
How to Use PN532: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
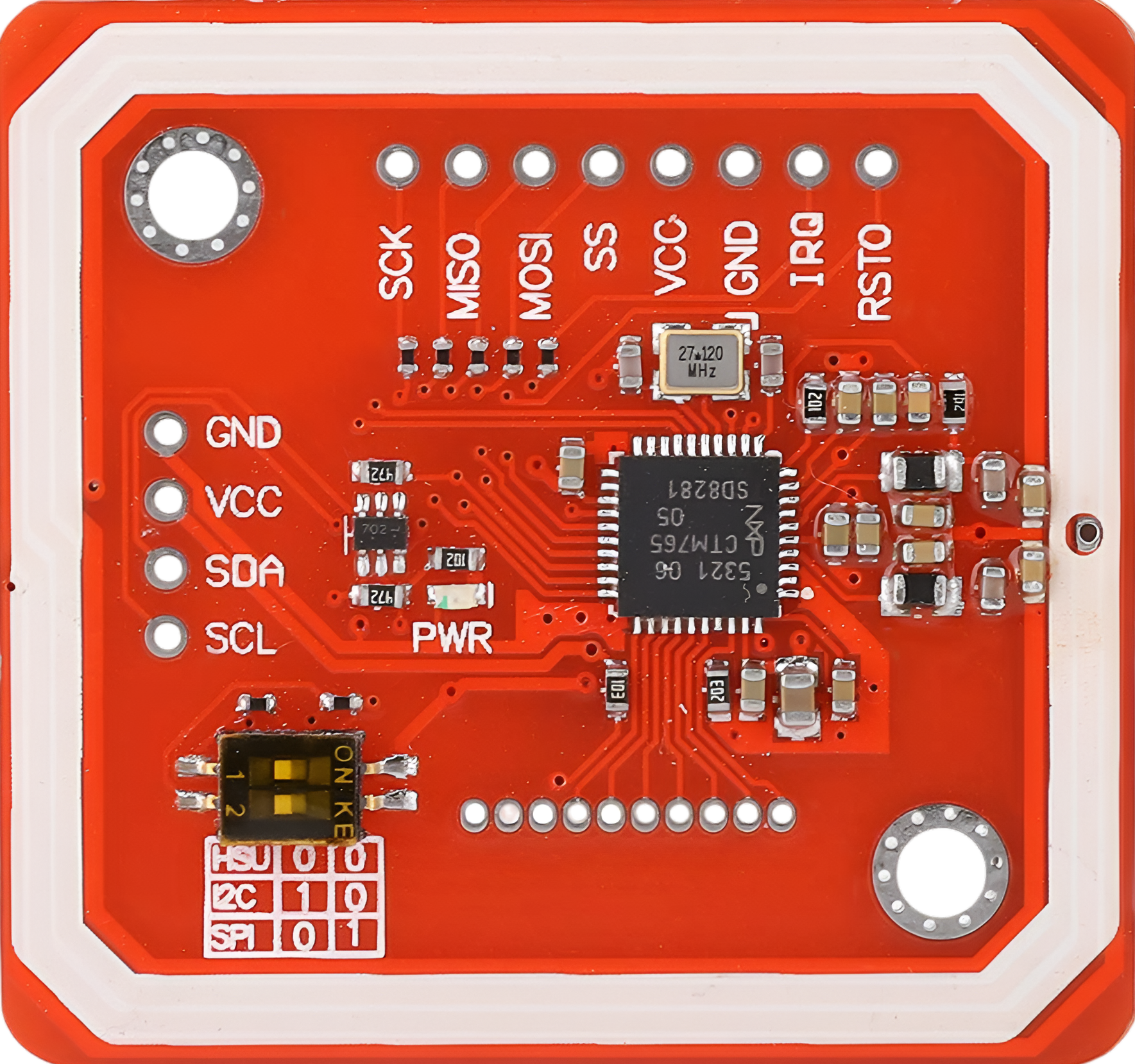
 Design with PN532 in Cirkit Designer
Design with PN532 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The PN532 is a versatile NFC (Near Field Communication) controller that enables seamless communication with NFC-enabled devices. It supports multiple modes of operation, including reader/writer, peer-to-peer, and card emulation. This makes it a popular choice for a wide range of applications such as contactless payments, access control, and data exchange. Its robust design and compatibility with various communication protocols (I2C, SPI, and UART) make it a go-to solution for NFC-based projects.
