
How to Use Current Sensor ACS712 : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
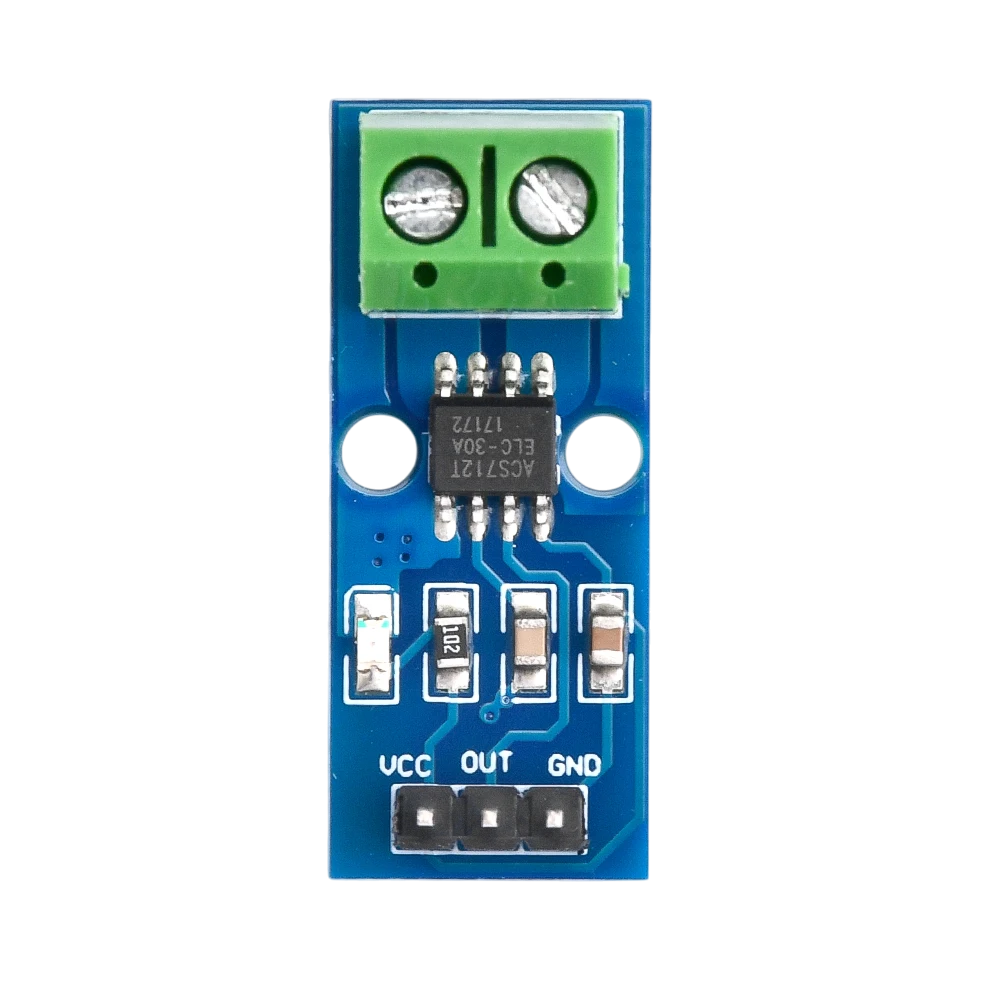
 Design with Current Sensor ACS712 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Current Sensor ACS712 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ACS712 is a Hall effect-based current sensor that provides an analog output proportional to the current flowing through it. It is capable of measuring both AC and DC currents, making it a versatile component for a wide range of applications. The sensor is available in different variants to measure currents up to ±5A, ±20A, or ±30A. Its compact design and ease of use make it a popular choice for current monitoring and control in electrical systems.
