
How to Use ADS1115: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ADS1115 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ADS1115 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ADS1115 is a high-precision, 16-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an I2C interface. It is capable of measuring up to four single-ended inputs or two differential inputs, making it ideal for applications requiring accurate sensor data acquisition. The device features a programmable gain amplifier (PGA) for handling a wide range of input voltages and operates with low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-powered devices.
Explore Projects Built with ADS1115
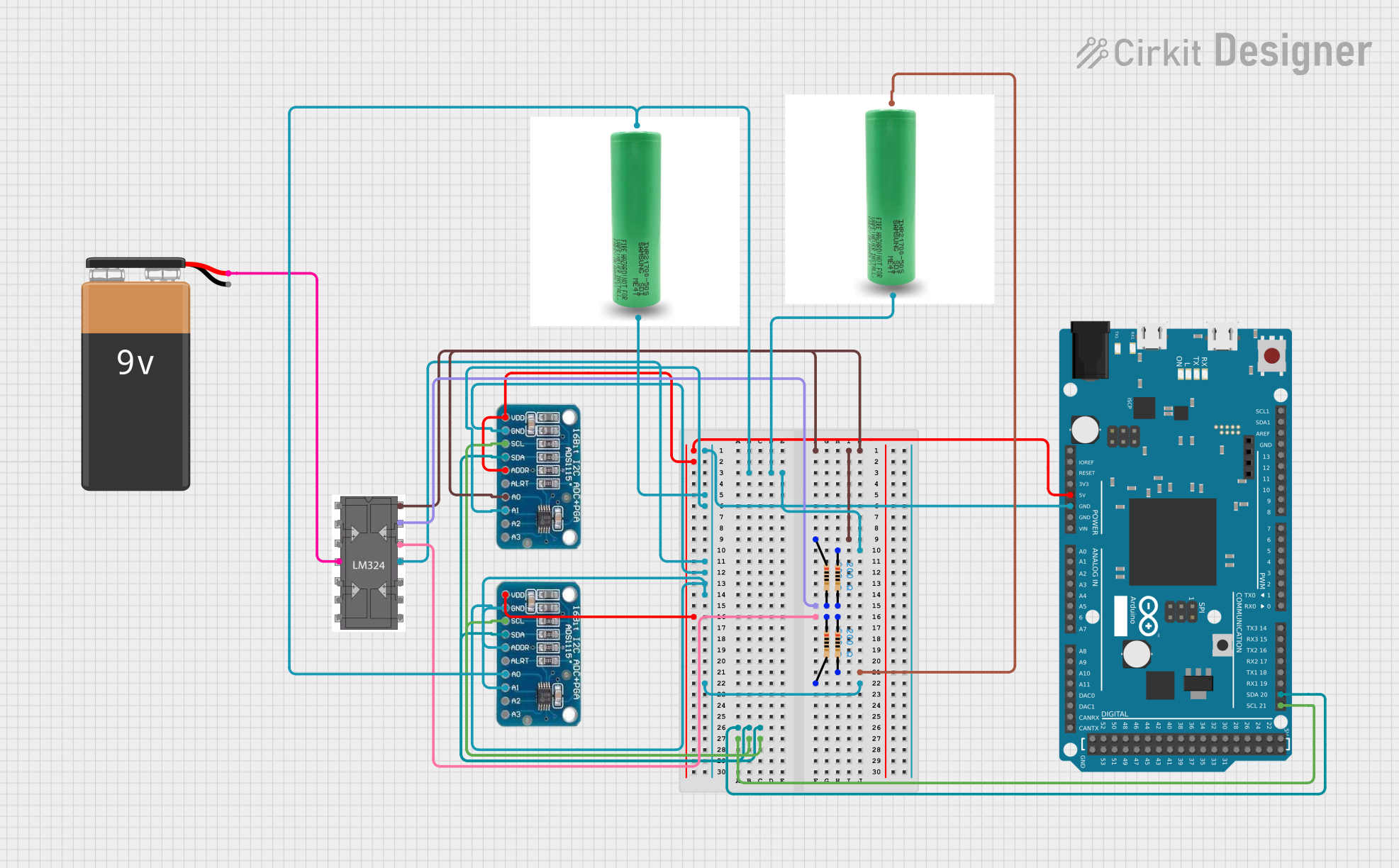
