
How to Use esp8266 nodemcu : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
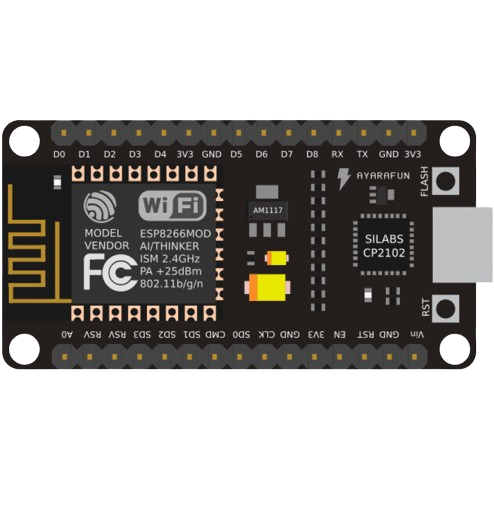
 Design with esp8266 nodemcu in Cirkit Designer
Design with esp8266 nodemcu in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP8266 NodeMCU is an open-source IoT platform that incorporates the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module. It is designed for the Internet of Things (IoT) and is programmable via the Arduino Integrated Development Environment (IDE). The NodeMCU board is favored for its Wi-Fi capability, ease of use, and the extensive community support available. Common applications include smart home devices, wireless sensors, and internet-connected automation.
Explore Projects Built with esp8266 nodemcu
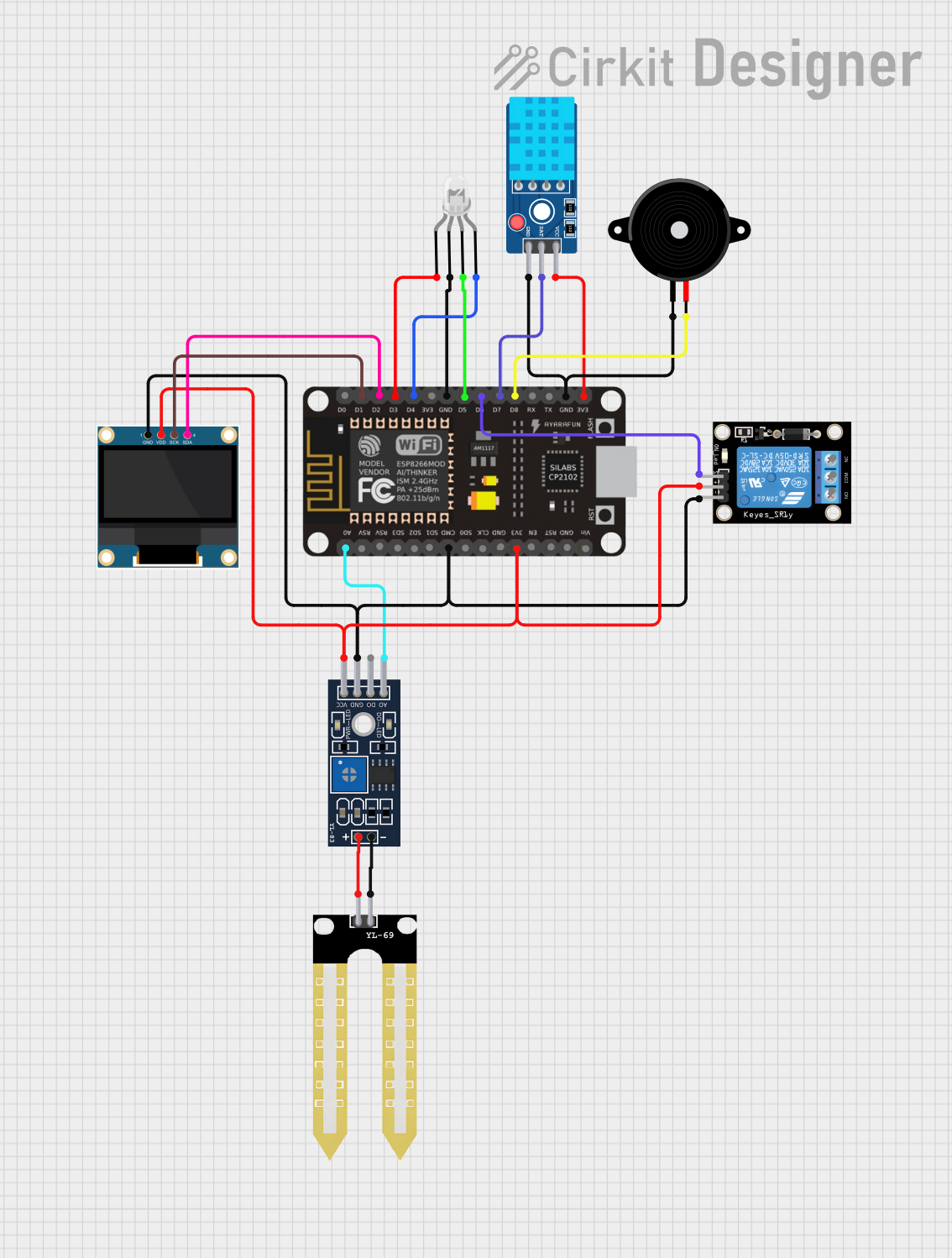
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer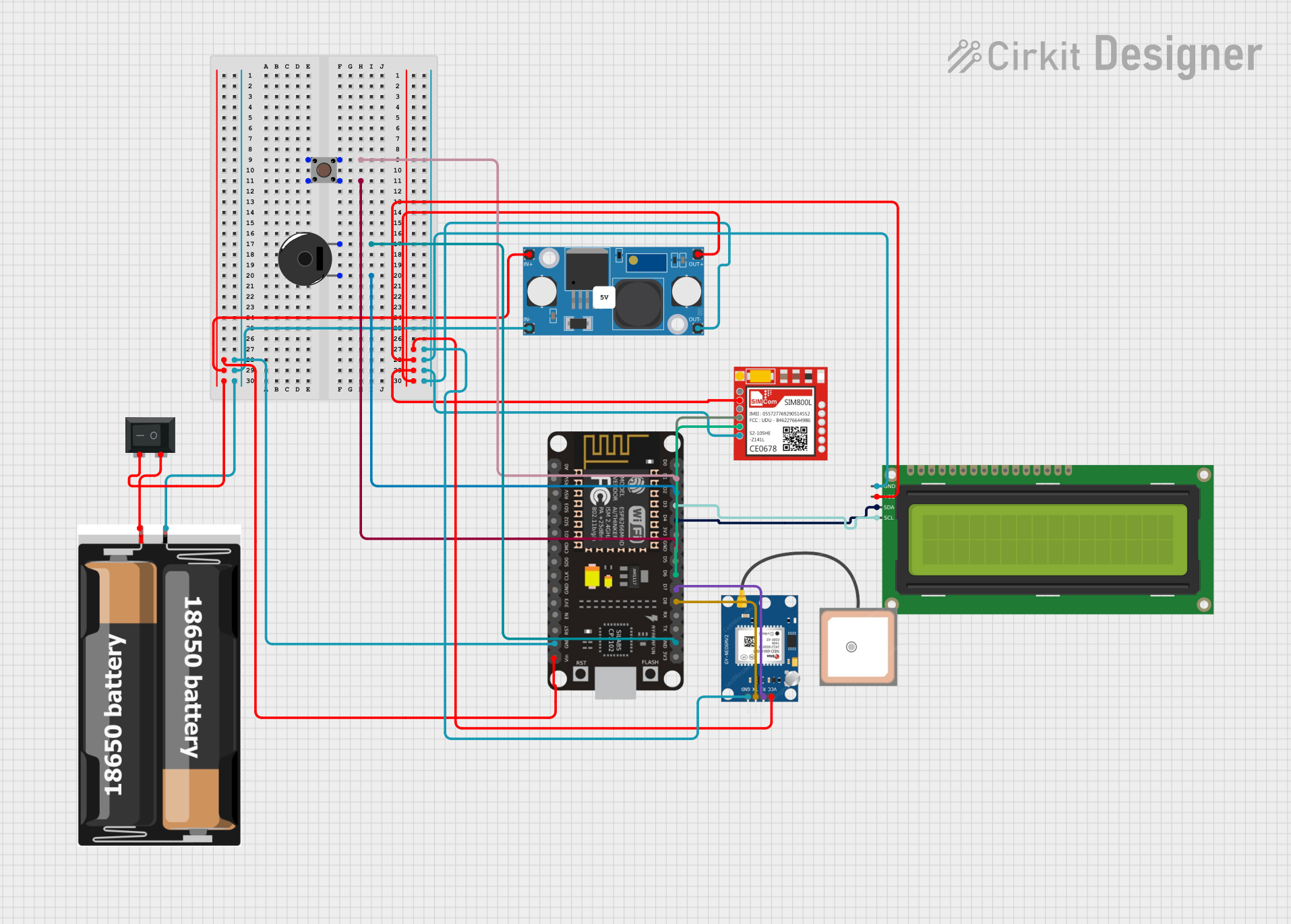
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer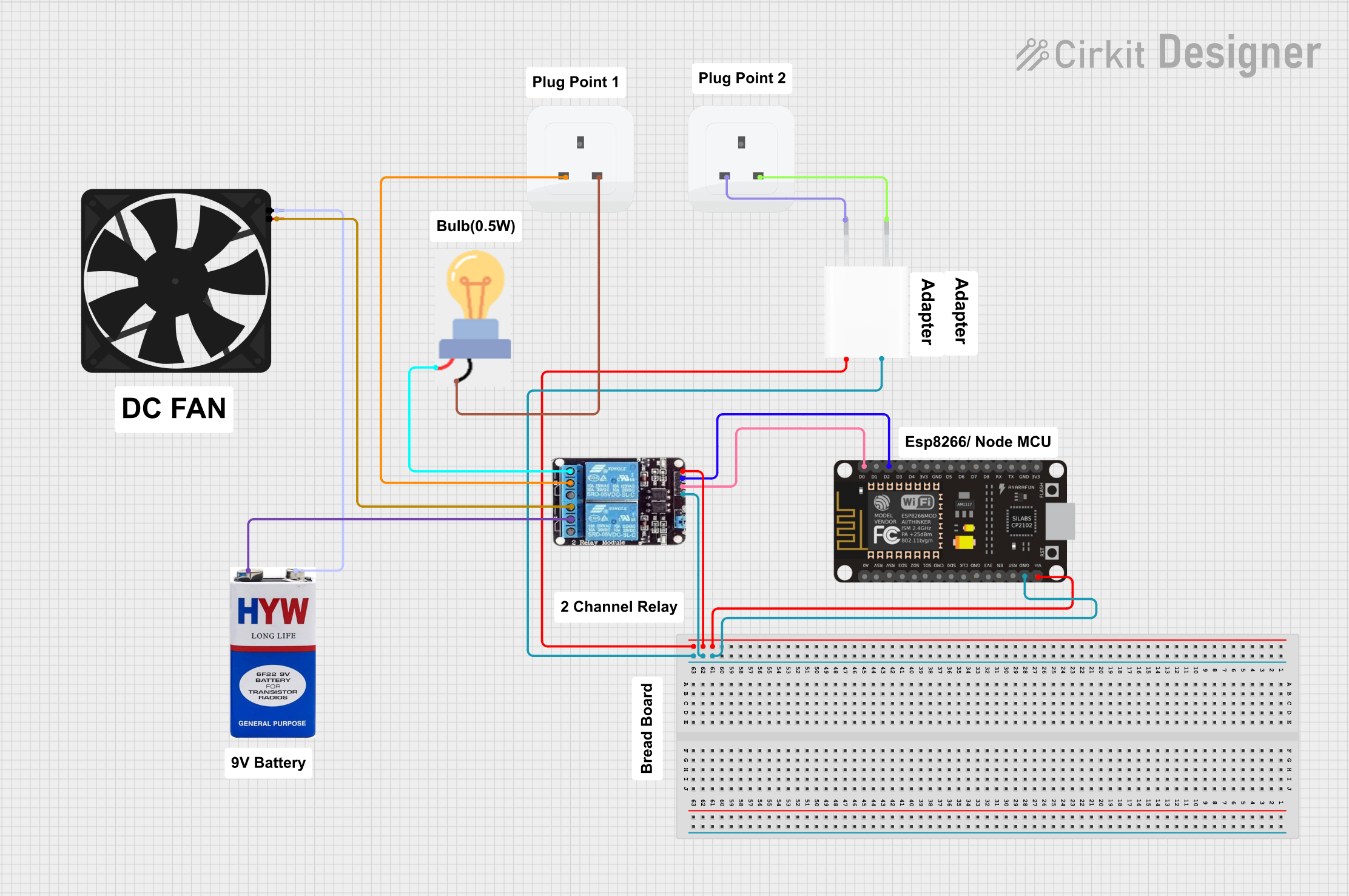
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with esp8266 nodemcu

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ESP8266
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Input Voltage: 7-12V (via Vin pin), 5V (via micro USB)
