
How to Use 433 MHz RF Receiver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 433 MHz RF Receiver in Cirkit Designer
Design with 433 MHz RF Receiver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 433 MHz RF Receiver is a wireless communication module designed to receive radio frequency signals at 433 MHz. It is widely used in applications requiring low-power, short-range communication. This component is commonly paired with a 433 MHz RF Transmitter to create a complete wireless communication system.
Explore Projects Built with 433 MHz RF Receiver
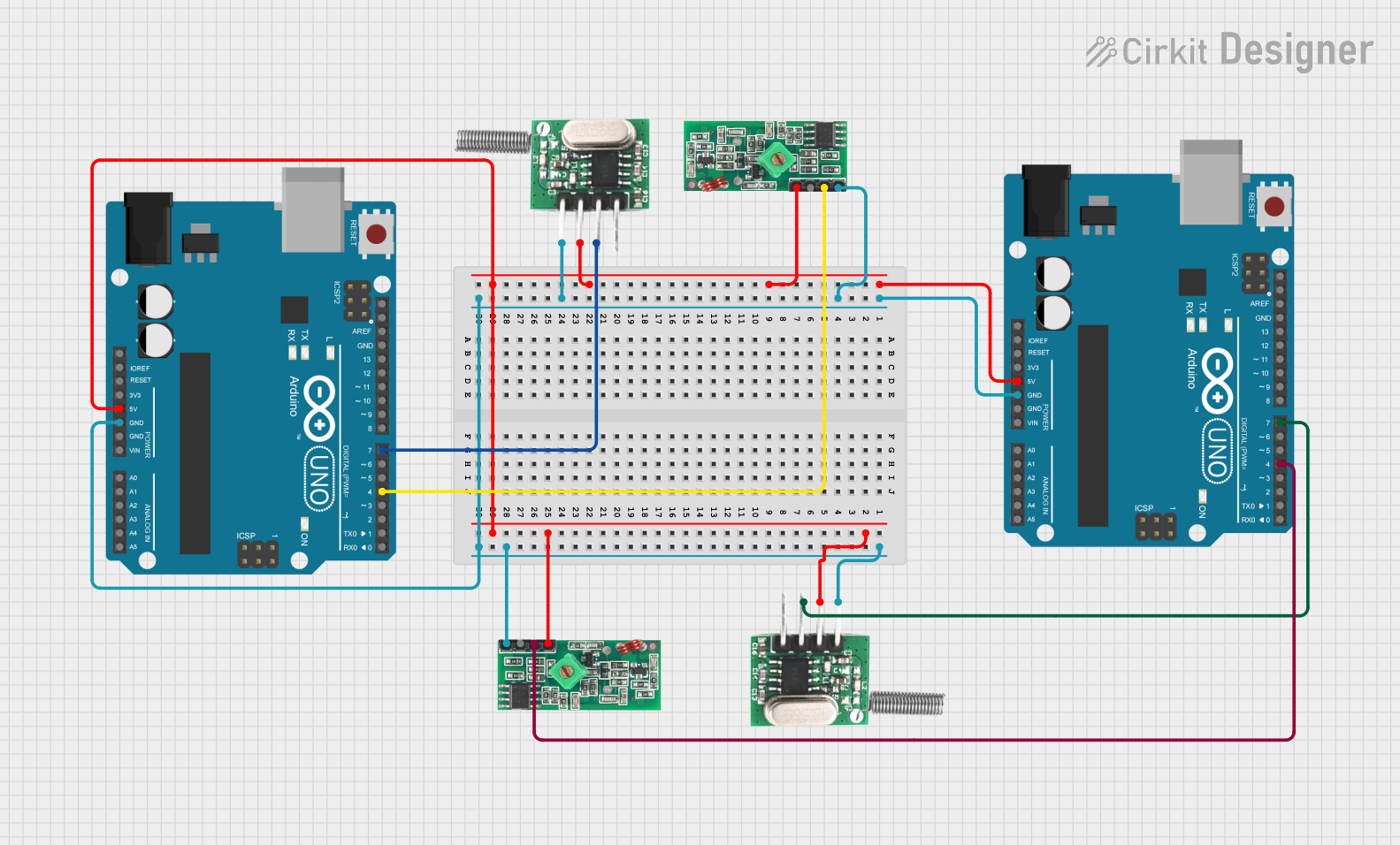
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer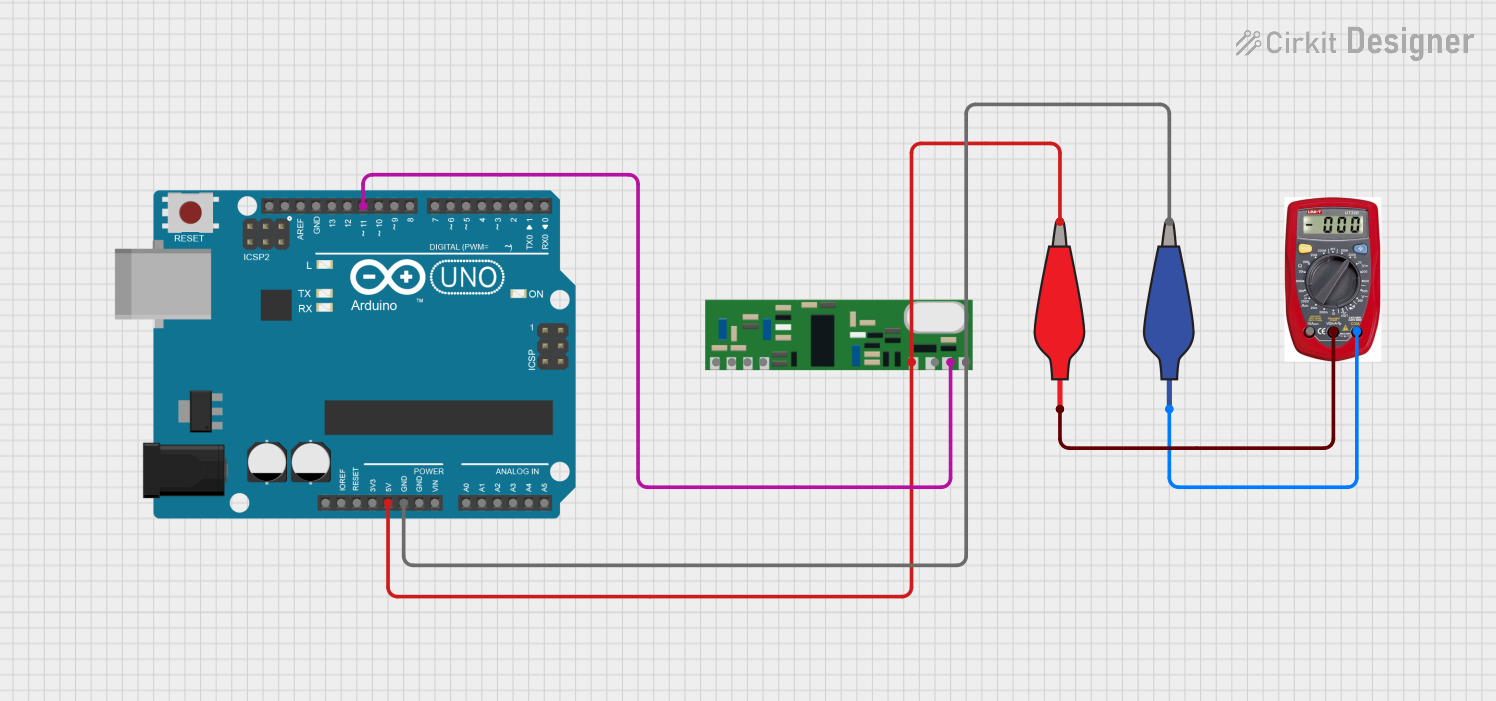
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer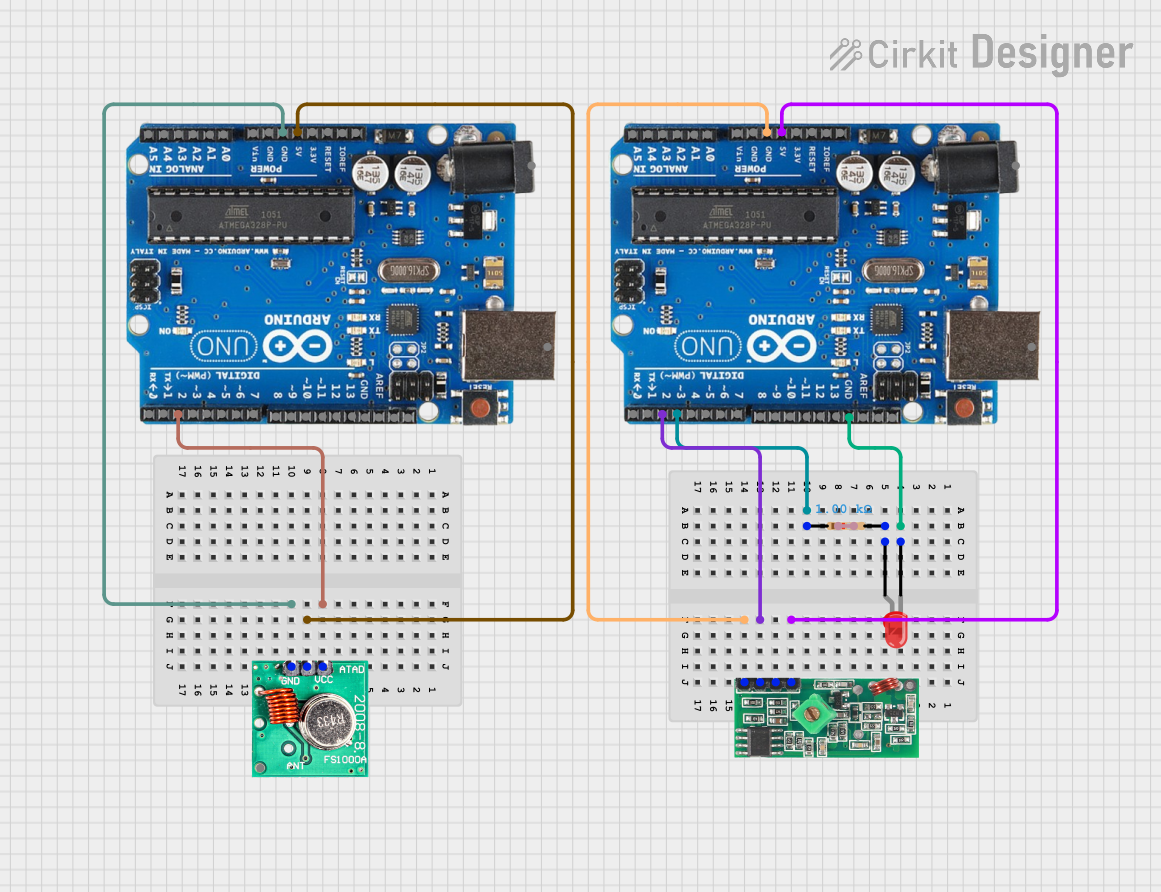
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 433 MHz RF Receiver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Remote controls for home automation systems
- Wireless alarm and security systems
- Sensor networks for IoT (Internet of Things) devices
- Data transmission in hobbyist projects, such as Arduino-based systems
- Wireless weather stations
Technical Specifications
The 433 MHz RF Receiver is a compact and efficient module with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Frequency | 433 MHz |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Operating Current | 4 mA to 5.5 mA |
| Sensitivity | -105 dBm (typical) |
| Data Rate | Up to 10 kbps |
| Communication Range | Up to 50-100 meters (line of sight) |
| Modulation Type | Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 433 MHz RF Receiver typically has 4 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply pin. Connect to 3.3V or 5V depending on your system requirements. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of your circuit. |
| 3 | DATA | Data output pin. Outputs the received signal for further processing. |
| 4 | ANT | Antenna pin. Connect to an external antenna for better signal reception. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 433 MHz RF Receiver in a Circuit
