
How to Use HW-958: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
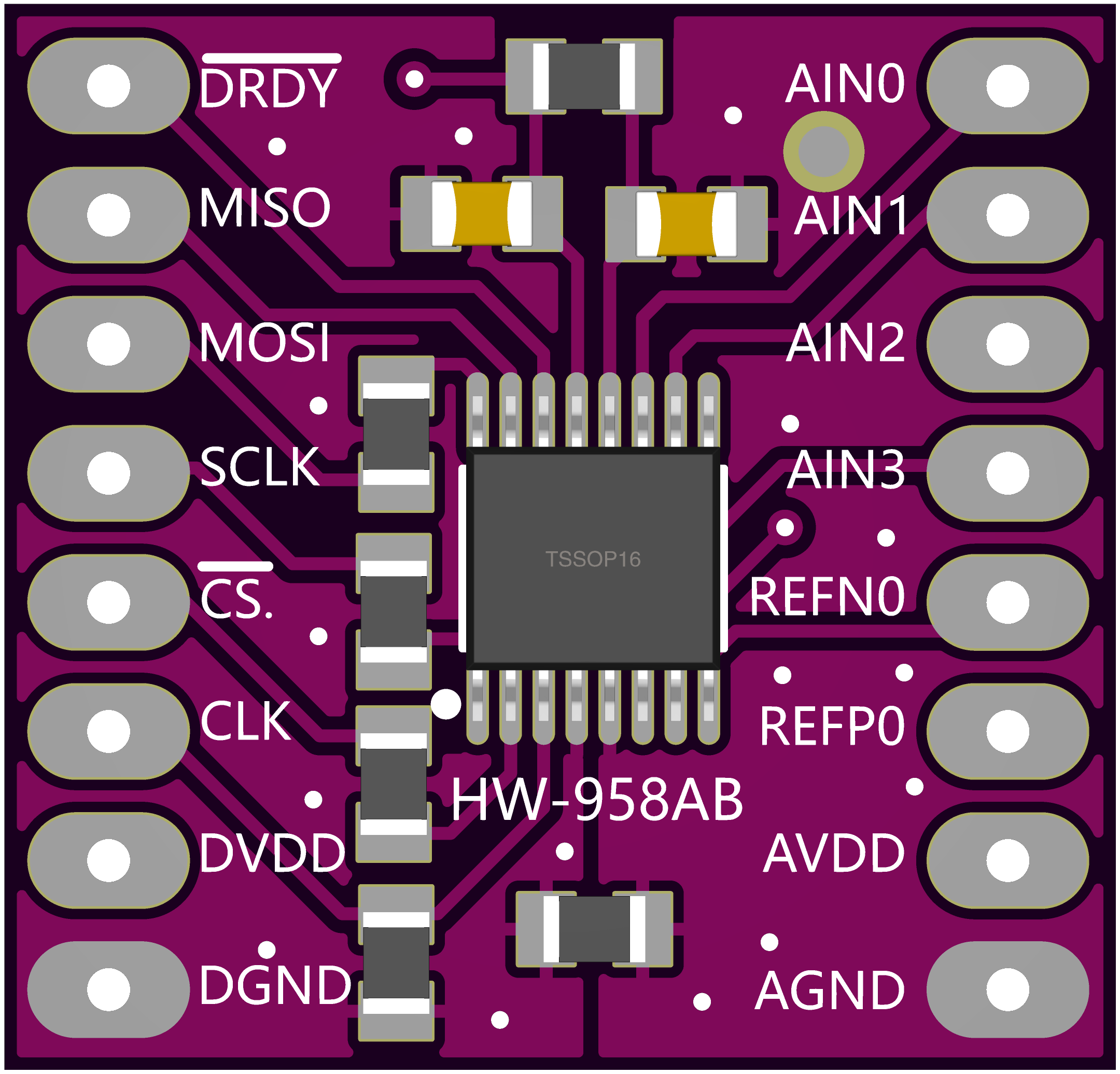
 Design with HW-958 in Cirkit Designer
Design with HW-958 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The HW-958, manufactured by 宏维微 (part ID: ADS1120), is a high-performance electronic component designed for precision signal processing and power management applications. It is widely used in systems requiring accurate analog-to-digital conversion, such as sensor interfacing, industrial automation, and medical devices. Known for its reliability and efficiency, the HW-958 is an essential component in circuits where precise electrical signal handling is critical.
