
How to Use TFT-DISPLAY: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TFT-DISPLAY in Cirkit Designer
Design with TFT-DISPLAY in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) display is a type of LCD screen that leverages thin-film transistor technology to enhance image quality, color accuracy, and response time. TFT displays are widely used in applications requiring high-resolution visuals, such as smartphones, tablets, industrial control panels, and embedded systems. Their compact size, vibrant color reproduction, and fast refresh rates make them ideal for portable devices and interactive interfaces.
Explore Projects Built with TFT-DISPLAY
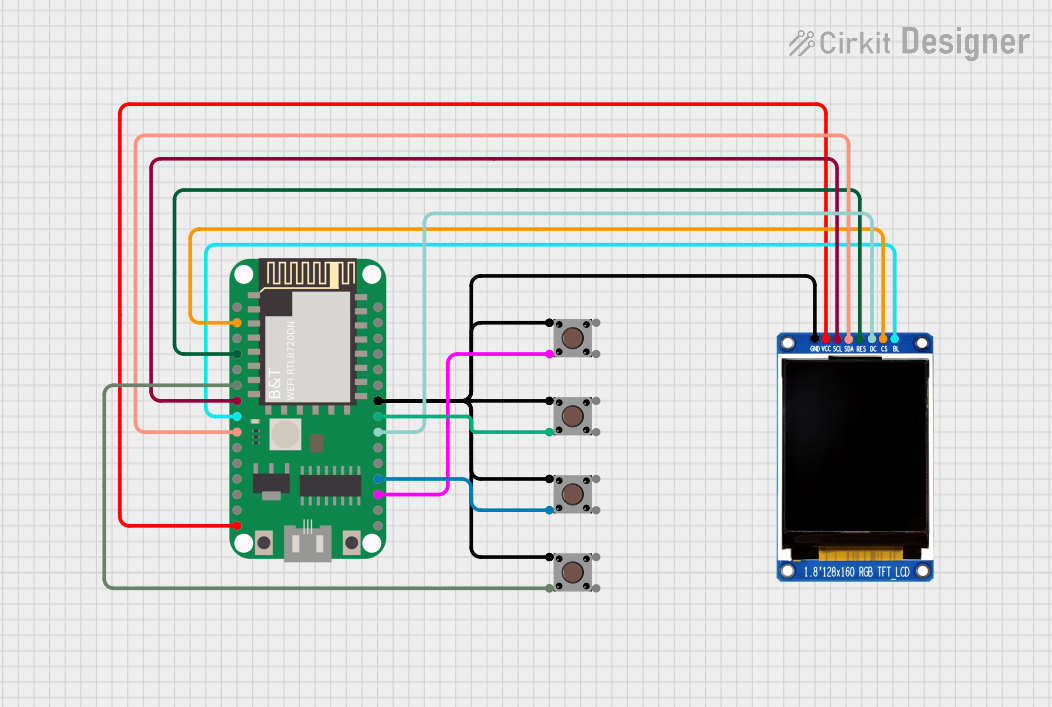
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer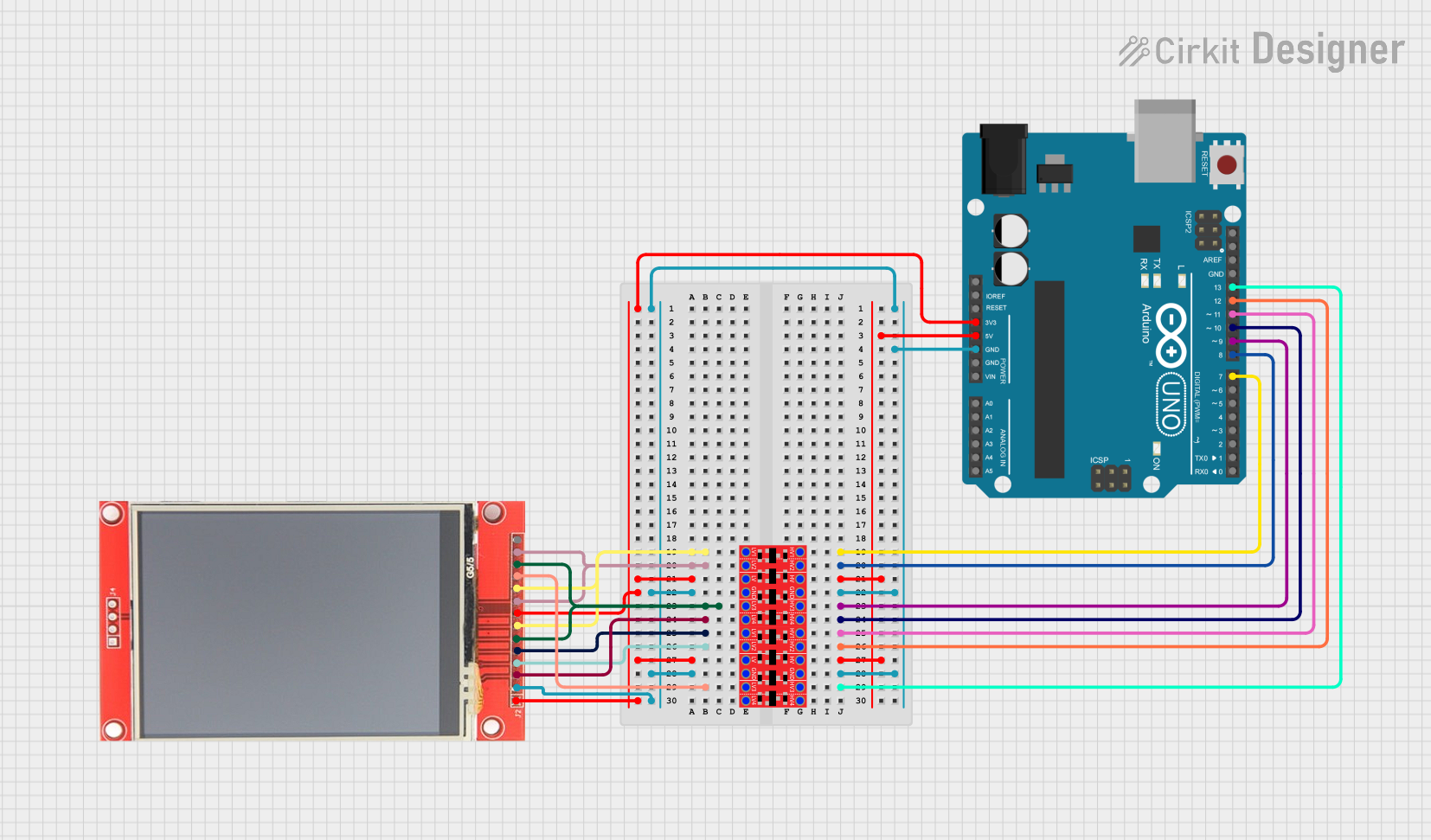
