
How to Use Socket: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Socket in Cirkit Designer
Design with Socket in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A socket is a versatile electronic component that serves as an interface between electronic circuits and devices such as integrated circuits (ICs), transistors, or other electronic components. Sockets are commonly used in electronic systems to allow for the easy insertion and removal of components, facilitating easy replacements, upgrades, and testing without the need for soldering. They are essential in prototyping, production, and maintenance of electronic devices.
Explore Projects Built with Socket
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer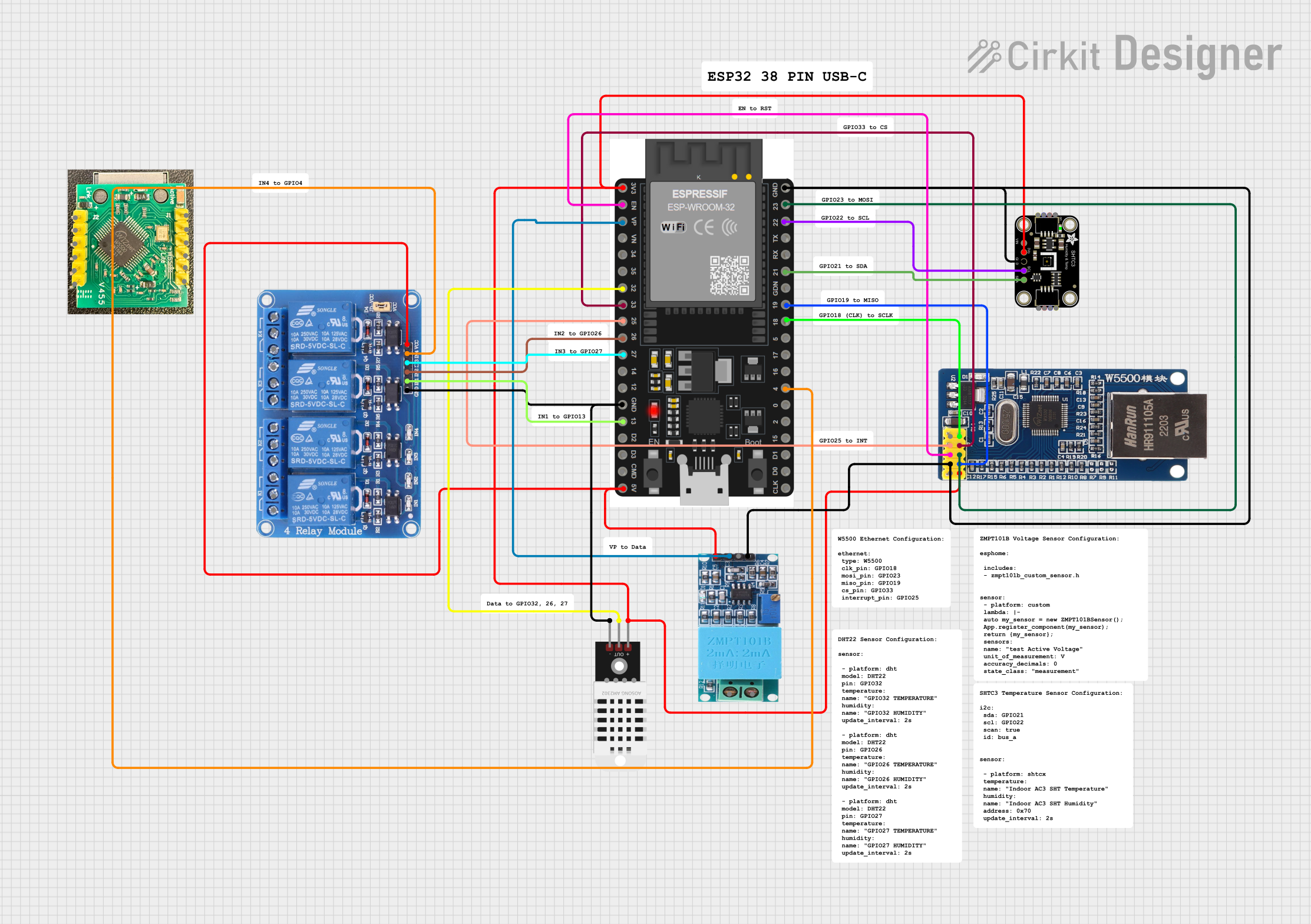
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Socket

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Prototyping: Sockets are used on breadboards and prototyping boards to test circuit designs.
- Consumer Electronics: Used in devices like computers and gaming consoles for CPU, memory, and expansion cards.
- Industrial Electronics: In machinery and equipment for easy replacement of sensors and modules.
- Automotive: For relays, fuses, and control modules that require regular maintenance or replacement.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Voltage Rating: The maximum voltage the socket can handle without breakdown.
- Current Rating: The maximum current the socket can carry continuously.
- Contact Resistance: The electrical resistance between the socket contacts and the inserted component.
- Insulation Resistance: The electrical resistance between the socket's insulated parts.
- Dielectric Strength: The maximum electric field the socket material can withstand without breakdown.
- Operating Temperature Range: The range of temperatures over which the socket can operate reliably.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power Supply (Vcc) | Connect to positive voltage |
| 2 | Ground (GND) | Connect to circuit ground |
| 3-n | Signal/Control Pins | For data or control signals |
Note: The actual pin configuration will vary depending on the type of socket and the device it is designed for.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Socket in a Circuit
- Identify the Pinout: Refer to the datasheet of both the socket and the component to understand the pin configuration.
- Insertion: Carefully align the pins of the component with the socket and gently press to insert.
- Soldering (if applicable): Some sockets require soldering to the PCB. Ensure proper soldering techniques to avoid cold joints or short circuits.
- Power Supply: Connect the power supply and ground pins to the appropriate sources.
- Signal Connections: Connect any signal or control pins as per the circuit design.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Force: Never force a component into a socket, as this can bend or break pins.
- Check Orientation: Many components have a specific orientation. Inserting them incorrectly can damage the component or the socket.
- Power Ratings: Ensure that the socket's voltage and current ratings are suitable for the application.
- Clean Contacts: Keep the socket pins clean to ensure good electrical contact.
- Secure Mounting: Ensure the socket is securely mounted to the PCB to prevent movement that could cause intermittent connections.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Poor Contact: If a device is not working, check for loose connections or dirt on the socket contacts.
- Heat Generation: Excessive heat may indicate that the socket is carrying more current than its rating.
- Physical Damage: Bent pins or cracked sockets can cause malfunctions.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Re-seat the Component: Remove and re-insert the component to improve contact.
- Clean Contacts: Use a contact cleaner or isopropyl alcohol to clean the contacts.
- Check for Damage: Inspect the socket and component for any physical damage.
- Measure Voltage and Current: Use a multimeter to ensure the socket is receiving the correct voltage and current.
FAQs
Q: Can I use any socket for my component? A: No, sockets are specific to the component type and pin configuration. Always use the correct socket for your component.
Q: How do I know if the socket is properly connected? A: Verify that all connections are secure and that the component is correctly oriented and fully inserted into the socket.
Q: Can I replace a soldered component with a socket for easier maintenance? A: Yes, you can desolder the component and replace it with a socket, provided there is enough space on the PCB and the socket meets the necessary specifications.
Q: Are there sockets for surface-mount components? A: Yes, there are sockets designed for surface-mount technology (SMT) components, but they are less common than those for through-hole components.
For specific code examples related to sockets commonly connected to an Arduino UNO, please refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or contact technical support for guidance, as code will vary based on the component being used with the socket.