
How to Use LCD: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with LCD in Cirkit Designer
Design with LCD in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a flat-panel display technology that uses liquid crystals to modulate light. It is widely used in various applications, including televisions, computer monitors, mobile devices, and embedded systems. LCDs are known for their lightweight design, energy efficiency, and ability to display clear images and text. In electronics, smaller LCD modules are commonly used to display information in projects, such as temperature readings, sensor data, or user interfaces.
Explore Projects Built with LCD
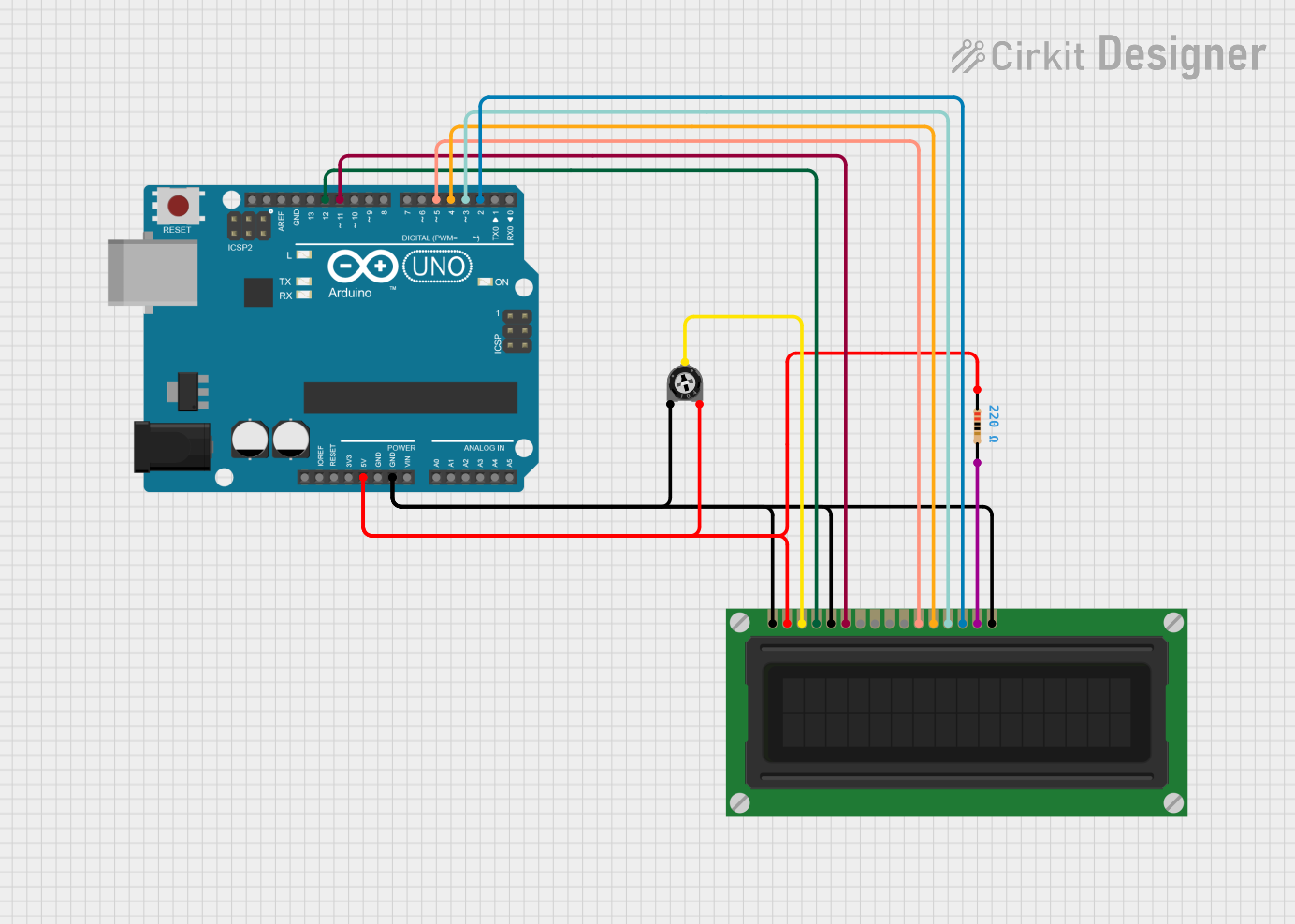
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer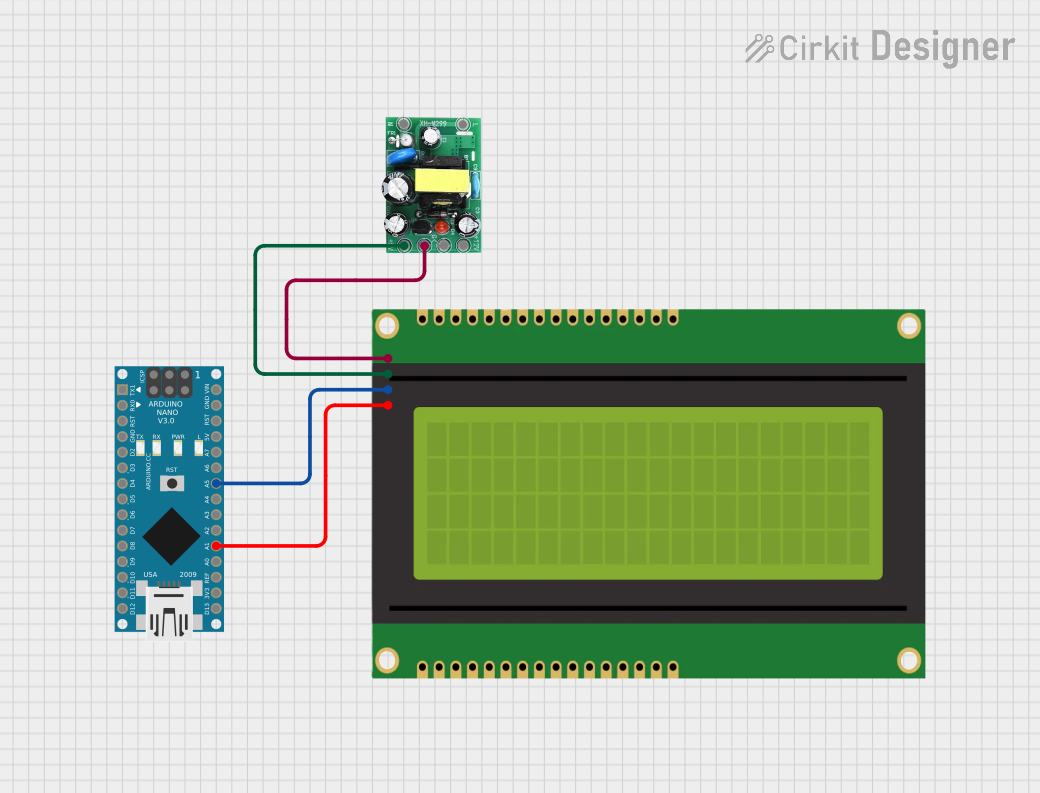
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer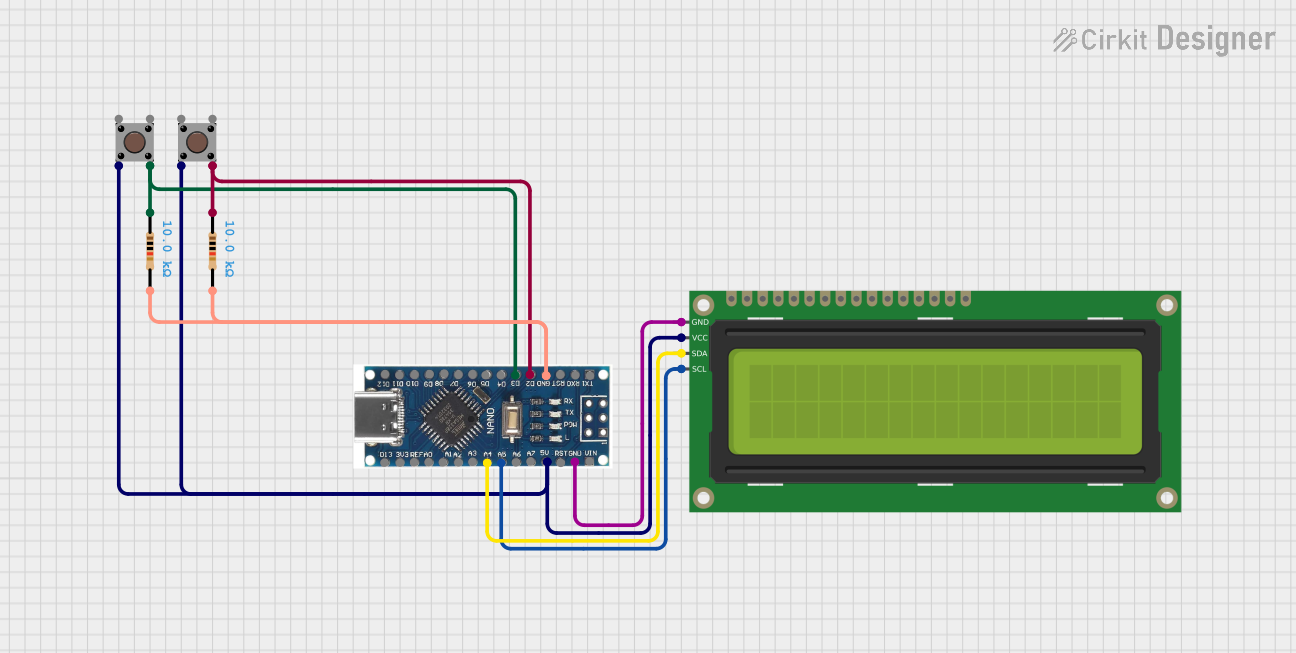
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer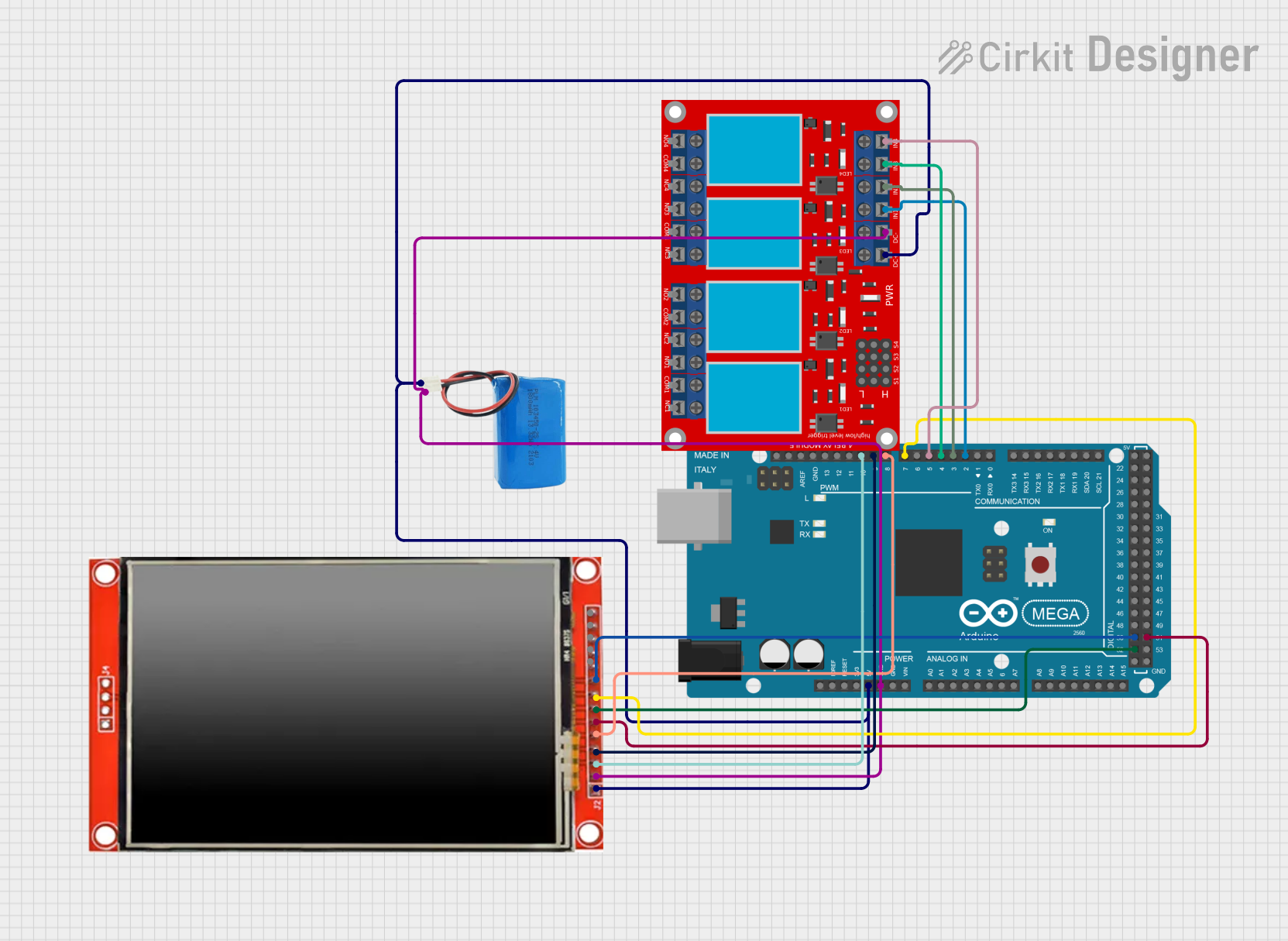
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with LCD

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Displaying text and numerical data in embedded systems
- User interfaces for microcontroller-based projects
- Digital clocks, thermometers, and other small devices
- Industrial control panels and instrumentation
- Consumer electronics such as calculators and remote controls
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard 16x2 LCD module (16 characters per row, 2 rows), which is one of the most commonly used LCD types in electronics projects.