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer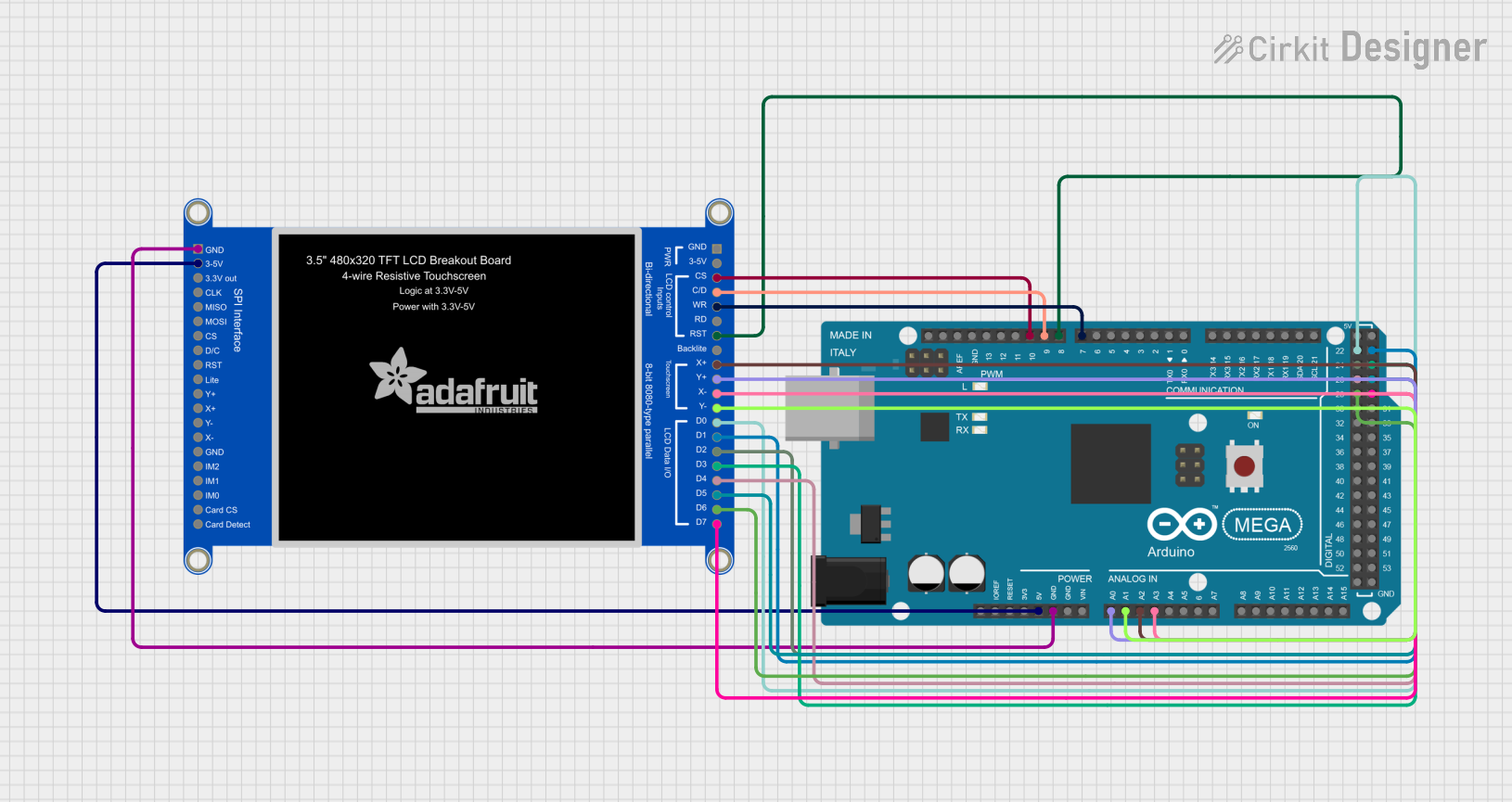
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer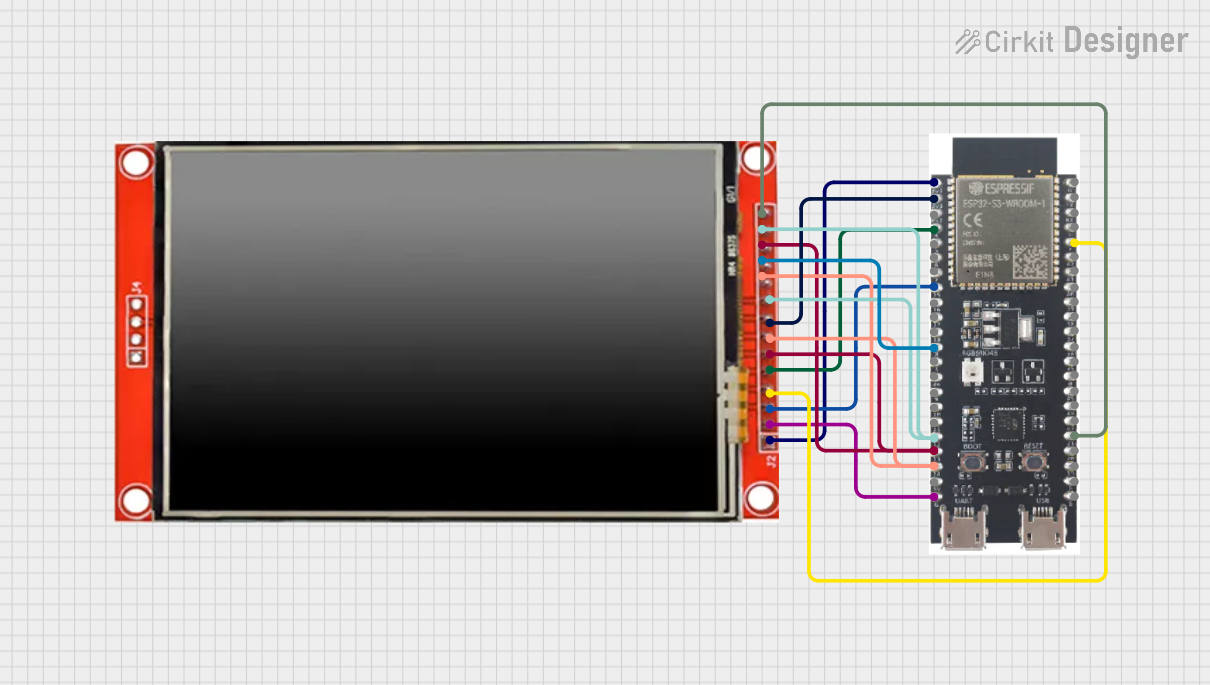
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TFT-DISPLAY

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical TFT display. Note that specific values may vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
General Specifications
- Display Type: Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) LCD
- Resolution: Varies (e.g., 320x240, 480x320, 800x480)
- Color Depth: 16-bit or 24-bit (65K or 16M colors)
- Interface: SPI, I2C, or Parallel (depending on the model)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V or 5V (check model-specific requirements)
- Backlight: LED
- Viewing Angle: Typically 160° or higher
- Touchscreen: Optional (Resistive or Capacitive)
Pin Configuration
The pin configuration of a TFT display may vary depending on the model. Below is an example of a common 2.4-inch TFT display with an SPI interface:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply (3.3V or 5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| CS | Chip Select (active low) |
| RESET | Reset pin (active low) |
| DC (RS) | Data/Command control |
| MOSI (SDA) | Master Out Slave In (SPI data) |
| SCK | Serial Clock (SPI clock) |
| LED | Backlight control (connect to VCC) |
For parallel-interface TFT displays, additional data pins (e.g., D0-D7) will be present.
