
How to Use 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo Battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
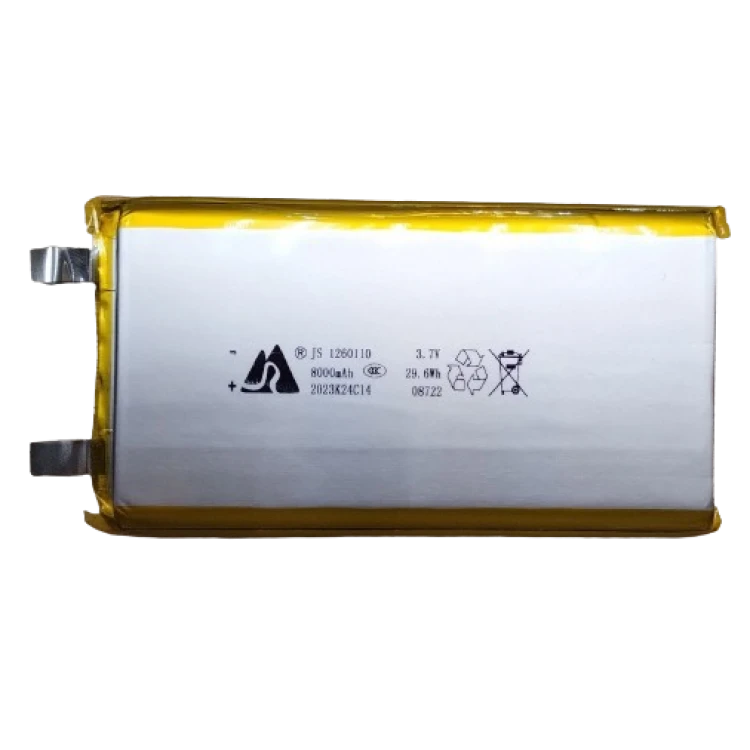

 Design with 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo Battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo Battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo battery is a high-capacity lithium polymer battery designed for applications requiring lightweight, high-energy-density power sources. With a nominal voltage of 3.7V and a capacity of 12000mAh, this battery is ideal for powering portable electronics, remote-controlled (RC) devices, drones, IoT devices, and backup power systems. Its compact size and high discharge rate make it a versatile choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo Battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer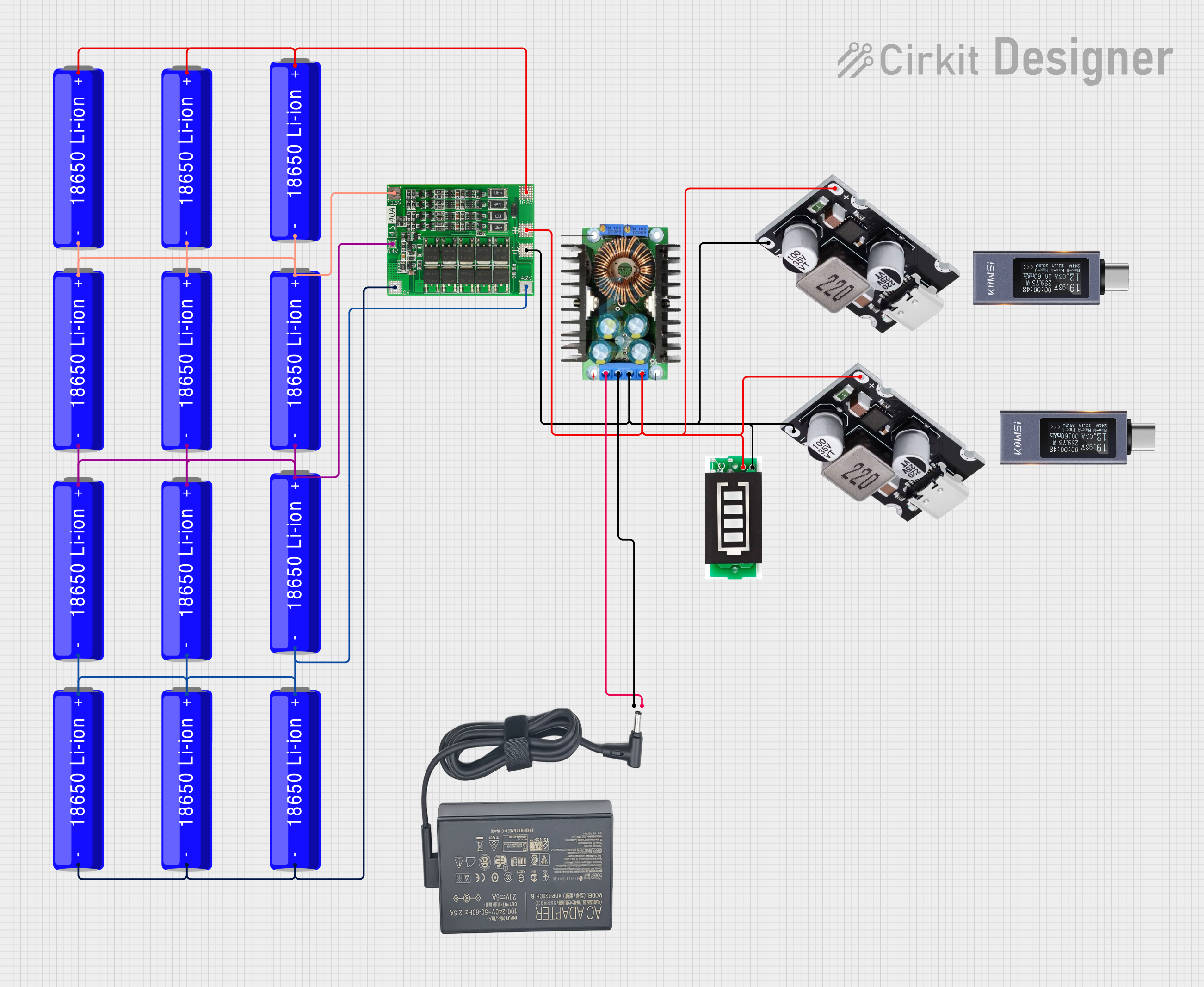
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer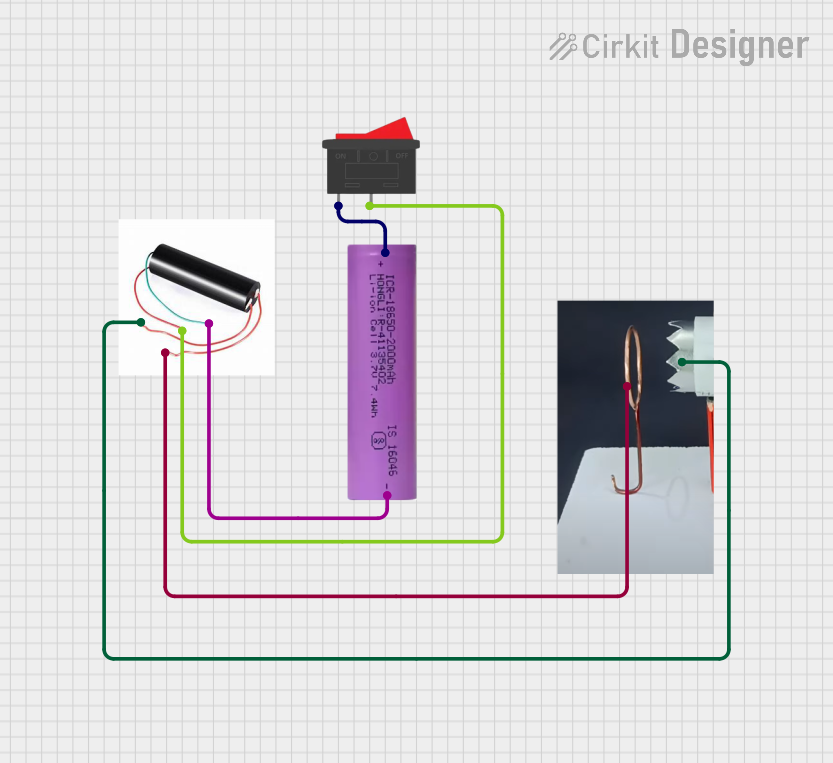
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer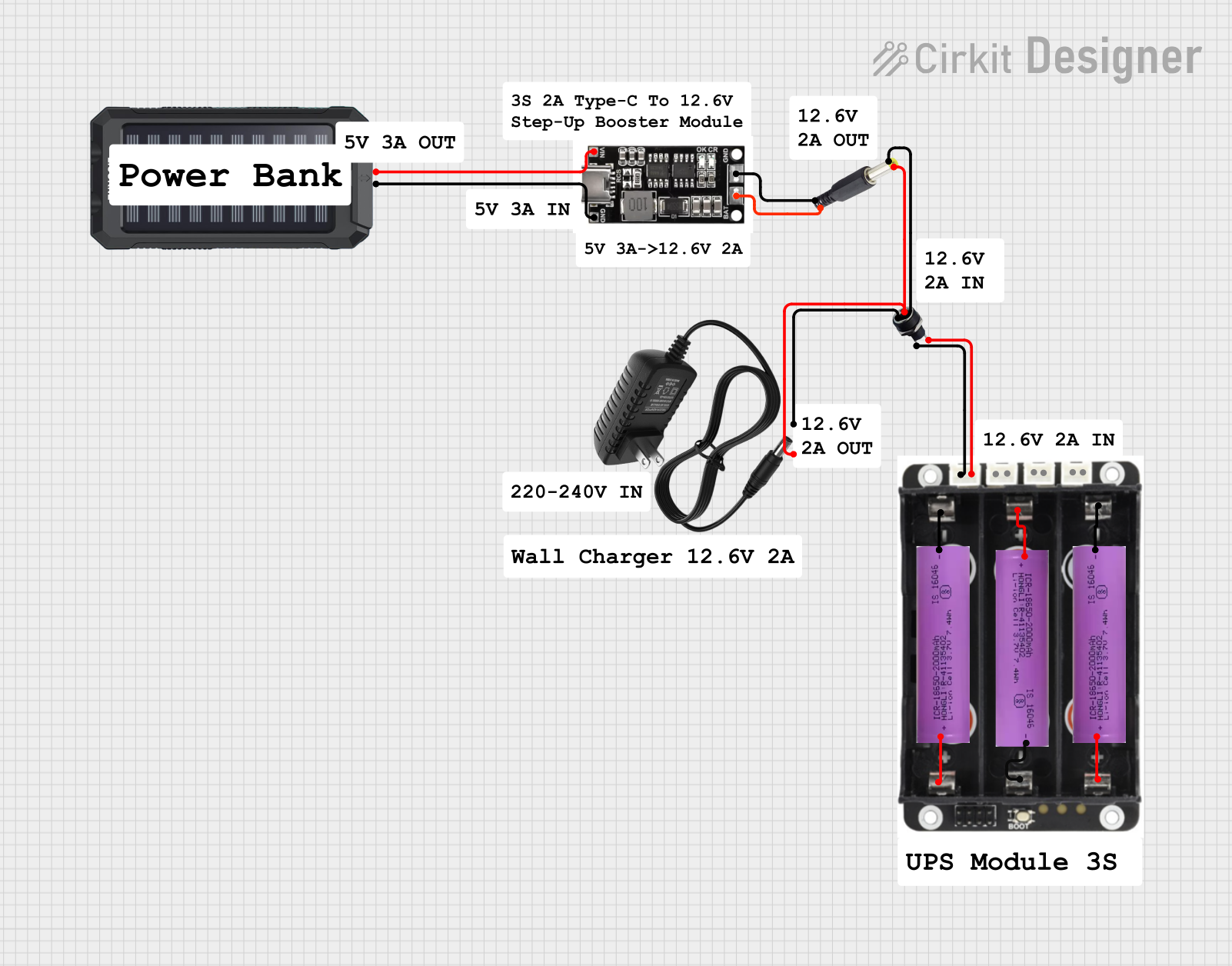
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo Battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- RC vehicles, drones, and quadcopters
- Portable electronic devices (e.g., tablets, handheld consoles)
- IoT devices and embedded systems
- Backup power supplies for small electronics
- DIY electronics projects
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo battery:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.7V |
| Capacity | 12000mAh (12Ah) |
