
How to Use micro:bit: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
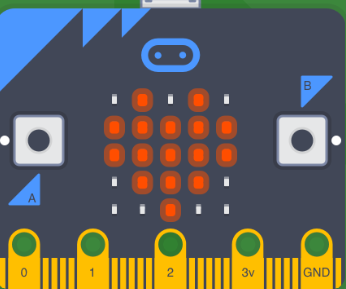
 Design with micro:bit in Cirkit Designer
Design with micro:bit in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The micro:bit is a small, programmable microcontroller board designed for educational purposes. It features an array of built-in sensors, buttons, and a 5x5 LED matrix, making it an excellent tool for learning coding and creating interactive projects. Its compact size and versatility allow users to explore a wide range of applications, from simple games to complex IoT projects.
Explore Projects Built with micro:bit
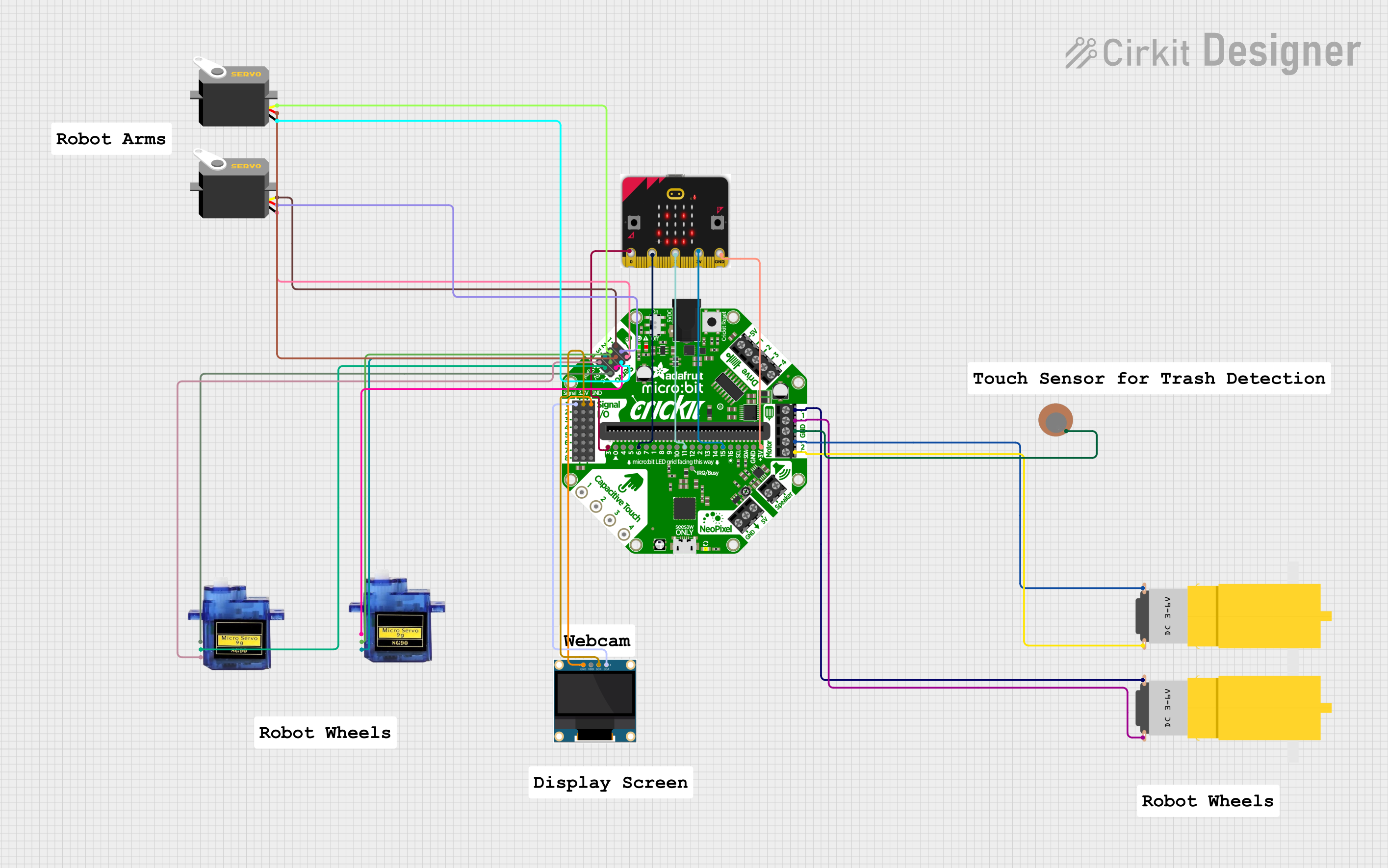
