
How to Use speaker: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with speaker in Cirkit Designer
Design with speaker in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A speaker, manufactured by JBL (Part ID: speaker), is an electroacoustic transducer designed to convert electrical energy into sound waves. This component is essential for producing audible audio signals in a wide range of applications. Speakers are widely used in consumer electronics, professional audio systems, automotive sound systems, and public address systems.
Explore Projects Built with speaker
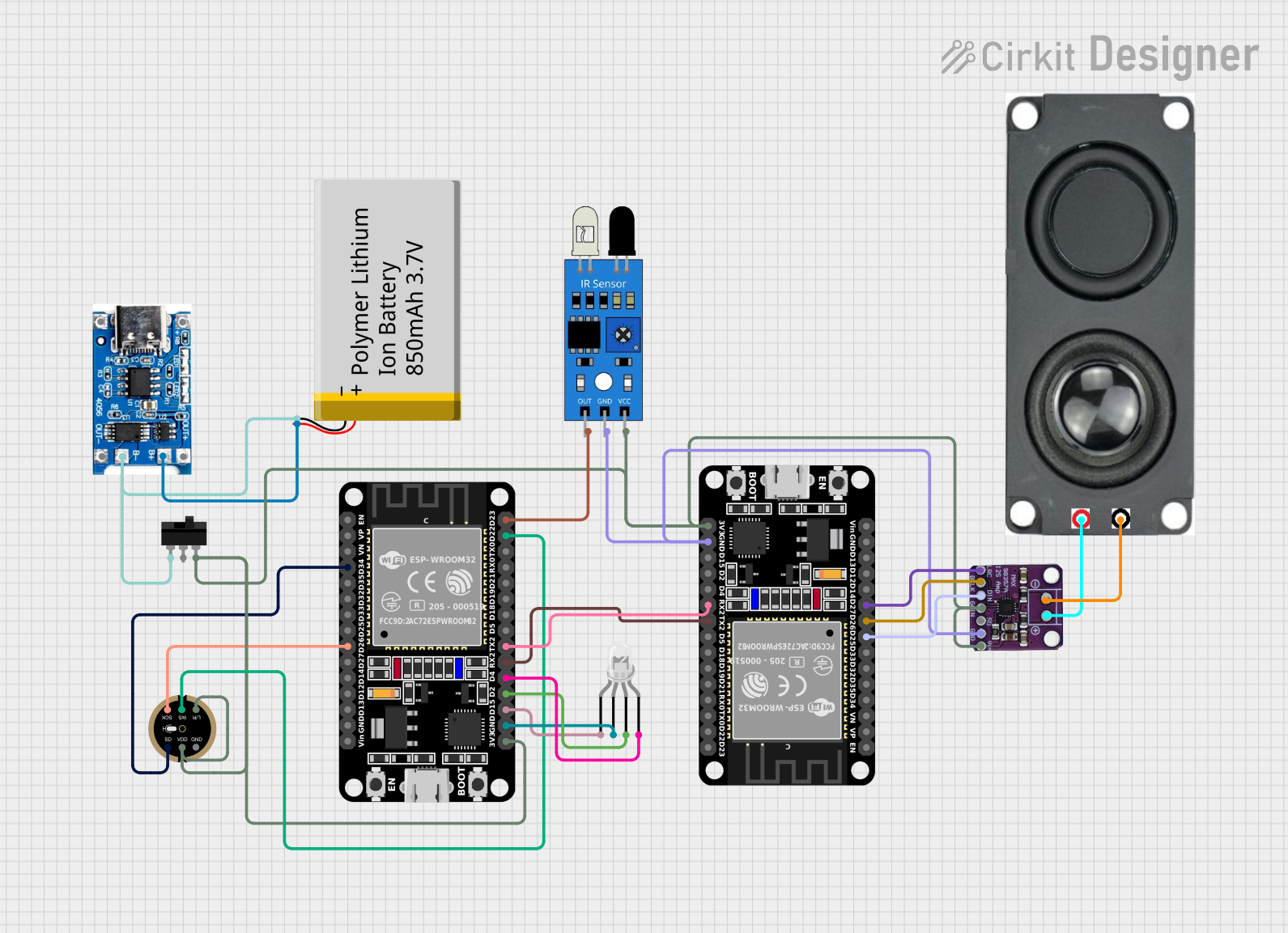
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer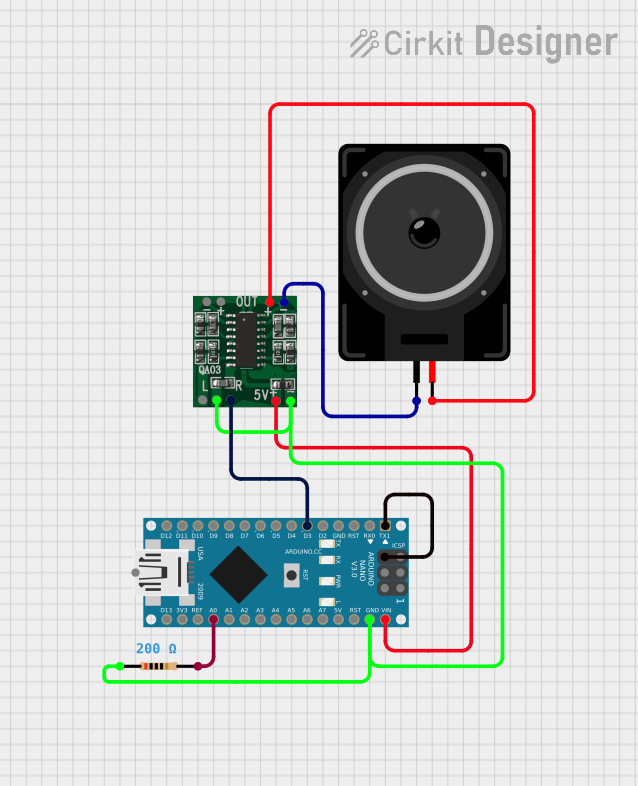
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer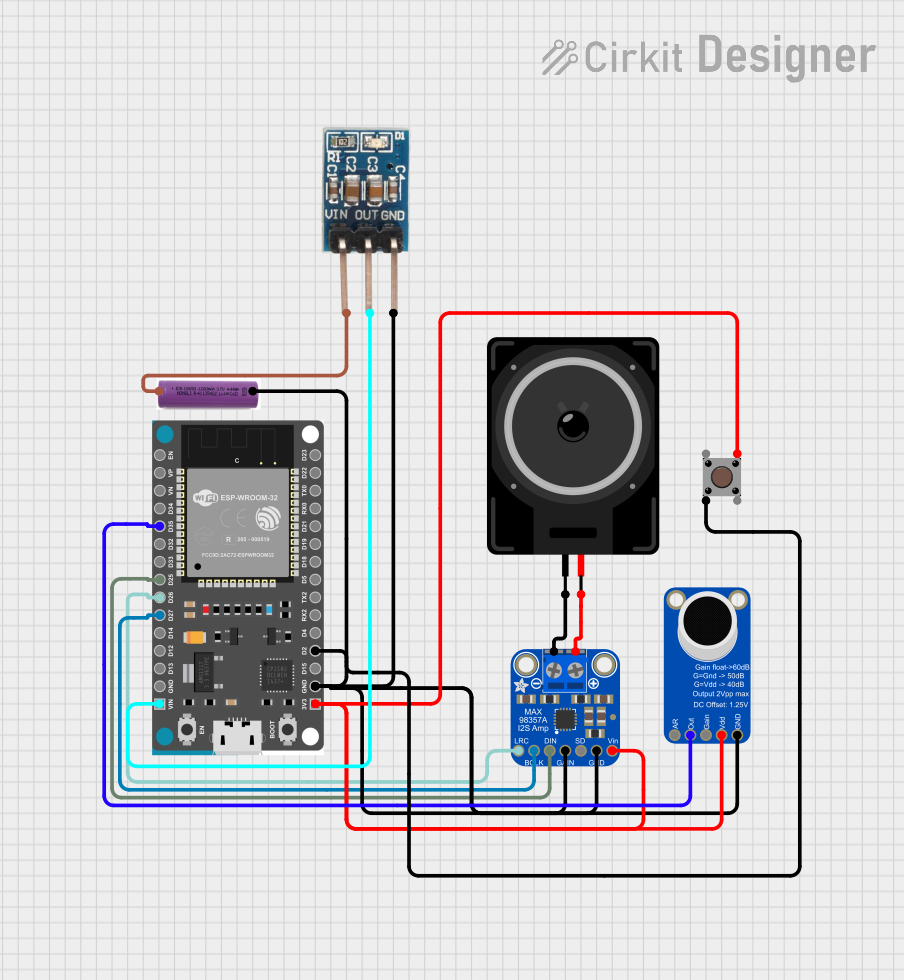
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with speaker

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home audio systems and portable Bluetooth speakers
- Public address systems and stage sound reinforcement
- Automotive audio systems
- Multimedia devices such as TVs, computers, and gaming consoles
- DIY electronics projects involving sound output
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the JBL speaker (Part ID: speaker):
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | JBL |
| Part ID | speaker |
| Type | Dynamic speaker |
| Impedance | 8 Ω |
| Power Handling | 10 W (RMS) |
| Frequency Response | 50 Hz – 20 kHz |
| Sensitivity | 90 dB SPL @ 1 W/1 m |
| Cone Material | Polypropylene |
| Magnet Type | Ferrite |
| Dimensions | 3 inches (diameter) |
| Weight | 200 g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The speaker has two terminals for electrical connections:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Positive terminal (connect to the amplifier's positive output) |
| - | Negative terminal (connect to the amplifier's ground or negative output) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Speaker in a Circuit
Connect to an Amplifier:
- The speaker requires an audio amplifier to drive it. Connect the positive terminal of the speaker to the amplifier's positive output and the negative terminal to the amplifier's ground or negative output.
