
How to Use BTS7960 (IBT-2) Motor Driver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
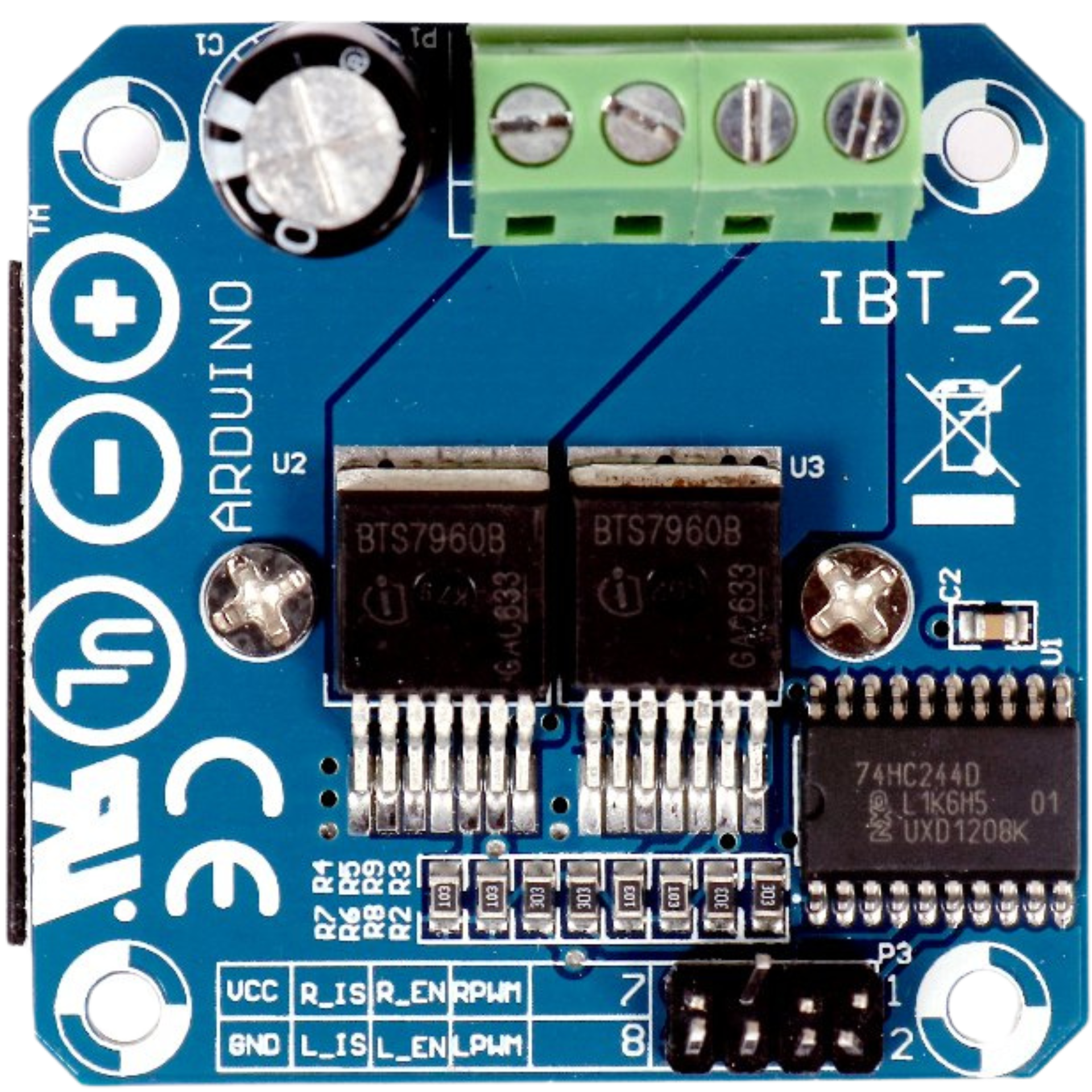
 Design with BTS7960 (IBT-2) Motor Driver in Cirkit Designer
Design with BTS7960 (IBT-2) Motor Driver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BTS7960 (commonly referred to as the IBT-2) is a high-current H-bridge motor driver designed for controlling DC motors. It is capable of handling high currents (up to 43A) and operates efficiently with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signals. The module features built-in protection mechanisms, including overcurrent and thermal overload protection, making it a reliable choice for motor control applications.
