
How to Use SparkFun Electret Microphone Breakout: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with SparkFun Electret Microphone Breakout in Cirkit Designer
Design with SparkFun Electret Microphone Breakout in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SparkFun Electret Microphone Breakout is a compact and versatile module designed to capture audio signals through its onboard electret microphone. This breakout board amplifies the weak electrical signals from the microphone, providing a usable analog output that can be easily interfaced with a variety of microcontrollers, such as the Arduino UNO, for audio detection and recording applications. Common use cases include sound level meters, audio recording, voice recognition, and simple audio-triggered systems.
Explore Projects Built with SparkFun Electret Microphone Breakout
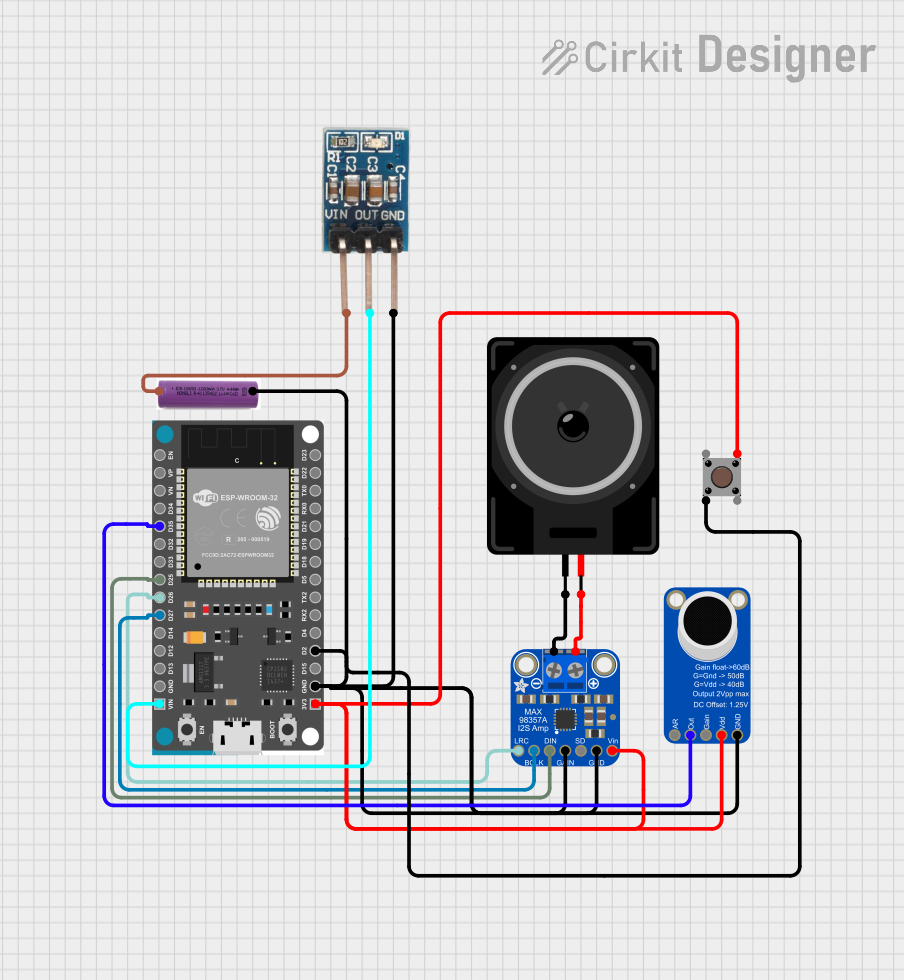
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer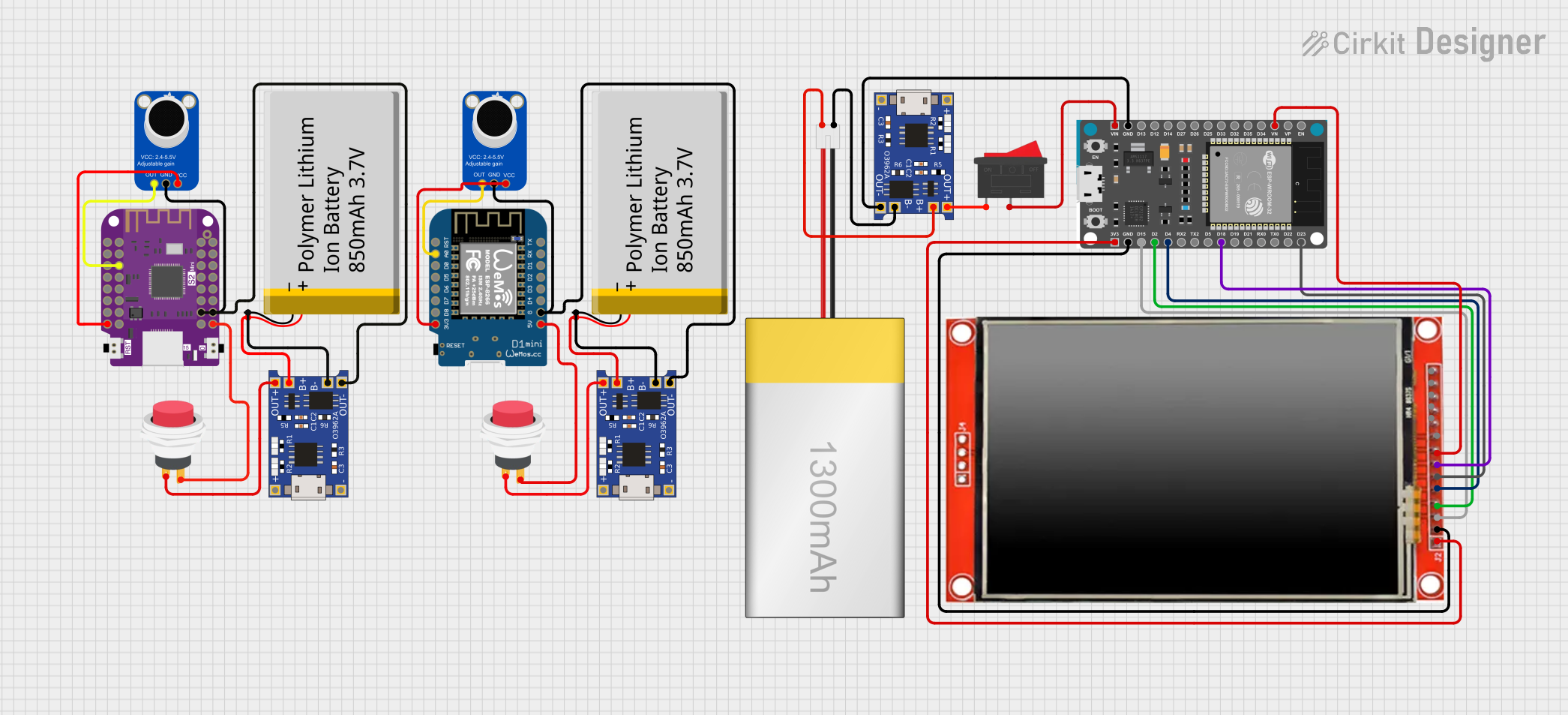