- Power the Module: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Connect the Data Pin: Attach the DATA pin to the input pin of a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) or a decoder IC for signal processing.
- Attach an Antenna: For optimal performance, connect a 17 cm wire to the ANT pin to act as an antenna.
- Pair with a Transmitter: Ensure the 433 MHz RF Transmitter is configured to send data to the receiver.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Antenna Placement: Use a straight wire of approximately 17 cm as an antenna for maximum range and signal quality.
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable power supply to avoid noise and interference in the received signal.
- Interference: Avoid placing the module near high-frequency devices or metal objects that may cause interference.
- Data Decoding: Use a microcontroller or decoder IC to process the received data. Libraries like
VirtualWireorRadioHeadcan simplify this process when using an Arduino.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the 433 MHz RF Receiver with an Arduino UNO to receive data:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the VCC pin of the receiver to the 5V pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin of the receiver to the GND pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the DATA pin of the receiver to digital pin 11 on the Arduino.
- Attach a 17 cm wire to the ANT pin for the antenna.
Arduino Code Example
#include <VirtualWire.h> // Include the VirtualWire library
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
vw_setup(2000); // Set the data rate to 2000 bits per second
vw_set_rx_pin(11); // Set the receiver data pin to digital pin 11
vw_rx_start(); // Start the receiver
}
void loop() {
uint8_t buffer[VW_MAX_MESSAGE_LEN]; // Buffer to store received messages
uint8_t bufferLength = VW_MAX_MESSAGE_LEN; // Length of the buffer
if (vw_get_message(buffer, &bufferLength)) { // Check if a message is received