| Energy | 44.4Wh |
| Discharge Rate (C-Rating) | Typically 1C to 3C (varies by model) |
| Maximum Discharge Current | 12A to 36A (depending on C-rating) |
| Charging Voltage | 4.2V (maximum) |
| Cutoff Voltage | 3.0V (minimum) |
| Chemistry | Lithium Polymer (LiPo) |
| Weight | ~200-300g (varies by manufacturer) |
| Dimensions | Varies (e.g., ~100mm x 60mm x 20mm) |
| Connector Type | JST, XT60, or bare leads (varies) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
LiPo batteries typically have two main wires for power and an optional balance connector for charging. Below is a description of the connections:
| Pin/Wire | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (Red Wire) | Main positive terminal for power and charging |
| Negative (Black Wire) | Main negative terminal for power and charging |
| Balance Connector Pins | Used for balancing individual cells during charging |
Note: Always check the specific connector type and pinout provided by the manufacturer.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo Battery in a Circuit
Connect the Battery:
- Identify the positive (red) and negative (black) wires.
- Connect the wires to the corresponding terminals of your circuit or device.
- If using a balance charger, connect the balance connector to the charger.
Charging the Battery:
- Use a LiPo-compatible charger with a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile.
- Set the charger to 3.7V nominal voltage and ensure the maximum charging current does not exceed 1C (12A for this battery).