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer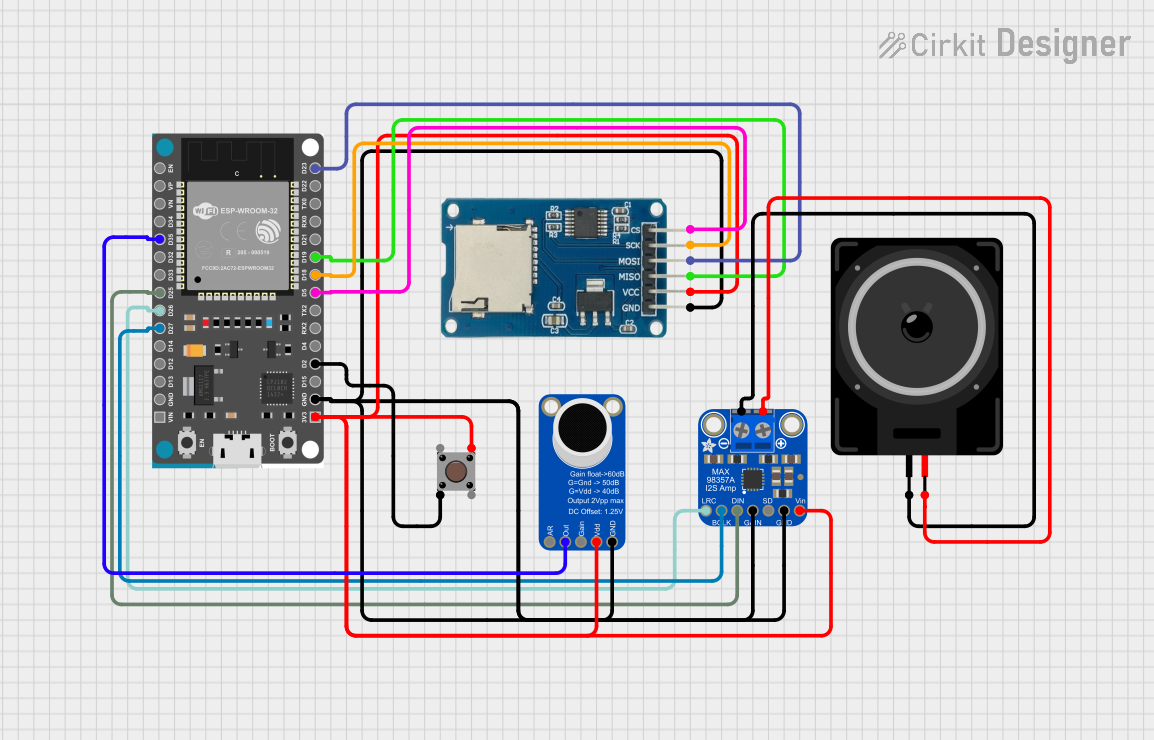
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer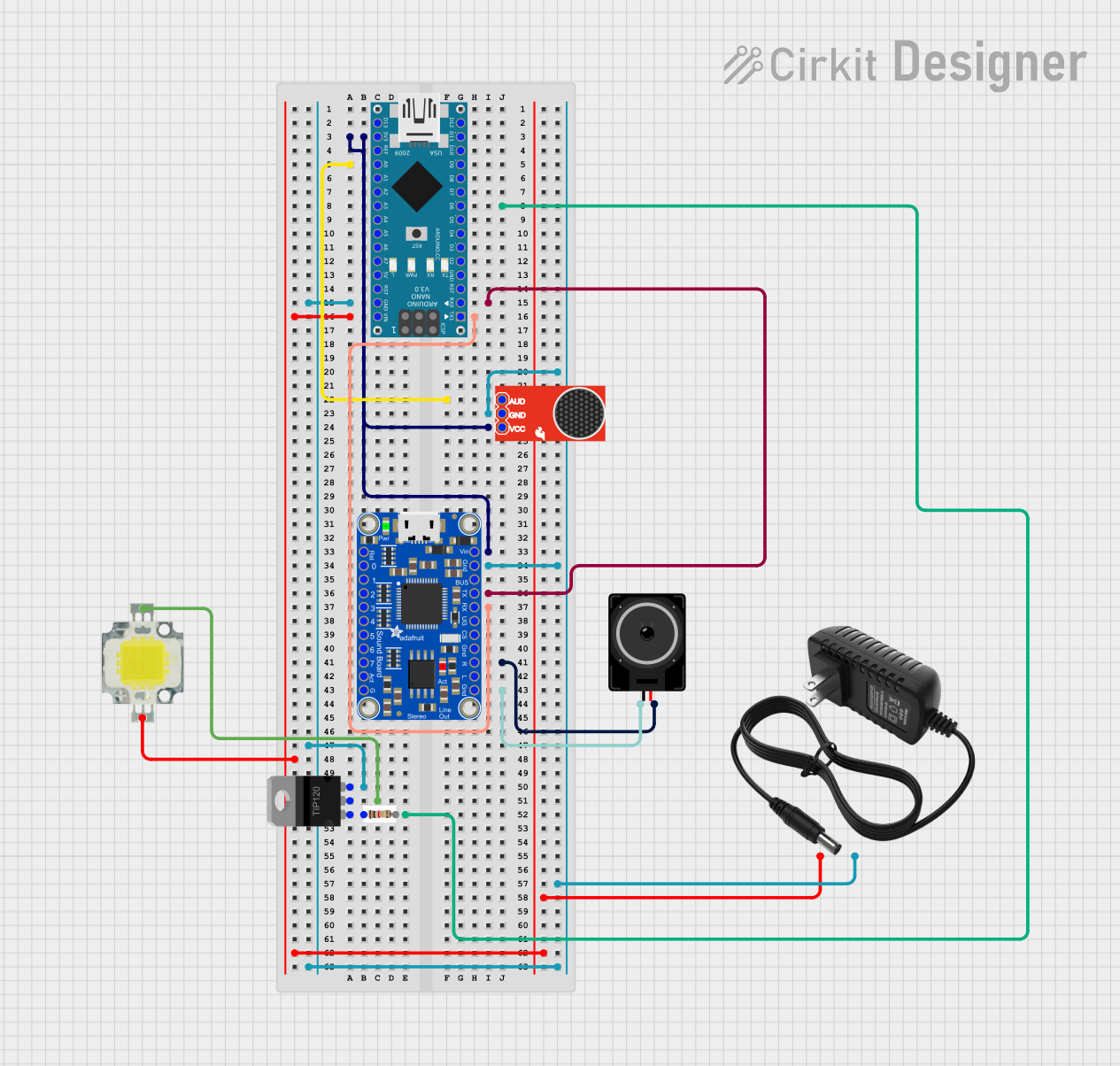
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SparkFun Electret Microphone Breakout

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage (Vcc): 2.7V to 5.5V
- Output Voltage (Vout): 1.25V (typical at Vcc = 3.3V)
- Frequency Response: 20Hz to 20kHz
- Gain: Adjustable with onboard potentiometer
- Current Consumption: 2mA (typical)
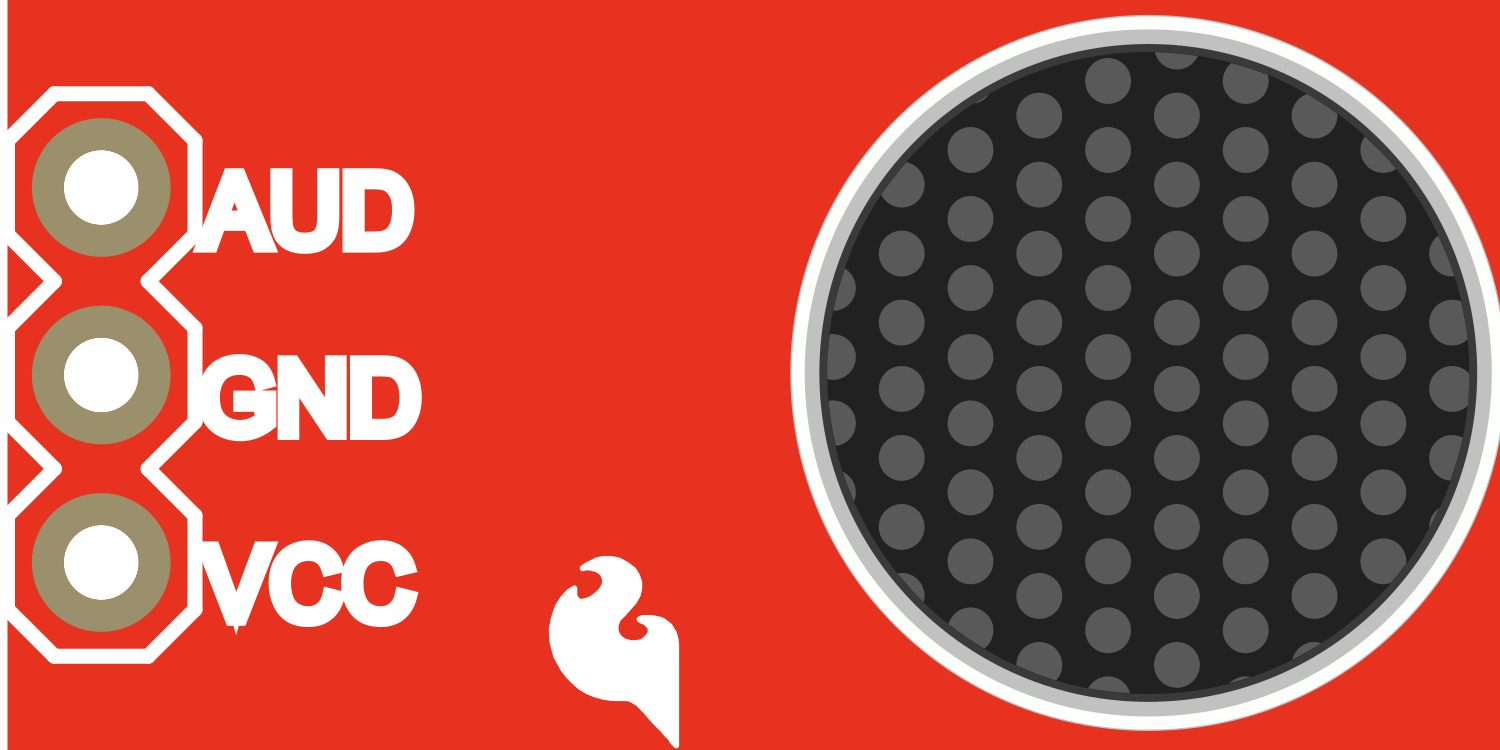
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| AUD | Audio output signal |
| GND | Ground |
| VCC | Power supply (2.7V to 5.5V) |
| Gain | Gain adjustment (potentiometer onboard) |
Usage Instructions
Interfacing with a Circuit
Powering the Module:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 2.7V to 5.5V power supply.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your power supply.