- Digital I/O Pins: 16
- Analog Input Pins: 1 (A0)
- Flash Memory: 4MB
- Clock Speed: 80MHz (can be overclocked to 160MHz)
- Wi-Fi: Built-in 802.11 b/g/n
- I2C, SPI, UART: Available
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| D0 - D8 | GPIO, PWM, I2C, SPI | General-purpose input/output pins with various functions |
| A0 | Analog Input | Single analog input, max input of 3.3V |
| RX | UART Receive | Serial communication (receiving) |
| TX | UART Transmit | Serial communication (transmitting) |
| RST | Reset | Resets the module |
| VIN | Voltage Input | External power supply (7-12V) |
| 3V3 | 3.3V Power | Power output (3.3V) |
| GND | Ground | Common ground for power and logic |
Usage Instructions
Integrating with a Circuit
- Powering the NodeMCU: The NodeMCU can be powered via the micro USB port or through the VIN pin with a 7-12V power supply.
- Programming: Use the micro USB port to connect the NodeMCU to a computer for programming with the Arduino IDE.
- Digital I/O: Connect sensors, actuators, or other modules to the GPIO pins, ensuring they are 3.3V compatible.
- Analog Input: The A0 pin can be used for analog sensors, with a maximum input voltage of 3.3V.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: The NodeMCU operates at 3.3V logic levels. Ensure that any connected components are compatible to avoid damage.
- Wi-Fi Connectivity: When using Wi-Fi, place the NodeMCU in a location with minimal interference and a strong signal.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the NodeMCU firmware up to date for the best performance and security.
- Static Electricity: Handle the NodeMCU with care to avoid damage from static discharge.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "your_SSID";
const char* password = "your_PASSWORD";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Start serial communication at 115200 baud
WiFi.begin(ssid, password); // Connect to Wi-Fi
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected.");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); // Print the local IP address
}
void loop() {
// Your code here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- NodeMCU not connecting to Wi-Fi: Ensure the SSID and password are correct. Check the signal strength and router settings.
- NodeMCU not recognized by computer: Check the USB cable and drivers. Try a different USB port or cable.
- GPIO pin not working: Verify the pin number in your code. Check for shorts or damage to the board.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Wi-Fi Connectivity: If you have trouble connecting to Wi-Fi, try moving closer to the router or eliminating sources of interference.
- Driver Installation: Ensure that the correct USB drivers for the NodeMCU are installed on your computer.
- Code Debugging: Use
Serial.print()statements to debug and track the flow of your program.
FAQs
Q: Can I use 5V components with the NodeMCU? A: No, the NodeMCU operates at 3.3V. Use a logic level converter for 5V components.
Q: How do I reset the NodeMCU? A: Briefly press the RST button on the board to reset it.
Q: Can I use the Arduino IDE for programming the NodeMCU? A: Yes, the NodeMCU is compatible with the Arduino IDE. Make sure to install the ESP8266 board package.
Q: How many digital pins can be used for PWM? A: All digital pins on the NodeMCU can be used for PWM.
This documentation provides an overview of the ESP8266 NodeMCU, its technical specifications, usage instructions, example code, and troubleshooting tips. For further assistance, consult the NodeMCU community forums and resources.