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer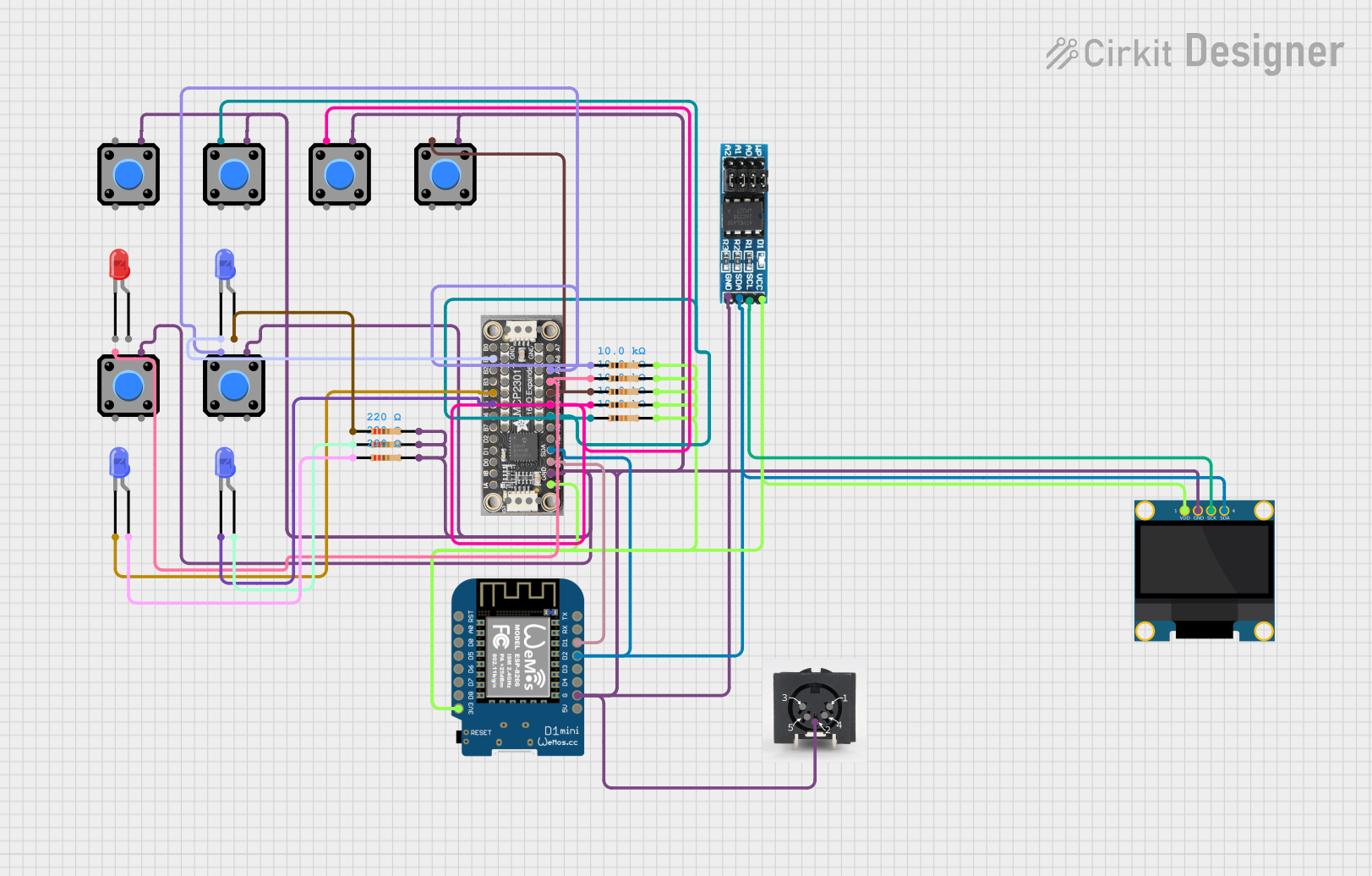
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer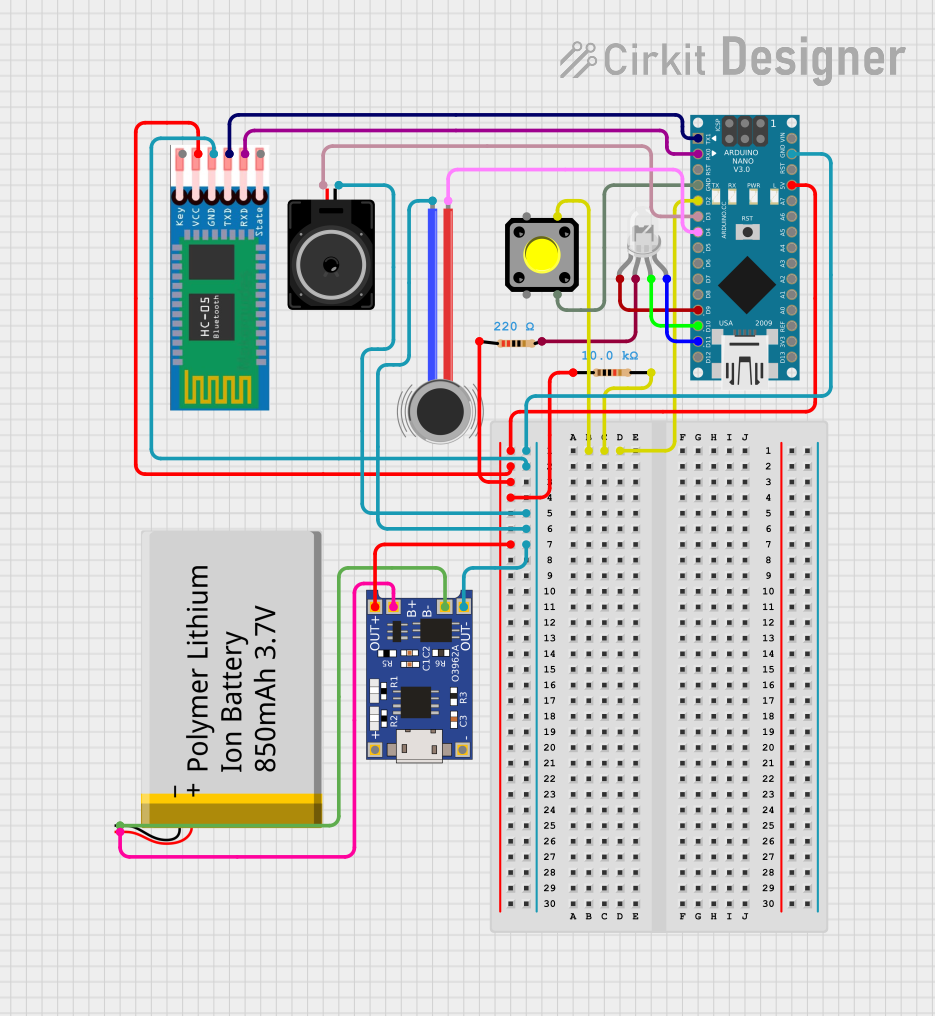
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer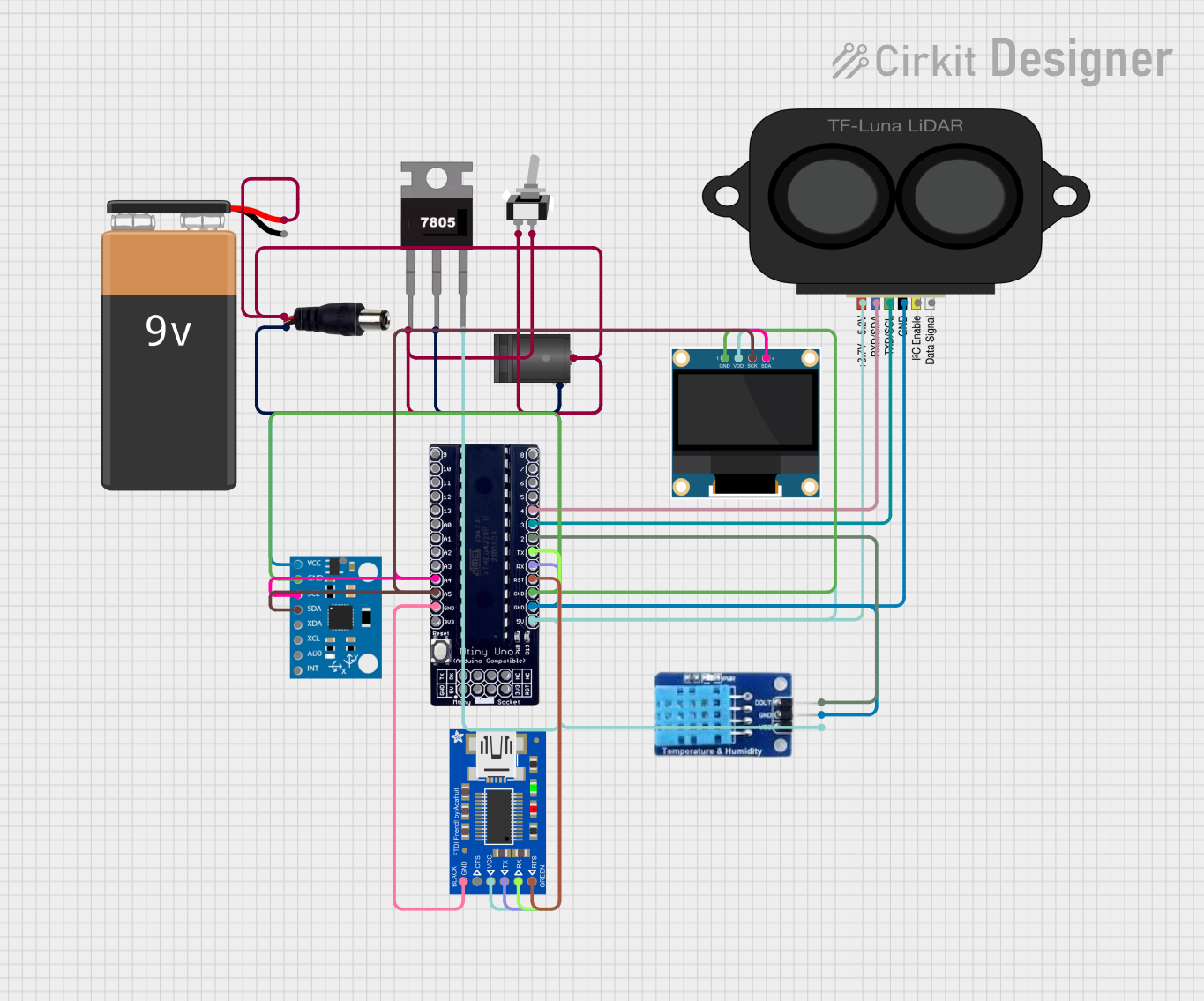
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with micro:bit

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Educational tools for teaching programming and electronics
- Interactive games and animations
- Prototyping IoT devices and smart systems
- Robotics and motor control
- Environmental monitoring using built-in sensors
Technical Specifications
The micro:bit is equipped with a variety of features that make it a powerful and versatile tool for beginners and advanced users alike.
