
How to Use 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery is a rechargeable nickel-metal hydride (Ni-MH) battery designed to provide reliable power for a wide range of electronic devices. With a nominal voltage of 4.8 volts and a capacity of 2000 milliampere-hours (mAh), this battery is ideal for applications requiring moderate energy storage and consistent performance. It is commonly used in remote-controlled devices, cordless phones, portable tools, and other battery-powered electronics.
Explore Projects Built with 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery
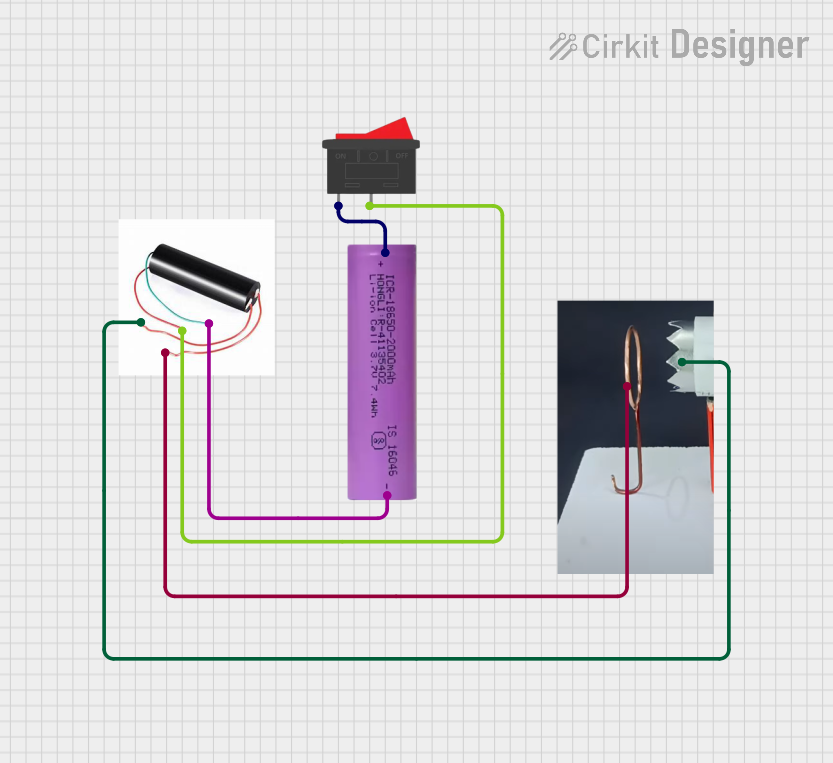
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer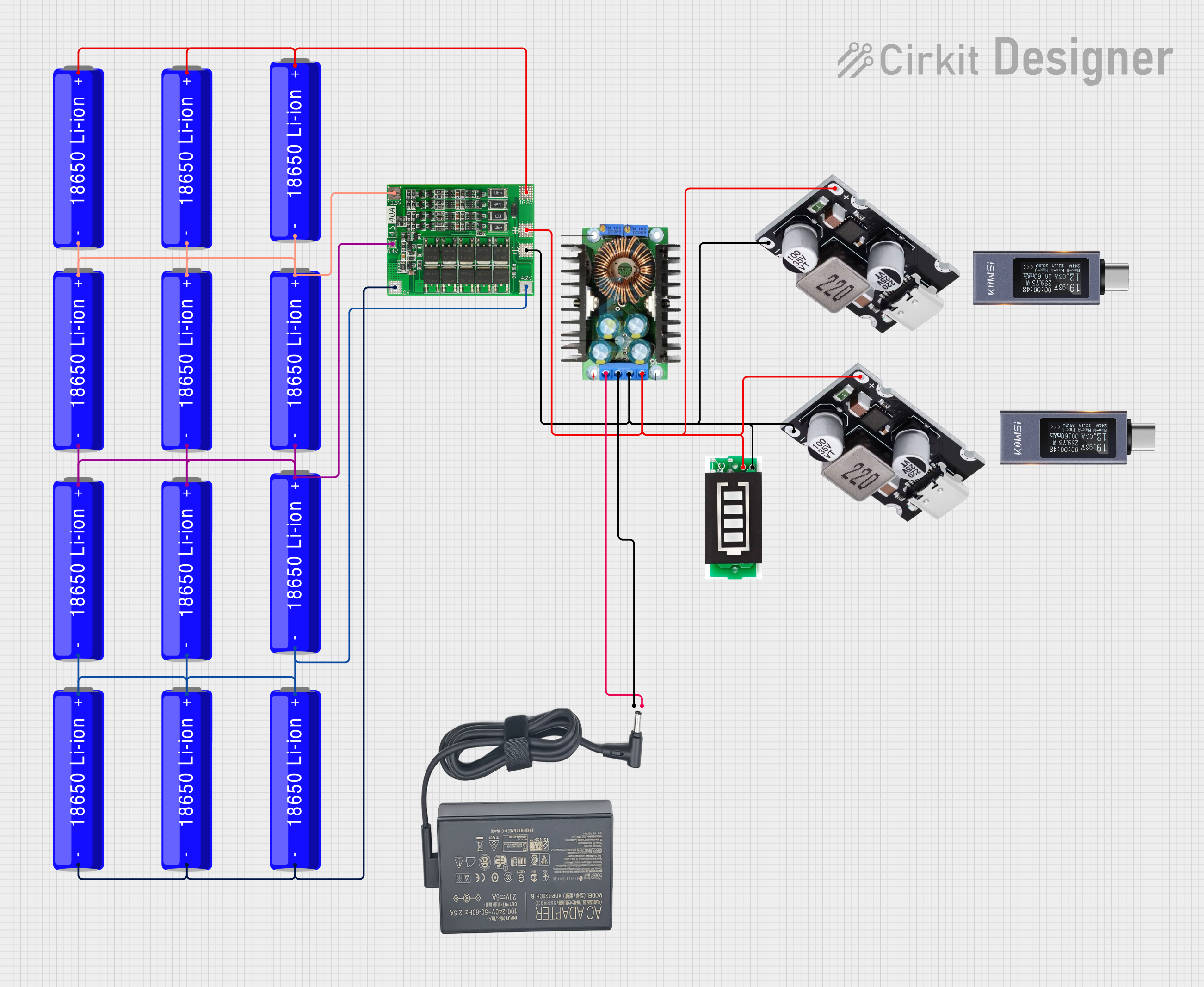
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer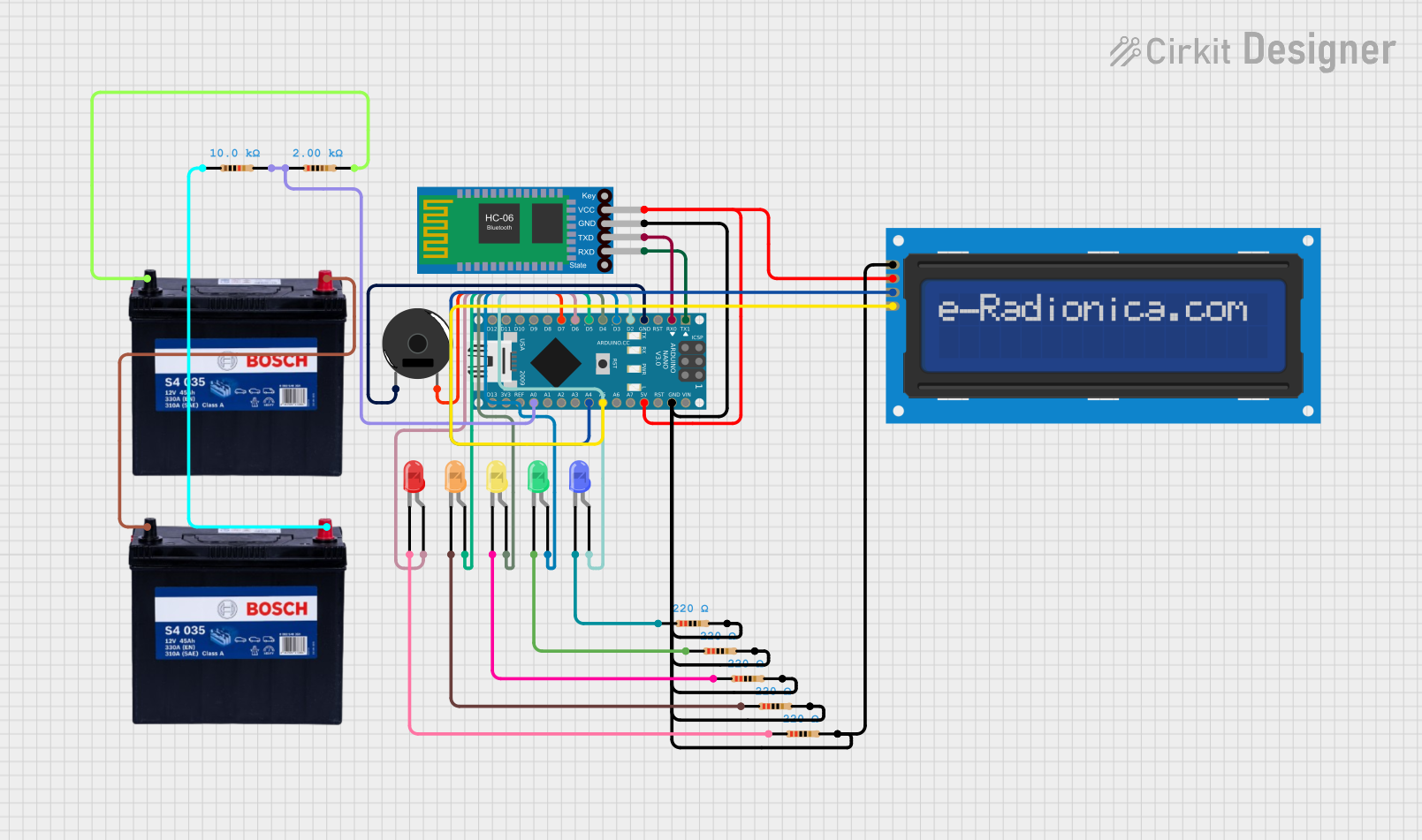
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer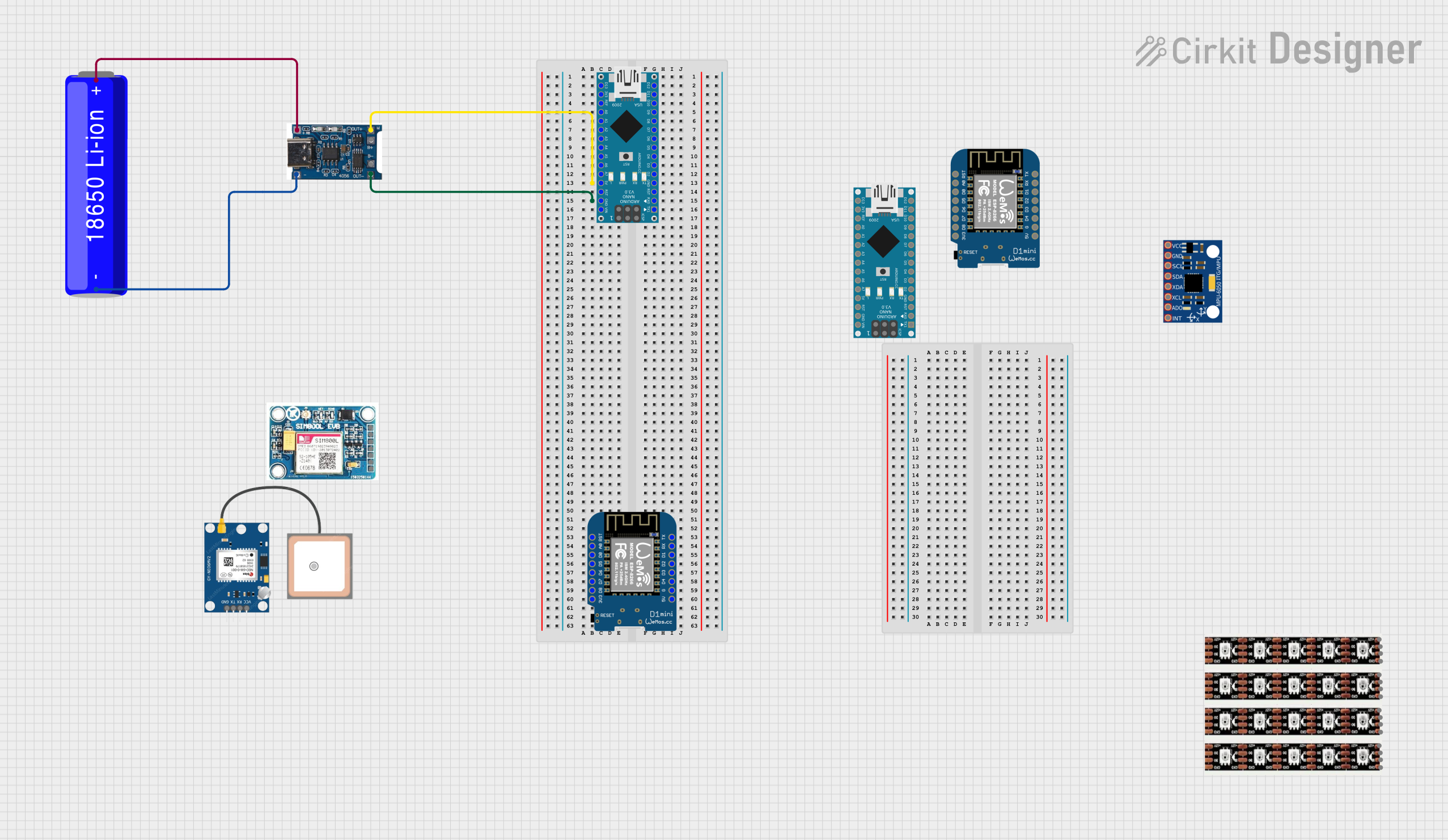
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Remote-controlled toys and vehicles
- Cordless phones and communication devices
- Portable tools and equipment
- Emergency lighting systems
- Backup power for small electronics
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 4.8V |
| Capacity | 2000mAh |
| Chemistry | Nickel-Metal Hydride (Ni-MH) |
| Rechargeable | Yes |
| Standard Charge Rate | 200mA (for 14-16 hours) |
