
How to Use RTC DS1302: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with RTC DS1302 in Cirkit Designer
Design with RTC DS1302 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The DS1302 is a real-time clock (RTC) chip designed to keep track of the current time and date, including seconds, minutes, hours, day, date, month, and year. It features a serial interface for communication with microcontrollers and includes a battery backup, allowing it to maintain accurate timekeeping even during power outages. The DS1302 is widely used in applications requiring precise timekeeping, such as data loggers, clocks, alarms, and embedded systems.
Explore Projects Built with RTC DS1302
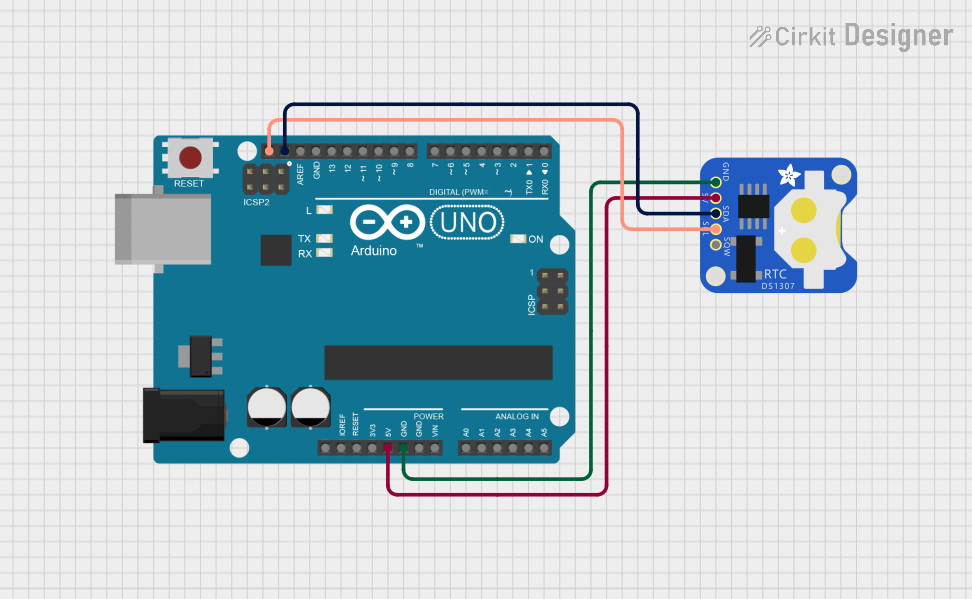
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer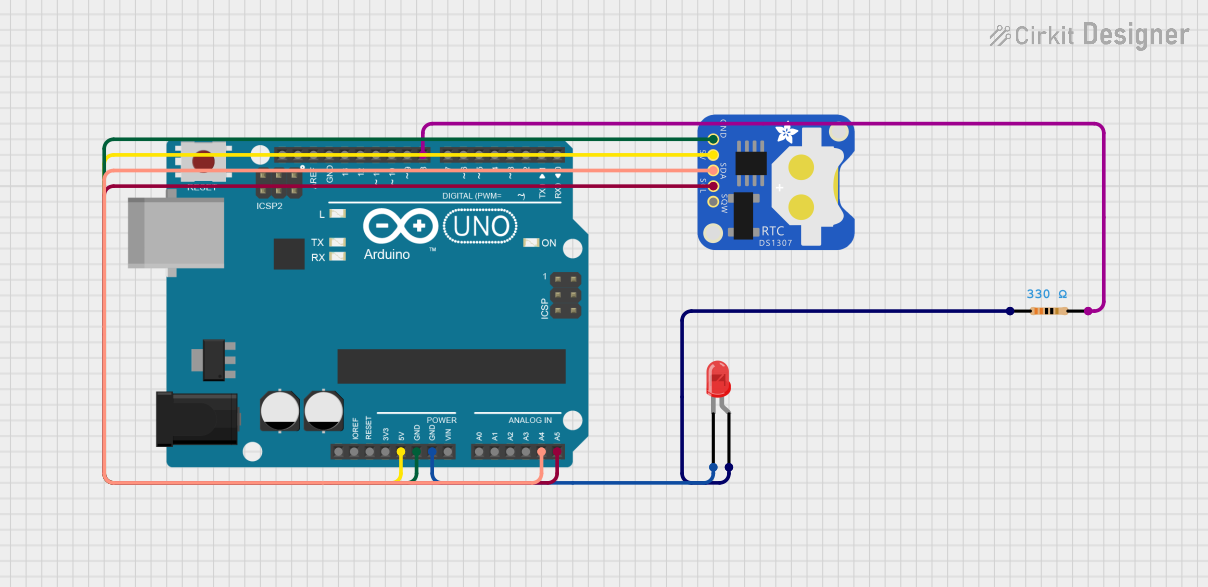
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer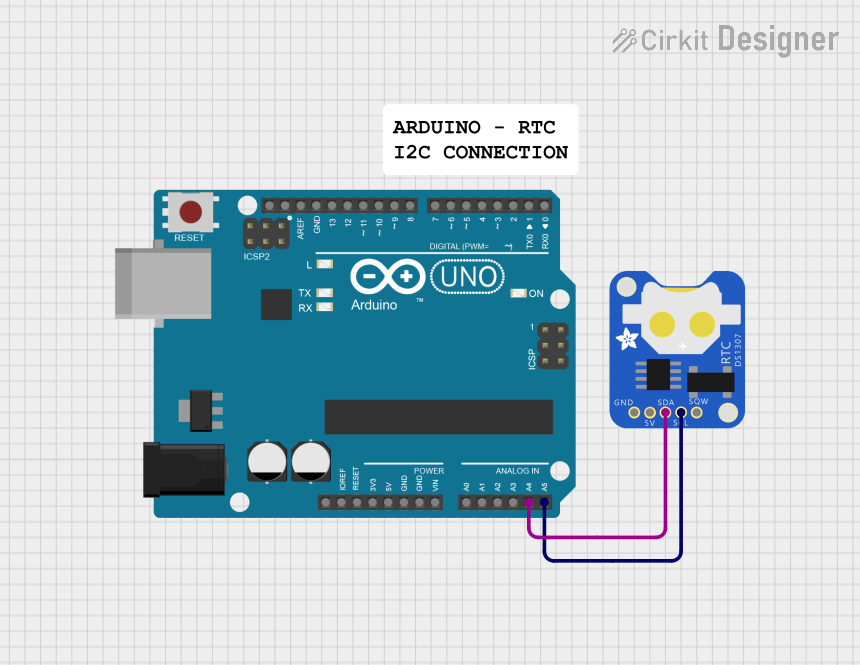
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer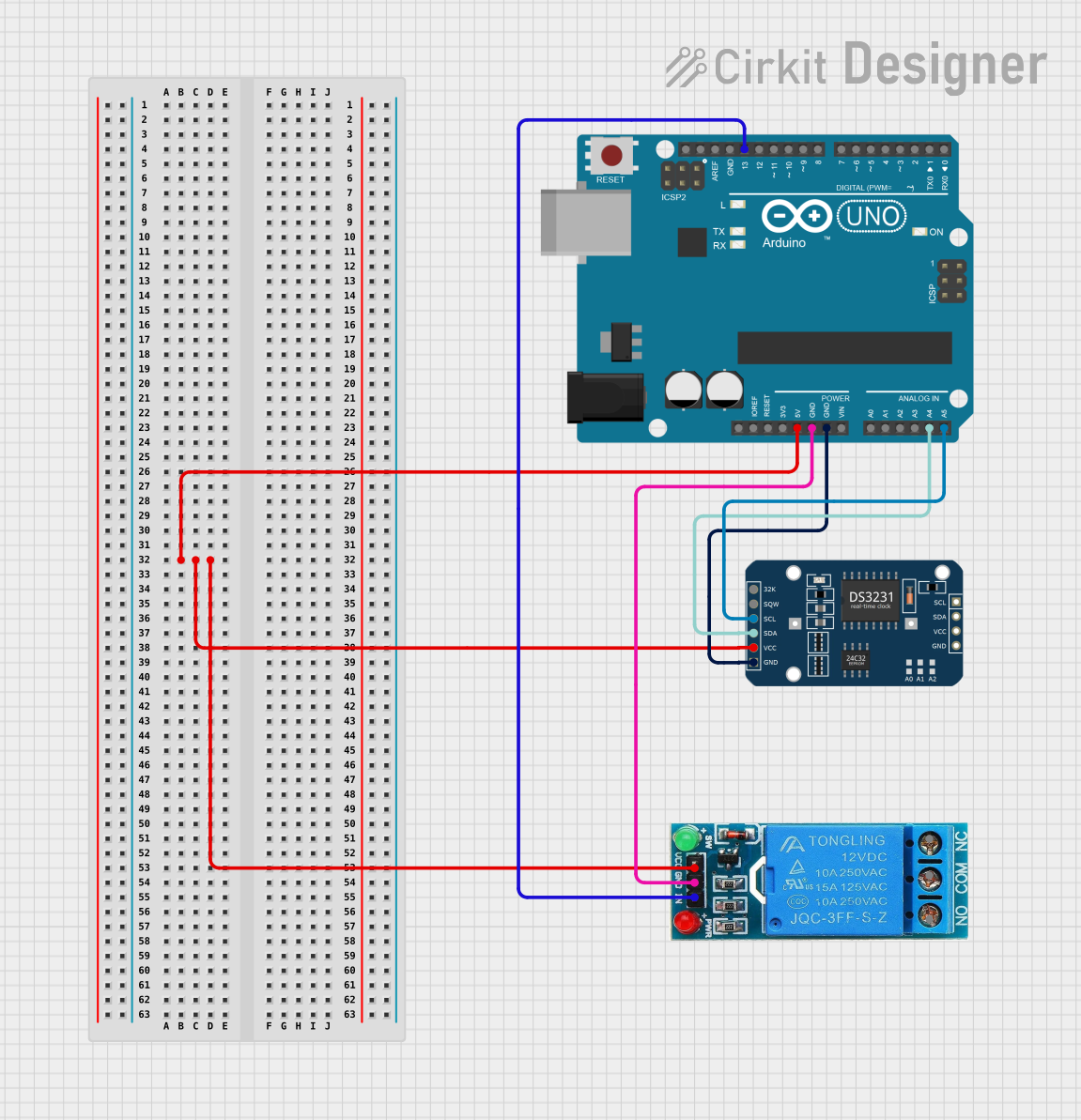
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with RTC DS1302

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Digital clocks and alarms
- Data logging systems
- Home automation
- Time-stamping in embedded systems
- Industrial control systems
Technical Specifications
The DS1302 is a low-power RTC chip with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 2.0V to 5.5V |
| Backup Battery Voltage | 2.0V to 3.5V |
| Operating Current | 300 µA (typical at 5V) |
| Timekeeping Current | 1 µA (typical at 2.0V) |
| Communication Interface | Serial (3-wire) |
| Clock Accuracy | ±2 minutes per month (at 25°C) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Maximum Clock Frequency | 2 MHz |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DS1302 has an 8-pin DIP/SOIC package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC1 | Primary power supply (2.0V to 5.5V). |
| 2 | X1 | Oscillator input. Connect to a 32.768 kHz crystal. |
| 3 | X2 | Oscillator output. Connect to a 32.768 kHz crystal. |
| 4 | GND | Ground. |