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 4.7V to 5.3V DC
- Current Consumption: 1mA to 2mA (without backlight), ~20mA (with backlight)
- Interface: Parallel (4-bit or 8-bit mode)
- Character Resolution: 16x2 (16 characters per row, 2 rows)
- Backlight: LED (optional, typically white or green)
- Controller IC: HD44780 or compatible
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 70°C
- Dimensions: ~80mm x 36mm x 12mm (varies by model)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The standard 16x2 LCD module typically has 16 pins. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VSS | Ground (0V) connection |
| 2 | VDD | Power supply (4.7V to 5.3V) |
| 3 | V0 | Contrast adjustment (connect to a potentiometer) |
| 4 | RS | Register Select (0: Command mode, 1: Data mode) |
| 5 | RW | Read/Write (0: Write, 1: Read) |
| 6 | E | Enable pin (triggers data read/write) |
| 7 | D0 | Data pin 0 (used in 8-bit mode only) |
| 8 | D1 | Data pin 1 (used in 8-bit mode only) |
| 9 | D2 | Data pin 2 (used in 8-bit mode only) |
| 10 | D3 | Data pin 3 (used in 8-bit mode only) |
| 11 | D4 | Data pin 4 (used in both 4-bit and 8-bit modes) |
| 12 | D5 | Data pin 5 (used in both 4-bit and 8-bit modes) |
| 13 | D6 | Data pin 6 (used in both 4-bit and 8-bit modes) |
| 14 | D7 | Data pin 7 (used in both 4-bit and 8-bit modes) |
| 15 | LED+ | Backlight anode (connect to power through a resistor) |
| 16 | LED- | Backlight cathode (connect to ground) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the LCD in a Circuit
- Power the LCD: Connect the VSS pin to ground and the VDD pin to a 5V power supply.
- Adjust Contrast: Connect the V0 pin to the middle terminal of a 10kΩ potentiometer. Connect the other two terminals of the potentiometer to VDD and ground. Adjust the potentiometer to set the desired contrast.
- Connect Control Pins:
- Connect the RS pin to a digital output pin of your microcontroller.
- Connect the RW pin to ground (for write-only mode).
- Connect the E pin to another digital output pin of your microcontroller.
- Connect Data Pins:
- For 4-bit mode, connect D4 to D7 to four digital output pins of your microcontroller. Leave D0 to D3 unconnected.
- For 8-bit mode, connect D0 to D7 to eight digital output pins of your microcontroller.
- Backlight (Optional): Connect LED+ to 5V through a current-limiting resistor (e.g., 220Ω). Connect LED- to ground.
- Initialize the LCD: Use the appropriate initialization sequence in your microcontroller code to configure the LCD.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always use a current-limiting resistor for the backlight to prevent damage.
- Ensure proper grounding to avoid noise or flickering issues.
- Use 4-bit mode to save microcontroller pins if pin availability is limited.
- Follow the timing requirements specified in the LCD datasheet for reliable operation.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a 16x2 LCD with an Arduino UNO in 4-bit mode:
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
// Initialize the library with the pins connected to the LCD
// RS, E, D4, D5, D6, D7
LiquidCrystal lcd(7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12);
void setup() {
// Set up the LCD's number of columns and rows
lcd.begin(16, 2);
// Print a message to the LCD
lcd.print("Hello, World!");
}
void loop() {
// Move the cursor to the second row, first column
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
// Print a dynamic message
lcd.print("Count: ");
lcd.print(millis() / 1000); // Display elapsed time in seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Display on the LCD:
- Check the power connections (VSS, VDD).
- Adjust the contrast using the potentiometer connected to V0.
- Ensure the backlight is connected properly (if used).
Flickering or Unstable Display:
- Verify proper grounding of the circuit.
- Check for loose connections or poor soldering.
- Ensure the microcontroller timing matches the LCD's requirements.
Incorrect or Garbled Characters:
- Double-check the data pin connections (D4 to D7 in 4-bit mode).
- Ensure the LCD initialization sequence in the code is correct.
Backlight Not Working:
- Verify the LED+ and LED- connections.
- Use an appropriate current-limiting resistor for the backlight.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the LCD with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you may need a level shifter or a 3.3V-compatible LCD module. Check the datasheet for compatibility.
Q: How do I display custom characters?
A: Use the createChar() function in the LiquidCrystal library to define and display custom characters.
Q: Can I use the LCD without a potentiometer for contrast adjustment?
A: Yes, you can use a fixed resistor or connect V0 to ground for maximum contrast, but a potentiometer provides better control.