Explore Projects Built with BTS7960 (IBT-2) Motor Driver
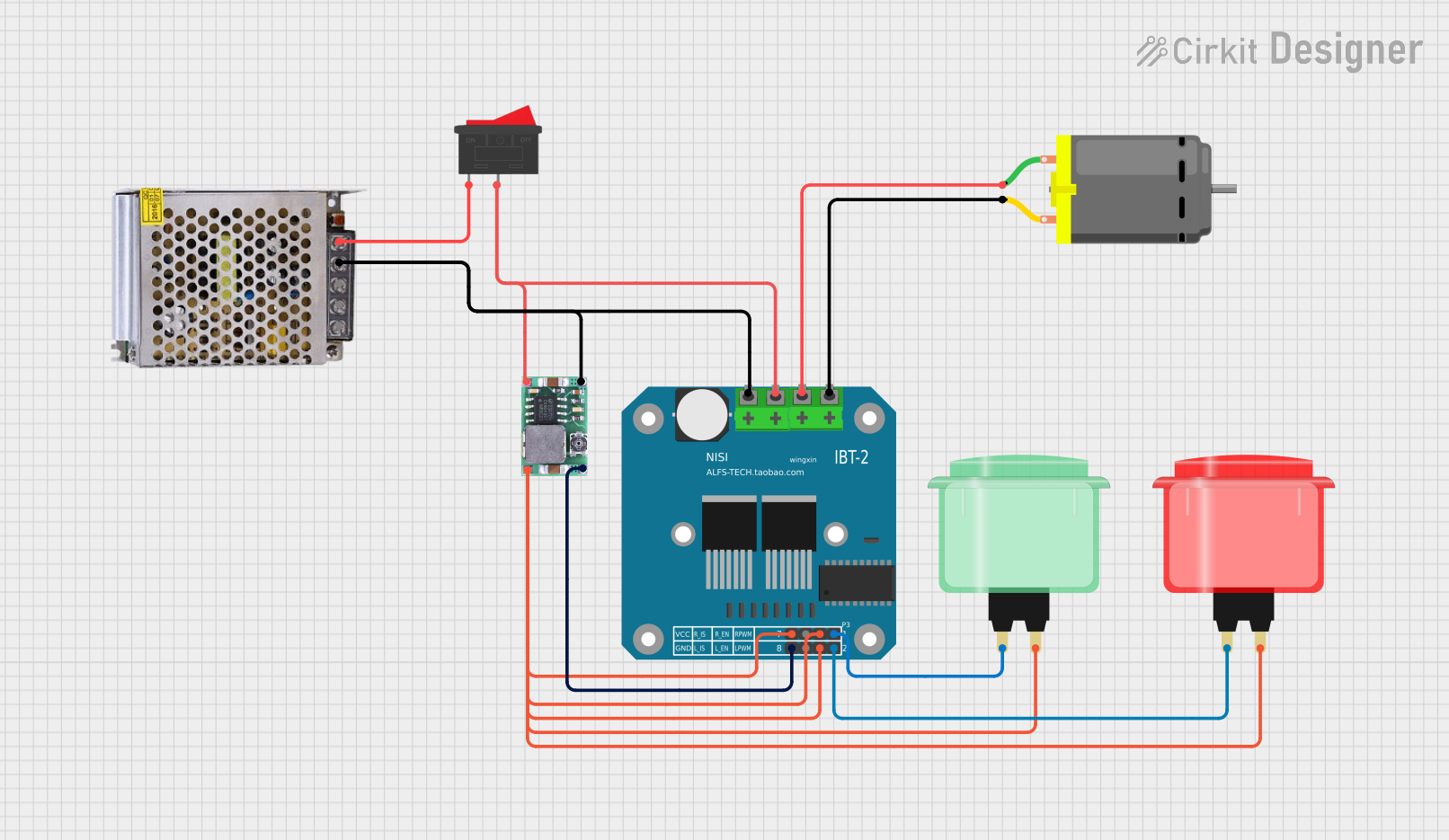
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer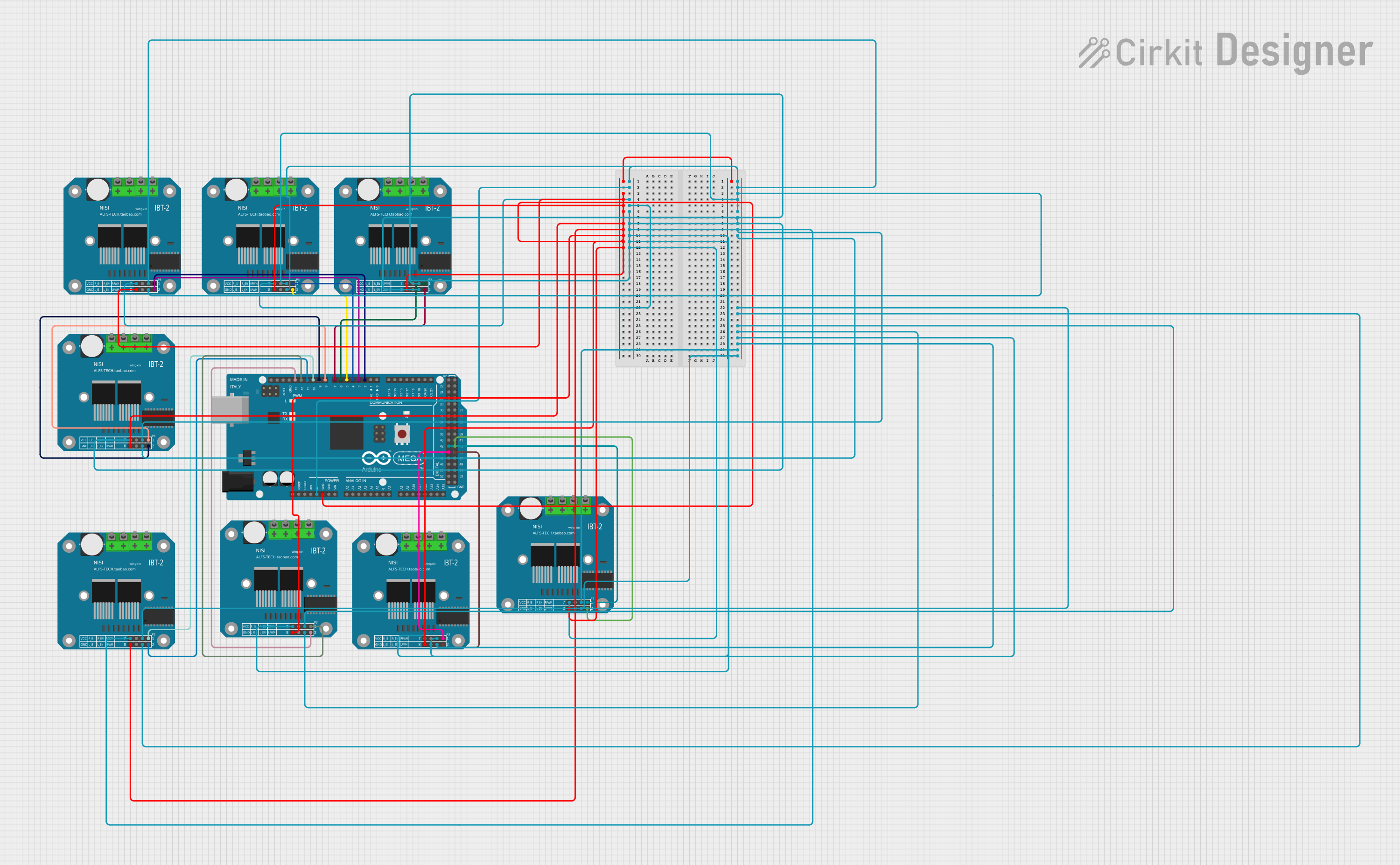
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer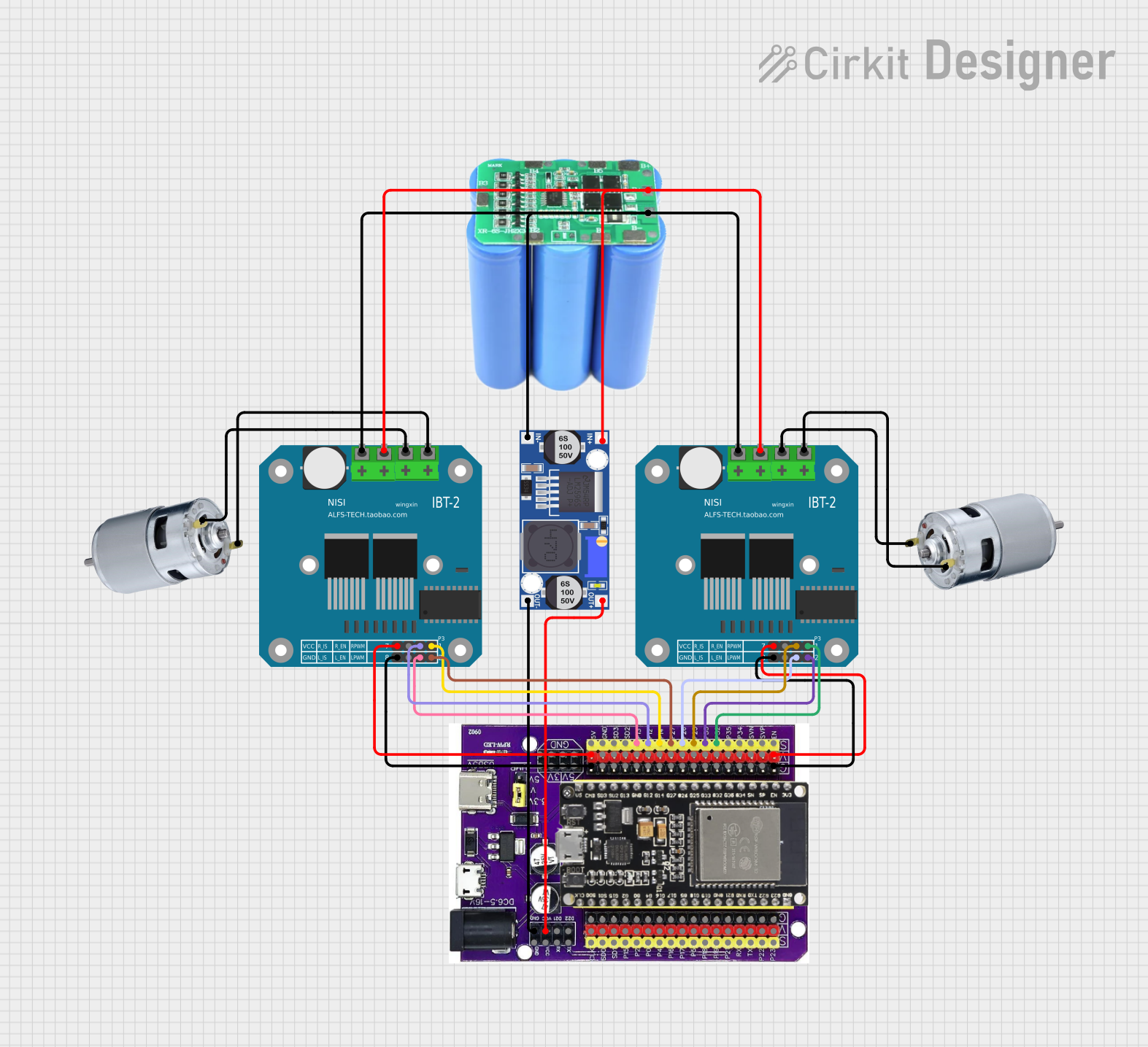
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer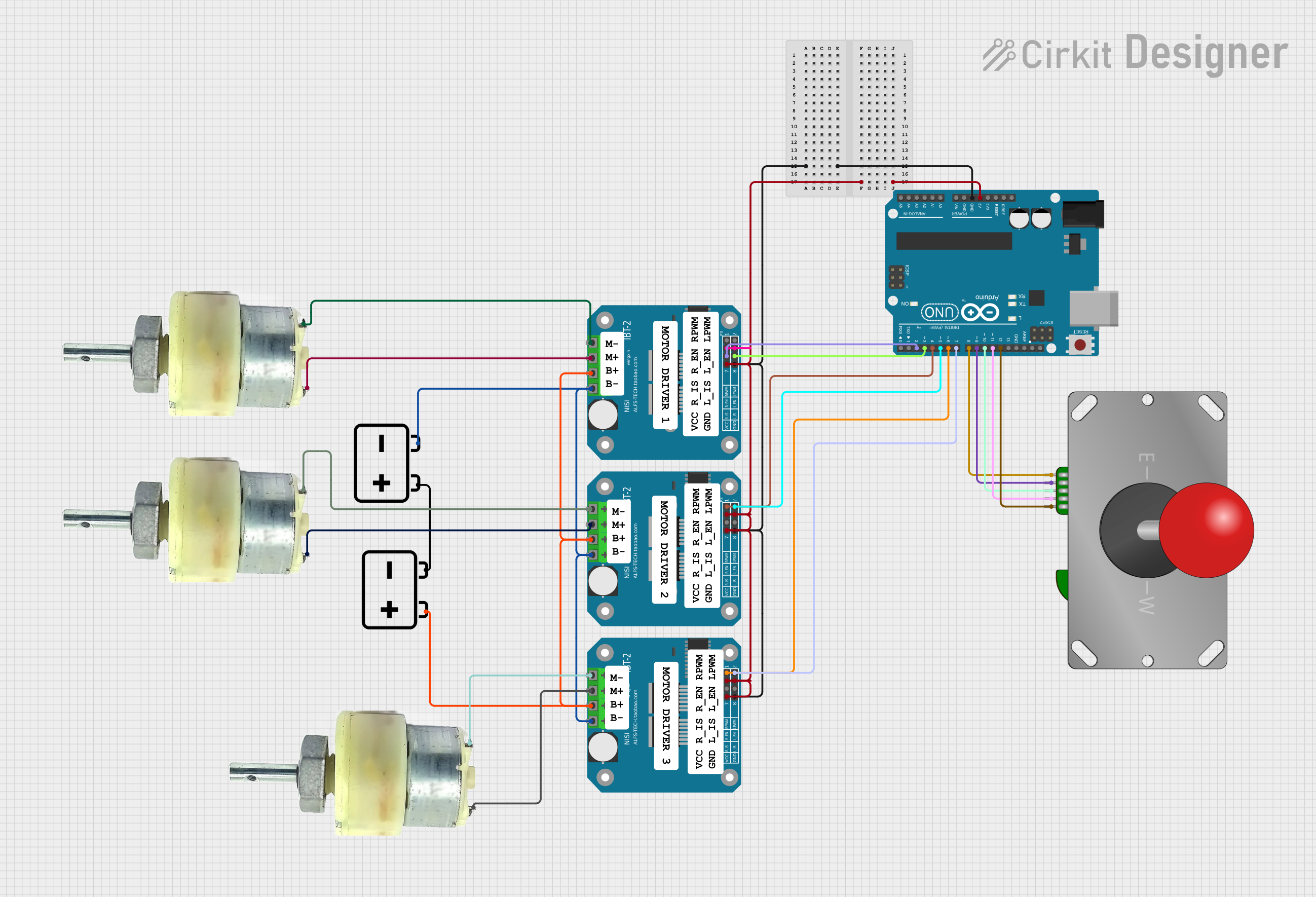
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BTS7960 (IBT-2) Motor Driver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics and automation systems
- Electric vehicle motor control
- Conveyor belt systems
- High-power DC motor control in industrial applications
- DIY projects involving Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or other microcontrollers
Technical Specifications
The BTS7960 motor driver is designed to handle high-power DC motors with ease. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V logic, 6V–27V motor supply |
| Maximum Continuous Current | 43A |
| Peak Current | 50A |
| PWM Frequency | Up to 25kHz |
| Logic Level Voltage | 3.3V or 5V compatible |
| Overcurrent Protection | Yes |
