
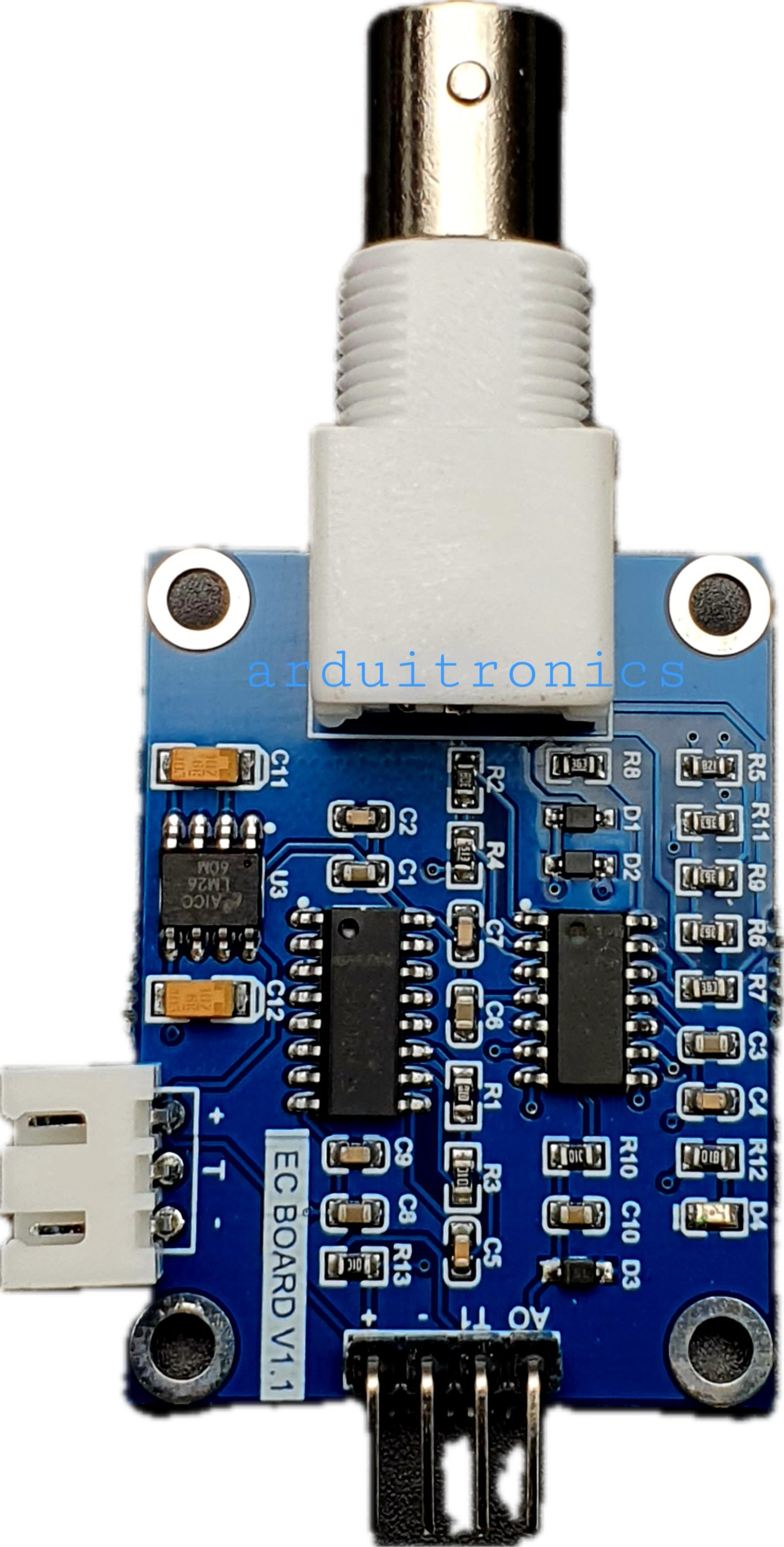
How to Use EC Board v1.1: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with EC Board v1.1 in Cirkit Designer
Design with EC Board v1.1 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The EC Board v1.1, manufactured by Arduitronics (Part ID: AS10323), is a versatile electronic circuit board designed for prototyping and development. It provides multiple input/output (I/O) ports, power supply connections, and compatibility with a wide range of sensors and modules. This makes it an excellent choice for educational purposes, experimental projects, and rapid prototyping.
