
How to Use Buzzer Passive: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
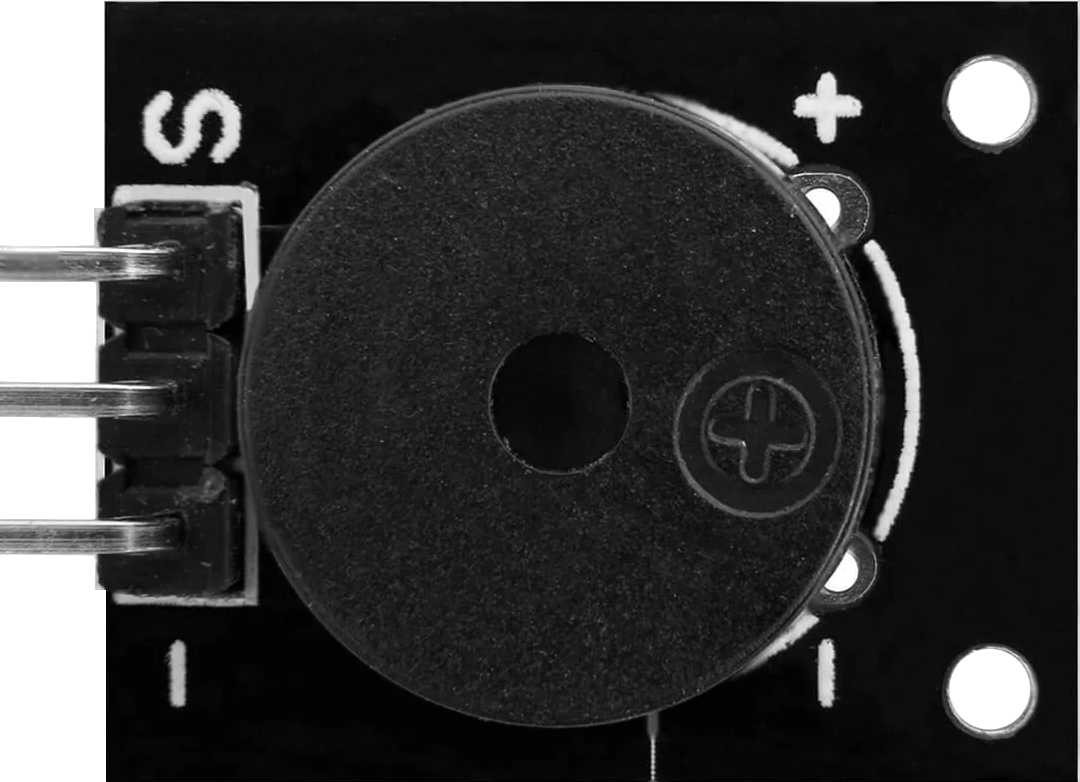
 Design with Buzzer Passive in Cirkit Designer
Design with Buzzer Passive in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The AZDelivery KY-006 Passive Buzzer is an audio signaling device that produces sound when an alternating current (AC) signal is applied. Unlike an active buzzer, the passive buzzer requires an external signal, such as a square wave, to generate sound. This makes it versatile for applications where precise control over sound frequency and duration is needed.
