
How to Use TB6612 (motor driver/PWM controller): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
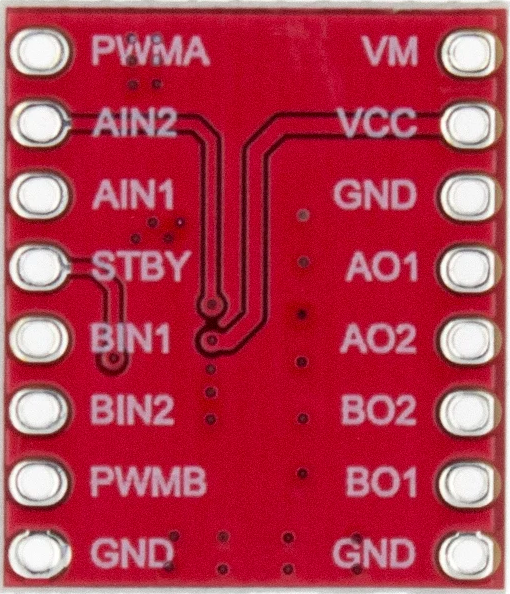
 Design with TB6612 (motor driver/PWM controller) in Cirkit Designer
Design with TB6612 (motor driver/PWM controller) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TB6612 is a versatile and efficient motor driver and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller designed to drive DC motors in various applications, including robotics, automation systems, and hobbyist projects. It offers the ability to control both the speed and direction of one or two DC motors and is known for its low power consumption and high efficiency.
Explore Projects Built with TB6612 (motor driver/PWM controller)
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer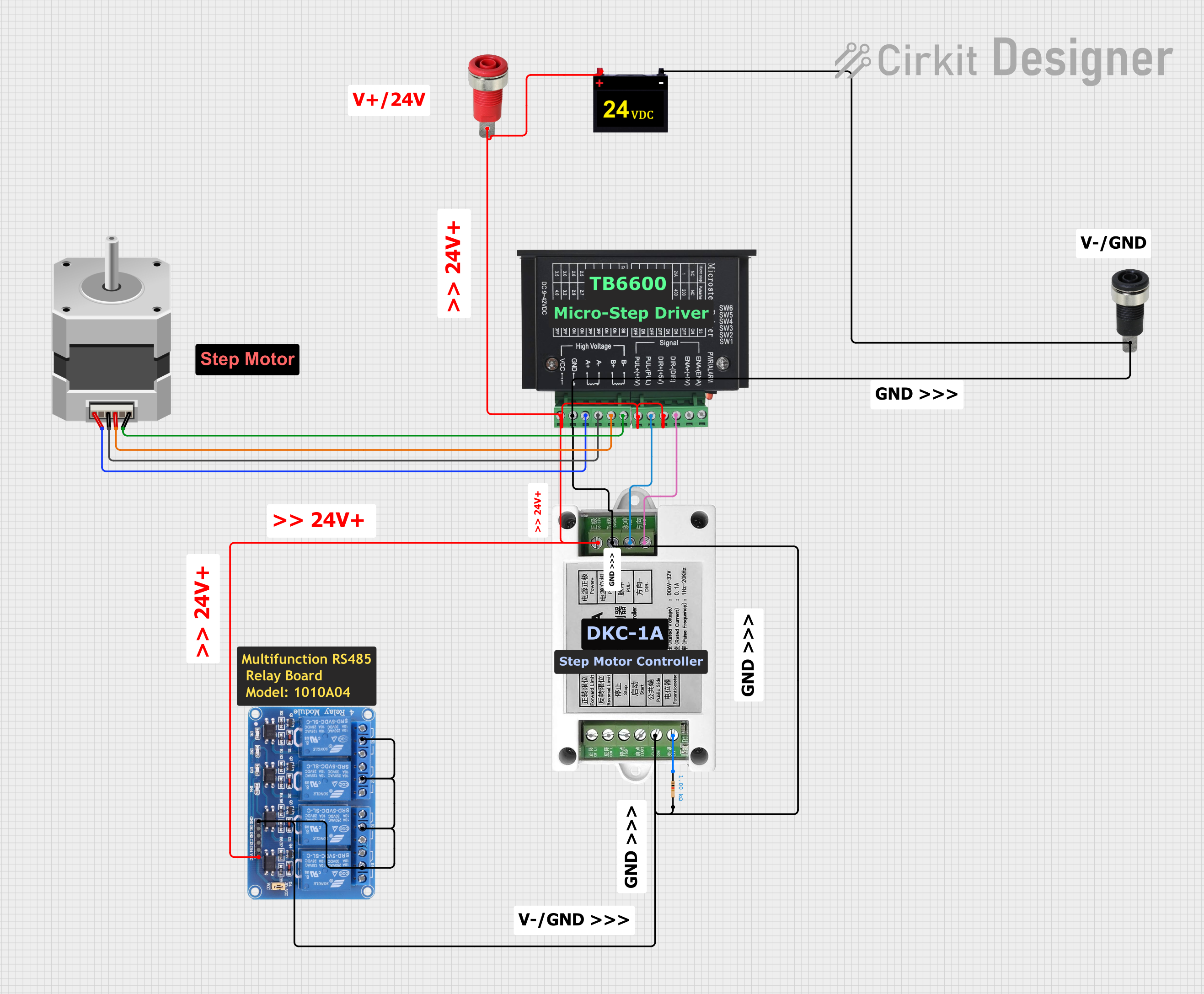
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TB6612 (motor driver/PWM controller)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Driving wheels or actuator motors.