Serial.print("Received: ");
for (int i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
Serial.print((char)buffer[i]); // Print each character of the message
}
Serial.println(); // Print a new line after the message
}
}
Notes on the Code
- The
VirtualWirelibrary is used to simplify communication with the RF module. - Ensure the transmitter is configured to send data at the same data rate (2000 bps in this example).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Signal Received
- Ensure the transmitter and receiver are operating at the same frequency (433 MHz).
- Check the antenna connection and placement for both modules.
- Verify that the power supply is stable and within the specified range.
Interference or Noise in the Signal
- Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) across the power supply pins to reduce noise.
- Avoid placing the module near other RF devices or metal objects.
Short Communication Range
- Ensure the antenna is the correct length (17 cm for 433 MHz).
- Check for obstacles or interference in the line of sight.
Data Not Decoded Properly
- Verify that the data rate and protocol match between the transmitter and receiver.
- Use a library like
VirtualWireorRadioHeadto simplify data decoding.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the 433 MHz RF Receiver with a 3.3V system?
A: Yes, the module supports an operating voltage range of 3.3V to 5V. Ensure the transmitter is also compatible with the same voltage.
Q: What is the maximum range of the 433 MHz RF Receiver?
A: The range is typically 50-100 meters in an open, line-of-sight environment. Obstacles and interference may reduce the range.
Q: Do I need an external antenna?
A: Yes, connecting a 17 cm wire to the ANT pin significantly improves signal reception and range.
Q: Can I use multiple receivers with one transmitter?
A: Yes, a single transmitter can send data to multiple receivers as long as they are within range and configured to the same frequency and data rate.