
How to Use esp32 UWB: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
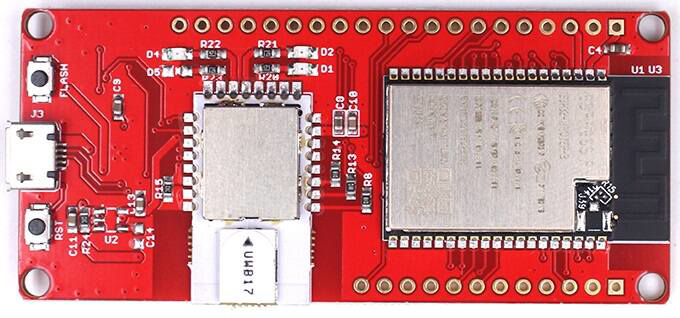
 Design with esp32 UWB in Cirkit Designer
Design with esp32 UWB in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32 UWB (Ultra-Wideband) is a microcontroller developed by Demo, with the part ID Esp32 DW3000(UWB). This component integrates UWB technology, enabling precise location tracking and short-range communication. It also features Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it a versatile choice for IoT applications. The ESP32 UWB is particularly suited for scenarios requiring high positioning accuracy and low power consumption.
Explore Projects Built with esp32 UWB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer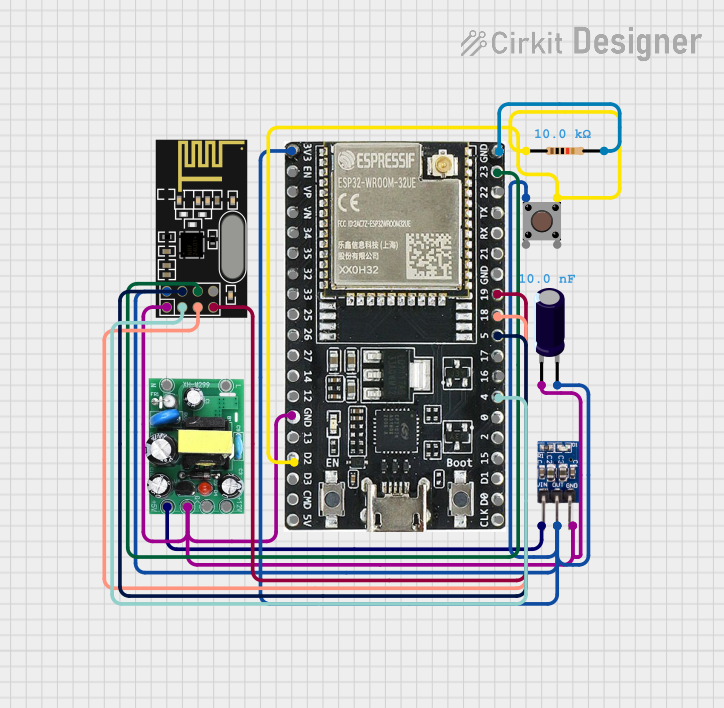
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer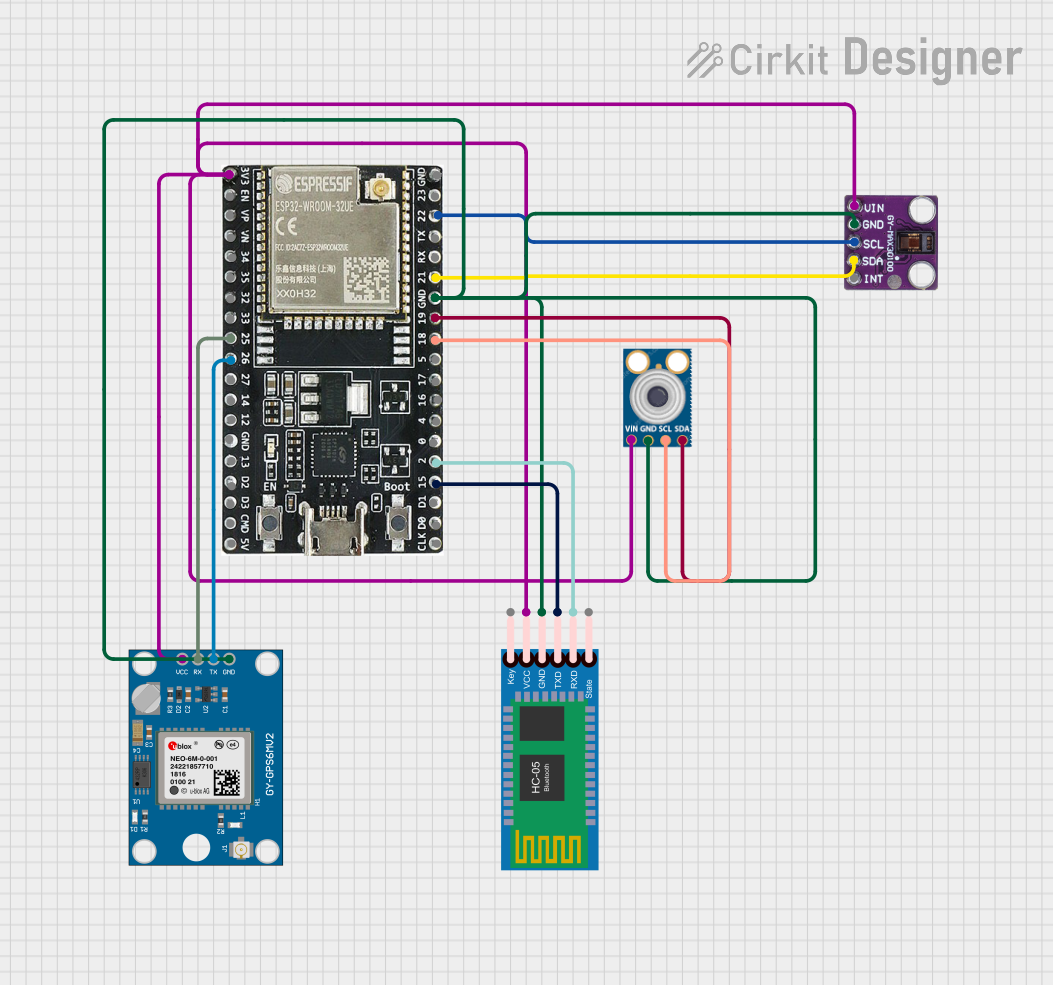
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer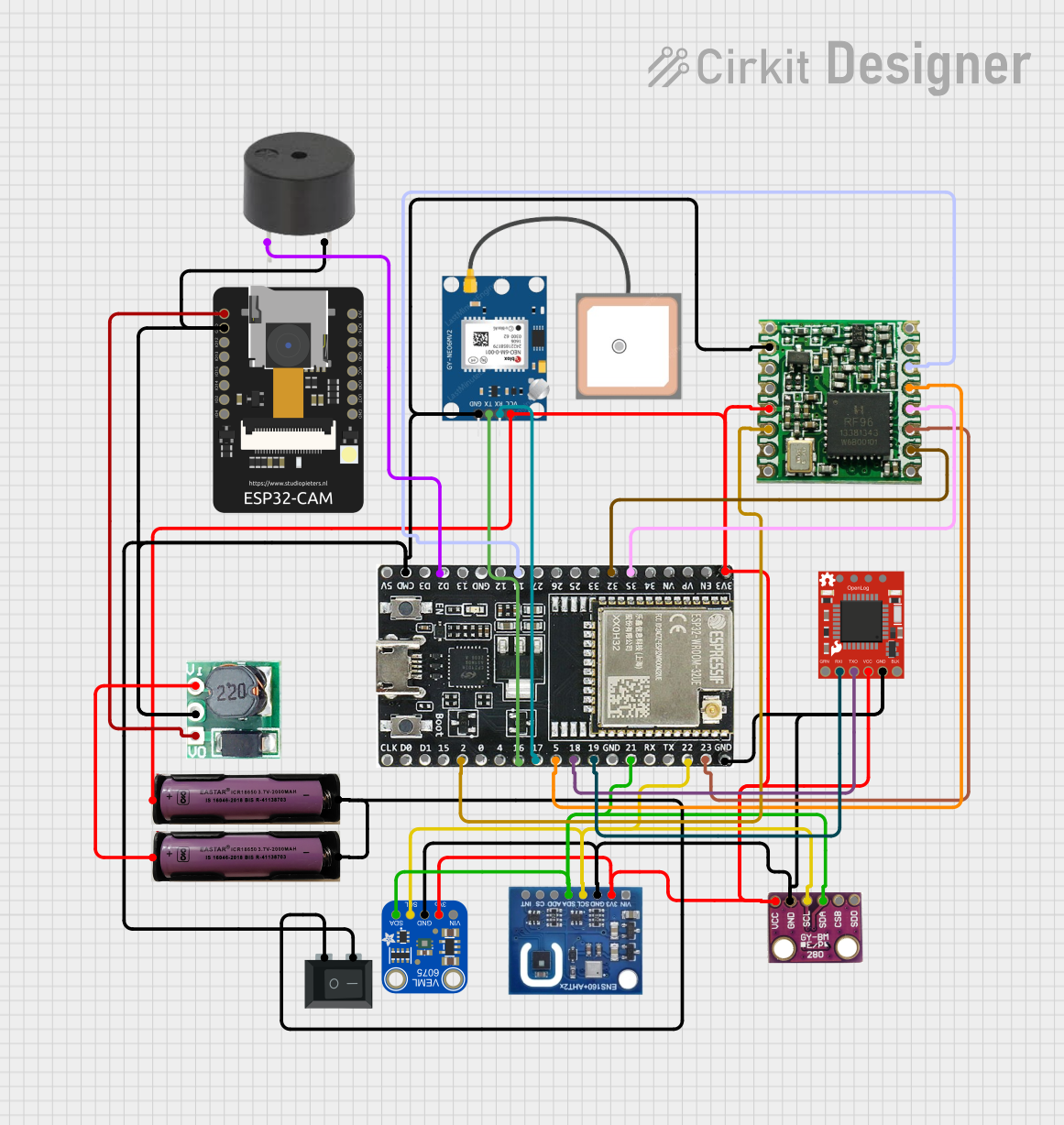
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with esp32 UWB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Indoor navigation and positioning systems
- Asset tracking in warehouses and factories
- Proximity-based access control
- Smart home automation
- Real-time location systems (RTLS)
- IoT devices requiring precise spatial awareness
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Demo |
| Part ID | Esp32 DW3000(UWB) |
| Microcontroller Core | Dual-core Xtensa LX6 |
| UWB Frequency Range | 3.1 GHz to 10.6 GHz |
| UWB Data Rate | Up to 6.8 Mbps |
| Wi-Fi Standard | 802.11 b/g/n |
| Bluetooth Version | Bluetooth 4.2 (BLE) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Power Consumption | Low power (varies by mode) |
| Positioning Accuracy | ±10 cm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 18 mm x 25 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | TXD | UART Transmit Data |
| 4 | RXD | UART Receive Data |