| 5 | RST | Reset pin. Used to enable communication with the chip. Active high. |
| 6 | I/O | Serial data input/output. |
| 7 | SCLK | Serial clock input. |
| 8 | VCC2 | Backup battery input (2.0V to 3.5V). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the DS1302 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the primary power supply to the VCC1 pin and the ground to the GND pin. For backup power, connect a 3V coin cell battery to the VCC2 pin.
- Crystal Oscillator: Attach a 32.768 kHz crystal between the X1 and X2 pins. No external capacitors are required.
- Microcontroller Interface: Connect the RST, I/O, and SCLK pins to the corresponding GPIO pins of your microcontroller.
- Pull-Up Resistor: Use a pull-up resistor (typically 10kΩ) on the I/O line to ensure proper communication.
Important Considerations
- Ensure the backup battery is connected to VCC2 to maintain timekeeping during power loss.
- Avoid using long wires for the crystal oscillator to prevent signal degradation.
- The DS1302 operates in 24-hour or 12-hour mode. Configure the mode as needed in your code.
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF) near the VCC1 pin to reduce noise.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the DS1302 with an Arduino UNO to read and set the time:
#include <DS1302.h> // Include the DS1302 library
// Define the DS1302 pins connected to the Arduino
#define RST_PIN 7 // Reset pin connected to Arduino pin 7
#define IO_PIN 6 // I/O pin connected to Arduino pin 6
#define SCLK_PIN 5 // Serial clock pin connected to Arduino pin 5
// Create an instance of the DS1302 class
DS1302 rtc(RST_PIN, IO_PIN, SCLK_PIN);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
rtc.halt(false); // Start the RTC
rtc.writeProtect(false); // Disable write protection
// Set the date and time (Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second)
rtc.setDateTime(2023, 10, 15, 14, 30, 0); // Example: 15th Oct 2023, 14:30:00
}
void loop() {
// Read the current date and time
DS1302::DateTime now = rtc.getDateTime();