Key Technical Details
- Processor: 32-bit ARM Cortex-M0 CPU
- Flash Memory: 256 KB
- RAM: 16 KB
- Power Supply: 3V (via battery pack) or 5V (via USB)
- Connectivity: Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), USB
- Sensors: Accelerometer, Magnetometer (Compass)
- I/O Pins: 25 edge connector pins (3 are large and user-friendly)
- Display: 5x5 LED matrix
- Buttons: 2 programmable buttons (A and B)
- Other Features: Temperature sensor, light sensor, and touch-sensitive logo
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The micro:bit has 25 edge connector pins, but the most commonly used pins are the 3 large ones (P0, P1, P2) and the power pins. Below is a table summarizing the key pins:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| P0 | Pin 0 | General-purpose I/O pin, often used for analog or digital input/output. |
| P1 | Pin 1 | General-purpose I/O pin, often used for analog or digital input/output. |
| P2 | Pin 2 | General-purpose I/O pin, often used for analog or digital input/output. |
| 3V | 3V Power | Provides 3V power output for external components. |
| GND | Ground | Ground connection for completing circuits. |
| P3-P22 | Other GPIO Pins | Additional general-purpose I/O pins available via the edge connector. |
Usage Instructions
The micro:bit is designed to be beginner-friendly and can be programmed using block-based editors like Microsoft MakeCode, Python, or JavaScript. Below are the steps to use the micro:bit in a circuit and some best practices.
How to Use the micro:bit
- Power the micro:bit:
- Connect the micro:bit to your computer using a micro-USB cable.
- Alternatively, use a battery pack with 2 AAA batteries for portable projects.
- Write and Upload Code:
- Use the Microsoft MakeCode editor or Python editor to write your program.
- Download the compiled
.hexfile and drag it onto the micro:bit drive that appears on your computer.
- Connect External Components:
- Use alligator clips or a breakout board to connect external components (e.g., LEDs, sensors) to the edge connector pins.
- Run the Program:
- Once the code is uploaded, the micro:bit will automatically start running the program.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid shorting the pins or connecting components that draw excessive current.
- Use resistors when connecting LEDs to prevent damage to the micro:bit.
- Ensure the micro:bit is powered off when connecting or disconnecting external components.
- For wireless communication, ensure Bluetooth is enabled in your code.
Example: Using the micro:bit with an Arduino UNO
The micro:bit can communicate with an Arduino UNO via serial communication. Below is an example of Python code for the micro:bit and Arduino code for the UNO.
micro:bit Python Code
from microbit import *
Send data to Arduino via serial communication
while True: # Send a message every second uart.write("Hello Arduino!\n") sleep(1000)
Arduino UNO Code
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
// Read data from the micro:bit
String message = Serial.readString();
Serial.println("Received: " + message); // Print the received message
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
micro:bit Not Detected by Computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is a data cable (not just a charging cable).
- Try a different USB port or restart your computer.
- Check if the micro:bit's power LED is on.
Code Not Running on the micro:bit:
- Verify that the
.hexfile was successfully copied to the micro:bit drive. - Ensure the code is free of syntax errors.
- Reset the micro:bit by pressing the reset button on the back.
- Verify that the
External Components Not Working:
- Double-check the wiring and connections.
- Ensure the components are compatible with the micro:bit's voltage and current ratings.
- Test the components separately to confirm they are functional.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the micro:bit without a computer?
A: Yes, you can power the micro:bit using a battery pack and run pre-uploaded programs.
Q: How do I reset the micro:bit?
A: Press the small reset button on the back of the micro:bit to restart it.
Q: Can I connect the micro:bit to Wi-Fi?
A: The micro:bit does not have built-in Wi-Fi, but you can use external modules like the ESP8266 or ESP32 for Wi-Fi connectivity.
Q: What programming languages are supported?
A: The micro:bit supports block-based coding (MakeCode), Python, and JavaScript.