| 5 | GPIO0 | General Purpose I/O Pin 0 |
| 6 | GPIO1 | General Purpose I/O Pin 1 |
| 7 | SPI_MOSI | SPI Master Out Slave In |
| 8 | SPI_MISO | SPI Master In Slave Out |
| 9 | SPI_CLK | SPI Clock |
| 10 | SPI_CS | SPI Chip Select |
| 11 | UWB_TX | UWB Transmit |
| 12 | UWB_RX | UWB Receive |
| 13 | RESET | Reset Pin |
| 14 | EN | Enable Pin (used to wake the module) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP32 UWB in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V power source and GND to ground.
- Communication Interface: Use UART or SPI for communication with a microcontroller or host device.
- UWB Antenna: Ensure the UWB antenna is properly connected and positioned for optimal signal transmission and reception.
- GPIO Pins: Configure GPIO pins as needed for additional functionality, such as controlling LEDs or reading sensors.
- Reset and Enable: Use the RESET pin to restart the module and the EN pin to wake it from sleep mode.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable 3.3V power supply to avoid damage or erratic behavior.
- Antenna Placement: Place the UWB antenna in an open area, away from metal objects, to minimize interference.
- Heat Management: Operate the module within the specified temperature range (-40°C to +85°C) to prevent overheating.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly update the firmware to ensure compatibility and access to the latest features.
Example: Connecting ESP32 UWB to Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and use the ESP32 UWB with an Arduino UNO for basic communication:
Wiring Diagram
| ESP32 UWB Pin | Arduino UNO Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| TXD | RX (Pin 0) |
| RXD | TX (Pin 1) |
Arduino Code Example
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial UWBSerial(10, 11); // RX = Pin 10, TX = Pin 11
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication with the ESP32 UWB
Serial.begin(9600); // Communication with PC
