
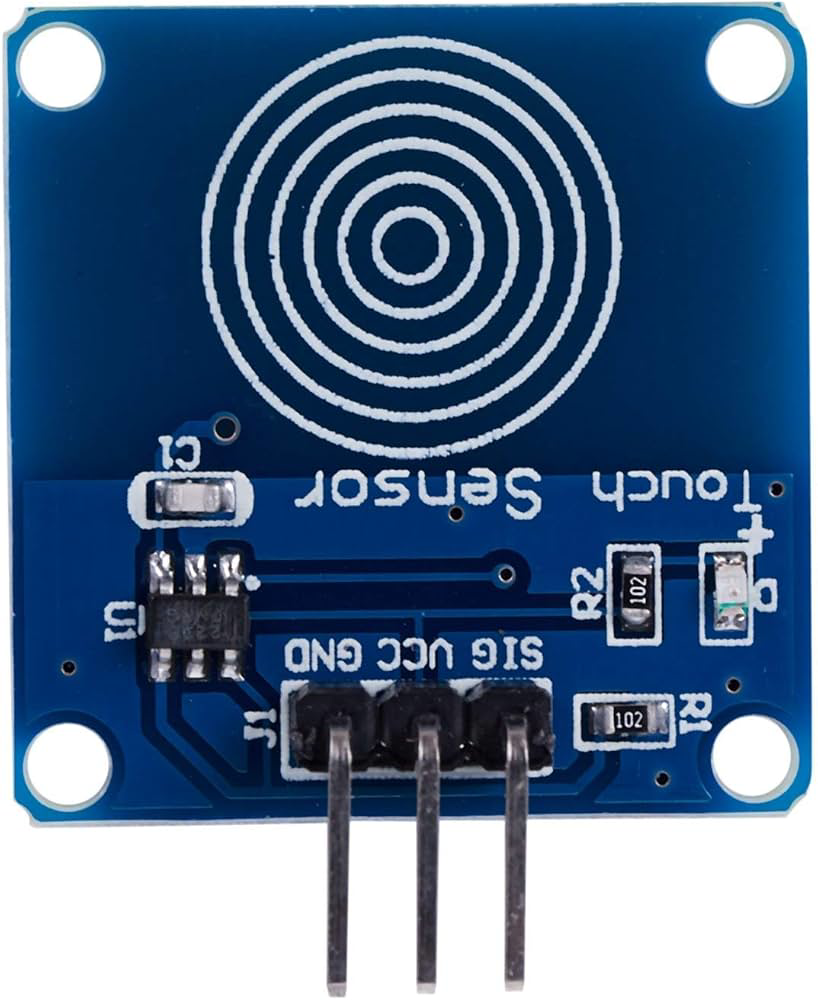
How to Use Touch Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Touch Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Touch Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A touch sensor detects physical touch or pressure and converts it into an electrical signal. It is widely used in user interfaces, control systems, and interactive devices. Touch sensors are commonly employed in applications such as touchscreens, home automation systems, robotics, and wearable devices. They provide a simple and intuitive way for users to interact with electronic systems.
Explore Projects Built with Touch Sensor
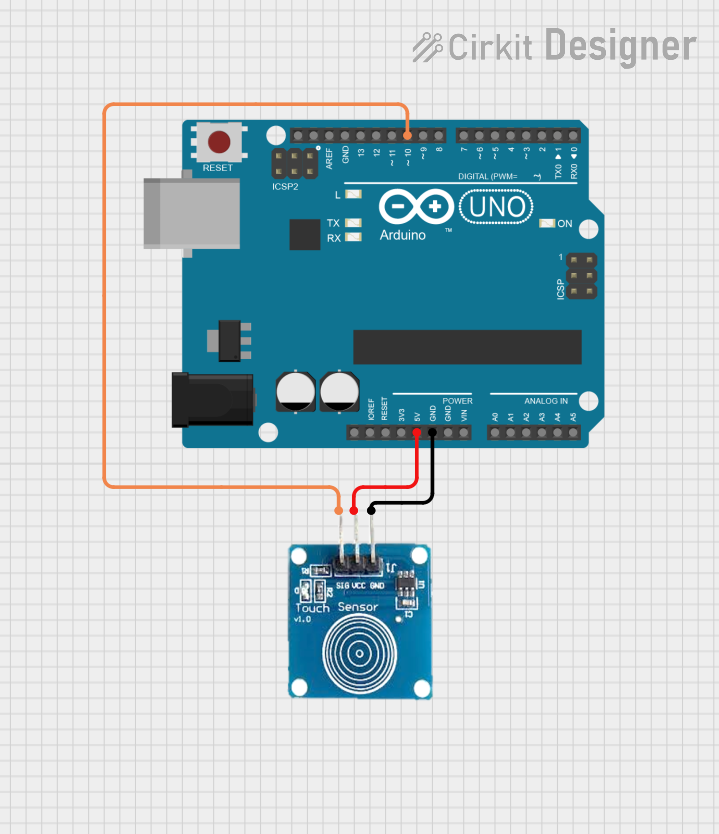
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer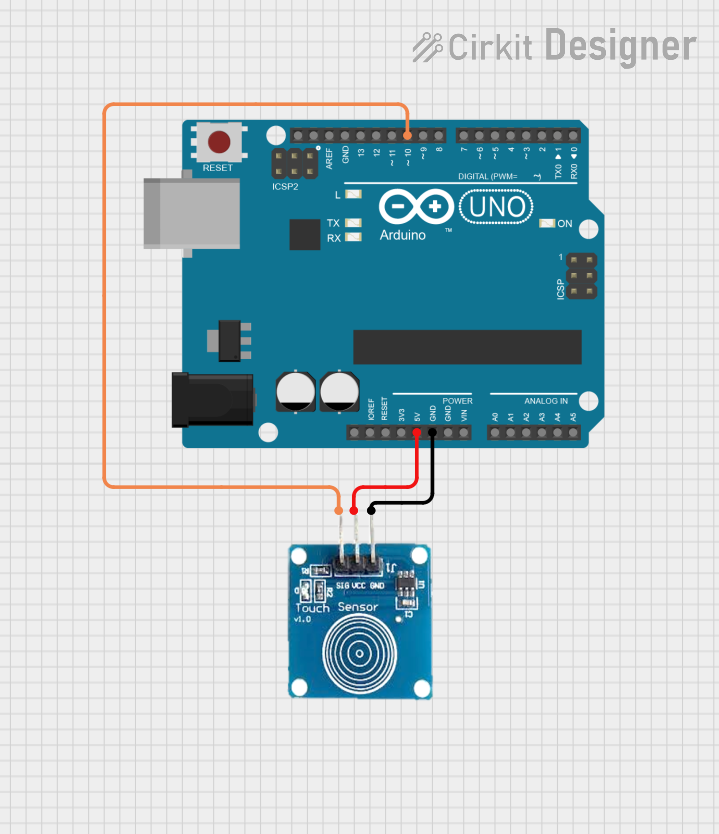
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer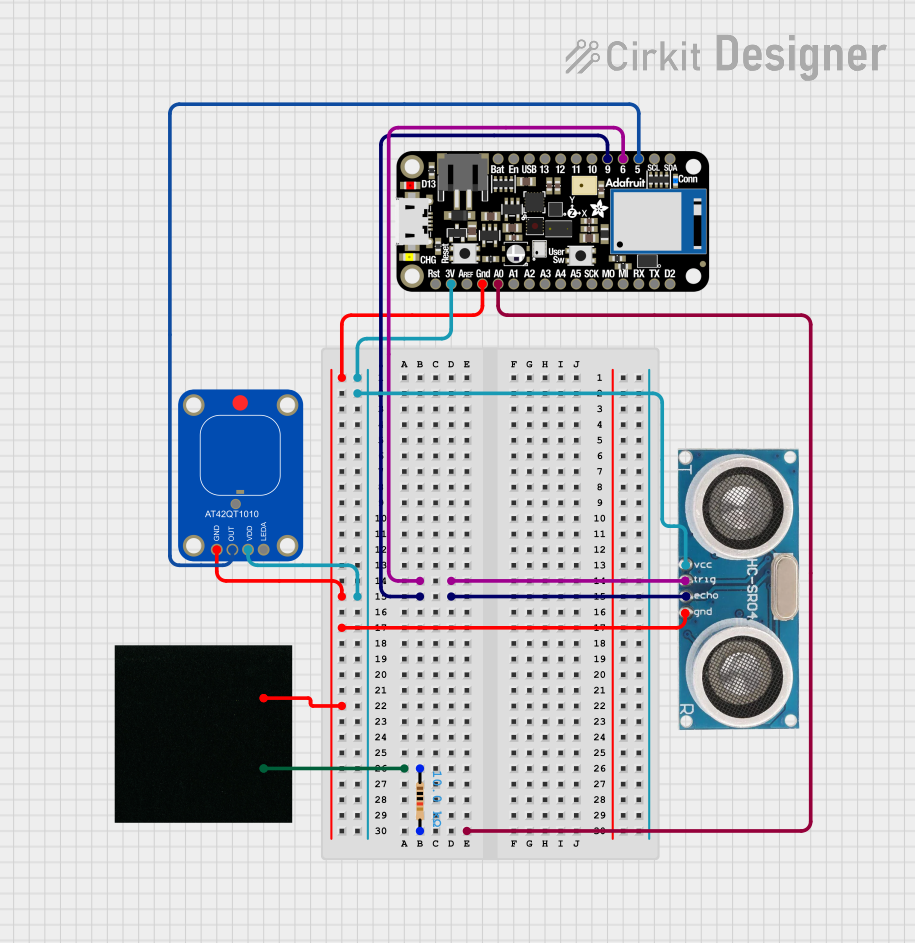
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer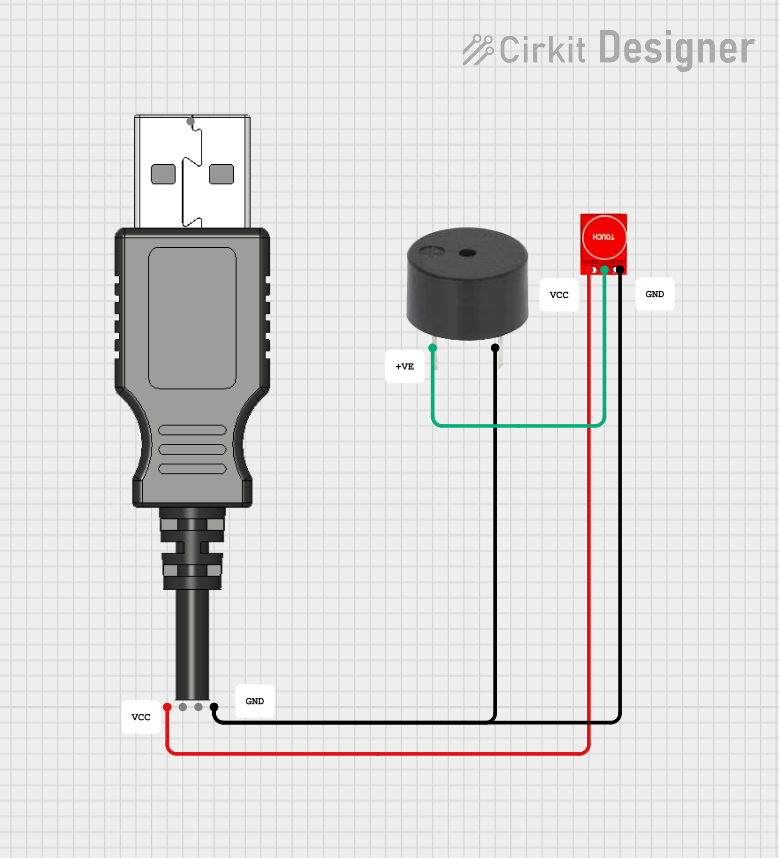
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Touch Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 2.0V to 5.5V
- Operating Current: < 20mA
- Response Time: ~60ms
- Output Type: Digital (High/Low)
- Interface: Single output pin
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 70°C
- Sensitivity: Adjustable in some models (varies by manufacturer)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply pin (2.0V to 5.5V) |
| GND | Ground pin |
| OUT | Digital output pin (High when touched) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Touch Sensor in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect the Output: Attach the