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer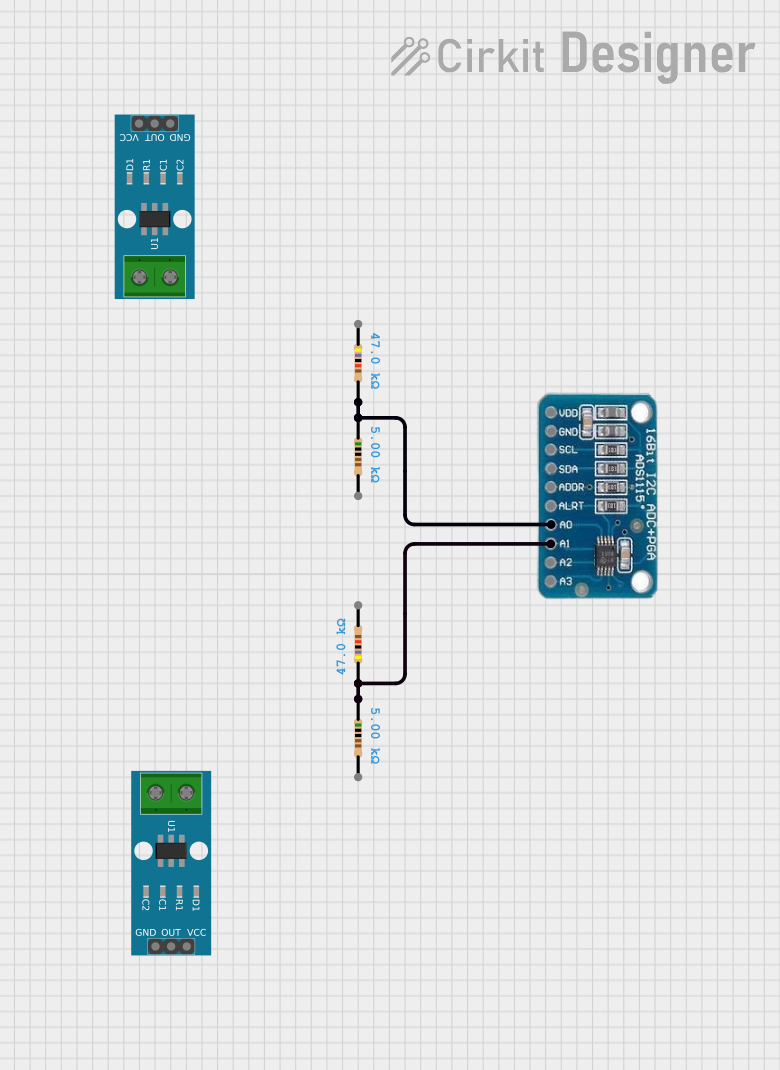
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer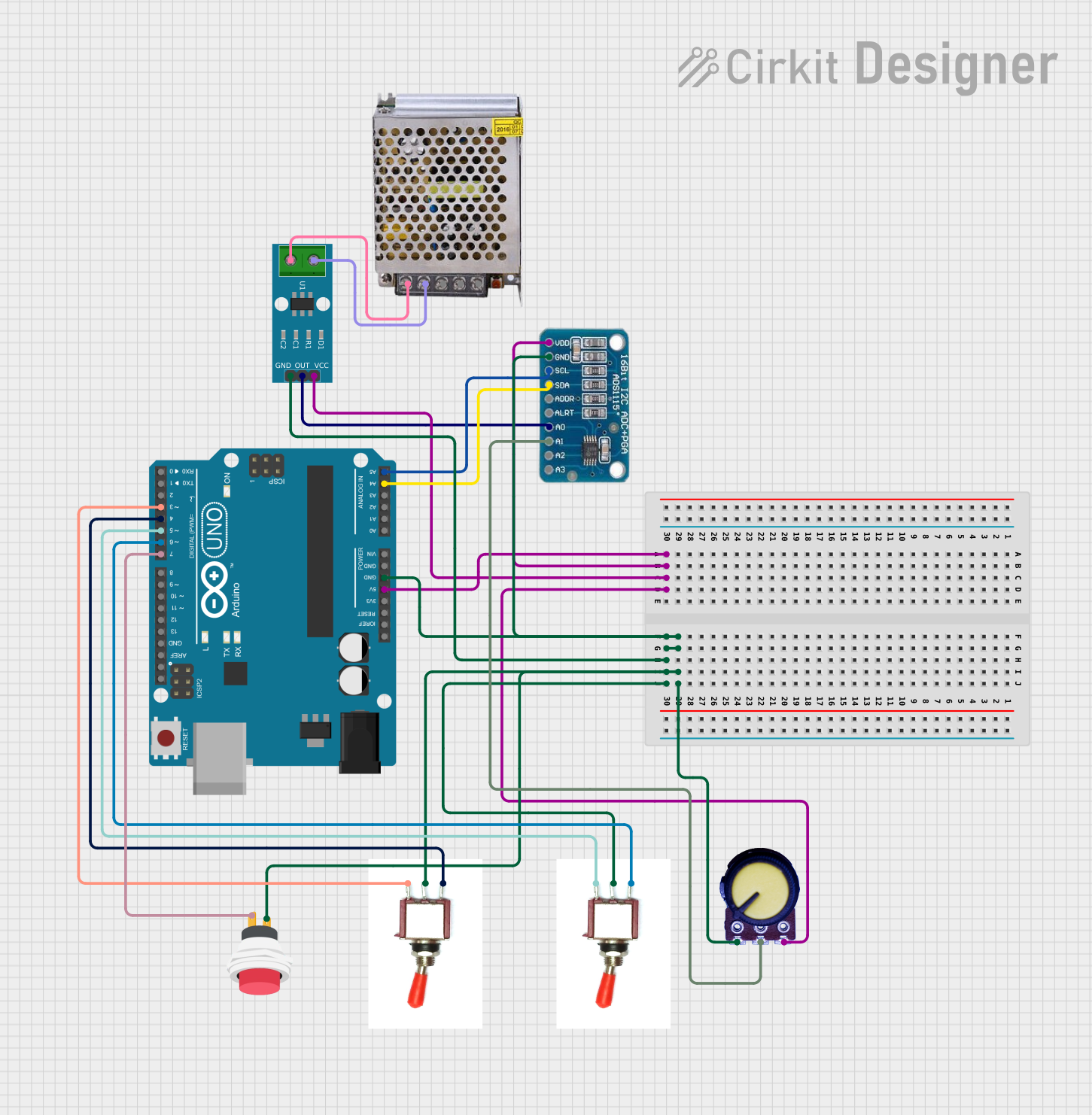
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer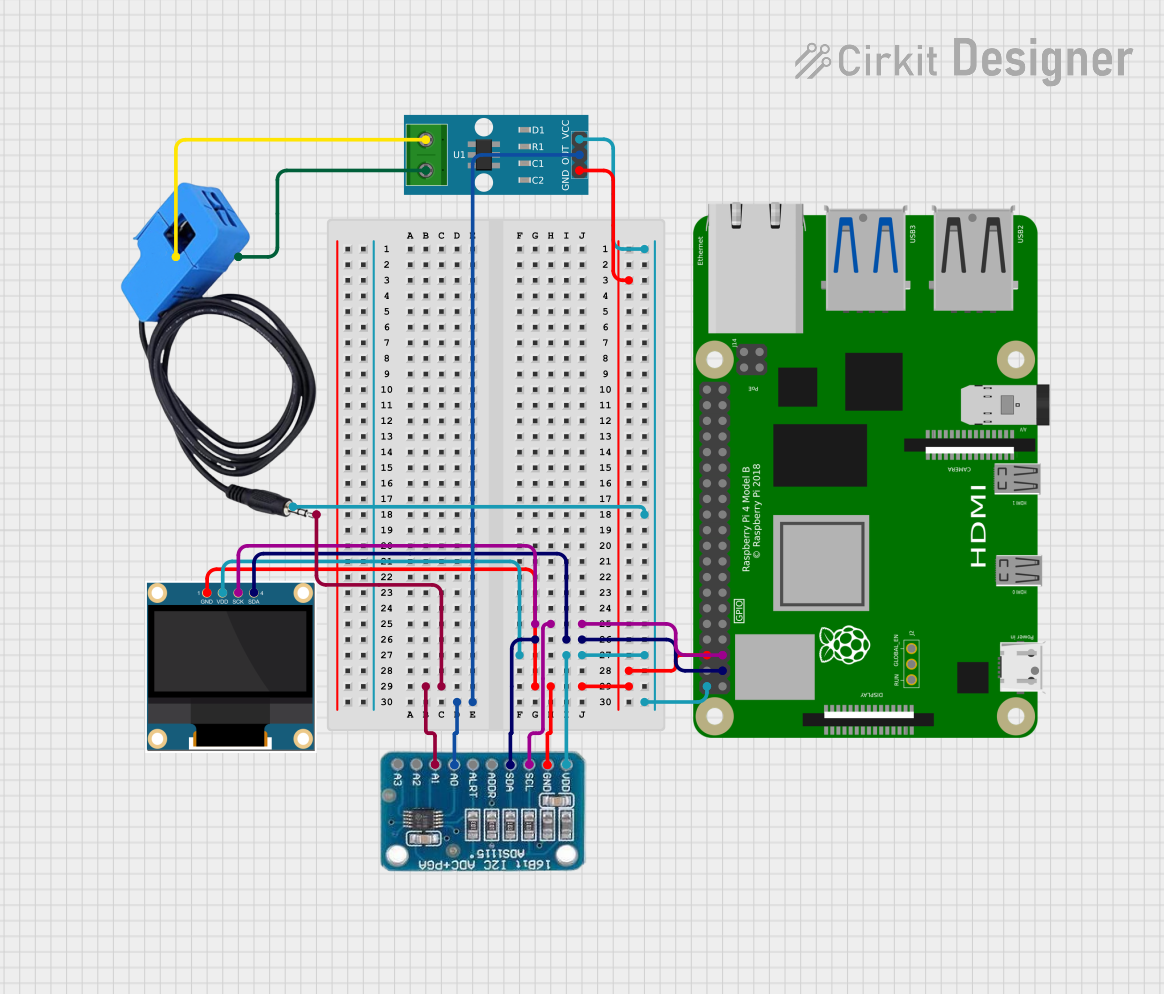
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ADS1115

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Sensor data acquisition (e.g., temperature, pressure, light sensors)
- Data logging systems
- Portable measurement devices
- Industrial automation
- IoT devices requiring precise analog measurements
Technical Specifications
The ADS1115 offers a range of features that make it versatile and reliable for various applications. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Resolution: 16-bit