// Print the date and time to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Date: ");
Serial.print(now.year); Serial.print("-");
Serial.print(now.month); Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(now.day);
Serial.print("Time: ");
Serial.print(now.hour); Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(now.minute); Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(now.second);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before updating
}
Notes:
- Install the
DS1302library in the Arduino IDE before uploading the code. - Modify the
rtc.setDateTime()function to set the desired initial time and date.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
RTC Not Keeping Time
- Ensure the backup battery is properly connected to the VCC2 pin.
- Verify that the crystal oscillator is correctly connected to the X1 and X2 pins.
Incorrect Time or Date
- Check the initialization code to ensure the correct time and date are set.
- Verify that the microcontroller is communicating with the DS1302 correctly.
No Communication with Microcontroller
- Ensure the RST, I/O, and SCLK pins are properly connected to the microcontroller.
- Check for loose connections or damaged wires.
- Use a pull-up resistor on the I/O line if communication issues persist.
RTC Stops Working After Power Loss
- Verify that the backup battery voltage is within the specified range (2.0V to 3.5V).
- Replace the backup battery if it is depleted.
FAQs
Q: Can the DS1302 operate without a backup battery?
A: Yes, but it will lose the current time and date when the primary power supply is disconnected.
Q: What type of crystal oscillator should I use?
A: Use a 32.768 kHz crystal oscillator with a load capacitance of 6pF to 12.5pF.
Q: How accurate is the DS1302?
A: The DS1302 has an accuracy of ±2 minutes per month at 25°C. For higher accuracy, consider temperature-compensated RTCs.
Q: Can I use the DS1302 with 3.3V microcontrollers?
A: Yes, the DS1302 operates within a voltage range of 2.0V to 5.5V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the DS1302 RTC into your projects for reliable timekeeping.