| Thermal Shutdown | Yes |
| Dimensions | 43mm x 45mm x 28mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The BTS7960 module has a total of 8 pins for interfacing with a microcontroller and motor. Below is the pinout:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power Input | 5V input for logic circuitry. |
| GND | Ground | Common ground for logic and motor power. |
| RPWM | Input | PWM signal for controlling motor rotation in one direction. |
| LPWM | Input | PWM signal for controlling motor rotation in the opposite direction. |
| R_EN | Input | Enable pin for the right half-bridge (active HIGH). |
| L_EN | Input | Enable pin for the left half-bridge (active HIGH). |
| MOTOR+ | Power Output | Positive terminal of the motor. |
| MOTOR- | Power Output | Negative terminal of the motor. |
Usage Instructions
The BTS7960 motor driver is straightforward to use with a microcontroller like an Arduino. Below are the steps to integrate it into your project:
Connecting the BTS7960 to a Microcontroller
Power Connections:
- Connect the
VCCpin to the 5V output of your microcontroller. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your microcontroller and power supply. - Connect a suitable power source (6V–27V) to the motor power input terminals.
- Connect the
Motor Connections:
- Connect the motor terminals to the
MOTOR+andMOTOR-pins.
- Connect the motor terminals to the
Control Pins:
- Connect the
RPWMandLPWMpins to PWM-capable pins on your microcontroller. - Connect the
R_ENandL_ENpins to digital output pins on your microcontroller.
- Connect the
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example of how to control a DC motor using the BTS7960 with an Arduino UNO:
// Define control pins for the BTS7960 motor driver
const int RPWM = 5; // PWM pin for forward rotation
const int LPWM = 6; // PWM pin for reverse rotation
const int R_EN = 7; // Enable pin for right half-bridge
const int L_EN = 8; // Enable pin for left half-bridge
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(RPWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LPWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(R_EN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(L_EN, OUTPUT);
// Enable both half-bridges