- Input Channels: 4 single-ended or 2 differential
- Input Voltage Range: ±0.256V to ±6.144V (configurable via PGA)
- Supply Voltage: 2.0V to 5.5V
- Interface: I2C (up to 3.4 MHz)
- Data Rate: Programmable, 8 SPS to 860 SPS
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +125°C
- Current Consumption: 150 µA (typical in continuous mode)
- Address Pins: Configurable I2C address (4 possible addresses)
Pin Configuration
The ADS1115 comes in an 8-pin package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin | Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Power | Power supply input (2.0V to 5.5V). |
| 2 | GND | Ground | Ground reference for the device. |
| 3 | SCL | Input | I2C clock line. |
| 4 | SDA | Input/Output | I2C data line. |
| 5 | ALERT/RDY | Output | Configurable as an alert pin or data-ready signal. |
| 6 | A0 | Input | Address pin 0 for I2C address configuration. |
| 7 | A1 | Input | Address pin 1 for I2C address configuration. |
| 8 | AIN0-AIN3 | Analog Input | Analog input channels for single-ended or differential measurements. |
Usage Instructions
The ADS1115 is straightforward to use in a circuit, especially with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO. Below are the steps and considerations for using the ADS1115:
Connecting the ADS1115
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source, and the GND pin to ground.