UWBSerial.begin(115200); // Communication with ESP32 UWB
Serial.println("ESP32 UWB Test Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the ESP32 UWB
if (UWBSerial.available()) {
String data = UWBSerial.readString();
Serial.print("Received from ESP32 UWB: ");
Serial.println(data);
}
// Send data to the ESP32 UWB
if (Serial.available()) {
String command = Serial.readString();
UWBSerial.println(command);
Serial.print("Sent to ESP32 UWB: ");
Serial.println(command);
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication with Host Device
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or baud rate mismatch.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure the baud rate in the code matches the ESP32 UWB's default baud rate.
Inaccurate Positioning
- Cause: Poor antenna placement or interference.
- Solution: Reposition the antenna in an open area, away from metal objects or other sources of interference.
Module Not Powering On
- Cause: Insufficient or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Verify the power source provides a stable 3.3V and sufficient current.
Overheating
- Cause: Operating outside the recommended temperature range.
- Solution: Ensure the module is used within the specified temperature range (-40°C to +85°C).
FAQs
Q1: Can the ESP32 UWB be used outdoors?
A1: Yes, but ensure the module is protected from environmental factors like moisture and extreme temperatures.
Q2: What is the maximum range of the UWB communication?
A2: The maximum range is approximately 10-50 meters, depending on the environment and antenna configuration.
Q3: Can I use the ESP32 UWB with other microcontrollers?
A3: Yes, the module supports UART and SPI interfaces, making it compatible with most microcontrollers.
Q4: How do I update the firmware?
A4: Firmware updates can be performed via the UART interface using the manufacturer's update tool. Refer to the official documentation for detailed instructions.