Usage Instructions
Connecting the TFT Display to an Arduino UNO
To use a TFT display with an Arduino UNO, follow these steps:
Wiring: Connect the TFT display pins to the Arduino as shown below:
- VCC → 5V
- GND → GND
- CS → Pin 10
- RESET → Pin 9
- DC → Pin 8
- MOSI → Pin 11
- SCK → Pin 13
- LED → 5V (via a 220-ohm resistor for current limiting)
Install Libraries: Install the required libraries in the Arduino IDE:
- Adafruit_GFX
- Adafruit_TFTLCD (or a library specific to your TFT model)
Upload Example Code: Use the following example code to test the display:
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h> // Core graphics library
#include <Adafruit_TFTLCD.h> // Hardware-specific library
// Define pin connections for the TFT display
#define LCD_CS A3 // Chip Select
#define LCD_CD A2 // Command/Data
#define LCD_WR A1 // LCD Write
#define LCD_RD A0 // LCD Read
#define LCD_RESET A4 // Reset
// Create an instance of the TFT display
Adafruit_TFTLCD tft(LCD_CS, LCD_CD, LCD_WR, LCD_RD, LCD_RESET);
void setup() {
tft.reset(); // Reset the display
tft.begin(0x9341); // Initialize with the display driver ID (e.g., ILI9341)
tft.fillScreen(0x0000); // Clear the screen (black)
tft.setTextColor(0xFFFF); // Set text color to white
tft.setTextSize(2); // Set text size
tft.setCursor(10, 10); // Set cursor position
tft.println("Hello, TFT!"); // Display text
}
void loop() {
// No actions in the loop for this example
}
Important Considerations
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the TFT display is compatible with the voltage levels of your microcontroller (e.g., 3.3V or 5V). Use level shifters if necessary.
- Backlight Control: Use a current-limiting resistor or a PWM pin to control the brightness of the backlight.
- Driver Compatibility: Verify the driver IC of your TFT display (e.g., ILI9341, ST7735) and use the appropriate library.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Blank Screen:
- Check wiring connections and ensure all pins are correctly connected.
- Verify that the power supply voltage matches the display's requirements.
- Confirm that the correct driver ID is used in the code.
Flickering or Distorted Display:
- Ensure proper grounding between the display and the microcontroller.
- Check for loose or poor-quality connections.
- Use shorter wires to reduce noise in SPI or parallel communication.
Touchscreen Not Responding:
- Verify that the touchscreen pins (if present) are connected to the correct microcontroller pins.
- Install and configure the touchscreen library (e.g., Adafruit_TouchScreen).
FAQs
Q: Can I use a TFT display with a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, most TFT displays can be used with a Raspberry Pi. Use the GPIO pins or SPI interface and install the appropriate drivers.
Q: How do I identify the driver IC of my TFT display?
A: The driver IC is often printed on the back of the display module. Alternatively, consult the product datasheet or seller's documentation.
Q: Can I use multiple TFT displays with one microcontroller?
A: Yes, you can use multiple displays by assigning unique Chip Select (CS) pins for each display. However, this may require additional resources and careful management of communication.
Q: How do I control the backlight brightness?
A: Connect the LED pin to a PWM-capable pin on your microcontroller and use analogWrite() to adjust brightness.
By following this documentation, you can successfully integrate and operate a TFT display in your projects!