Explore Projects Built with PN532

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer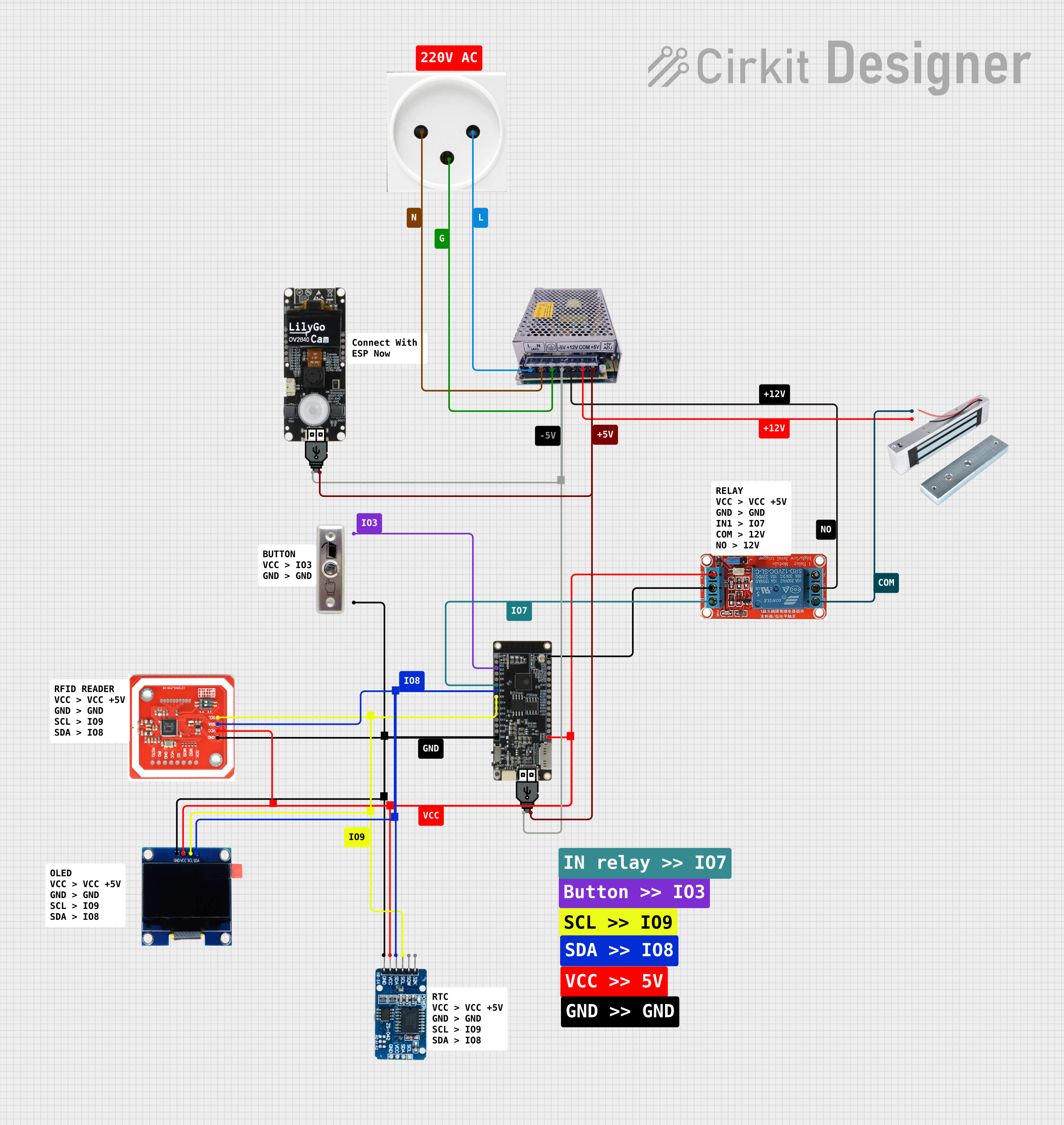
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer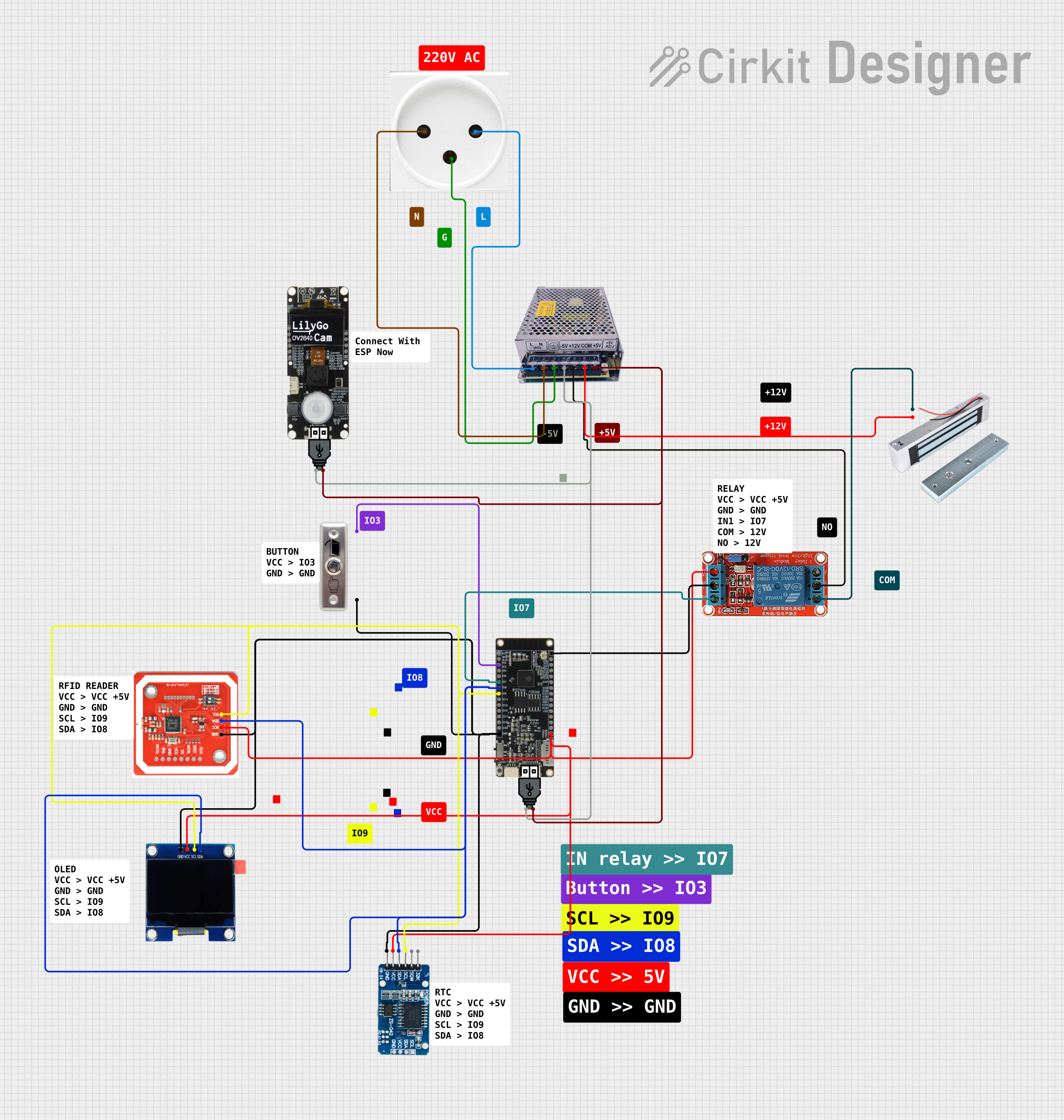
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PN532

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Contactless payment systems
- Access control and authentication
- Data exchange between NFC-enabled devices
- Smart posters and NFC tags
- IoT applications requiring short-range communication
Technical Specifications
The PN532 is a highly capable NFC controller with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 2.7V to 5.5V |
| Communication Interfaces | I2C, SPI, UART |
| Operating Frequency | 13.56 MHz |
| Maximum Communication Range | Up to 5 cm (depending on antenna design) |
| Current Consumption | ~50 mA (active mode), ~100 µA (low-power mode) |
| Supported NFC Modes | Reader/Writer, Peer-to-Peer, Card Emulation |
| Supported Protocols | ISO/IEC 14443A/B, FeliCa, NFC Forum Type 1-4 |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The PN532 module typically comes with the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input (2.7V to 5.5V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| SCL | I2C clock line (used in I2C mode) |
| SDA | I2C data line (used in I2C mode) |
| MOSI | Master Out Slave In (used in SPI mode) |
| MISO | Master In Slave Out (used in SPI mode) |
| SCK | Serial Clock (used in SPI mode) |
| NSS | SPI chip select (used in SPI mode) |
| RX | UART receive line (used in UART mode) |
| TX | UART transmit line (used in UART mode) |
| IRQ | Interrupt request output |
| RST | Reset pin |
Usage Instructions
The PN532 can be used in various modes depending on the application. Below are general steps and considerations for using the PN532 in a circuit:
Connecting the PN532 to an Arduino UNO (I2C Mode)
- Wiring: Connect the PN532 module to the Arduino UNO as follows:
- VCC → 5V (Arduino)
- GND → GND (Arduino)
- SDA → A4 (Arduino I2C data line)
- SCL → A5 (Arduino I2C clock line)
- Install Libraries: Use the Adafruit PN532 library for Arduino. Install it via the Arduino Library Manager.