Explore Projects Built with Current Sensor ACS712
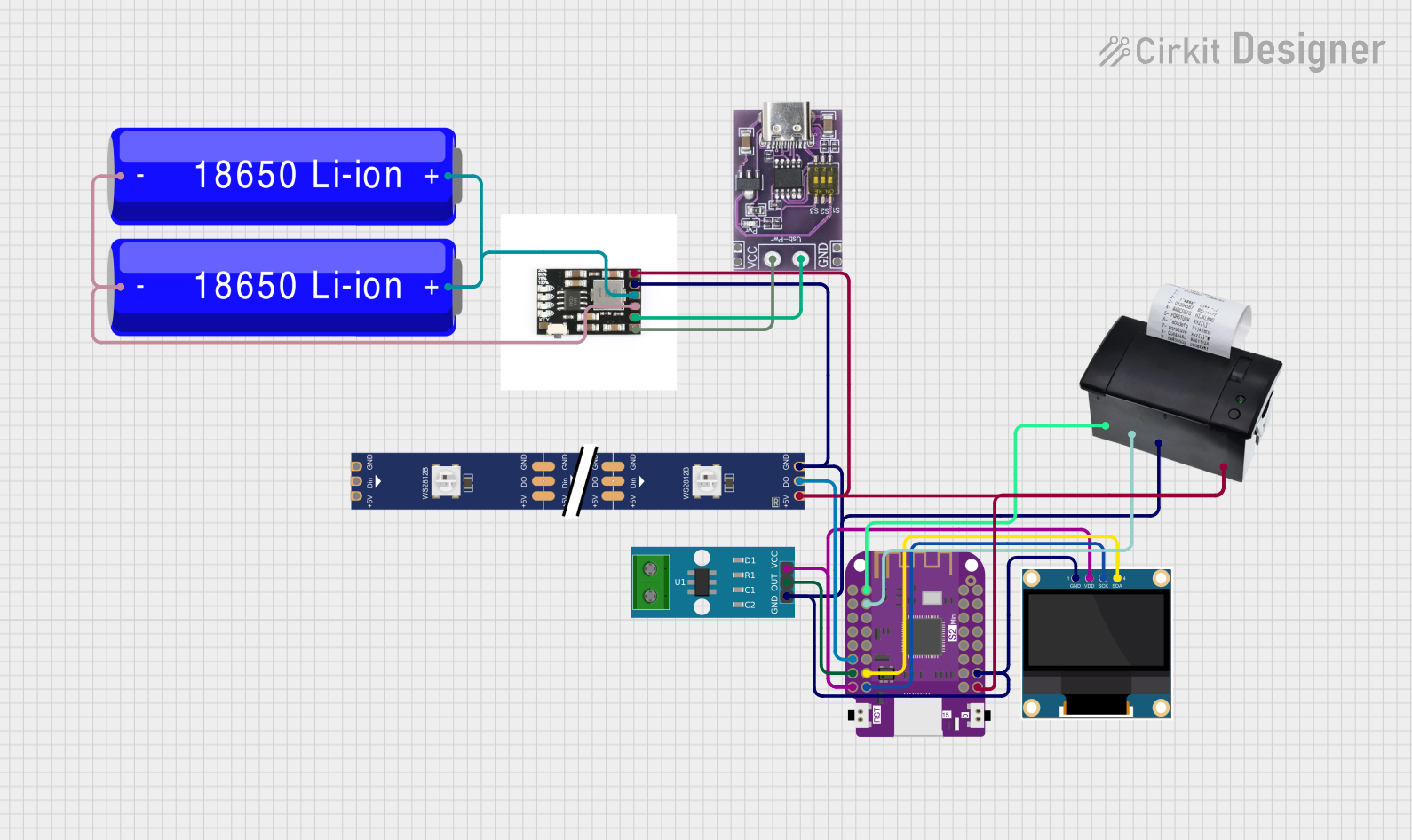
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer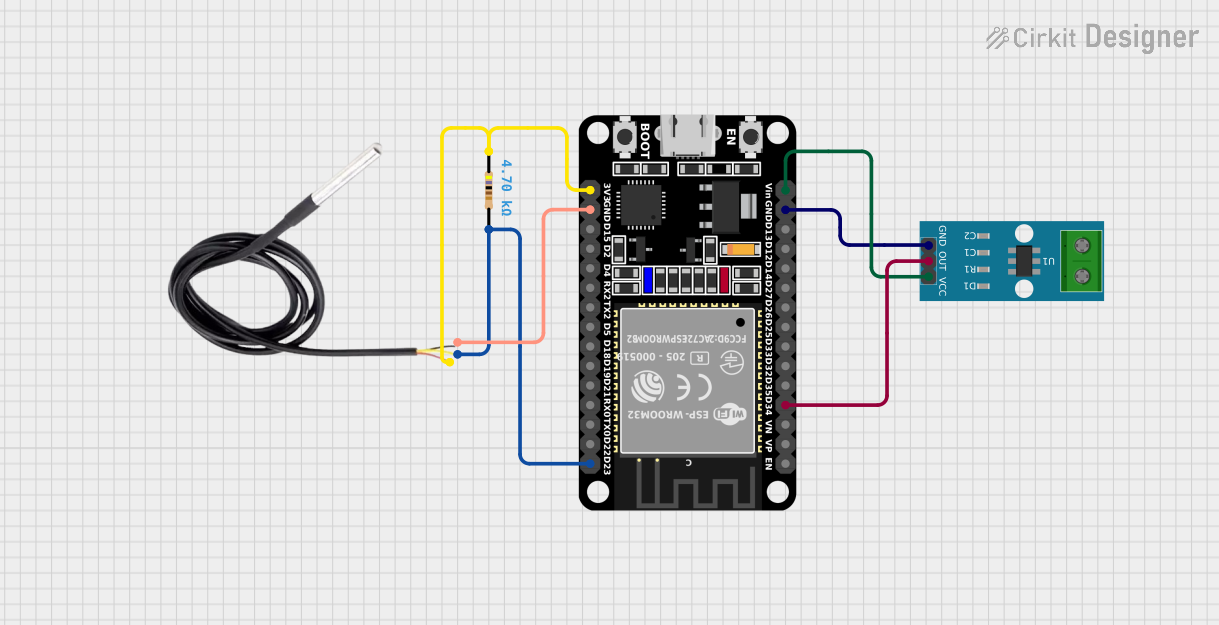
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer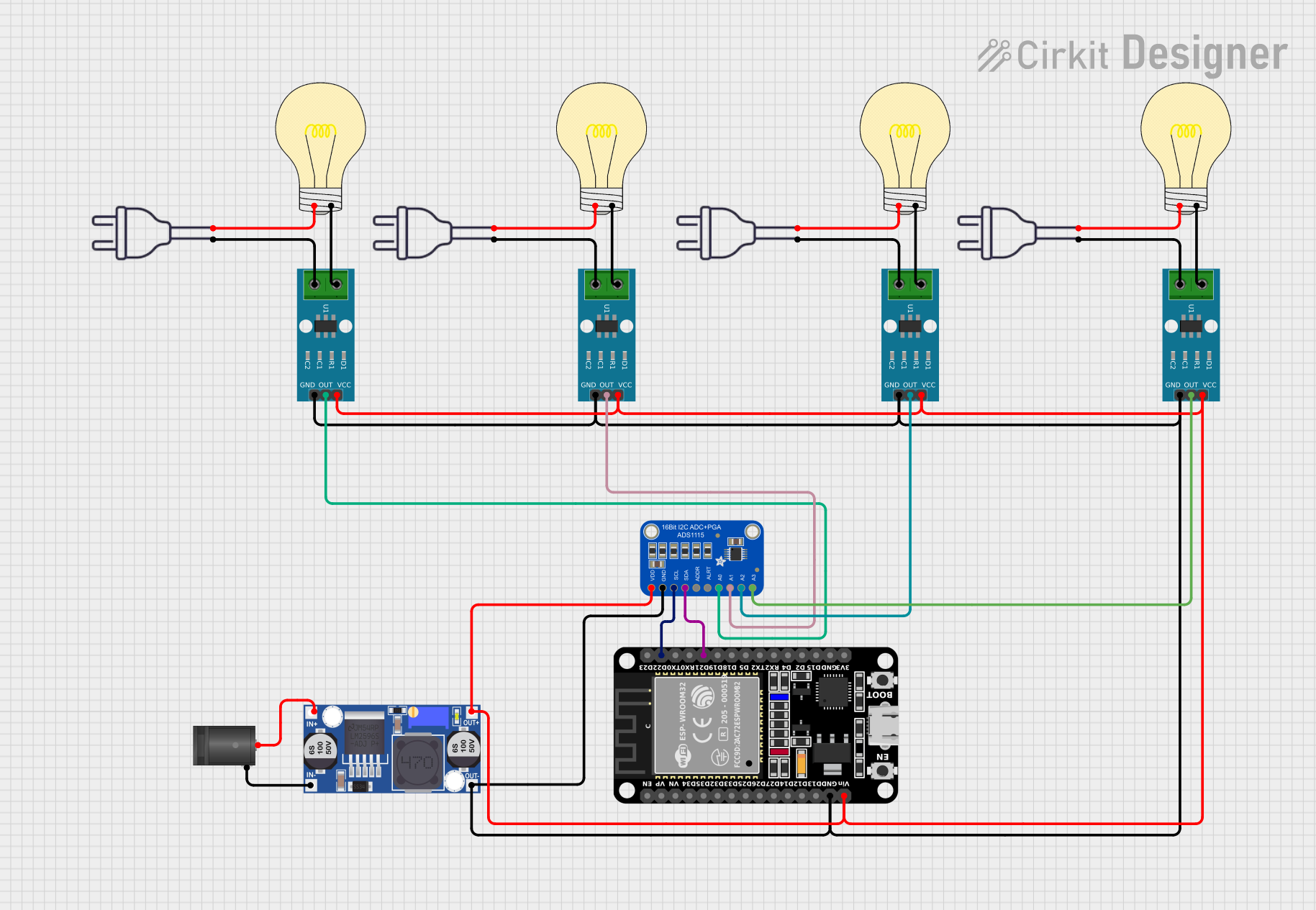
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer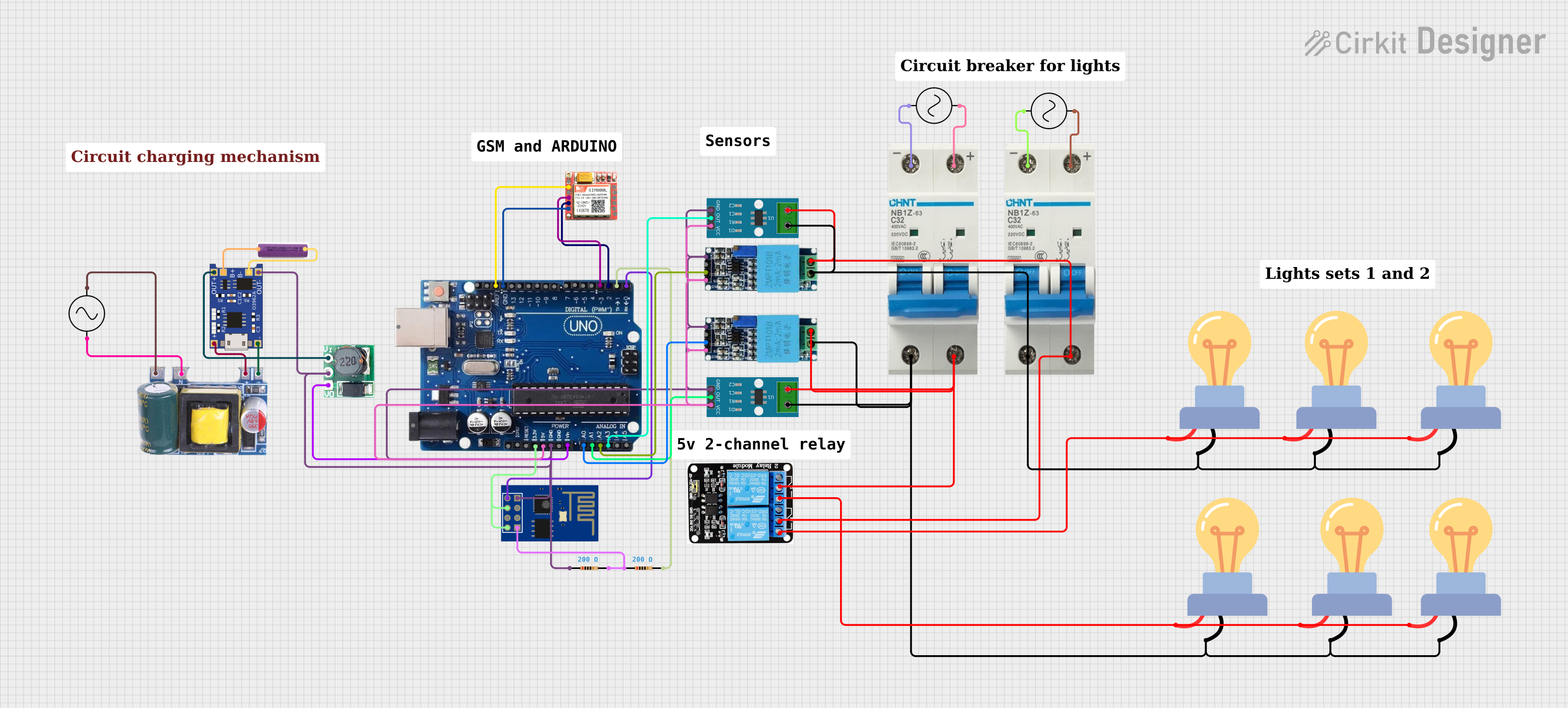
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Current Sensor ACS712

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Power monitoring in household and industrial devices
- Overcurrent protection in circuits
- Battery management systems
- Motor control and monitoring
- Energy metering and load detection
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the ACS712 current sensor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 4.5V to 5.5V |
| Measurement Range | ±5A, ±20A, or ±30A (depending on model) |
| Sensitivity (Typ.) | 185mV/A (±5A), 100mV/A (±20A), 66mV/A (±30A) |
| Output Voltage | Analog, centered at Vcc/2 |
| Response Time | 5 µs |
| Bandwidth | 80 kHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
| Package Type | SOIC-8 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ACS712 has 8 pins, but only a few are typically used in most applications. Below is the pinout:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1, 2, 3 | IP+ | Current input terminal (positive side of load) |
