
How to Use ups rechargable battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ups rechargable battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with ups rechargable battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) rechargeable battery is an essential component for maintaining the reliability and stability of electronic systems, particularly in the context of the ESP32 microcontroller. The ESP32, known for its Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, is often used in IoT applications where consistent power is crucial. The UPS battery ensures that the ESP32 can continue to operate during power interruptions, making it ideal for applications such as home automation, data logging, and remote monitoring.
Explore Projects Built with ups rechargable battery
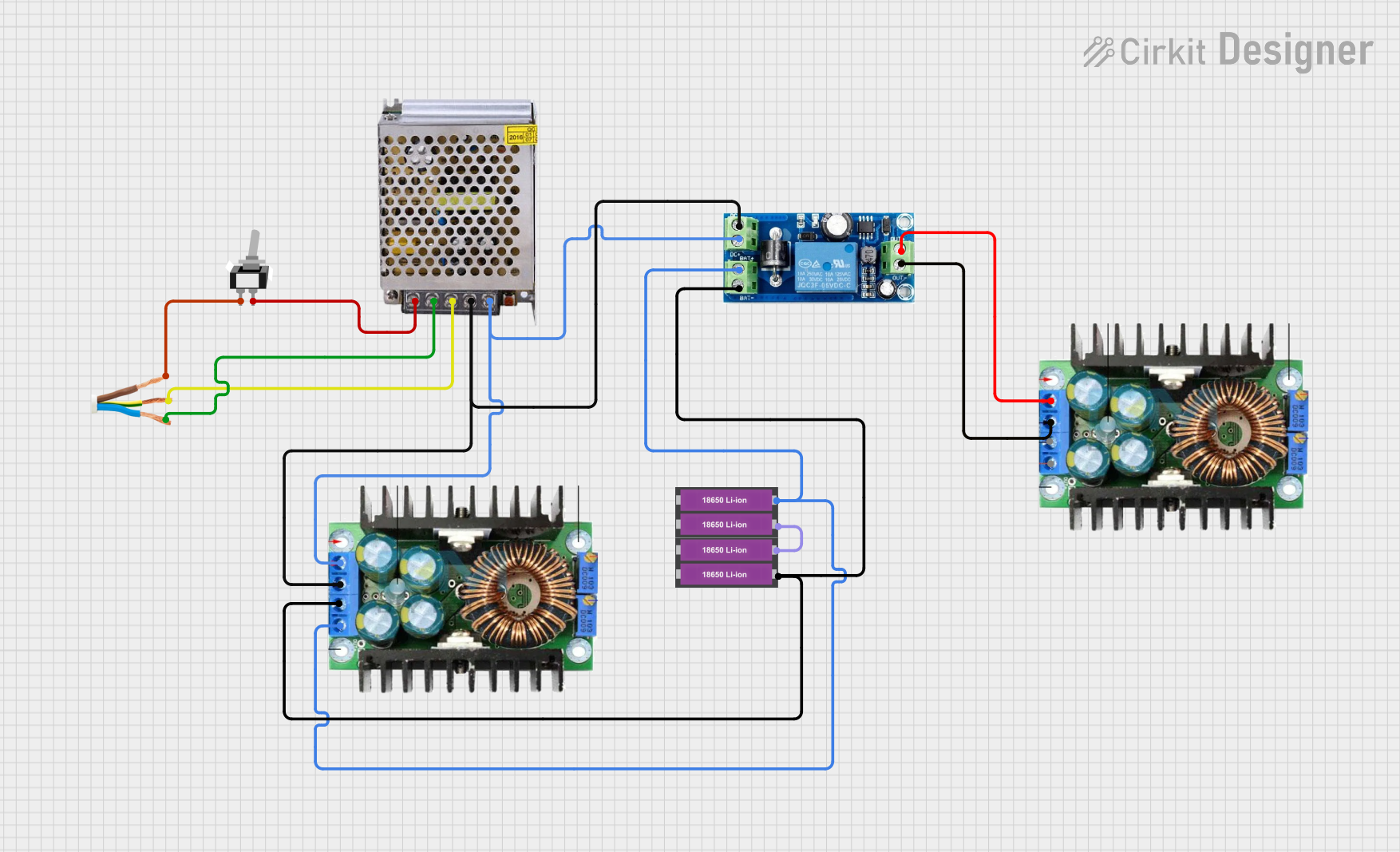
