
How to Use DRV8825 : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with DRV8825 in Cirkit Designer
Design with DRV8825 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The DRV8825 is a high-performance stepper motor driver designed to control bipolar stepper motors with precision and efficiency. Manufactured by Arduino, this component (Part ID: Stepper motor driver) supports microstepping, allowing for smooth and accurate motor operation. It features adjustable current control, over-temperature protection, and a wide operating voltage range, making it ideal for applications in robotics, 3D printing, CNC machines, and other automation systems.
Explore Projects Built with DRV8825
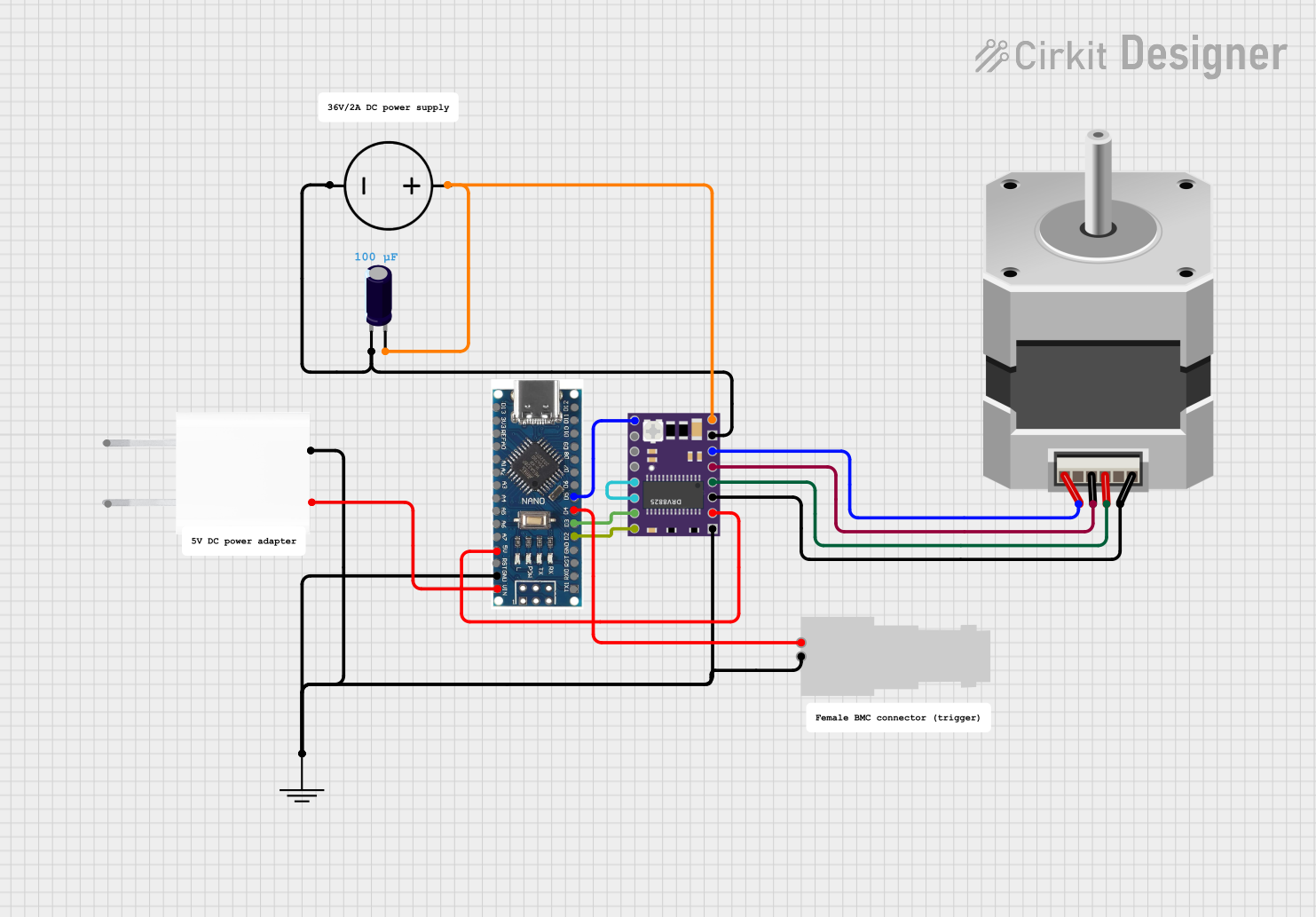
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer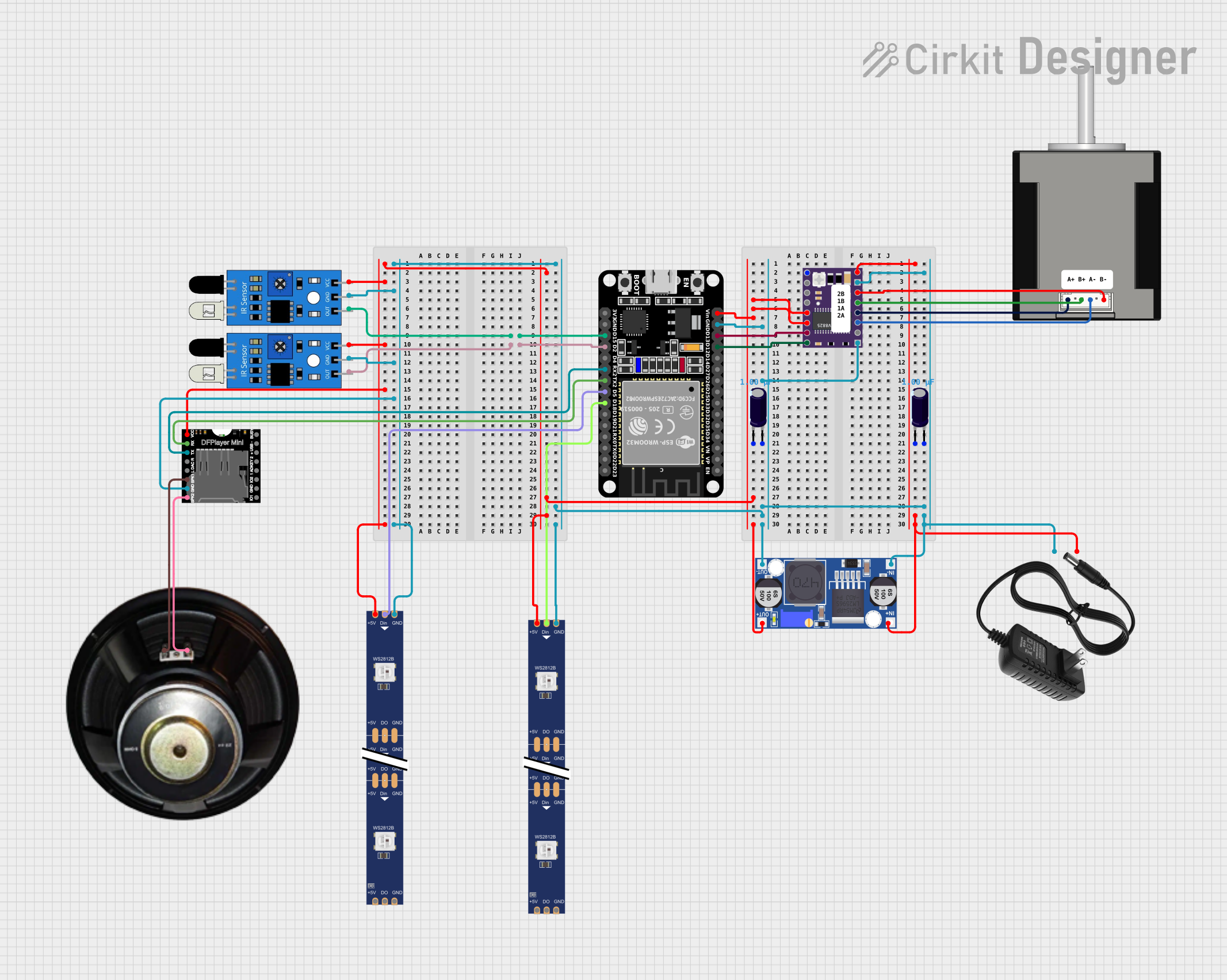
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer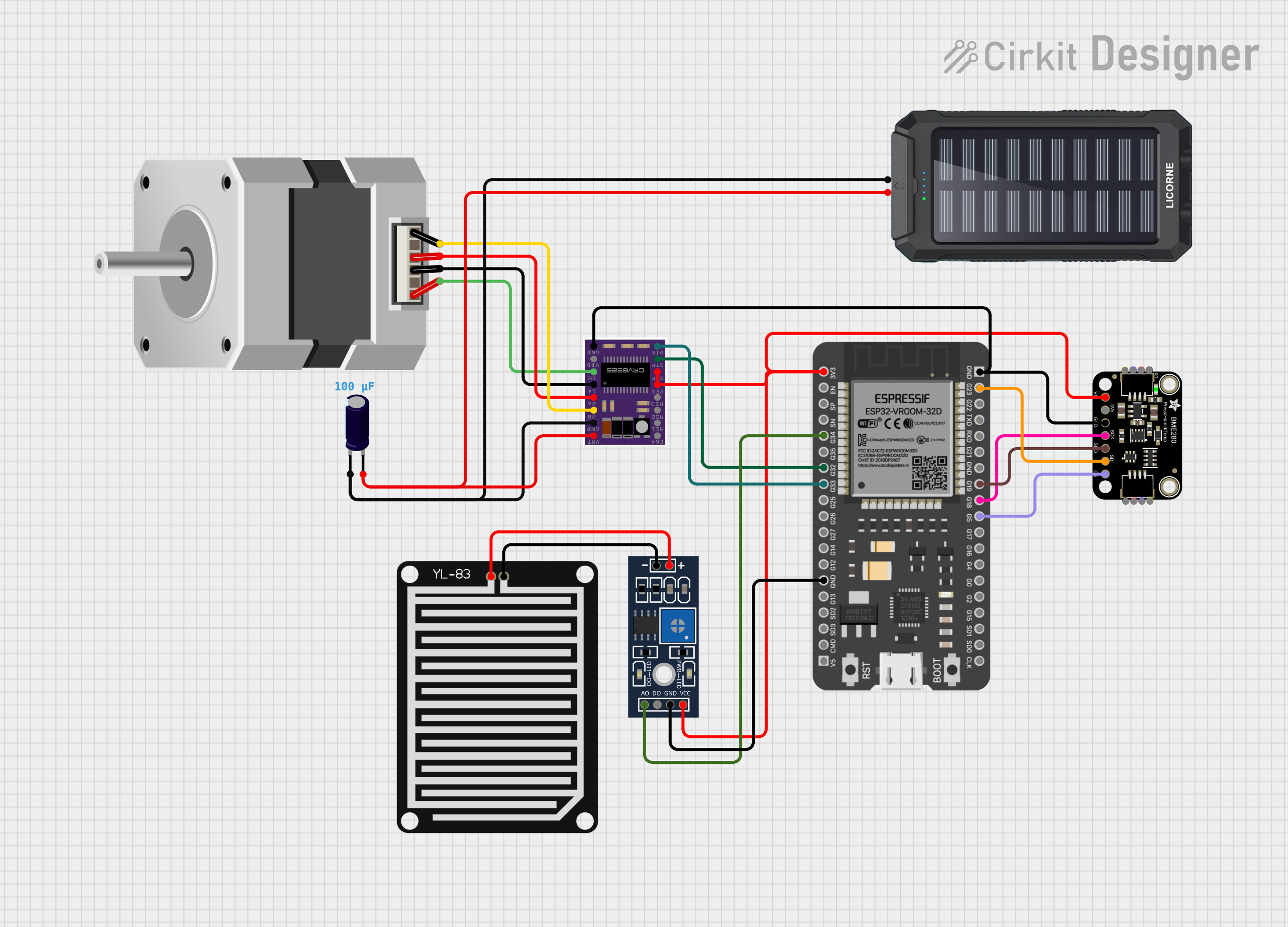
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DRV8825

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Robotics and automation systems
- 3D printers
- CNC machines
- Camera sliders and gimbals
- Precision positioning systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details:
- Operating Voltage Range: 8.2V to 45V
- Maximum Output Current: 2.2A per coil (with sufficient cooling)
- Microstepping Modes: Full-step, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, and 1/32 steps
- Logic Voltage: 3.3V or 5V compatible
- Current Control: Adjustable via potentiometer
- Protection Features: Over-temperature, over-current, and under-voltage lockout
- Dimensions: 15mm x 20mm (approx.)