digitalWrite(R_EN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(L_EN, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor forward at 50% speed
analogWrite(RPWM, 128); // 50% duty cycle (128 out of 255)
analogWrite(LPWM, 0); // No reverse rotation
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Rotate motor backward at 75% speed
analogWrite(RPWM, 0); // No forward rotation
analogWrite(LPWM, 192); // 75% duty cycle (192 out of 255)
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(RPWM, 0);
analogWrite(LPWM, 0);
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the motor's current and voltage ratings are within the BTS7960's specifications.
- Use a heat sink or active cooling if operating at high currents for extended periods.
- Always connect the ground of the motor driver, microcontroller, and power supply to ensure proper operation.
- Avoid sudden changes in PWM signals to prevent stress on the motor and driver.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor does not spin:
- Verify all connections, especially the power supply and motor terminals.
- Ensure the
R_ENandL_ENpins are set to HIGH. - Check the PWM signal using an oscilloscope or multimeter.
Motor spins in the wrong direction:
- Swap the connections of the
MOTOR+andMOTOR-terminals. - Verify the logic levels on the
RPWMandLPWMpins.
- Swap the connections of the
Driver overheats:
- Ensure the current drawn by the motor does not exceed 43A.
- Use a heat sink or active cooling to dissipate heat.
Erratic motor behavior:
- Check for loose connections or insufficient power supply.
- Ensure the PWM frequency is within the supported range (up to 25kHz).
FAQs
Q: Can I use the BTS7960 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the BTS7960 is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels.
Q: What happens if the motor draws more than 43A?
A: The BTS7960 has built-in overcurrent protection and will shut down to prevent damage.
Q: Can I control two motors with one BTS7960 module?
A: No, the BTS7960 is designed to control a single DC motor. For dual-motor control, use two modules.
Q: Is it possible to use the BTS7960 for stepper motors?
A: No, the BTS7960 is not suitable for stepper motors. Use a dedicated stepper motor driver instead.