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer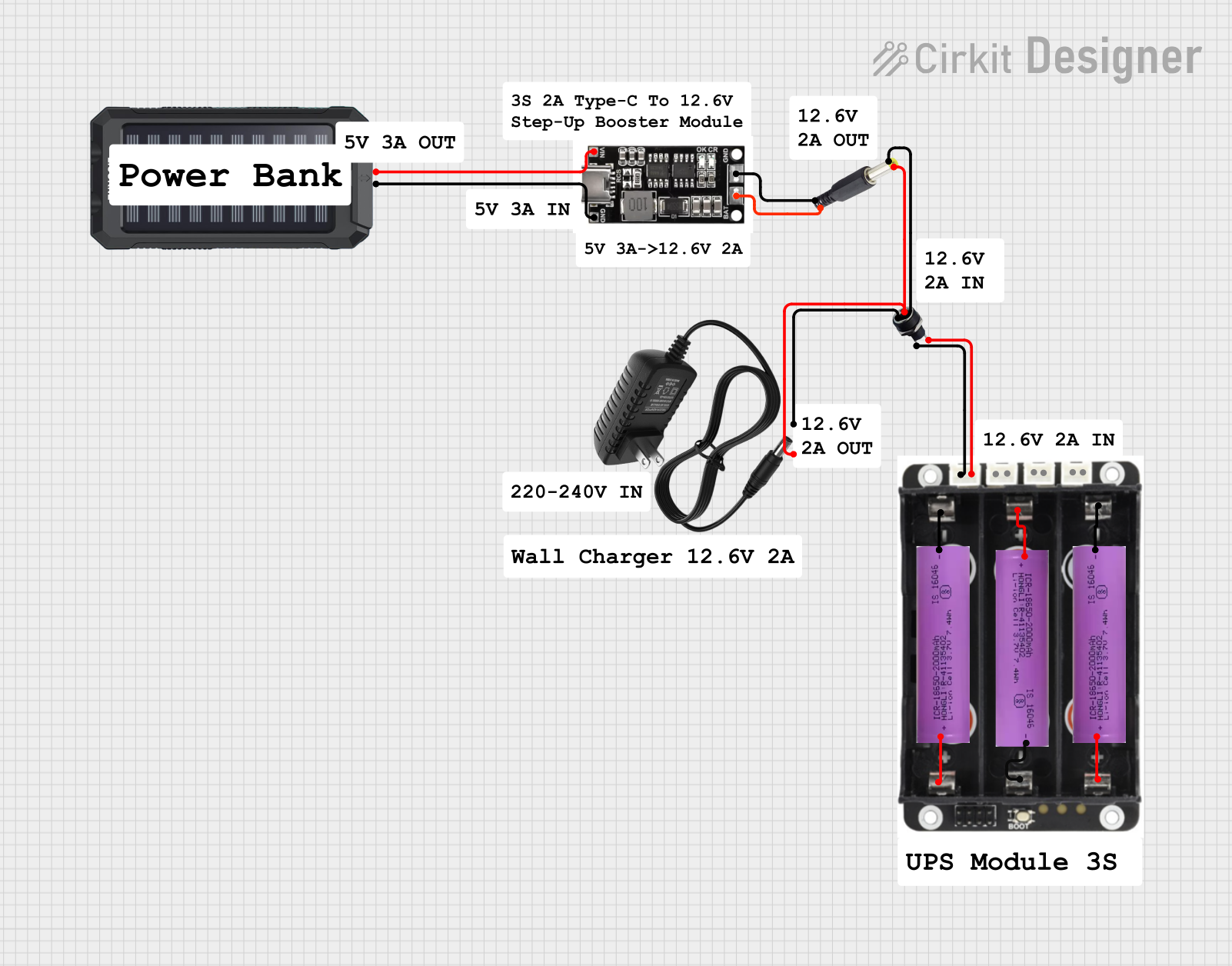
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer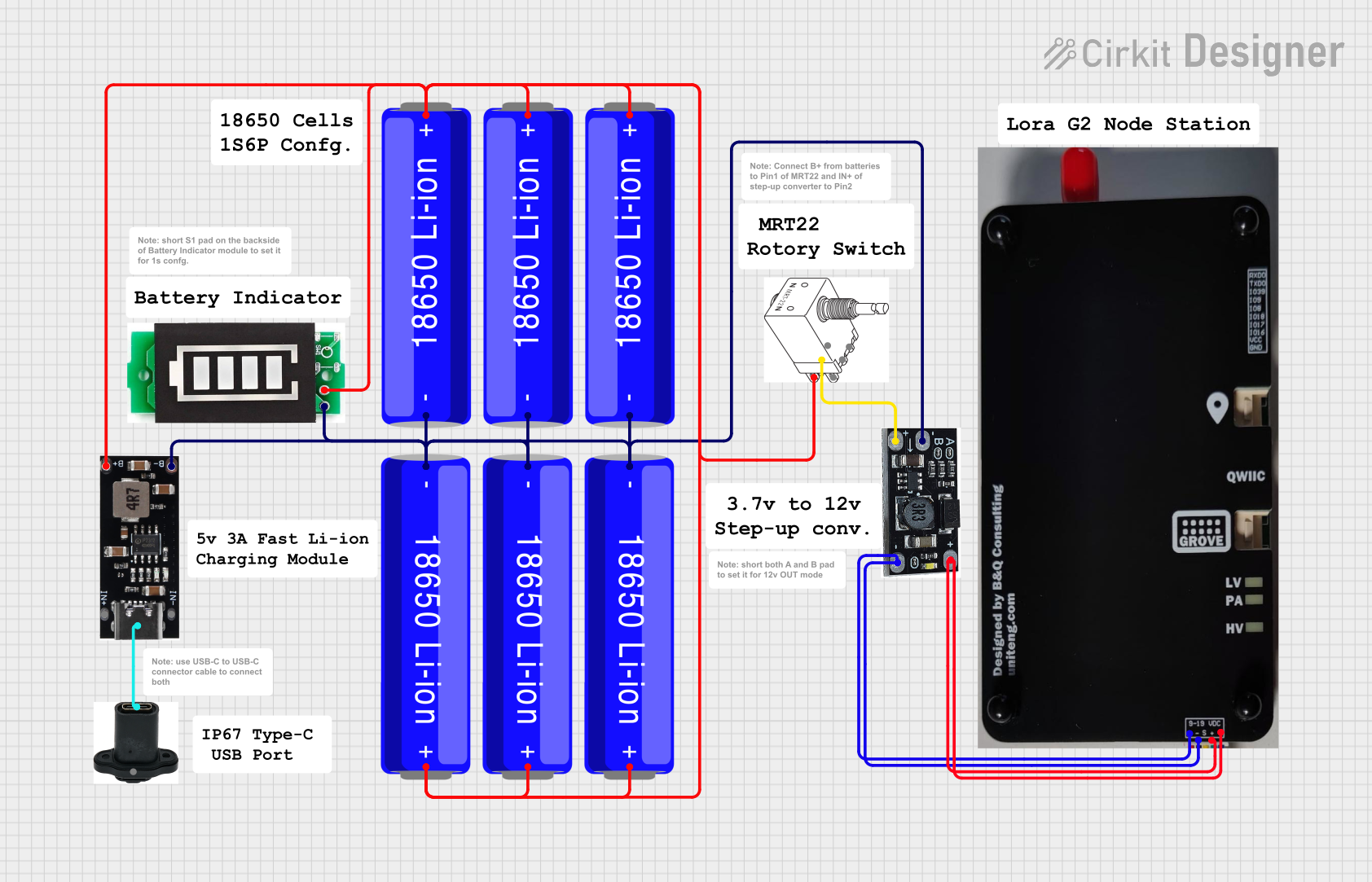
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ups rechargable battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT Devices: Maintaining power to ensure continuous data transmission and operation.