- Automation systems: Conveyor belts, positioning motors.
- Hobby projects: Remote-controlled vehicles, DIY electronic gadgets.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage (VM): 2.5V to 13.5V
- Logic Voltage (VCC): 2.7V to 5.5V
- Output Current (continuous): 1.2A per channel
- Output Current (peak): 3.2A per channel
- Standby Control to Save Power
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VM | Motor voltage supply (2.5V to 13.5V) |
| 2 | VCC | Logic voltage supply (2.7V to 5.5V) |
| 3 | GND | Ground |
| 4 | STBY | Standby (Low: Standby mode, High: Normal operation) |
| 5 | AIN1 | Input A channel 1 |
| 6 | AIN2 | Input A channel 2 |
| 7 | PWMA | PWM input for A channel |
| 8 | BIN1 | Input B channel 1 |
| 9 | BIN2 | Input B channel 2 |
| 10 | PWMB | PWM input for B channel |
| 11 | AOUT1 | Output A channel 1 |
| 12 | AOUT2 | Output A channel 2 |
| 13 | BOUT1 | Output B channel 1 |
| 14 | BOUT2 | Output B channel 2 |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TB6612 in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect the motor supply voltage (VM) to pin 1.
- Connect the logic supply voltage (VCC) to pin 2.
- Connect the ground (GND) to pin 3.
Motor Connections:
- Connect the terminals of motor A to AOUT1 and AOUT2.
- Connect the terminals of motor B to BOUT1 and BOUT2, if using a second motor.
Control Connections:
- Connect the microcontroller or control device to AIN1, AIN2, PWMA for motor A.
- Connect the microcontroller or control device to BIN1, BIN2, PWMB for motor B.
Standby Mode:
- Connect STBY to a digital pin on the microcontroller to enable or disable the motor driver.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure that the supply voltage does not exceed the maximum ratings.
- Use a common ground for both the logic and motor power supplies.
- Avoid running motors at the peak current for extended periods to prevent overheating.
- Implement proper decoupling using capacitors close to the motor driver to minimize noise.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
#include <Arduino.h>
// Define TB6612 control pins connected to the Arduino
const int PWMA = 3; // Speed control for motor A
const int AIN1 = 4; // Direction control for motor A
const int AIN2 = 5; // Direction control for motor A
const int STBY = 6; // Standby
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(PWMA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(STBY, OUTPUT);
// Disable standby mode
digitalWrite(STBY, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Set motor A direction to clockwise
digitalWrite(AIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW);
// Set motor A speed to 50%
analogWrite(PWMA, 128);
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Set motor A direction to counter-clockwise
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2, HIGH);
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop motor A
digitalWrite(AIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2, LOW);
delay(2000); // Stop for 2 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Motor not running: Check power supply connections, ensure STBY is set to HIGH.
- Motor running only in one direction: Verify the logic inputs AIN1 and AIN2.
- Motor stuttering or weak: Ensure the power supply can deliver sufficient current.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Double-check wiring against the pin configuration table.
- Use a multimeter to verify the voltage levels at the power supply and logic inputs.
- Ensure that the PWM frequency is within the acceptable range for the TB6612.
FAQs
Q: Can the TB6612 drive stepper motors? A: No, the TB6612 is designed for DC motors. Stepper motors require a different type of driver.
Q: What is the maximum frequency for PWM input? A: The TB6612 can handle PWM frequencies up to 100kHz.
Q: How do I put the TB6612 in standby mode? A: Set the STBY pin to LOW to put the TB6612 in standby mode and reduce power consumption.
Q: Can I use the TB6612 to drive a single motor at 2.4A? A: No, the continuous current per channel is 1.2A. To drive a motor with higher current, consider using a motor driver with a higher current rating or paralleling the outputs with proper current sharing.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the TB6612 motor driver/PWM controller. For further information, consult the manufacturer's datasheet and application notes.