Adjusting Gain:
- Use the onboard potentiometer to adjust the gain as needed for your application.
Reading Audio Signal:
- Connect the AUD pin to an analog input pin on your microcontroller to read the audio signal.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply is within the specified range to avoid damaging the module.
- Signal Clipping: Adjust the gain to prevent the output signal from clipping at the peaks of the audio waveform.
- Noise Reduction: Keep the breakout board away from high-frequency switching devices to minimize noise.
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion: When using with a microcontroller, ensure that the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) resolution is sufficient for your application.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the pin connected to the audio output
const int microphonePin = A0;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud rate
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the microphone
int audioLevel = analogRead(microphonePin);
// Print the audio level to the Serial Monitor
Serial.println(audioLevel);
// Delay for a short period to avoid flooding the serial output
delay(10);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Low Audio Output: If the audio output is too low, adjust the onboard potentiometer to increase the gain.
- No Audio Output: Ensure that the module is correctly powered and that the AUD pin is connected to the correct analog input on your microcontroller.
- Distorted Audio: If the audio signal is distorted, the gain may be set too high, causing clipping. Adjust the potentiometer to lower the gain.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Verify that all connections are secure and correct.
- Power Supply: Confirm that the power supply voltage is within the specified range.
- Gain Adjustment: Use a screwdriver to carefully adjust the onboard potentiometer.
- Isolate Noise: Keep the microphone breakout away from noise sources such as motors or high-frequency electronics.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this module with a 5V Arduino? A: Yes, the module can be powered with a 5V supply, making it compatible with 5V Arduinos.
Q: How do I adjust the gain on the module? A: Use a small screwdriver to turn the onboard potentiometer. Clockwise increases the gain, while counterclockwise decreases it.
Q: What is the purpose of the AUD pin? A: The AUD pin outputs the amplified audio signal from the microphone, which can be read by an analog input on a microcontroller.
Q: Can I connect this module directly to a speaker? A: No, the output is an analog signal meant for microcontroller ADCs. To drive a speaker, additional amplification is needed.
For further assistance, please refer to the SparkFun Electret Microphone Breakout product page and forums for community support and resources.