- Home Automation Systems: Providing backup power to smart home devices during outages.
- Remote Monitoring Stations: Ensuring uninterrupted data collection in environments with unstable power.
- Portable Electronics: Allowing for mobility without the need for a constant external power source.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Nominal Voltage: 3.7V
- Capacity: Typically ranges from 1000mAh to 10,000mAh
- Charge/Discharge Cycles: 500-1000 cycles before significant capacity loss
- Charge Voltage: 4.2V
- Maximum Charging Current: 1C (Capacity in Ah)
- Maximum Discharge Current: Varies by model, often 1-2C
- Operating Temperature Range: -20°C to 60°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive Terminal | Connect to V_in on the ESP32 |
| 2 | Negative Terminal | Connect to GND on the ESP32 |
| 3 | Thermistor (optional) | For monitoring battery temperature |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connecting the Battery:
- Connect the positive terminal of the UPS battery to the V_in pin of the ESP32.
- Connect the negative terminal to the GND pin.
Charging the Battery:
- Use a compatible charger that matches the battery's charging specifications.
- Ensure the charging current does not exceed the battery's maximum rating.
Monitoring Battery Voltage:
- Use an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) channel on the ESP32 to monitor the battery voltage.
- Implement voltage divider circuitry if necessary to match the ADC input range.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Protection: Always use a battery with a built-in protection circuit to prevent overcharging, deep discharge, and short circuits.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Avoid exposing the battery to extreme temperatures during operation and charging.
- Charging Safety: Use a charger with an auto-cutoff feature to prevent overcharging.
- Disposal: Follow local regulations for the disposal of lithium-based batteries.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Battery Not Charging: Ensure the charger is functioning and compatible with the battery's specifications.
- Reduced Runtime: If the battery does not hold a charge as expected, it may be nearing the end of its life cycle.
- Device Resets During Brownouts: Ensure the battery capacity is sufficient for the load and that connections are secure.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Loose connections can cause intermittent power issues.
- Monitor Charge Cycles: Keep track of charge/discharge cycles to anticipate battery replacement.
- Battery Storage: Store the battery at 50% charge in a cool, dry place if not in use for extended periods.
FAQs
Q: Can I use any charger with my UPS battery? A: No, you must use a charger that complies with the battery's charging specifications.
Q: How do I know when to replace the battery? A: When the battery can no longer hold a significant charge or if it fails to power the ESP32 for an expected duration, it may be time to replace it.
Q: Is it safe to leave the battery charging overnight? A: It is generally safe if you are using a charger with overcharge protection, but it's best to charge the battery when you can monitor it.
Example Code for ESP32
Here's a simple Arduino sketch to monitor the battery voltage using the ESP32's ADC.
#define BATTERY_PIN 34 // ADC pin connected to battery voltage divider
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
int batteryRaw = analogRead(BATTERY_PIN);
float batteryVoltage = map(batteryRaw, 0, 4095, 0, 3300) / 1000.0; // Convert to voltage
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.println(batteryVoltage);
delay(1000);
}
Note: The map function in the code assumes a 3.3V reference voltage and a 12-bit ADC resolution. Adjust the values accordingly if your setup differs.