Explore Projects Built with HW-958
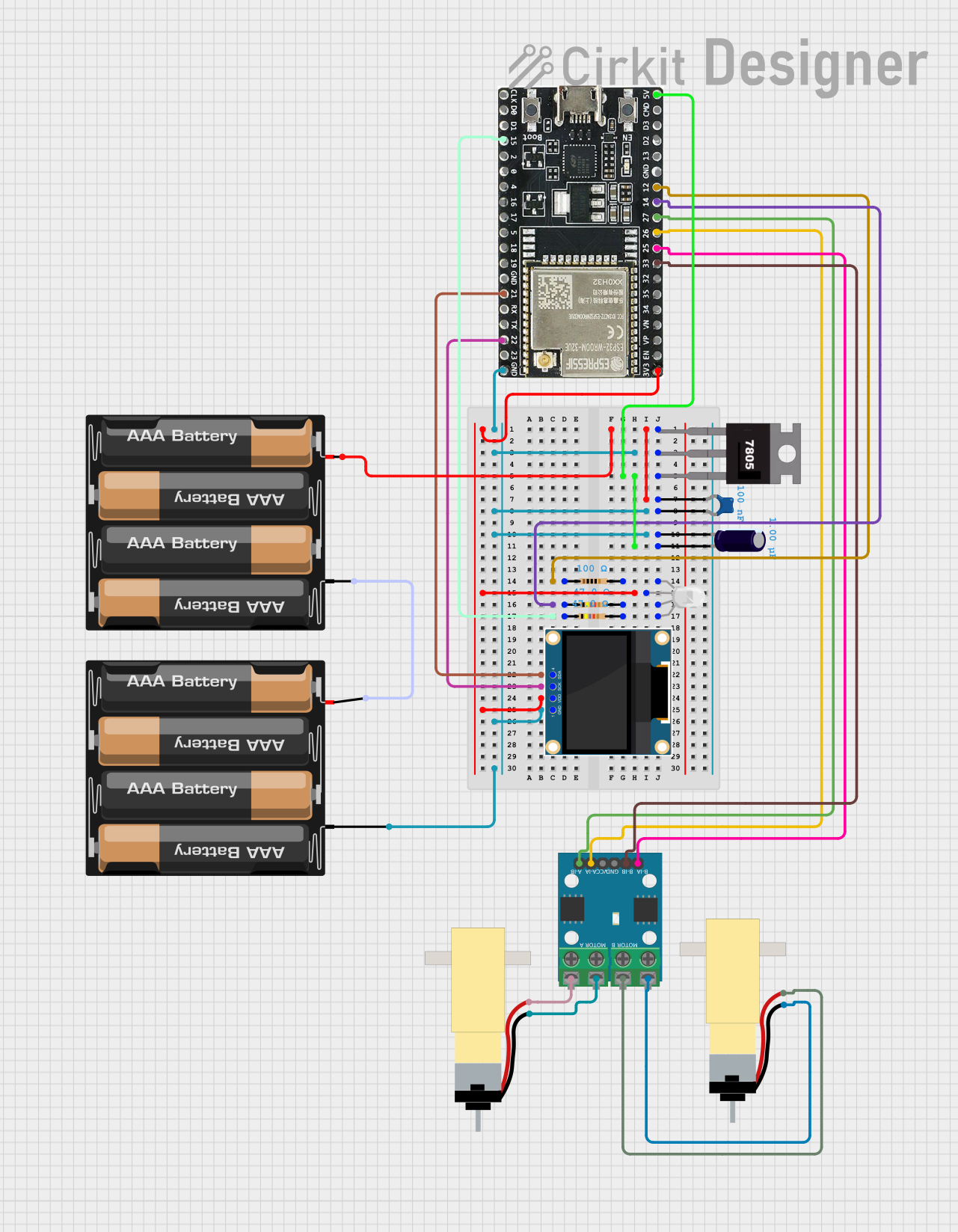
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer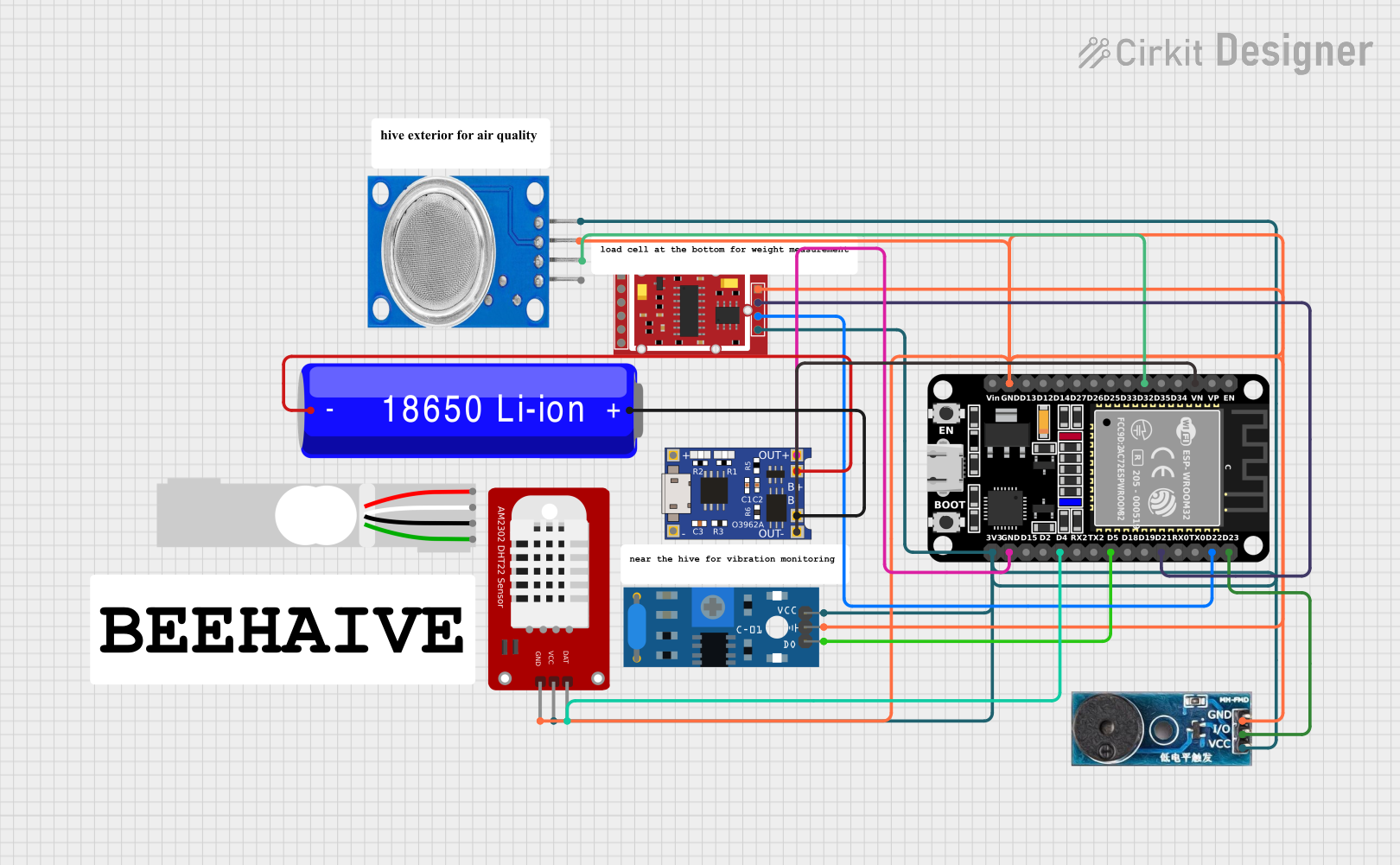
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer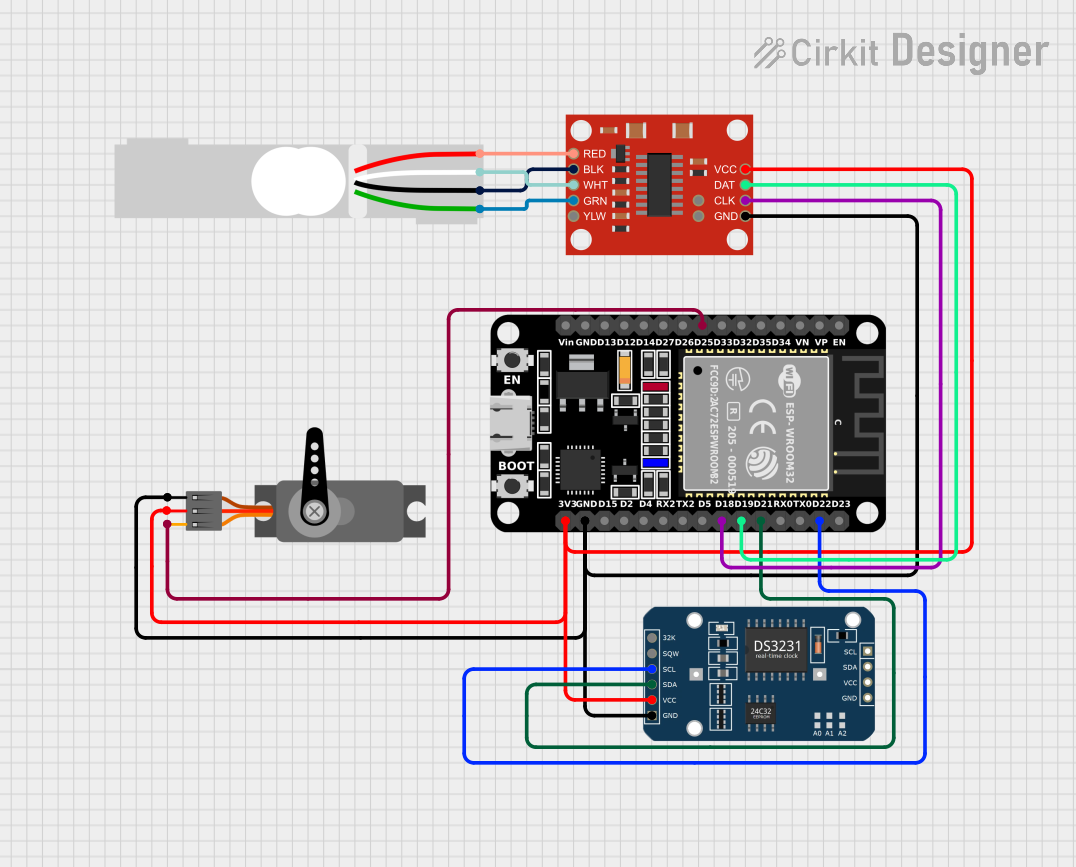
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with HW-958

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Sensor data acquisition (e.g., temperature, pressure, or load sensors)
- Industrial process control systems
- Medical instrumentation
- Battery monitoring and power management
- Embedded systems requiring low-power, high-accuracy ADCs
Technical Specifications
The HW-958 is based on the ADS1120, a 16-bit, low-power, precision analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Below are its key technical details:
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Resolution | 16-bit |
| Input Channels | 4 (multiplexed) |
| Operating Voltage Range | 2.3V to 5.5V |
| Power Consumption | 315 µA (typical) |
| Data Rate | Up to 2 kSPS |
| Input Impedance | >10 GΩ |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Communication Interface | SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The HW-958 module typically features a 10-pin interface. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Power supply input (2.3V to 5.5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | SCLK | SPI clock input |
| 4 | DIN | SPI data input (MOSI) |
| 5 | DOUT/DRDY | SPI data output (MISO) / Data ready signal |
| 6 | CS | Chip select (active low) |
| 7 | AIN0 | Analog input channel 0 |
| 8 | AIN1 | Analog input channel 1 |
| 9 | AIN2 | Analog input channel 2 |
| 10 | AIN3 | Analog input channel 3 |
Usage Instructions
The HW-958 is straightforward to integrate into a circuit, especially for applications requiring analog-to-digital conversion. Below are the steps and best practices for using the component:
How to Use the HW-958 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a stable power source (2.3V to 5.5V) and the GND pin to the ground.
