
How to Use Precision RTC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
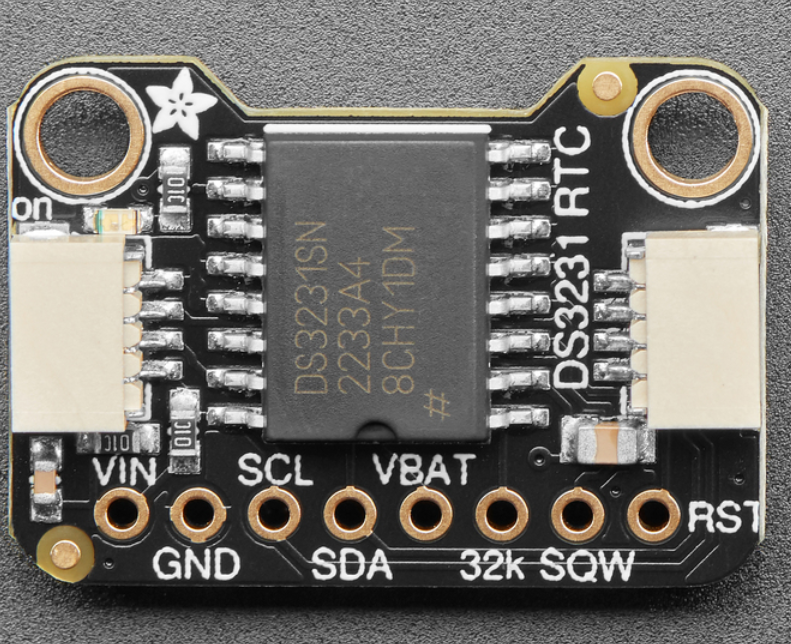
 Design with Precision RTC in Cirkit Designer
Design with Precision RTC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Adafruit DS3231 Precision Real-Time Clock (RTC) is a highly accurate timekeeping device designed for applications requiring precise time and date information. Unlike standard RTC modules, the DS3231 integrates a temperature-compensated crystal oscillator (TCXO) to maintain exceptional accuracy, even under varying environmental conditions. It also includes a backup battery feature to retain timekeeping during power outages.
Explore Projects Built with Precision RTC
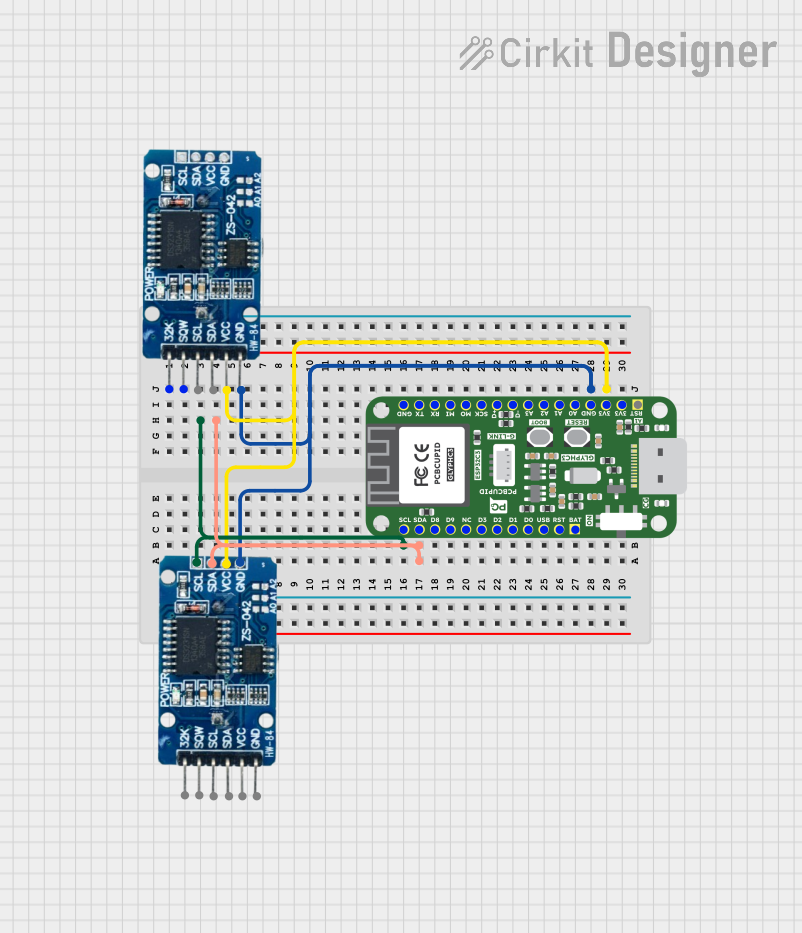
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer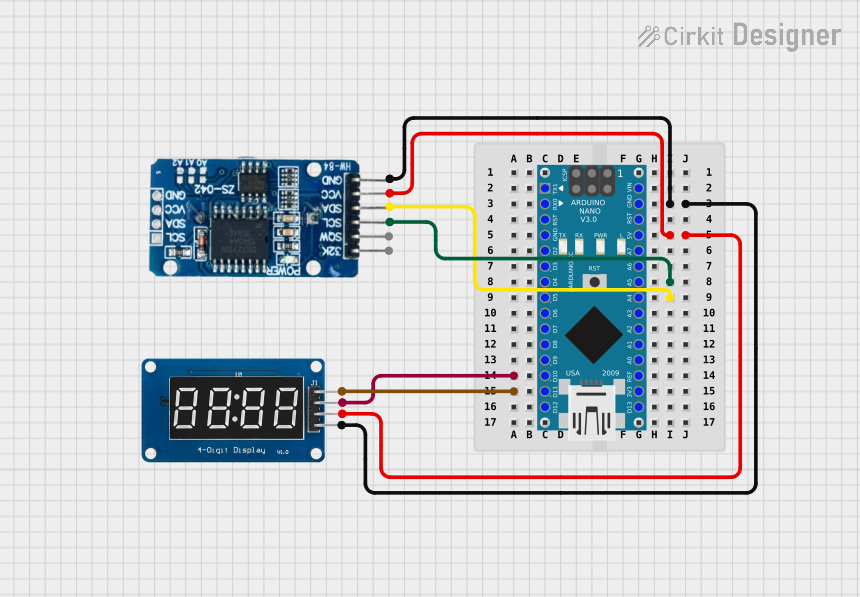
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer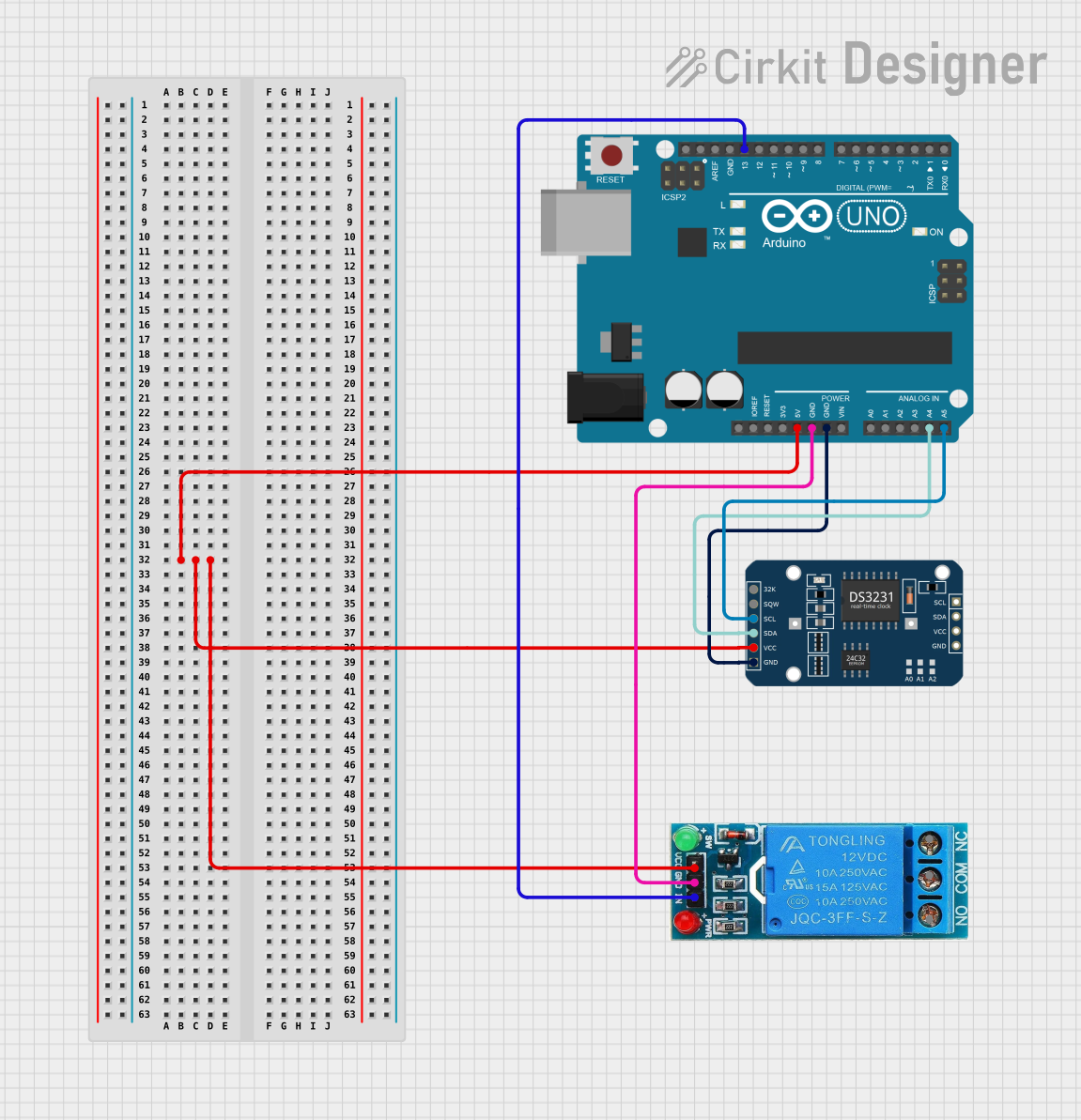
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer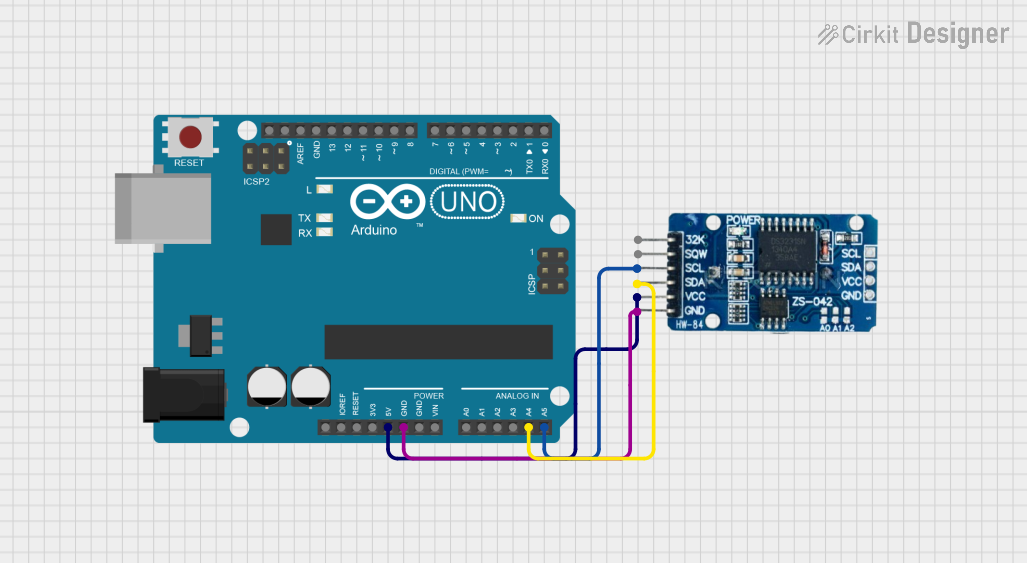
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Precision RTC

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Data logging systems
- Alarm clocks and timers
- IoT devices requiring time synchronization
- Scheduling and automation systems
- Embedded systems with low-power requirements
Technical Specifications
The DS3231 RTC module offers the following key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | 2.3V to 5.5V |
| Timekeeping Accuracy | ±2 ppm (±0.1728 seconds/day) from 0°C to +40°C |