- Upload Code: Use the example code below to test the PN532 in I2C mode.
Example Code for Reading NFC Tags
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_PN532.h>
// Define the I2C pins for the PN532
#define SDA_PIN A4
#define SCL_PIN A5
// Create an instance of the Adafruit_PN532 class
Adafruit_PN532 nfc(SDA_PIN, SCL_PIN);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Initializing PN532...");
// Initialize the PN532
nfc.begin();
// Check if the PN532 is connected
uint32_t versiondata = nfc.getFirmwareVersion();
if (!versiondata) {
Serial.println("Didn't find PN532 board");
while (1); // Halt execution if the board is not found
}
// Display firmware version
Serial.print("Found PN532 with firmware version: ");
Serial.print((versiondata >> 16) & 0xFF, HEX);
Serial.print('.');
Serial.println((versiondata >> 8) & 0xFF, HEX);
// Configure the board to read NFC tags
nfc.SAMConfig();
Serial.println("Waiting for an NFC tag...");
}
void loop() {
uint8_t success;
uint8_t uid[] = { 0 }; // Buffer to store the UID
uint8_t uidLength;
// Try to read an NFC tag
success = nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, uid, &uidLength);
if (success) {
Serial.println("NFC tag detected!");
Serial.print("UID Length: "); Serial.print(uidLength, DEC); Serial.println(" bytes");
Serial.print("UID Value: ");
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < uidLength; i++) {
Serial.print(" 0x"); Serial.print(uid[i], HEX);
}
Serial.println();
delay(1000); // Wait before scanning again
}
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the PN532 module is powered within its operating voltage range (2.7V to 5.5V).
- Antenna Placement: For optimal performance, avoid placing the antenna near metal objects or other sources of interference.
- Communication Mode: Configure the module for the desired communication mode (I2C, SPI, or UART) using the appropriate jumpers or settings on the module.
- Library Compatibility: Use a reliable library, such as the Adafruit PN532 library, to simplify communication with the module.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
PN532 Not Detected
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or communication mode.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure the module is configured for the correct communication mode (e.g., I2C, SPI, or UART).
NFC Tags Not Detected
- Cause: Antenna placement or unsupported tag type.
- Solution: Ensure the tag is within range (up to 5 cm) and is of a supported type (e.g., ISO/IEC 14443A/B).
Intermittent Communication
- Cause: Noise or interference in the circuit.
- Solution: Use shorter wires and ensure proper grounding. Add decoupling capacitors if necessary.
Firmware Version Not Displayed
- Cause: Faulty module or incorrect initialization.
- Solution: Verify the module's power supply and reinitialize the PN532 using the library.
FAQs
Q: Can the PN532 read all types of NFC tags?
A: The PN532 supports ISO/IEC 14443A/B, FeliCa, and NFC Forum Type 1-4 tags. Ensure your tag is compatible with these standards.
Q: How do I switch between I2C, SPI, and UART modes?
A: The PN532 module typically has jumpers or solder pads to configure the communication mode. Refer to the module's datasheet for specific instructions.
Q: What is the maximum range of the PN532?
A: The maximum range is approximately 5 cm, depending on the antenna design and environmental factors.
Q: Can the PN532 be used for peer-to-peer communication?
A: Yes, the PN532 supports peer-to-peer mode for data exchange between two NFC-enabled devices.