Explore Projects Built with Buzzer Passive
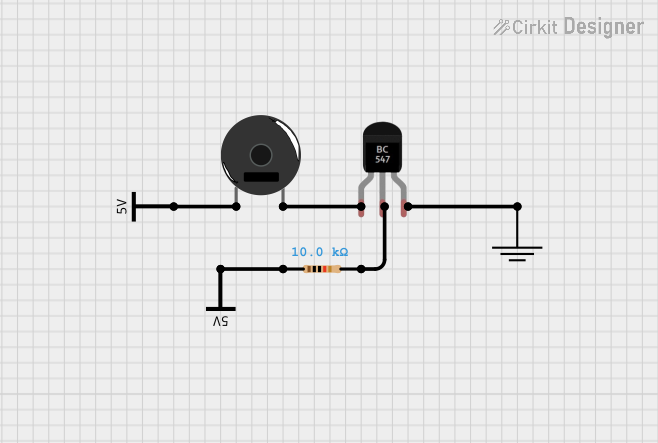
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer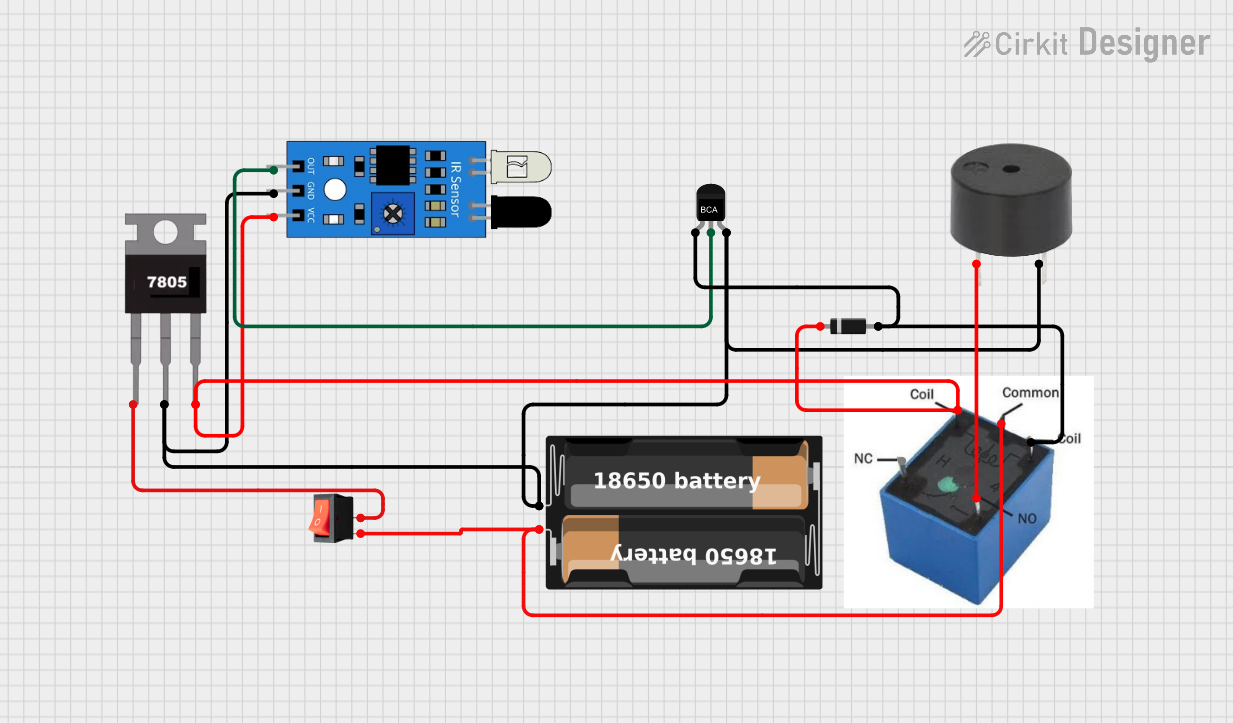
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer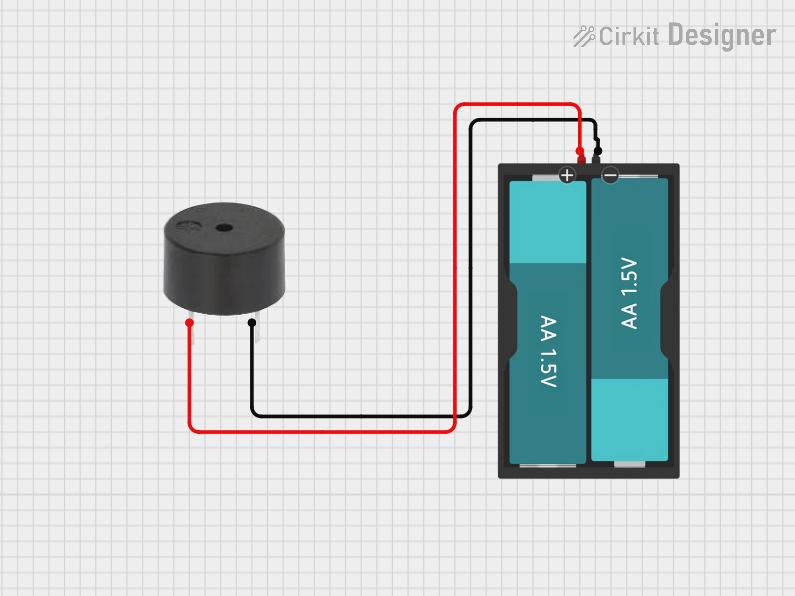
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Buzzer Passive

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Alarms and notifications in electronic devices
- Sound effects in embedded systems
- Timers and reminders
- Educational projects and prototyping with microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the AZDelivery KY-006 Passive Buzzer:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | AZDelivery |
| Part ID | KY-006 |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Operating Current | ≤ 25mA |
| Sound Frequency Range | 1kHz to 10kHz (external signal dependent) |
| Dimensions | 18mm x 11mm x 8mm |
| Weight | ~2g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The KY-006 Passive Buzzer module has three pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Signal (S) | Input pin for the external signal (e.g., square wave) |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply pin (3.3V to 5V) |
| 3 | GND | Ground connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the KY-006 Passive Buzzer in a Circuit
Connect the Pins:
- Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect the
Signal (S)pin to a microcontroller's PWM-capable pin or an external signal generator.
- Connect the
Generate a Signal:
- Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) to generate a square wave signal on the
Signal (S)pin. The frequency of the square wave determines the sound pitch.
- Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) to generate a square wave signal on the
Test the Buzzer:
- Upload a test program to your microcontroller to verify the buzzer's operation. The buzzer should produce sound when the signal is applied.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Signal Frequency: Ensure the signal frequency is within the buzzer's operating range (1kHz to 10kHz) for optimal sound output.
- Power Supply: Do not exceed the recommended operating voltage (5V) to avoid damaging the component.
- Mounting: Secure the buzzer module to prevent vibrations that could affect sound quality.
- PWM Pins: Use a PWM-capable pin on your microcontroller for precise control over sound frequency and duration.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example Arduino sketch to generate a tone using the KY-006 Passive Buzzer:
