
How to Use Hall Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
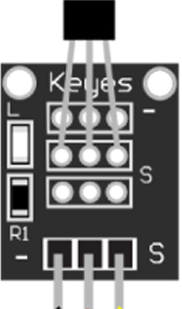
 Design with Hall Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Hall Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Hall sensor is an electronic device that is designed to detect the presence and magnitude of magnetic fields. Utilizing the Hall effect principle, it outputs a voltage proportional to the magnetic field strength. Hall sensors are widely used in various applications, including position sensing, speed detection, and current sensing.
Explore Projects Built with Hall Sensor
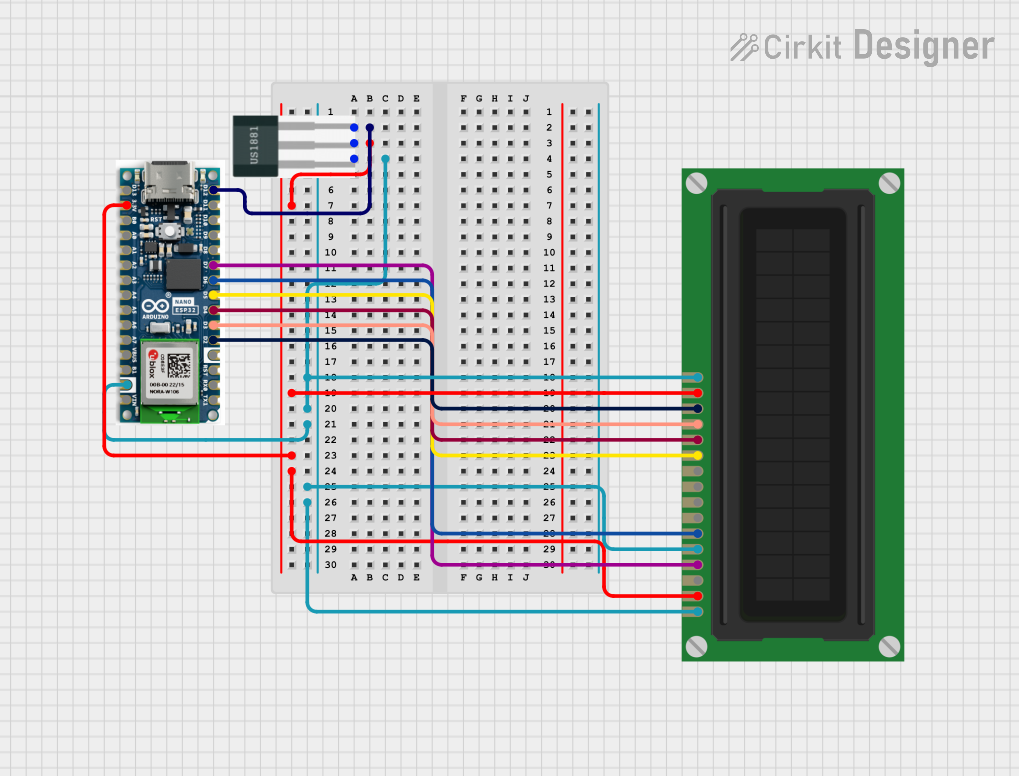
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer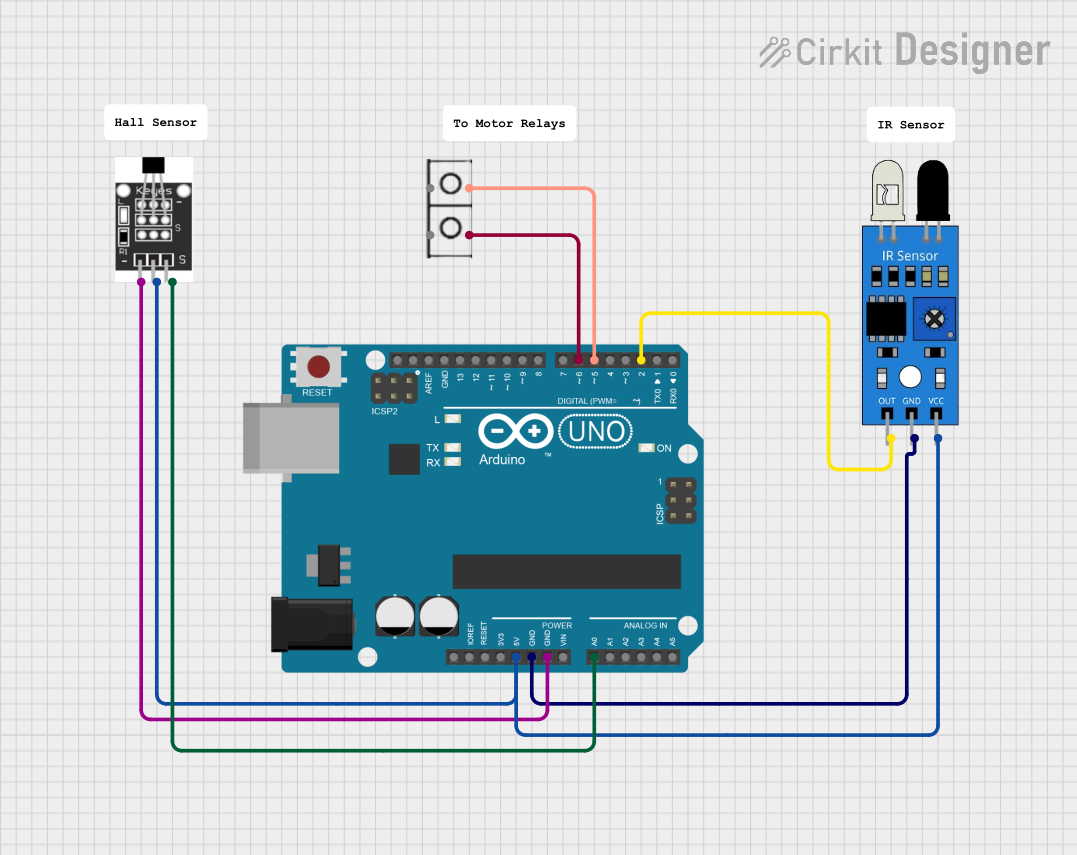
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer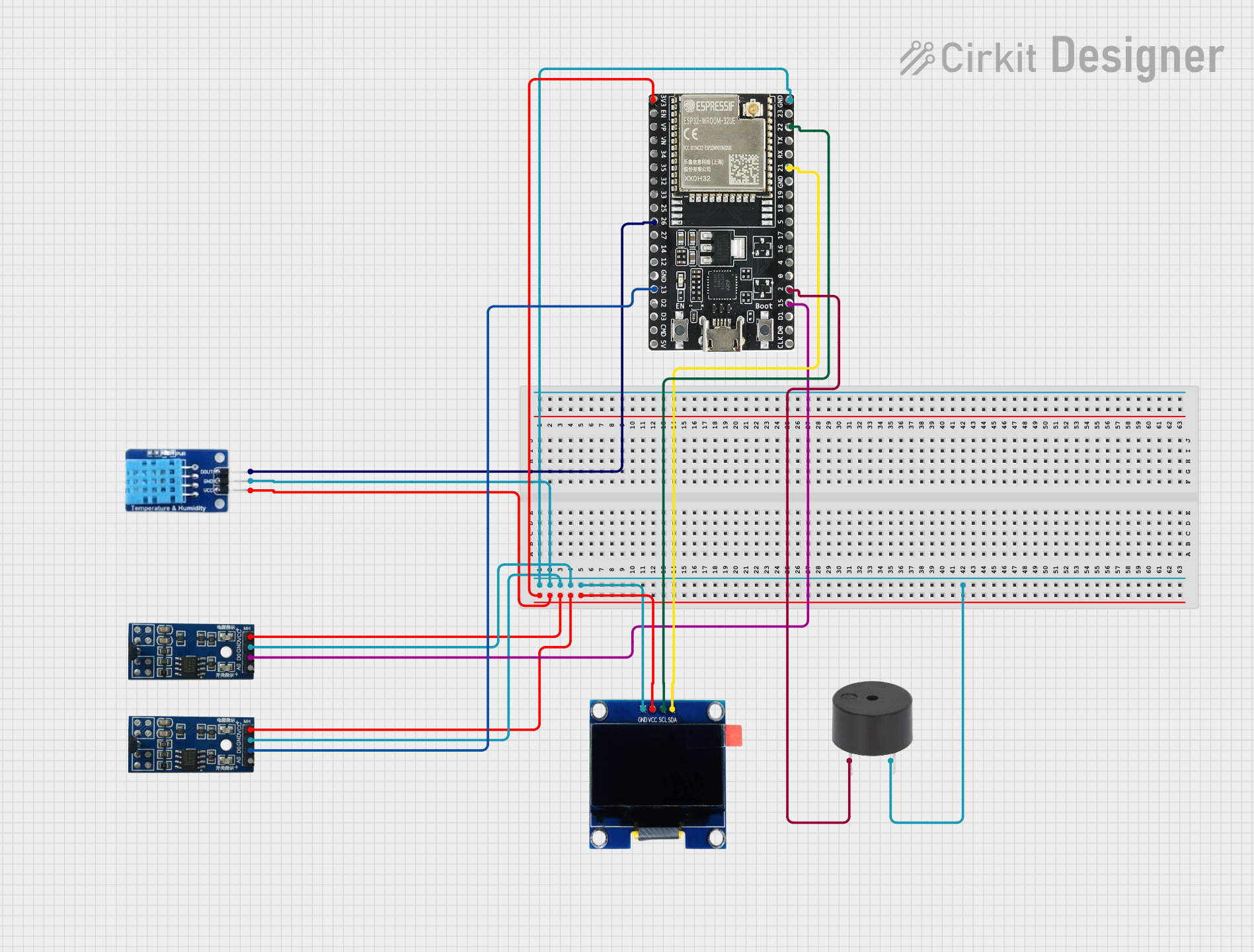
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Hall Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Position Sensing: Detecting the position of a magnet attached to a moving part.
- Speed Detection: Measuring the speed of a rotating object with a magnetic encoder.
- Current Sensing: Non-contact measurement of current flow by detecting the magnetic field around a conductor.
- Brushless DC Motors: Determining the rotor position for proper commutation.
- Automotive Sensors: Wheel speed sensors for ABS systems.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage (Vcc): 3.3V to 5V
- Output Type: Digital (on/off) or Analog (linear)
- Sensitivity: Typically measured in mV/Gauss