| Backup Battery Voltage | 2.3V to 3.7V (e.g., CR2032 coin cell) |
| Communication Interface | I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Current Consumption | 1.5 µA (timekeeping mode with battery backup) |
| Alarm Functions | 2 programmable alarms |
| Additional Features | 32kHz output, square wave generator |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DS3231 module typically includes the following pins:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | Ground connection |
| VCC | 2 | Power supply input (2.3V to 5.5V) |
| SDA | 3 | I²C data line (connect to Arduino's A4 pin for communication) |
| SCL | 4 | I²C clock line (connect to Arduino's A5 pin for communication) |
| SQW/INT | 5 | Square wave output or interrupt output (optional, programmable via registers) |
| 32K | 6 | 32kHz output (optional, for external clocking purposes) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the DS3231 in a Circuit
- Power the Module: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- I²C Communication: Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I²C pins on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO: SDA to A4, SCL to A5).
- Backup Battery: Insert a CR2032 coin cell battery into the battery holder to enable timekeeping during power loss.
- Optional Outputs: Use the SQW/INT pin for alarms or square wave signals, and the 32K pin for an external clock signal if needed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Pull-Up Resistors: Ensure that the I²C lines (SDA and SCL) have pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ). Some modules include these resistors by default.
- Battery Backup: Always use a compatible backup battery to maintain timekeeping during power outages.
- Environmental Conditions: For optimal accuracy, operate the module within the specified temperature range.
- I²C Address: The default I²C address for the DS3231 is
0x68. Ensure no address conflicts if multiple I²C devices are used.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the DS3231 with an Arduino UNO to read and display the current time and date:
#include <Wire.h>
#include "RTClib.h" // Adafruit RTC library for DS3231
RTC_DS3231 rtc; // Create an RTC object
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I²C communication
if (!rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC. Check connections!");
while (1); // Halt execution if RTC is not found
}
if (rtc.lostPower()) {
Serial.println("RTC lost power, setting the time!");
// Set the RTC to the current date and time
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
}
void loop() {
DateTime now = rtc.now(); // Get the current time and date
// Print the current time and date to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print(now.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(now.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.second(), DEC);
Serial.println();
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before updating
}
Notes on the Code
- The
RTCliblibrary is required for this example. Install it via the Arduino Library Manager. - The