| 4, 5, 6 | IP- | Current input terminal (negative side of load) |
| 7 | Vcc | Power supply (4.5V to 5.5V) |
| 8 | OUT | Analog voltage output proportional to current |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ACS712 in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the Vcc pin to a 5V power supply and the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Connect the Load: Pass the current-carrying wire through the IP+ and IP- terminals. Ensure the current flows in the correct direction as indicated on the sensor.
- Read the Output: The OUT pin provides an analog voltage proportional to the current. At 0A, the output voltage is approximately Vcc/2 (2.5V for a 5V supply). The voltage increases or decreases based on the current direction.
Important Considerations
- Calibration: The sensor's output may vary slightly due to manufacturing tolerances. Calibrate the sensor in your application for accurate readings.
- Noise Filtering: Add a capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) between the OUT pin and GND to reduce noise in the output signal.
- Current Range: Ensure you select the correct ACS712 variant (±5A, ±20A, or ±30A) based on your application's current range.
- Isolation: The ACS712 provides electrical isolation between the current-carrying conductor and the sensor's output, enhancing safety.
Example: Using ACS712 with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the ACS712 with an Arduino UNO to measure current:
// Include necessary libraries (if any)
// Define the analog pin connected to the ACS712 OUT pin
const int sensorPin = A0;
// Define the sensitivity of the ACS712 (e.g., 185mV/A for ±5A model)
const float sensitivity = 0.185; // Sensitivity in V/A
// Define the supply voltage (Vcc) of the sensor
const float Vcc = 5.0; // Supply voltage in volts
// Define the zero-current voltage (Vcc/2)
const float zeroCurrentVoltage = Vcc / 2;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage
float sensorVoltage = (sensorValue / 1023.0) * Vcc;
// Calculate the current in amperes
float current = (sensorVoltage - zeroCurrentVoltage) / sensitivity;
// Print the current value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" A");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Notes:
- Replace
sensitivitywith the appropriate value for your ACS712 variant (e.g., 0.1 for ±20A, 0.066 for ±30A). - Ensure the current-carrying wire is properly connected to the IP+ and IP- terminals.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Readings
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, especially the Vcc, GND, and OUT pins.
High Noise in Output
- Cause: Electrical noise or lack of filtering.
- Solution: Add a 0.1 µF capacitor between the OUT pin and GND to filter noise.
Output Voltage Does Not Change
- Cause: Current is not flowing through the IP+ and IP- terminals.
- Solution: Ensure the current-carrying wire is properly connected and the load is active.
Inaccurate Current Measurements
- Cause: Sensor not calibrated or incorrect sensitivity value used.
- Solution: Calibrate the sensor by measuring a known current and adjusting calculations accordingly.
FAQs
Q: Can the ACS712 measure both AC and DC currents?
A: Yes, the ACS712 can measure both AC and DC currents. The output voltage will vary proportionally with the instantaneous current.
Q: How do I select the correct ACS712 variant?
A: Choose the variant based on the maximum current you need to measure. For example, use the ±5A model for small currents and the ±30A model for larger currents.
Q: Is the ACS712 safe to use with high voltages?
A: Yes, the ACS712 provides electrical isolation between the current-carrying conductor and the sensor's output, making it safe for high-voltage applications.
Q: Can I use the ACS712 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: While the ACS712 is designed for a 5V supply, it may work with a 3.3V microcontroller if the output voltage range is within the ADC input range. However, accuracy may be affected.