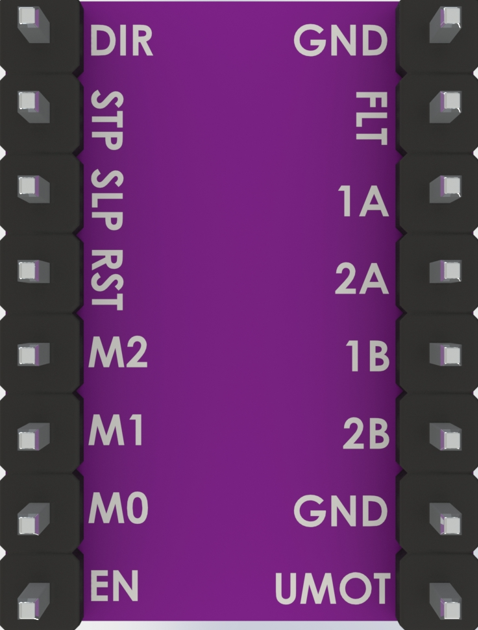
Pin Configuration and Descriptions:
The DRV8825 module has 16 pins. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VMOT | Power Input | Motor power supply (8.2V to 45V). Connect a capacitor (100µF or higher) nearby. |
| GND | Power Ground | Ground connection for motor power supply. |
| 2B, 2A | Motor Output | Connect to one coil of the stepper motor. |
| 1A, 1B | Motor Output | Connect to the other coil of the stepper motor. |
| VDD | Power Input | Logic power supply (3.3V or 5V). |
| GND | Power Ground | Ground connection for logic power supply. |
| STEP | Logic Input | Step signal input. Each pulse moves the motor one step. |
| DIR | Logic Input | Direction control input. |
| ENABLE | Logic Input | Enable/disable the driver (active low). |
| MS1, MS2, MS3 | Logic Input | Microstepping mode selection pins. |
| RESET | Logic Input | Resets the driver (active low). |
| SLEEP | Logic Input | Puts the driver into low-power sleep mode (active low). |
| FAULT | Logic Output | Indicates fault conditions (e.g., over-temperature). |
Microstepping Configuration:
The microstepping mode is configured using the MS1, MS2, and MS3 pins as shown below:
| MS1 | MS2 | MS3 | Microstepping Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Low | Low | Full Step |
| High | Low | Low | 1/2 Step |
| Low | High | Low | 1/4 Step |
| High | High | Low | 1/8 Step |
| Low | Low | High | 1/16 Step |
| High | High | High | 1/32 Step |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the DRV8825 to a Circuit:
Power Supply:
- Connect VMOT and GND to the motor power supply (8.2V to 45V).
- Add a capacitor (100µF or higher) across VMOT and GND to prevent voltage spikes.
- Connect VDD and GND to the logic power supply (3.3V or 5V).
Motor Connections:
- Connect the stepper motor coils to the 1A, 1B, 2A, and 2B pins. Ensure the correct pairing of motor wires.
Control Signals:
- Connect STEP and DIR pins to the microcontroller's digital output pins.
- Use MS1, MS2, and MS3 to set the desired microstepping mode.
- Optionally, connect ENABLE, RESET, and SLEEP pins for additional control.
Adjusting Current Limit:
- Use the onboard potentiometer to set the current limit. This prevents overheating and ensures safe operation.
- Formula for current limit:
Current Limit = VREF × 2
(where VREF is the voltage measured at the potentiometer).
Example Arduino UNO Code:
Below is an example code to control a stepper motor using the DRV8825 and an Arduino UNO:
// Define pin connections
#define STEP_PIN 3 // Connect to STEP pin on DRV8825
#define DIR_PIN 4 // Connect to DIR pin on DRV8825
void setup() {
pinMode(STEP_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set STEP pin as output
pinMode(DIR_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set DIR pin as output
digitalWrite(DIR_PIN, HIGH); // Set initial direction (HIGH or LOW)
}
void loop() {
// Generate step pulses
digitalWrite(STEP_PIN, HIGH); // Step pulse HIGH
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait 500 microseconds
digitalWrite(STEP_PIN, LOW); // Step pulse LOW
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait 500 microseconds
}
Best Practices:
- Always power off the system before connecting or disconnecting the motor.
- Use a heat sink or cooling fan if operating at high currents.
- Avoid exceeding the voltage and current ratings to prevent damage.
- Ensure proper grounding to avoid noise and instability.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions:
Motor Not Moving:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check motor connections and ensure the power supply meets voltage and current requirements.
Overheating Driver:
- Cause: Current limit set too high or inadequate cooling.
- Solution: Adjust the current limit using the potentiometer and add a heat sink or fan.
Erratic Motor Movement:
- Cause: Noise or incorrect microstepping configuration.
- Solution: Use decoupling capacitors and verify MS1, MS2, and MS3 settings.
FAULT Pin Active:
- Cause: Over-temperature or over-current condition.
- Solution: Allow the driver to cool down and reduce the current limit.
Motor Vibrates but Does Not Rotate:
- Cause: Incorrect stepper motor wiring.
- Solution: Verify the correct pairing of motor wires.
FAQs:
Q: Can the DRV8825 drive unipolar stepper motors?
A: No, the DRV8825 is designed for bipolar stepper motors only.Q: What is the maximum microstepping resolution?
A: The DRV8825 supports up to 1/32 microstepping.Q: Can I use the DRV8825 with a 12V power supply?
A: Yes, the DRV8825 operates within a voltage range of 8.2V to 45V.Q: How do I reset the driver?
A: Pull the RESET pin low momentarily to reset the driver.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the DRV8825 into their projects and troubleshoot common issues with ease.