Explore Projects Built with EC Board v1.1
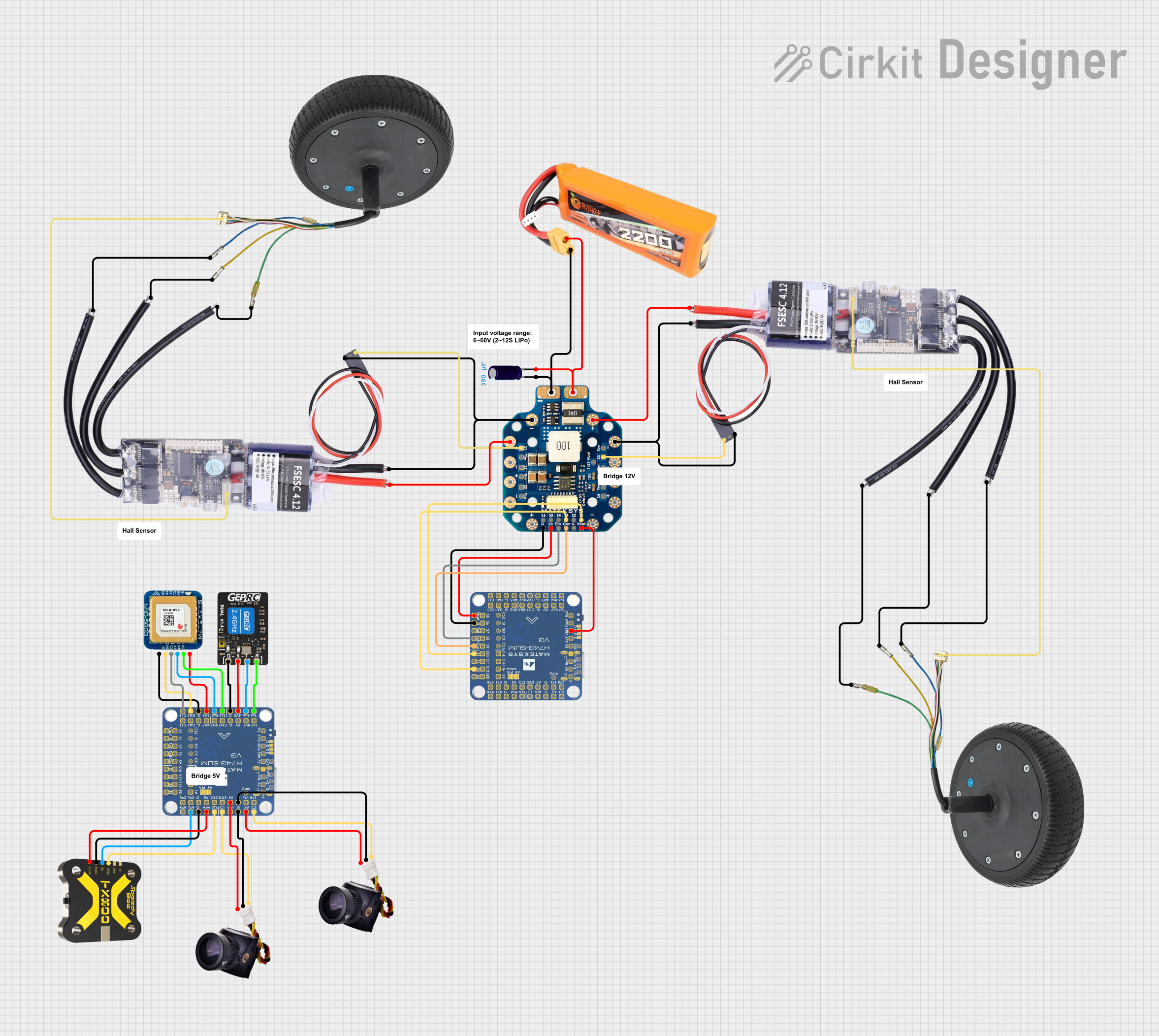
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer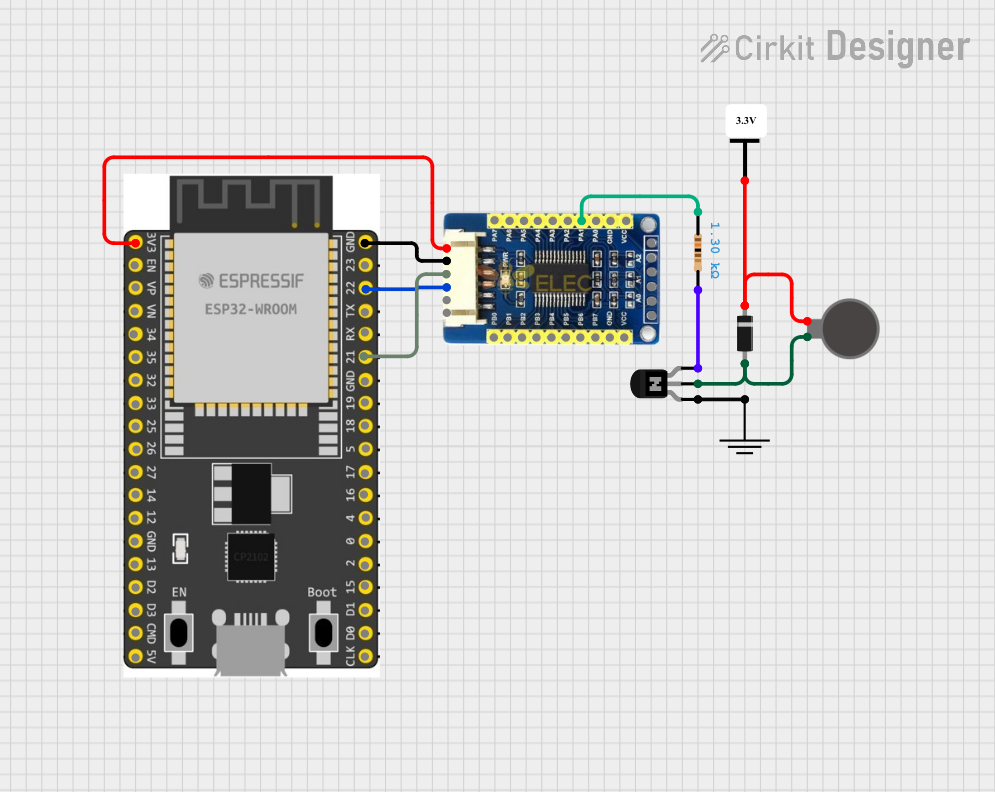
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer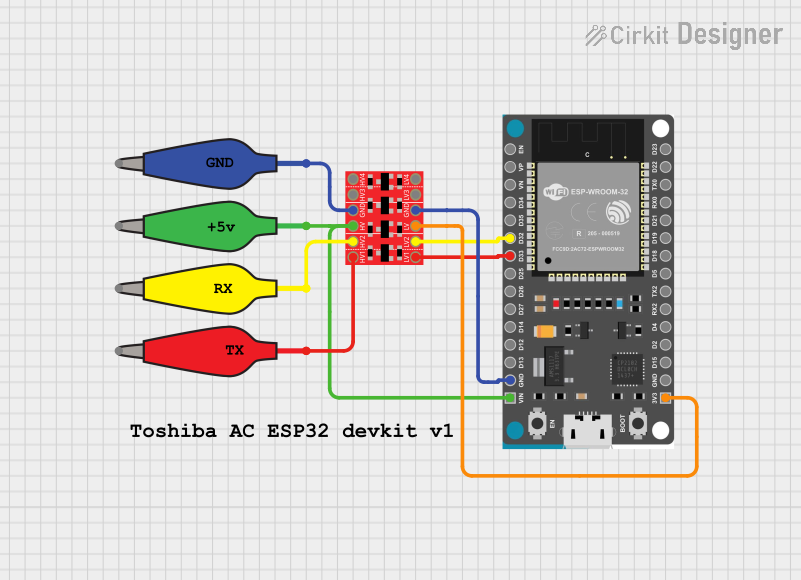
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with EC Board v1.1

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Educational projects for learning electronics and programming
- Rapid prototyping of circuits and embedded systems
- Integration with sensors and actuators for IoT applications
- Development of small-scale automation systems
- Experimentation with Arduino and other microcontroller platforms
Technical Specifications
The EC Board v1.1 is designed to simplify circuit development while offering robust functionality. Below are its key technical specifications:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Arduitronics |
| Part ID | AS10323 |
| Operating Voltage | 5V DC |
| Input Voltage Range | 7V–12V DC (via barrel jack) |
| Maximum Current Output | 1A |
| Dimensions | 80mm x 60mm |
| Weight | 50g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The EC Board v1.1 features a variety of pins for connecting sensors, modules, and other components. Below is the pin configuration:
Power Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage (7V–12V DC) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| 5V | Regulated 5V output for powering components |
| 3.3V | Regulated 3.3V output for low-power devices |