- SPI Communication: Connect the SCLK, DIN, DOUT/DRDY, and CS pins to the corresponding SPI pins of your microcontroller.
- Analog Inputs: Connect the analog signals to be measured to the AIN0–AIN3 pins. Ensure the input voltage levels are within the ADC's input range.
- Configuration: Use SPI commands to configure the ADC settings, such as gain, data rate, and input channel selection.
- Data Acquisition: Read the converted digital data via the SPI interface. Monitor the DOUT/DRDY pin for data readiness.
Important Considerations
- Input Signal Conditioning: Use appropriate filters or amplifiers to condition the input signals before feeding them into the ADC.
- Power Supply Decoupling: Place a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) close to the VDD pin to reduce noise.
- SPI Timing: Ensure the SPI clock frequency and timing meet the ADS1120's requirements.
- Temperature Effects: Operate the HW-958 within its specified temperature range to maintain accuracy.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the HW-958 with an Arduino UNO using SPI:
#include <SPI.h>
// Pin definitions
const int CS_PIN = 10; // Chip select pin for HW-958
void setup() {
// Initialize SPI communication
SPI.begin();
pinMode(CS_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Set CS pin high (inactive)
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
}
void loop() {
// Example: Read data from HW-958
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, LOW); // Select the HW-958
SPI.transfer(0x40); // Send a command (e.g., read register 0x00)
byte data = SPI.transfer(0x00); // Read data from the HW-958
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Deselect the HW-958
Serial.print("Data: ");
Serial.println(data, HEX); // Print the received data in hexadecimal format
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next read
}
Notes on the Code
- Replace
0x40with the appropriate command for your application. - Ensure the SPI clock speed is compatible with the HW-958 (ADS1120).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Data Output
- Cause: Incorrect SPI connections or configuration.
- Solution: Verify the SPI wiring and ensure the SPI settings (clock polarity, phase, and speed) match the HW-958's requirements.
Inaccurate Readings
- Cause: Noisy input signals or improper grounding.
- Solution: Use proper signal conditioning (e.g., filters) and ensure a solid ground connection.
Device Not Responding
- Cause: CS pin not toggled correctly.
- Solution: Ensure the CS pin is pulled low before sending SPI commands and pulled high afterward.
Overheating
- Cause: Exceeding the operating voltage or current limits.
- Solution: Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the specified range (2.3V to 5.5V).
FAQs
Q: Can the HW-958 handle differential inputs?
A: Yes, the HW-958 supports differential input configurations using its multiplexed input channels.
Q: What is the maximum sampling rate of the HW-958?
A: The maximum data rate is 2 kSPS, but lower rates can be configured for higher resolution.
Q: Is the HW-958 compatible with 3.3V systems?
A: Yes, the HW-958 operates within a voltage range of 2.3V to 5.5V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems.
Q: How do I reduce noise in my measurements?
A: Use proper shielding, grounding, and input signal filtering to minimize noise.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and using the HW-958 effectively in your projects.