- Ensure the amplifier's output power matches the speaker's power handling capacity (10 W RMS) to avoid damage.
Power Supply:
- The speaker itself does not require a direct power supply. It operates based on the amplified audio signal provided by the amplifier.
Mounting:
- Secure the speaker in an enclosure or mounting frame to enhance sound quality and protect the component.
Wiring:
- Use appropriate gauge wires to connect the speaker to the amplifier. For short distances, 18 AWG wire is sufficient.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Impedance Matching: Ensure the amplifier's output impedance matches the speaker's impedance (8 Ω) for optimal performance.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the speaker's power handling capacity (10 W RMS) to prevent damage.
- Enclosure Design: Use a properly designed enclosure to improve sound quality and bass response.
- Polarity: Maintain correct polarity when connecting the speaker to avoid phase cancellation in multi-speaker setups.
Example: Connecting the Speaker to an Arduino UNO
To use the speaker with an Arduino UNO, you can generate simple tones using the tone() function. Note that the Arduino cannot directly drive the speaker; you must use a transistor or an amplifier circuit.
Circuit Diagram
- Connect the speaker's positive terminal to the collector of an NPN transistor (e.g., 2N2222).
- Connect the speaker's negative terminal to the ground.
- Connect the emitter of the transistor to the ground.
- Connect a 1 kΩ resistor between the Arduino's digital pin (e.g., pin 9) and the transistor's base.
Arduino Code
// Example code to generate tones on a speaker using Arduino UNO
// Ensure the speaker is connected via a transistor or amplifier circuit
#define SPEAKER_PIN 9 // Define the digital pin connected to the transistor
void setup() {
// No setup required for tone generation
}
void loop() {
tone(SPEAKER_PIN, 440); // Generate a 440 Hz tone (A4 note)
delay(1000); // Play the tone for 1 second
noTone(SPEAKER_PIN); // Stop the tone
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before repeating
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Sound Output:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify the connections between the speaker, amplifier, and power source.
Distorted Sound:
- Cause: Overdriving the speaker or using an incompatible amplifier.
- Solution: Ensure the amplifier's output power and impedance match the speaker's specifications.
Low Volume:
- Cause: Insufficient amplifier power or poor enclosure design.
- Solution: Use a more powerful amplifier and ensure the speaker is mounted in a suitable enclosure.
Speaker Not Working with Arduino:
- Cause: Direct connection to Arduino without a transistor or amplifier.
- Solution: Use a transistor or amplifier circuit to drive the speaker.
FAQs
Q: Can I connect the speaker directly to a microcontroller like Arduino?
A: No, the speaker requires more current than a microcontroller can provide. Use a transistor or amplifier circuit.
Q: What happens if I exceed the speaker's power rating?
A: Exceeding the power rating can damage the speaker's voice coil or cause distortion.
Q: Can I use this speaker for stereo sound?
A: Yes, but you will need two speakers and a stereo amplifier to create a stereo setup.
Q: How do I improve the bass response of the speaker?
A: Use a well-designed enclosure with proper dimensions and acoustic damping materials.
This concludes the documentation for the JBL speaker (Part ID: speaker).