I/O Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| D0–D13 | Digital I/O pins (can be used as input/output) |
| A0–A5 | Analog input pins (10-bit resolution) |
| PWM Pins | D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, D11 (PWM output capable) |
Communication Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| TX (D1) | UART Transmit |
| RX (D0) | UART Receive |
| SDA | I2C Data Line |
| SCL | I2C Clock Line |
Usage Instructions
The EC Board v1.1 is designed for ease of use, especially for beginners. Follow the steps below to get started:
Connecting the Board
- Power Supply: Connect a 7V–12V DC power source to the VIN pin or the barrel jack. Alternatively, you can power the board via USB if connected to a microcontroller like Arduino.
- Peripheral Connections: Attach sensors, modules, or other components to the appropriate I/O pins. Use the 5V or 3.3V pins to power your peripherals.
Using with an Arduino UNO
The EC Board v1.1 is fully compatible with the Arduino UNO. Below is an example of how to use the board to read an analog sensor and control an LED:
Example Code
// Example: Reading an analog sensor and controlling an LED
// Connect the sensor to A0 and the LED to D9
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor
const int ledPin = 9; // Digital pin connected to the LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the value to the Serial Monitor
// Map the sensor value (0-1023) to PWM range (0-255)
int ledBrightness = map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
analogWrite(ledPin, ledBrightness); // Set the LED brightness
delay(100); // Wait for 100ms before the next reading
}
Important Considerations
- Voltage Levels: Ensure that connected components operate within the board's voltage range (5V or 3.3V).
- Current Limits: Do not exceed the maximum current output of 1A to avoid damaging the board.
- Pin Usage: Avoid using the same pin for multiple functions simultaneously (e.g., digital I/O and PWM).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Board Not Powering On
- Cause: Insufficient input voltage or loose connections.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is within the 7V–12V range and check all connections.
Components Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect pin connections or mismatched voltage levels.
- Solution: Verify the wiring and ensure the components are compatible with the board's voltage.
Serial Communication Not Working
- Cause: Incorrect baud rate or TX/RX pin usage.
- Solution: Match the baud rate in your code with the Serial Monitor and ensure TX/RX pins are correctly connected.
FAQs
Q: Can I power the board using a USB connection?
A: Yes, the board can be powered via USB when connected to a microcontroller like Arduino.
Q: Is the EC Board v1.1 compatible with 3.3V sensors?
A: Yes, the board provides a 3.3V output pin for low-power devices.
Q: Can I use all the digital pins for PWM?
A: No, only specific pins (D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, D11) support PWM output.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the EC Board v1.1 for your projects and experiments.