OUTpin to a digital input pin of your microcontroller or to an external circuit that processes the signal. - Test the Sensor: When the sensor is touched, the
OUTpin will output a HIGH signal (typically 3.3V or 5V, depending on the supply voltage). When not touched, the output will remain LOW.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Debouncing: The touch sensor may produce noise or false triggers. Use software debouncing techniques to filter out spurious signals.
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable power supply to avoid erratic behavior.
- Environmental Factors: Avoid exposing the sensor to extreme temperatures, moisture, or dust, as these can affect its performance.
- Pull-Down Resistor: If the sensor's output is unstable, consider adding a pull-down resistor (e.g., 10kΩ) to the
OUTpin.
Example: Connecting a Touch Sensor to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a touch sensor with an Arduino UNO to control an LED:
// Define pin connections
const int touchPin = 2; // Touch sensor output connected to digital pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // LED connected to digital pin 13
void setup() {
pinMode(touchPin, INPUT); // Set touch sensor pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
}
void loop() {
int touchState = digitalRead(touchPin); // Read the touch sensor state
if (touchState == HIGH) {
// If the sensor is touched, turn on the LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
Serial.println("Touch detected! LED ON");
} else {
// If not touched, turn off the LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
Serial.println("No touch detected. LED OFF");
}
delay(100); // Small delay to stabilize readings
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Sensor Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the power supply voltage is within the specified range.
False Triggers
- Cause: Electrical noise or environmental interference.
- Solution: Use a pull-down resistor on the
OUTpin and ensure proper grounding.
Output Signal is Unstable
- Cause: Fluctuations in the power supply or poor connections.
- Solution: Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) across the
VCCandGNDpins to stabilize the power supply.
Touch Sensor is Too Sensitive or Not Sensitive Enough
- Cause: Sensitivity settings (if adjustable) are not configured properly.
- Solution: Refer to the manufacturer's datasheet to adjust the sensitivity, if applicable.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the touch sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the touch sensor operates within a voltage range of 2.0V to 5.5V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems.Q: Can the touch sensor detect multiple touches simultaneously?
A: No, most basic touch sensors are designed to detect a single touch at a time.Q: How do I extend the touch area?
A: You can attach a conductive material (e.g., aluminum foil) to the sensor's touchpad to increase the touch area. Ensure the material is securely connected and does not short the circuit.Q: Is the touch sensor waterproof?
A: Most touch sensors are not waterproof. If water resistance is required, consider using a sealed enclosure or a specialized waterproof touch sensor.