
How to Use Raspberry Pi Zero 2W: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
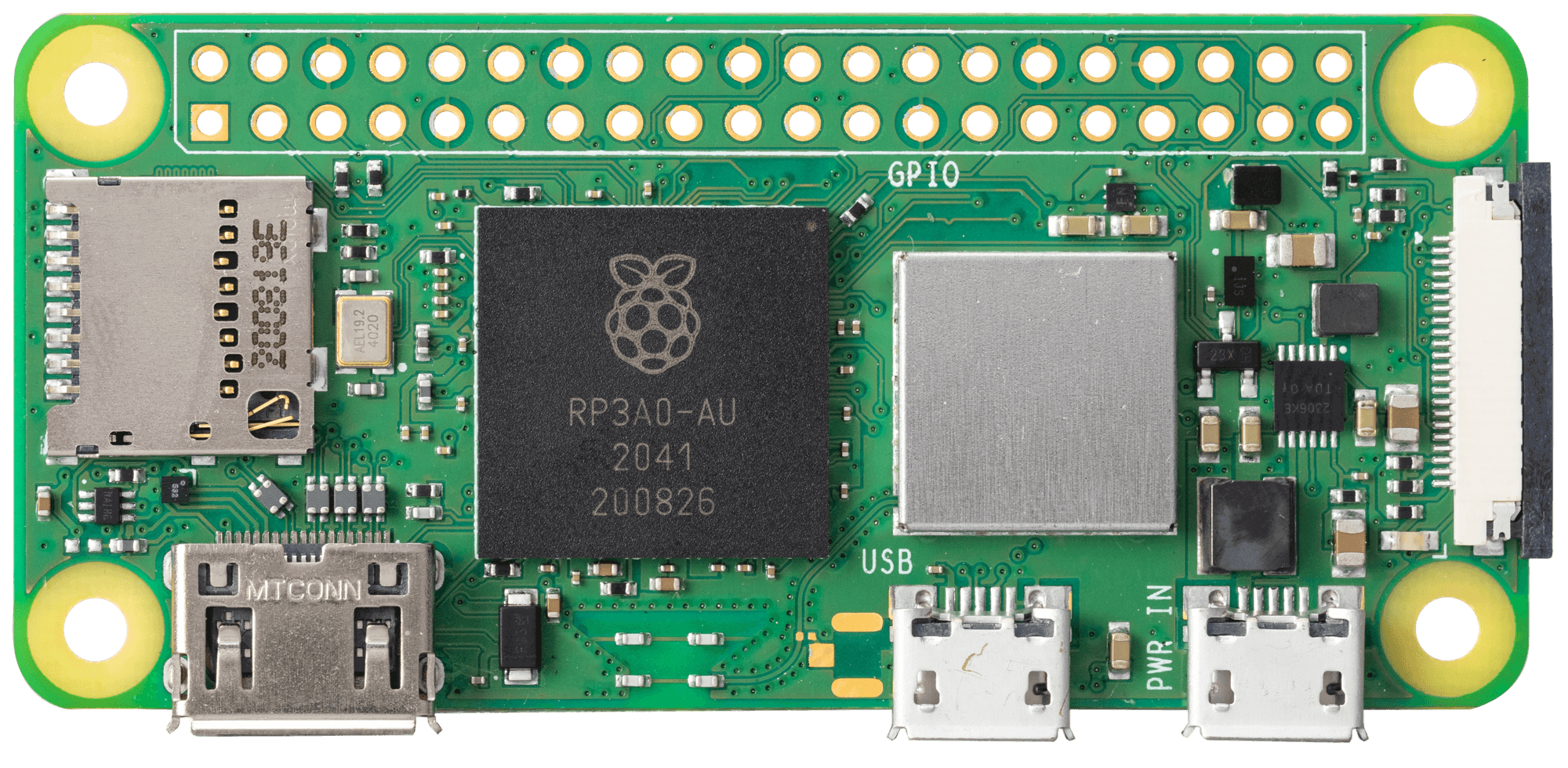
 Design with Raspberry Pi Zero 2W in Cirkit Designer
Design with Raspberry Pi Zero 2W in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W is a compact, low-cost single-board computer designed for DIY projects, embedded systems, and educational purposes. It features a quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor, wireless connectivity (Wi-Fi and Bluetooth), and a 40-pin GPIO header for interfacing with various electronic components. Its small form factor and versatile capabilities make it an excellent choice for applications such as IoT devices, robotics, media streaming, and home automation.