- I2C Interface: Connect the SCL and SDA pins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the SCL and SDA lines if not already present.
- Analog Inputs: Connect your analog signal(s) to the AIN0-AIN3 pins. For differential measurements, connect the positive signal to AIN0 or AIN2 and the negative signal to AIN1 or AIN3.
- Address Configuration: Set the A0 and A1 pins to configure the I2C address (e.g., GND for 0x48, VDD for 0x49, etc.).
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example of how to use the ADS1115 with an Arduino UNO to read a single-ended input:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_ADS1X15.h>
// Create an ADS1115 object
Adafruit_ADS1115 ads;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize the ADS1115
if (!ads.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize ADS1115!");
while (1); // Halt if initialization fails
}
Serial.println("ADS1115 initialized.");
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from channel 0 (single-ended)
int16_t adcValue = ads.readADC_SingleEnded(0);
// Convert the ADC value to voltage (assuming default gain of ±6.144V)
float voltage = adcValue * 0.1875 / 1000; // 0.1875 mV per bit
// Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage, 4); // Print with 4 decimal places
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Important Considerations
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure the input voltage does not exceed the configured PGA range to avoid damage or inaccurate readings.
- I2C Address: If using multiple ADS1115 devices, configure unique I2C addresses using the A0 and A1 pins.
- Pull-up Resistors: Verify that the I2C lines have appropriate pull-up resistors to ensure reliable communication.
- Data Rate: Adjust the data rate based on your application's speed and noise requirements.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No I2C Communication:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or missing pull-up resistors.
- Solution: Verify the SCL and SDA connections and ensure pull-up resistors are present.
Incorrect Readings:
- Cause: Input voltage exceeds the configured PGA range.
- Solution: Check the input voltage and adjust the PGA settings accordingly.
Device Not Detected:
- Cause: Incorrect I2C address or address pin configuration.
- Solution: Verify the A0 and A1 pin settings and ensure the correct address is used in the code.
Fluctuating Readings:
- Cause: Noise in the input signal or insufficient decoupling.
- Solution: Add a decoupling capacitor near the input pins and ensure proper grounding.
FAQs
Q1: Can the ADS1115 measure negative voltages?
A1: Yes, the ADS1115 can measure negative voltages in differential mode, provided the voltage stays within the configured PGA range.
Q2: What is the maximum sampling rate of the ADS1115?
A2: The maximum sampling rate is 860 samples per second (SPS), configurable via the data rate settings.
Q3: Can I use the ADS1115 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A3: Yes, the ADS1115 is compatible with 3.3V systems. Ensure the VDD pin is connected to 3.3V, and the I2C lines are properly level-shifted if necessary.
Q4: How do I connect multiple ADS1115 devices to the same I2C bus?
A4: Configure each device with a unique I2C address by setting the A0 and A1 pins to different combinations of GND and VDD.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the ADS1115 into your projects for precise analog-to-digital conversion.