rtc.adjust()function sets the RTC to the current time and date based on your computer's clock. This is only necessary if the RTC has lost power or needs to be initialized.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
RTC Not Detected
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or I²C address conflict.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the SDA and SCL pins are correctly connected. Verify the I²C address using an I²C scanner sketch.
Incorrect Time or Date
- Cause: RTC lost power or was not initialized.
- Solution: Use the
rtc.adjust()function to set the correct time and date.
No Output on Serial Monitor
- Cause: Serial communication not initialized or incorrect baud rate.
- Solution: Ensure
Serial.begin(9600)matches the baud rate in the Serial Monitor.
Backup Battery Not Working
- Cause: Dead or incompatible battery.
- Solution: Replace the battery with a new CR2032 coin cell.
FAQs
Q: Can the DS3231 be used with 3.3V microcontrollers?
A: Yes, the DS3231 operates with supply voltages from 2.3V to 5.5V, making it compatible with both 3.3V and 5V systems.Q: How long does the backup battery last?
A: A typical CR2032 battery can last several years, depending on usage and environmental conditions.Q: Can I use multiple DS3231 modules on the same I²C bus?
A: No, the DS3231 has a fixed I²C address (0x68), so only one module can be used per I²C bus unless an I²C multiplexer is used.Q: What is the purpose of the SQW/INT pin?
A: The SQW/INT pin can output a square wave signal or act as an interrupt for alarms, depending on the configuration.
This concludes the documentation for the Adafruit DS3231 Precision RTC.