Explore Projects Built with Raspberry Pi Zero 2W
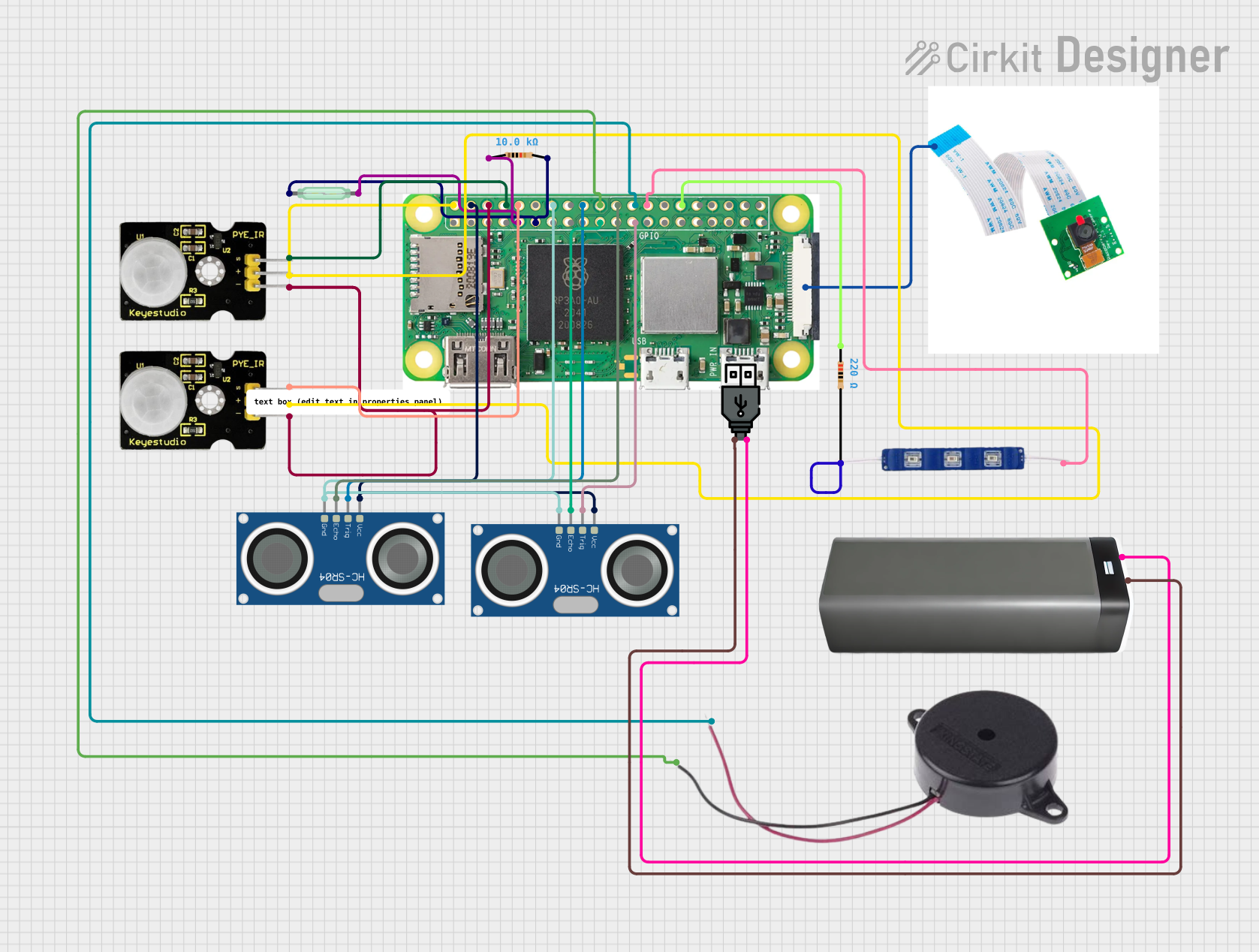
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer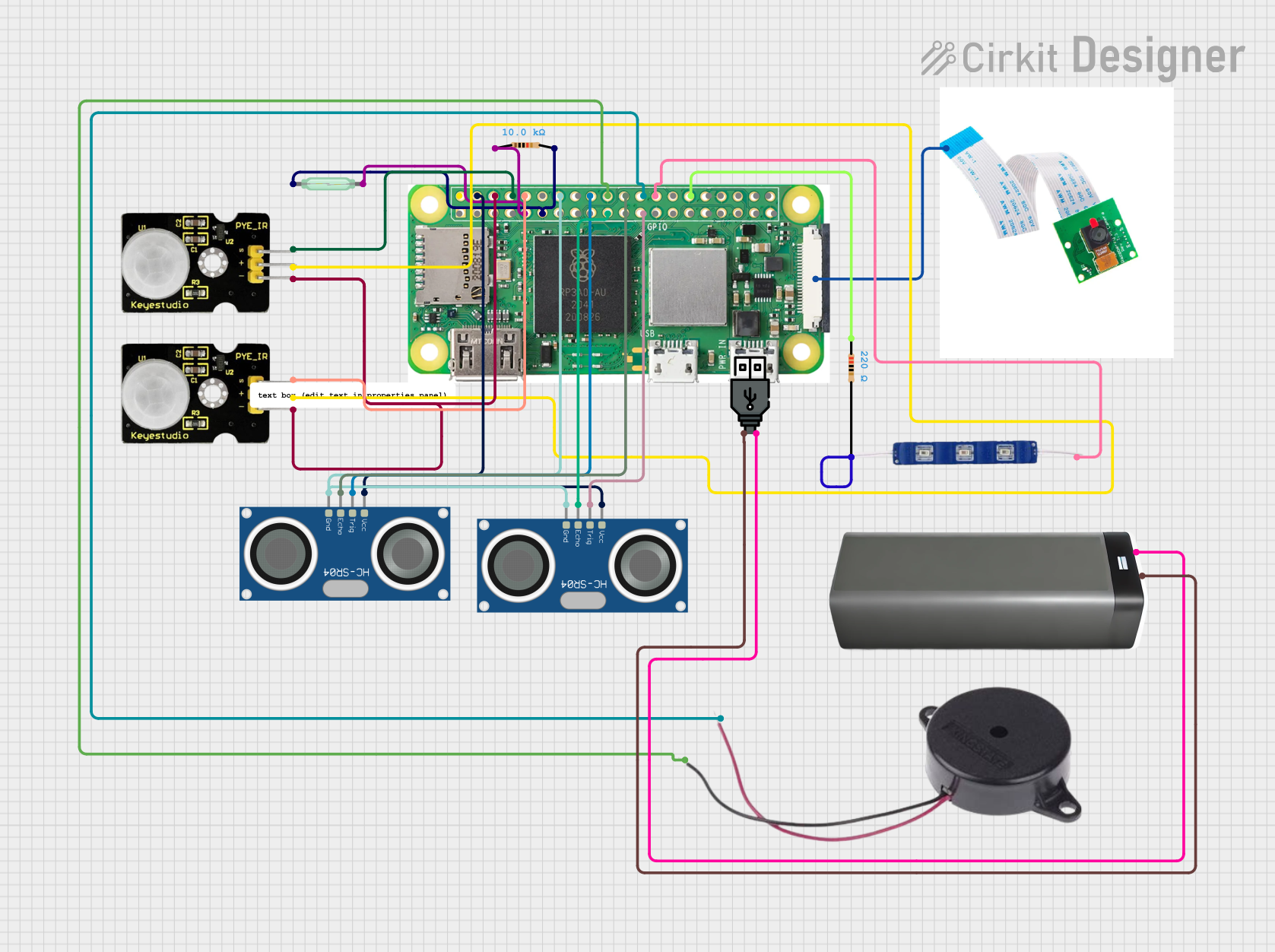
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer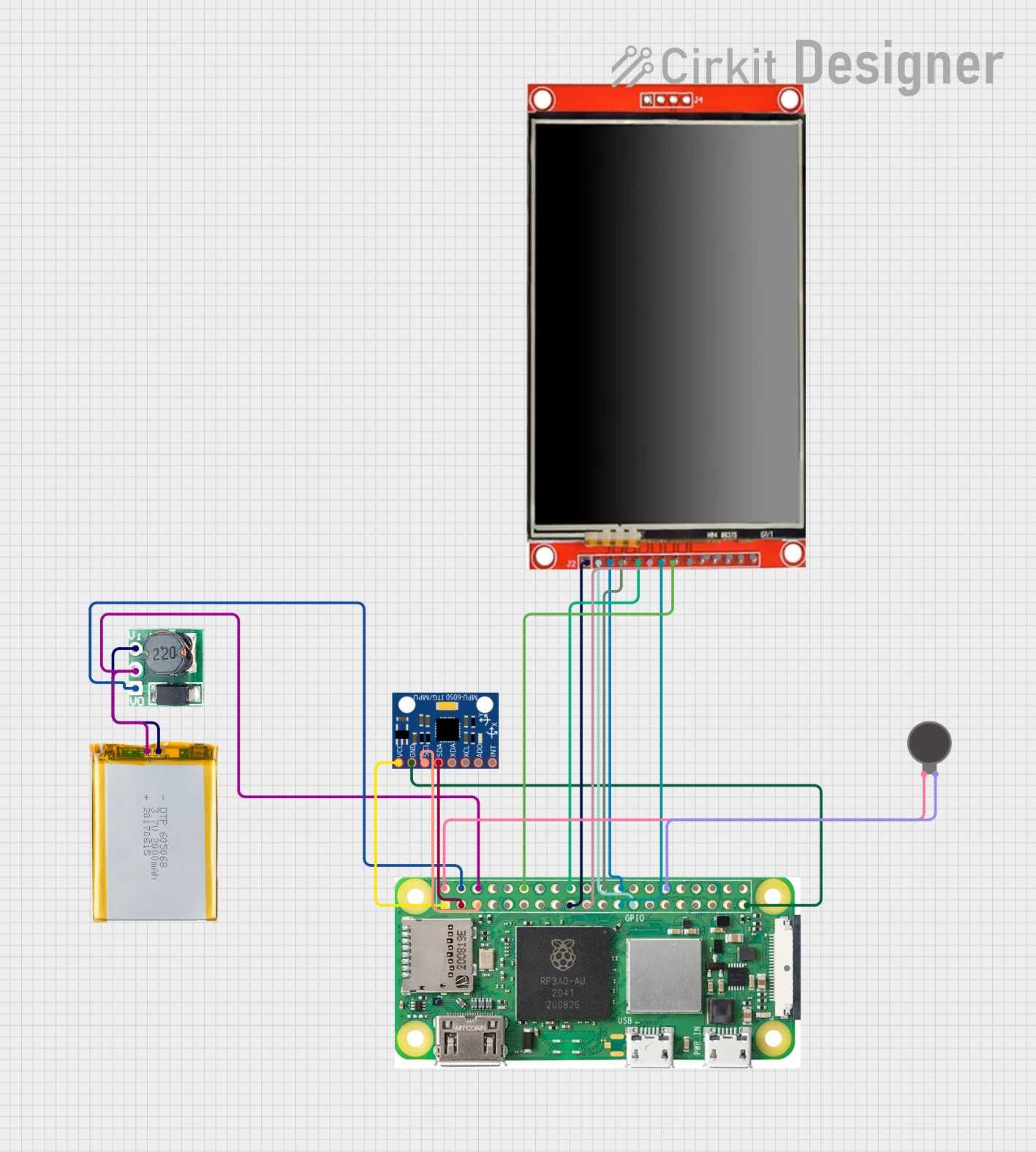
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Raspberry Pi Zero 2W

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- Robotics and automation projects
- Media streaming and playback
- Home automation systems
- Educational tools for learning programming and electronics
- Portable gaming consoles
- Networked sensors and data loggers