- Monitor the charging process and disconnect the battery once fully charged (4.2V).
Discharging the Battery:
- Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum discharge current (e.g., 12A for 1C or 36A for 3C).
- Avoid discharging below the cutoff voltage of 3.0V to prevent damage.
Connecting to an Arduino UNO:
- Use a voltage regulator (e.g., LM7805 or a buck converter) to step down the voltage to 5V for the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the regulated output to the Arduino's VIN or 5V pin.
Example Code for Monitoring Battery Voltage with Arduino UNO
The following code demonstrates how to monitor the battery voltage using an Arduino UNO and a voltage divider circuit:
// Define pins and constants
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 2.0; // Adjust based on your resistor values
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino's reference voltage (5V)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the voltage divider
int analogValue = analogRead(batteryPin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage
float batteryVoltage = (analogValue / 1023.0) * referenceVoltage * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Important: Use appropriate resistor values for the voltage divider to ensure the input voltage to the Arduino does not exceed 5V.
Best Practices
- Always use a LiPo-safe charger to prevent overcharging or overheating.
- Store the battery at ~3.8V per cell for long-term storage.
- Avoid puncturing, short-circuiting, or exposing the battery to high temperatures.
- Use a battery management system (BMS) for added safety in complex circuits.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Battery does not charge | Ensure the charger is LiPo-compatible and the balance connector is properly connected. |
| Battery heats up during use | Check if the load exceeds the maximum discharge current. Reduce the load if necessary. |
| Voltage drops below 3.0V | Stop using the battery immediately and recharge it to prevent permanent damage. |
| Swollen or puffed battery | Discontinue use and safely dispose of the battery. Do not attempt to charge it. |
| Arduino reads incorrect voltage | Verify the voltage divider resistor values and ensure proper connections. |
FAQs
Can I use this battery directly with a 5V device?
- No, you need a voltage regulator to step up or step down the voltage to match your device's requirements.
How long will this battery last on a single charge?
- Battery life depends on the load. For example, at a 1A load, the battery can last approximately 12 hours (12000mAh ÷ 1000mA).
Is it safe to leave the battery connected to the charger?
- No, disconnect the battery once it is fully charged to avoid overcharging.
What should I do if the battery is not holding a charge?
- This may indicate the battery has reached the end of its life cycle. Replace the battery with a new one.
By following this documentation, you can safely and effectively use the 3.7V 12000mAh LiPo battery in your projects. Always prioritize safety and adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines.