
How to Use Regulator Stepdown DC XL4015 CC CV: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
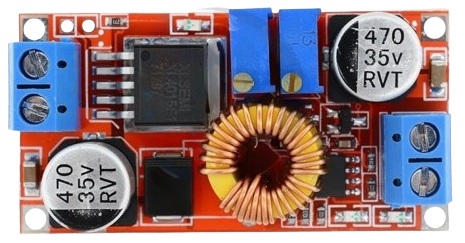
 Design with Regulator Stepdown DC XL4015 CC CV in Cirkit Designer
Design with Regulator Stepdown DC XL4015 CC CV in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The XL4015 is a highly efficient, DC-DC step-down (buck) converter module capable of regulating and stepping down input voltage levels to a lower, specified output voltage. It is equipped with both constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV) modes, making it versatile for regulating different types of loads. This module is commonly used in battery charging applications, power supplies, and as a driver for LEDs where precise voltage and current control is required.
Explore Projects Built with Regulator Stepdown DC XL4015 CC CV

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer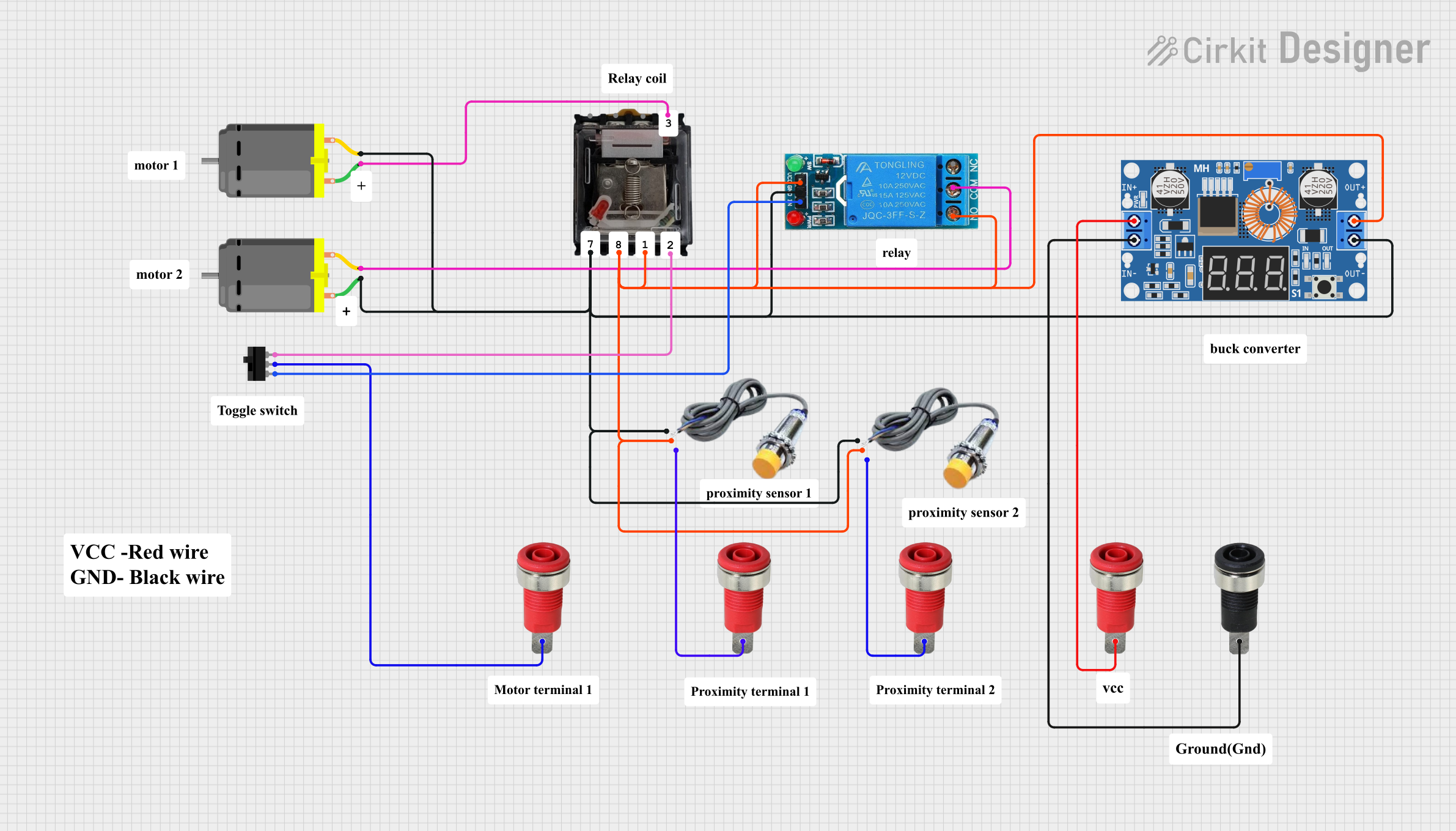
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer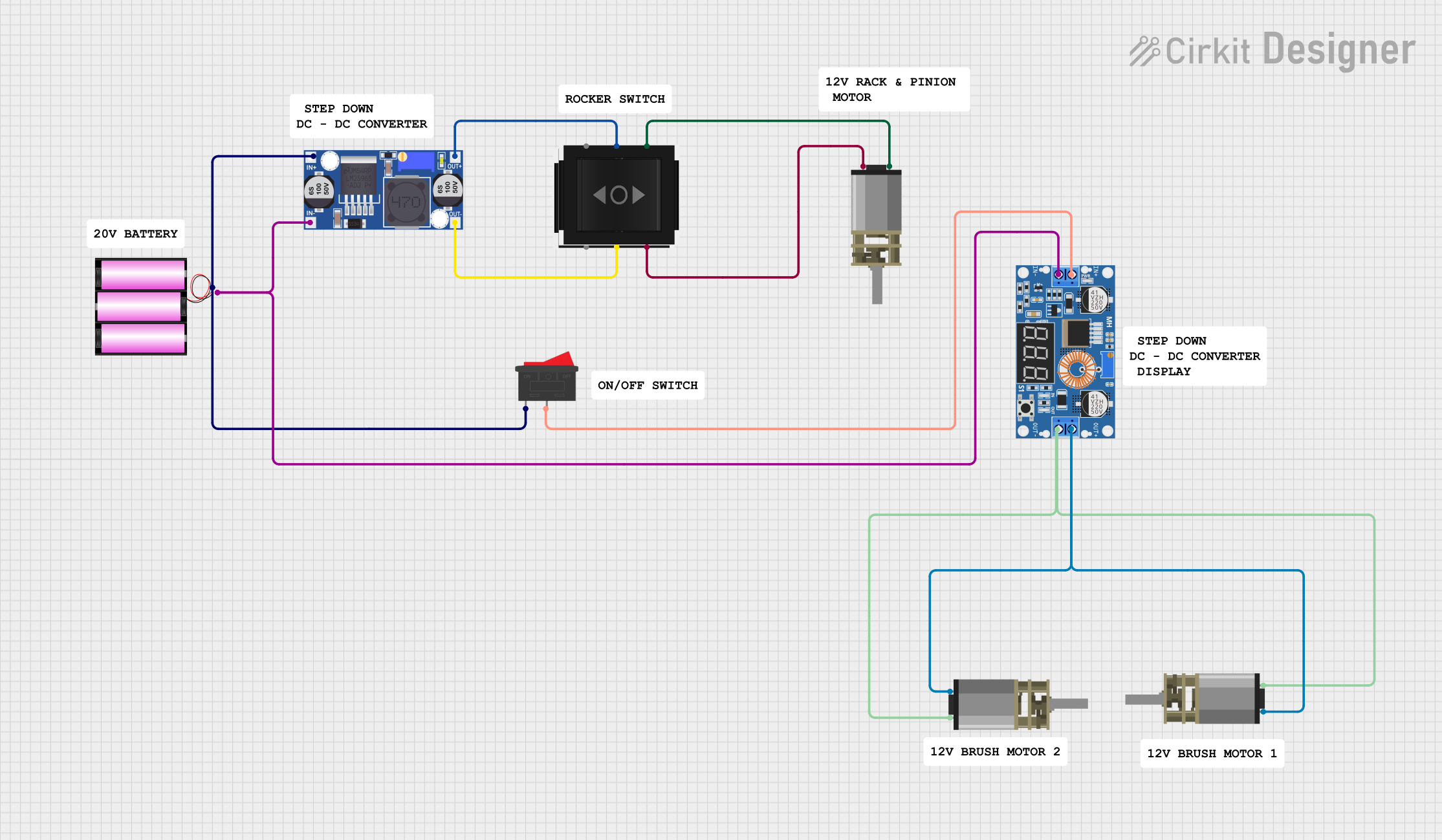
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Regulator Stepdown DC XL4015 CC CV

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: 4V to 38V DC
- Output Voltage Range: 1.25V to 36V DC (adjustable)
- Output Current: Up to 5A (with proper heat sinking)
- Maximum Output Power: 75W (with proper heat sinking)
- Conversion Efficiency: Up to 96%
- Switching Frequency: 180kHz
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IN+ | Input voltage positive terminal |
| 2 | IN- | Input voltage negative terminal |
| 3 | OUT+ | Output voltage positive terminal |
| 4 | OUT- | Output voltage negative terminal |
| 5 | CV | Constant voltage adjustment potentiometer |
| 6 | CC | Constant current adjustment potentiometer |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connection: Connect the input voltage to the IN+ and IN- terminals, ensuring that the input does not exceed the module's maximum voltage rating.
- Output Voltage Adjustment: Turn the CV potentiometer to adjust the output voltage to the desired level. Use a multimeter to monitor the voltage at the OUT+ and OUT- terminals.
- Output Current Adjustment: If operating in CC mode, adjust the CC potentiometer to set the maximum current limit. This is particularly useful when charging batteries or driving LEDs.
- Load Connection: Connect the load to the OUT+ and OUT- terminals. Ensure that the load does not draw more current than the module's maximum rating.
- Heat Management: For applications drawing high current or operating at high power, attach a heat sink to the module to prevent overheating.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always verify input and output voltages with a multimeter before connecting sensitive loads.
- Gradually adjust the potentiometers while monitoring the changes to prevent damage to the load.
- Ensure that the input voltage is at least 1.5V higher than the desired output voltage for proper regulation.
- Avoid adjusting the potentiometers while the module is under high load to prevent voltage/current spikes.
- Use adequate wiring thickness to handle the current without excessive voltage drop or overheating.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
- Output voltage does not match the setting: Re-calibrate the CV potentiometer and check for any loose connections.
- Module overheats: Ensure proper heat sinking is in place, reduce the load, or improve airflow around the module.
- Inconsistent output current: Verify that the CC potentiometer is correctly adjusted and that the load does not exceed the module's specifications.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the XL4015 to charge lithium batteries? A: Yes, the XL4015 can be used to charge lithium batteries by setting the CV to the battery's charge voltage and the CC to the desired charge current.
Q: What is the difference between CC and CV modes? A: In CV mode, the module regulates the output voltage to a fixed level regardless of the load, while in CC mode, it regulates the output current, which is useful for applications like battery charging or LED driving where current limiting is required.
Q: How do I know if I need a heat sink? A: If the module is operating at high power levels or the ambient temperature is high, a heat sink is recommended to prevent overheating and ensure reliable operation.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The XL4015 does not require any code for basic operation. However, if you wish to monitor the output voltage or current using an Arduino UNO, you can use the following example code to read analog values from the module's output.
// Define the analog input pin connected to the output voltage
const int analogPin = A0;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud rate
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the output voltage
int sensorValue = analogRead(analogPin);
// Convert the analog reading (which goes from 0 - 1023) to a voltage (0 - 5V)
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Print out the voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.println(voltage);
// Wait for a second before reading again
delay(1000);
}
Note: This code assumes that the output voltage of the XL4015 is within the 0-5V range that the Arduino can read. If the voltage is higher, you will need a voltage divider to scale down the voltage to a safe level for the Arduino's analog input.