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2710A1, quad-core ARM Cortex-A53, 64-bit, 1 GHz |
| RAM | 512 MB LPDDR2 SDRAM |
| Wireless Connectivity | 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.2, BLE |
| GPIO Header | 40-pin GPIO (unpopulated) |
| Video Output | Mini HDMI port, supports up to 1080p at 60 fps |
| USB Ports | 1x Micro USB for data, 1x Micro USB for power |
| Camera Interface | CSI-2 camera connector (requires adapter cable) |
| Power Supply | 5V/2.5A via Micro USB |
| Dimensions | 65mm × 30mm × 5mm |
| Weight | Approximately 9 grams |
GPIO Pin Configuration
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W features a 40-pin GPIO header. Below is a summary of the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3V | Power supply (3.3V) |
| 2 | 5V | Power supply (5V) |
| 3 | GPIO2 (SDA1) | I2C Data |
| 4 | 5V | Power supply (5V) |
| 5 | GPIO3 (SCL1) | I2C Clock |
| 6 | GND | Ground |
| 7 | GPIO4 | General-purpose I/O |
| 8 | GPIO14 (TXD) | UART Transmit |
| 9 | GND | Ground |
| 10 | GPIO15 (RXD) | UART Receive |
| ... | ... | ... (Refer to full GPIO pinout) |
For the complete GPIO pinout, refer to the official Raspberry Pi documentation.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W in a Circuit
- Powering the Board: Connect a 5V/2.5A power supply to the Micro USB power port.
