
How to Use HW-827: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with HW-827 in Cirkit Designer
Design with HW-827 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The HW-827 is a fixed-value resistor designed for use in electronic circuits. Resistors are passive components that oppose the flow of electric current, and the HW-827 is specifically engineered to provide a precise resistance value. This component is commonly used for controlling voltage and current within circuits, dividing voltages, biasing active elements like transistors, and in filter networks. Due to its specific resistance value and power rating, the HW-827 is suitable for a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial machinery.
Explore Projects Built with HW-827
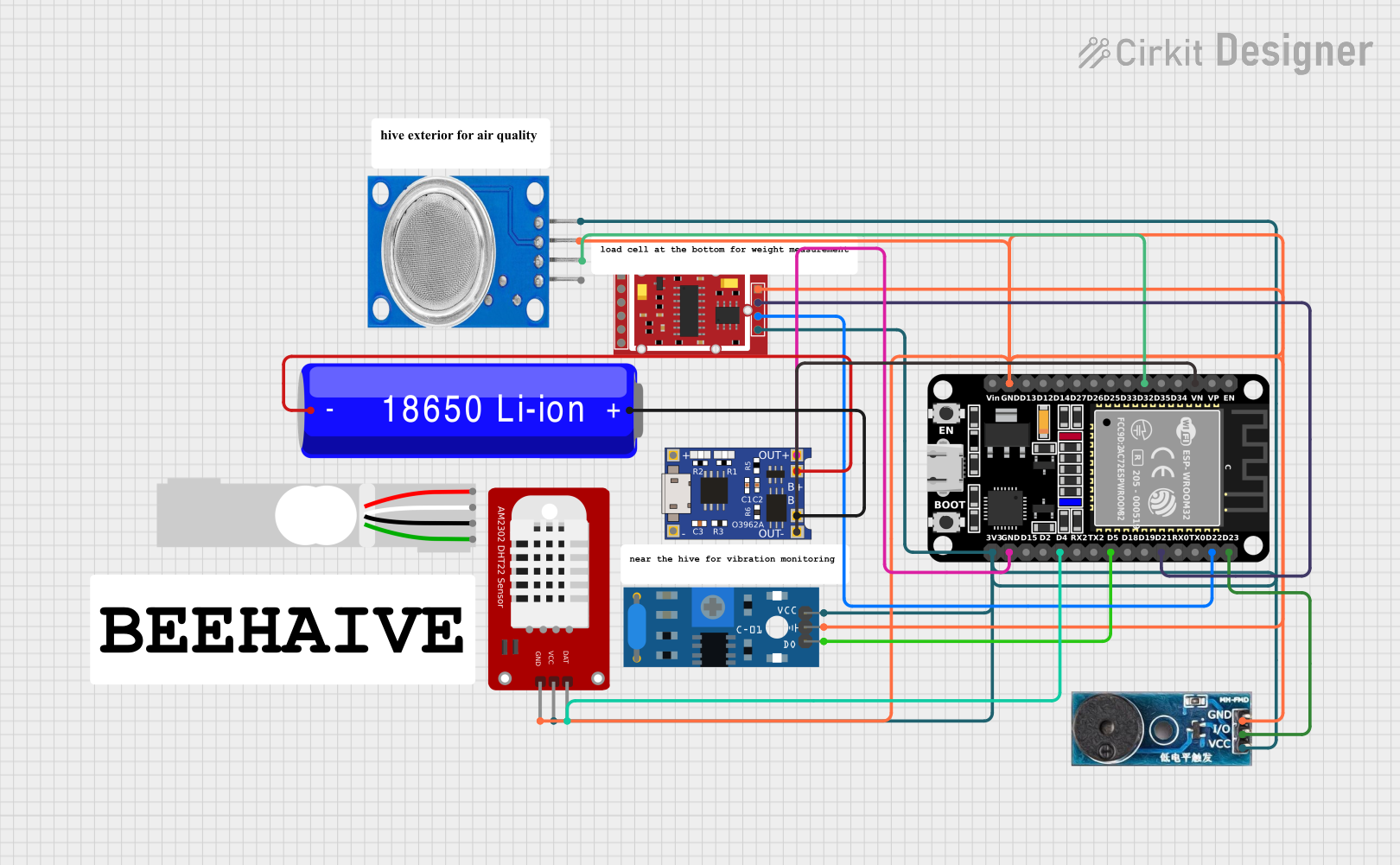
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer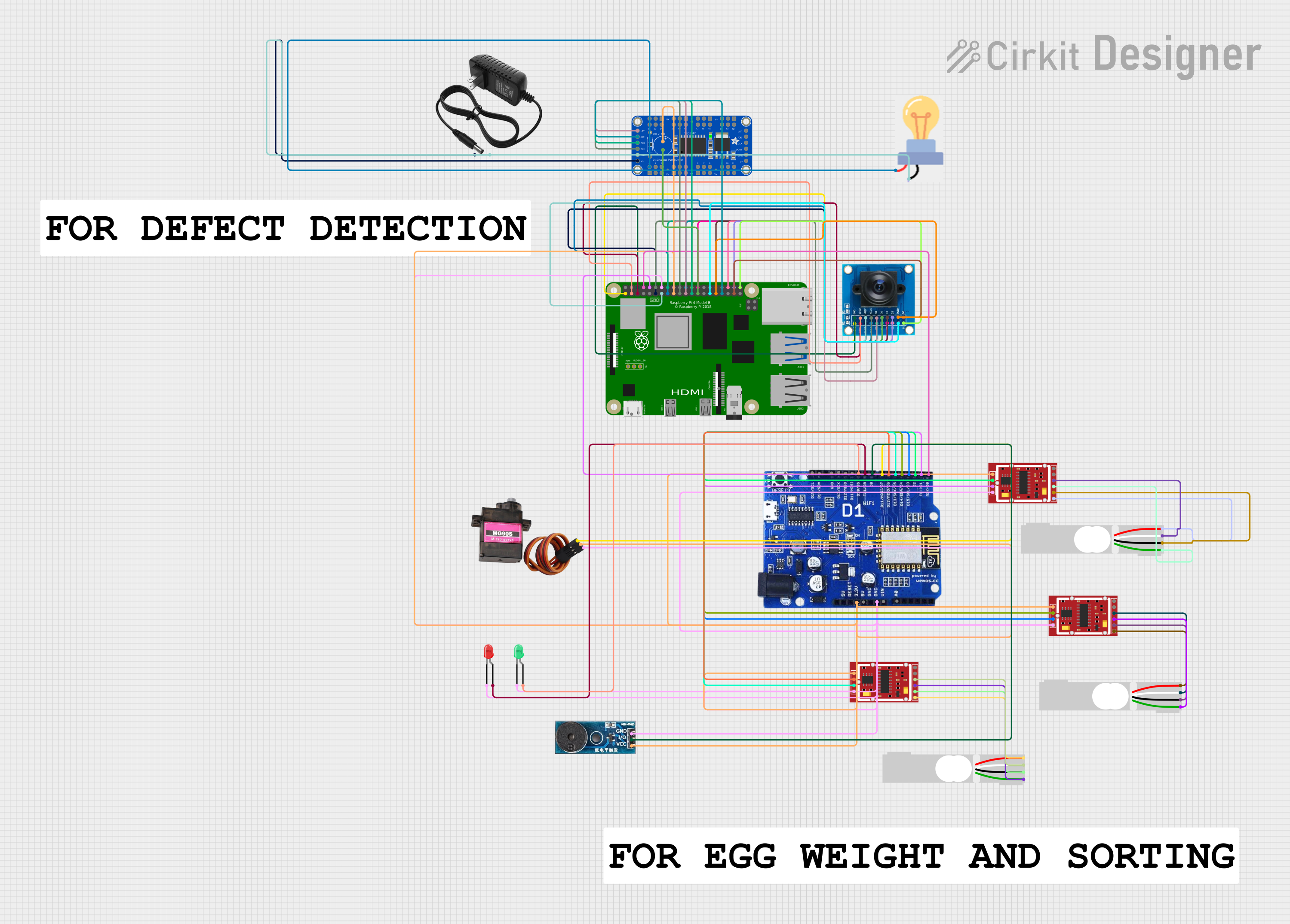
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer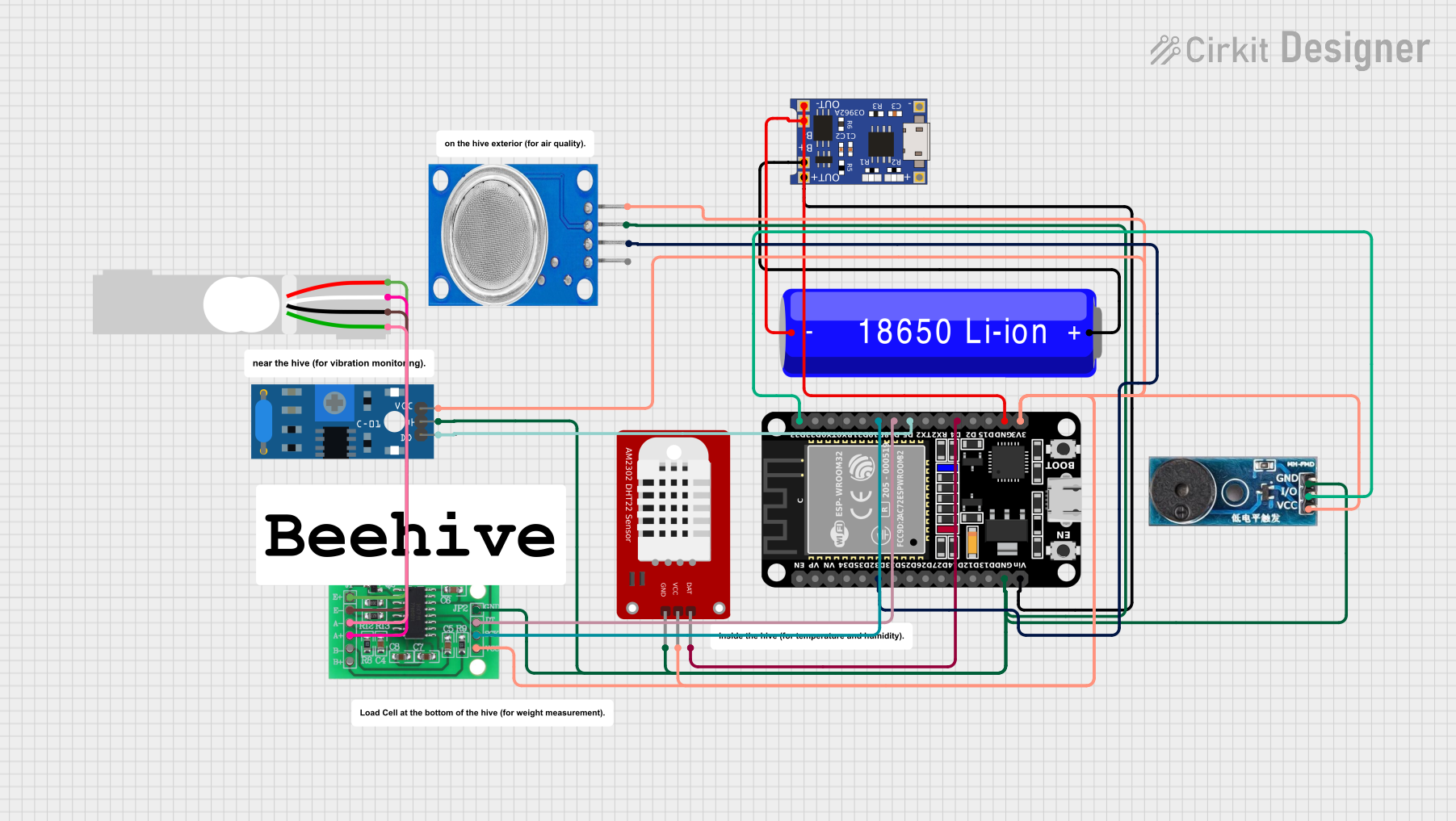
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with HW-827

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Resistance Value: Specified in ohms (Ω), the exact value should be marked on the component or specified in the datasheet.
- Tolerance: The permissible variation in the resistance value, typically expressed as a percentage (e.g., ±1%).
- Power Rating: The maximum power the resistor can dissipate without damage, usually given in watts (W).
- Temperature Coefficient: Indicates how the resistance value changes with temperature, expressed in parts per million per degree Celsius (ppm/°C).