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to 85°C (may vary by model)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vcc | Power supply input, typically 3.3V to 5V |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | OUT | Output signal, can be digital or analog depending on the sensor type |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the Vcc pin to a 3.3V or 5V power supply and the GND pin to the ground.
- Output Connection: Connect the OUT pin to an analog or digital input on your microcontroller, depending on the sensor's output type.
- Magnet Placement: Position a magnet near the sensing area of the Hall sensor. The polarity and distance will affect the output.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Magnetic Field Strength: Ensure the magnet's field is within the sensor's sensitivity range.
- Orientation: The sensor is typically sensitive to the magnetic field perpendicular to the face of the sensor.
- Noise Filtering: Use capacitors near the power supply pins to filter out noise.
- Cable Length: Keep the cable between the sensor and microcontroller short to minimize interference.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Example code for interfacing a Hall sensor with an Arduino UNO
int hallPin = 2; // Digital pin connected to Hall sensor's output
int hallState = 0; // Variable for storing the Hall sensor state
void setup() {
pinMode(hallPin, INPUT); // Initialize the hallPin as an input
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
hallState = digitalRead(hallPin); // Read the state of the Hall sensor
Serial.println(hallState); // Print the state to the Serial Monitor
delay(100); // Wait for 100 milliseconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- No Output Signal: Ensure the magnet is close enough and properly oriented relative to the sensor.
- Erratic Readings: Check for electrical noise or interference from nearby components or power supplies.
- Inconsistent Sensing: Verify that the magnet's strength is within the sensor's operating range.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Power Supply Issues: Confirm that the sensor is receiving the correct voltage.
- Connection Check: Inspect all connections for loose wires or poor solder joints.
- Magnet Placement: Adjust the position of the magnet to achieve consistent readings.
FAQs
Q: Can the Hall sensor detect non-magnetic materials? A: No, Hall sensors can only detect magnetic fields and will not respond to non-magnetic materials.
Q: How can I tell if my Hall sensor is analog or digital? A: Check the datasheet of your specific Hall sensor model. Digital sensors will have a binary output (on/off), while analog sensors will provide a continuous voltage range proportional to the magnetic field strength.
Q: What is the maximum distance a Hall sensor can detect a magnet? A: This depends on the magnet's strength and the sensor's sensitivity. Refer to the sensor's datasheet for specific detection range information.
Q: Can I use a Hall sensor to measure AC current? A: Yes, Hall sensors can be used to measure AC current by detecting the magnetic field generated by the current as it changes direction.