
| 3 | Orange | Signal (PWM) | Receives PWM signal for position control |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Servo SG90 in a Circuit
- Power Connection: Connect the red wire to a 5V power source and the brown wire to ground (GND). Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current (at least 500mA) to avoid voltage drops.
- Signal Connection: Connect the orange wire to a PWM-capable pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
- PWM Signal: Send a PWM signal to the servo to control its position. The pulse width determines the angle:
- 1ms pulse width corresponds to 0°.
- 1.5ms pulse width corresponds to 90° (center position).
- 2ms pulse width corresponds to 180°.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Avoid powering the servo directly from the microcontroller's 5V pin, as it may not provide enough current. Use an external power source if possible.
- PWM Frequency: The SG90 typically operates at a PWM frequency of 50Hz (20ms period).
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the torque rating to prevent damage to the servo.
- Mechanical Stops: The servo has built-in mechanical stops to limit its range to 180°. Forcing it beyond this range can damage the gears.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the Servo SG90 using an Arduino UNO:
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library
Servo myServo; // Create a Servo object to control the SG90
void setup() {
myServo.attach(9); // Attach the servo to pin 9 on the Arduino
}
void loop() {
myServo.write(0); // Move the servo to 0 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
myServo.write(90); // Move the servo to 90 degrees (center position)
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
myServo.write(180); // Move the servo to 180 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Code Explanation:
- The
Servolibrary simplifies controlling the SG90. - The
attach()function links the servo to a specific PWM pin. - The
write()function sets the servo's position in degrees (0° to 180°).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Servo Not Moving:
- Cause: Insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Use a dedicated power source capable of providing at least 500mA.
Servo Jittering:
- Cause: Electrical noise or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Add a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 100µF) across the power supply.
Servo Overheating:
- Cause: Prolonged operation under high torque or incorrect PWM signal.
- Solution: Ensure the servo is not overloaded and verify the PWM signal is within the correct range.
Limited Range of Motion:
- Cause: Incorrect PWM signal or mechanical obstruction.
- Solution: Check the PWM signal and ensure there are no physical obstructions.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the Servo SG90 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you must power the servo with 4.8V-6.0V and use a level shifter for the PWM signal if necessary.
Q: How many SG90 servos can I control with an Arduino?
A: The number depends on the available PWM pins and the power supply's capacity. Ensure the power supply can handle the total current draw.
Q: Can the SG90 rotate continuously?
A: No, the SG90 is a positional servo with a range of 0° to 180°. For continuous rotation, use a continuous rotation servo.
Q: What is the lifespan of the SG90?
A: The lifespan depends on usage conditions, but it is generally durable for hobby projects when operated within its specifications.