// Example code for KY-006 Passive Buzzer with Arduino UNO
// Generates a tone on the buzzer using a PWM signal
#define BUZZER_PIN 9 // Connect the Signal (S) pin of the buzzer to pin 9
void setup() {
pinMode(BUZZER_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set the buzzer pin as an output
}
void loop() {
// Generate a 1kHz tone for 500ms
tone(BUZZER_PIN, 1000); // tone(pin, frequency in Hz)
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms
// Stop the tone for 500ms
noTone(BUZZER_PIN); // Stop the tone
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms
}
Notes:
- The
tone()function generates a square wave signal on the specified pin. - The
noTone()function stops the signal, silencing the buzzer.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Sound from the Buzzer:
- Cause: No signal is being applied to the
Signal (S)pin. - Solution: Verify the connection between the microcontroller and the buzzer. Ensure the
tone()function or equivalent signal generator is active.
- Cause: No signal is being applied to the
Distorted or Weak Sound:
- Cause: Incorrect signal frequency or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Check that the signal frequency is within the buzzer's operating range (1kHz to 10kHz). Ensure the power supply voltage is stable and within the recommended range (3.3V to 5V).
Buzzer Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive voltage or prolonged operation at high current.
- Solution: Ensure the operating voltage does not exceed 5V. Avoid continuous operation for extended periods without breaks.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the KY-006 Passive Buzzer without a microcontroller?
A1: Yes, you can use an external signal generator to drive the buzzer. Ensure the signal frequency and voltage are within the specified range.
Q2: What is the difference between a passive and an active buzzer?
A2: A passive buzzer requires an external signal to produce sound, while an active buzzer has an internal oscillator and only needs a DC voltage to operate.
Q3: Can I control the volume of the buzzer?
A3: The volume is primarily determined by the input voltage and cannot be directly controlled. However, you can adjust the duty cycle of the PWM signal to influence the perceived loudness.
Q4: Is the KY-006 compatible with 3.3V systems?
A4: Yes, the KY-006 Passive Buzzer operates with both 3.3V and 5V systems, making it compatible with a wide range of microcontrollers.