- Connecting Peripherals: Use the Mini HDMI port for video output, and connect a USB OTG adapter to the Micro USB data port for peripherals like a keyboard or mouse.
- Interfacing with GPIO: Solder a 40-pin header to the GPIO pads if required. Use jumper wires to connect sensors, actuators, or other components to the GPIO pins.
- Wireless Setup: Configure Wi-Fi and Bluetooth through the Raspberry Pi OS settings or via the terminal.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Always use a reliable 5V/2.5A power supply to avoid instability.
- Heat Management: While the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W is energy-efficient, consider using a heatsink for prolonged high-performance tasks.
- Static Precautions: Handle the board with care to avoid damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD).
- GPIO Voltage Levels: The GPIO pins operate at 3.3V logic levels. Avoid applying higher voltages to prevent damage.
Example: Blinking an LED with GPIO
Below is an example of how to blink an LED using the GPIO pins and Python:
Import the GPIO library and time module
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO import time
Set the GPIO mode to BCM (Broadcom pin numbering)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
Define the GPIO pin connected to the LED
LED_PIN = 17
Set up the LED pin as an output
GPIO.setup(LED_PIN, GPIO.OUT)
try: while True: GPIO.output(LED_PIN, GPIO.HIGH) # Turn the LED on time.sleep(1) # Wait for 1 second GPIO.output(LED_PIN, GPIO.LOW) # Turn the LED off time.sleep(1) # Wait for 1 second except KeyboardInterrupt: # Clean up GPIO settings on exit GPIO.cleanup()
Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W can communicate with an Arduino UNO via UART, I2C, or SPI. Ensure proper voltage level shifting if required, as the Raspberry Pi operates at 3.3V logic while the Arduino operates at 5V.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W does not boot:
- Ensure the microSD card is properly inserted and contains a valid Raspberry Pi OS image.
- Verify that the power supply provides sufficient current (5V/2.5A).
Wi-Fi connectivity issues:
- Check the Wi-Fi credentials and ensure the network is within range.
- Update the Raspberry Pi OS to the latest version using
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade.
GPIO pins not working:
- Confirm that the correct GPIO pin numbering mode (BCM or BOARD) is used in your code.
- Check for loose connections or soldering issues on the GPIO header.
Overheating:
- Use a heatsink or active cooling if the board is used in a high-temperature environment or under heavy load.
FAQs
Can I power the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W via GPIO pins? Yes, you can power the board by supplying 5V to the 5V pin and connecting GND to a ground pin. However, this bypasses the onboard power protection circuitry, so proceed with caution.
What operating systems are compatible with the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W? The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W supports Raspberry Pi OS, as well as other Linux-based distributions like Ubuntu and specialized OSes for IoT and media applications.
Can I use the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W for AI/ML projects? While the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W is not as powerful as other Raspberry Pi models, it can handle lightweight AI/ML tasks using frameworks like TensorFlow Lite.
For additional support, refer to the official Raspberry Pi forums and documentation.