| Fast Charge Rate | 1000mA (for 2-3 hours, with proper charger) |
| Discharge Cutoff Voltage | 4.0V |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C to 45°C (charge), -20°C to 60°C (discharge) |
| Storage Temperature | -20°C to 35°C |
| Dimensions | Varies by manufacturer configuration |
| Weight | Approximately 120g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery typically comes in a pack with two terminals for connection. The pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Positive terminal for power output |
| Negative (-) | Negative terminal for power return |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connection: Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the positive input of your circuit and the negative terminal to the ground (GND) of your circuit.
- Charging: Use a compatible Ni-MH battery charger to recharge the battery. Ensure the charger supports the battery's voltage and capacity specifications.
- Discharge: Avoid discharging the battery below its cutoff voltage (4.0V) to prevent damage and reduce its lifespan.
- Series/Parallel Configuration: If higher voltage or capacity is required, multiple batteries can be connected in series (to increase voltage) or parallel (to increase capacity). Ensure proper balancing and safety precautions.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Charging Safety: Always use a charger specifically designed for Ni-MH batteries to prevent overcharging or overheating.
- Temperature Monitoring: Avoid charging or discharging the battery outside the recommended temperature range.
- Storage: Store the battery in a cool, dry place when not in use. Avoid prolonged storage in a fully discharged state.
- Recycling: Dispose of the battery responsibly at a certified recycling facility to minimize environmental impact.
Example: Using the Battery with an Arduino UNO
The 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery can be used to power an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of how to connect the battery to the Arduino:
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the VIN pin on the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the GND pin on the Arduino UNO.
Sample Code
The following Arduino code demonstrates reading the battery voltage using an analog pin:
// Define the analog pin connected to the battery voltage divider
const int batteryPin = A0;
// Define the reference voltage (5V for Arduino UNO)
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0;
// Define the voltage divider ratio (adjust based on your circuit)
const float voltageDividerRatio = 2.0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the battery pin
int analogValue = analogRead(batteryPin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage
float batteryVoltage = (analogValue / 1023.0) * referenceVoltage * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to ensure the battery voltage does not exceed the Arduino's input voltage range (0-5V).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Using an incompatible charger or faulty charging circuit.
- Solution: Verify the charger specifications and ensure it is designed for Ni-MH batteries.
Short Battery Life:
- Cause: Overcharging, deep discharging, or operating outside the recommended temperature range.
- Solution: Follow proper charging and discharging practices. Avoid extreme temperatures.
Battery Overheating:
- Cause: Charging at a rate higher than the recommended fast charge rate.
- Solution: Use a charger with a current limit suitable for the battery's specifications.
Voltage Drop Under Load:
- Cause: High current draw exceeding the battery's capacity.
- Solution: Use a battery with a higher capacity or connect multiple batteries in parallel.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion.
- Measure Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery's voltage and verify it is within the expected range.
- Inspect Charger: Confirm that the charger is functioning correctly and providing the appropriate voltage and current.
By following these guidelines and best practices, you can maximize the performance and lifespan of your 4.8V 2000mAh Ni-MH battery.