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Since the HW-827 is a resistor, it does not have a pin configuration in the traditional sense, as it is a two-terminal device. The terminals are identical and interchangeable, known as leads. Below is a representation of the resistor's physical configuration:
| Lead | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Connects to one end of the circuit or component |
| 2 | Connects to the other end of the circuit or component |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the HW-827 in a Circuit
- Identify the Resistance Value: Check the resistor's body for color bands or printed value to determine its resistance.
- Determine the Orientation: The HW-827 can be placed in any direction; its leads are non-polarized.
- Circuit Integration: Solder or insert the HW-827 into the circuit, ensuring a solid electrical connection to both leads.
- Power Considerations: Ensure that the power dissipated by the resistor does not exceed its power rating.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overheating: Ensure that the resistor operates within its specified temperature range to prevent damage.
- Placement: Position the resistor in a manner that allows for adequate air circulation to dissipate heat effectively.
- Series and Parallel Configurations: Combine multiple HW-827 resistors in series or parallel to achieve desired resistance values and power ratings.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Excessive Heat: If the resistor is too hot, it may be dissipating more power than its rating allows. Check the circuit for errors in voltage or current.
- Open Circuit: A lack of continuity could indicate a damaged resistor. Use a multimeter to check for an open circuit.
- Incorrect Resistance Value: Ensure the correct resistor value is used as per the circuit design.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Verify Circuit Parameters: Double-check the circuit design to ensure the correct resistor value and power rating are used.
- Inspect for Physical Damage: Look for signs of burning or deformation on the resistor body.
- Measure Resistance: Use a multimeter to measure the actual resistance of the HW-827 to confirm it matches the specified value.
FAQs
Q: Can I replace the HW-827 with a resistor of a different power rating? A: Yes, as long as the resistance value is the same and the power rating is equal to or greater than the original.
Q: What happens if I use a resistor with a lower power rating than required? A: The resistor may overheat, fail, or become a fire hazard if it cannot handle the power demands of the circuit.
Q: How do I calculate the power dissipation of the HW-827 in a circuit? A: Use the formula P = V^2/R or P = I^2*R, where P is power in watts, V is voltage across the resistor, I is current through the resistor, and R is the resistance value.
Q: Is the HW-827 suitable for high-frequency applications? A: The suitability for high-frequency applications depends on the resistor's construction. Consult the datasheet for frequency-related specifications.
For any further assistance or detailed information, refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or contact technical support.