
How to Use L298N: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
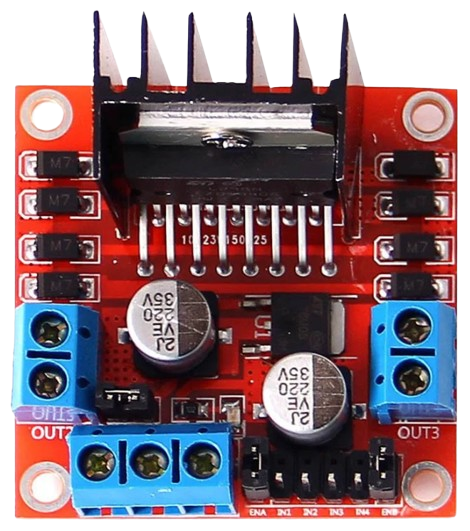
 Design with L298N in Cirkit Designer
Design with L298N in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The L298N is a dual H-bridge motor driver IC designed to control the direction and speed of DC motors and stepper motors. It is widely used in robotics and automation projects due to its ability to drive two motors simultaneously with a current capacity of up to 2A per channel. The L298N is a versatile and robust component, making it ideal for applications such as robotic arms, motorized vehicles, conveyor belts, and other motor-driven systems.
Explore Projects Built with L298N
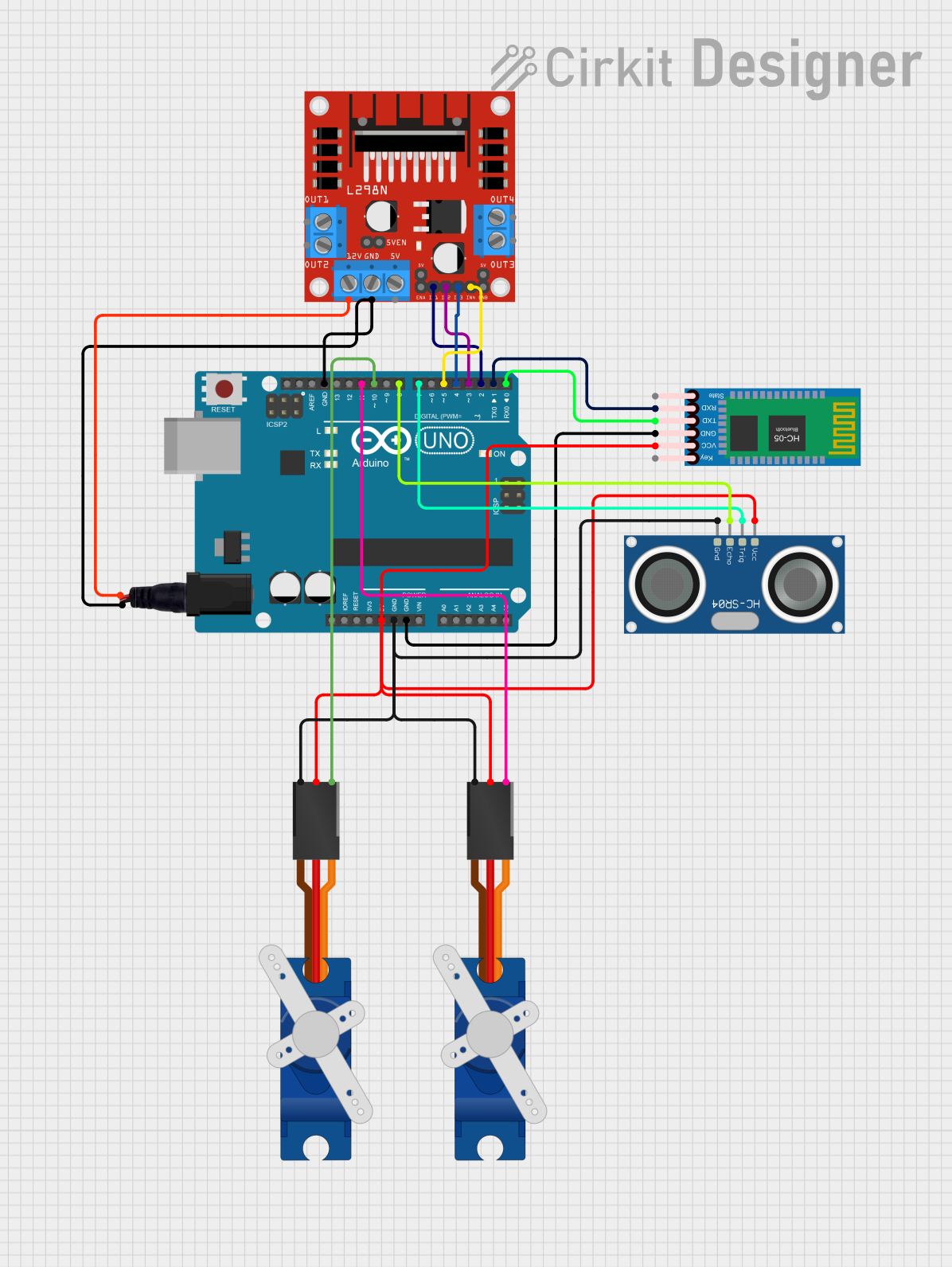
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer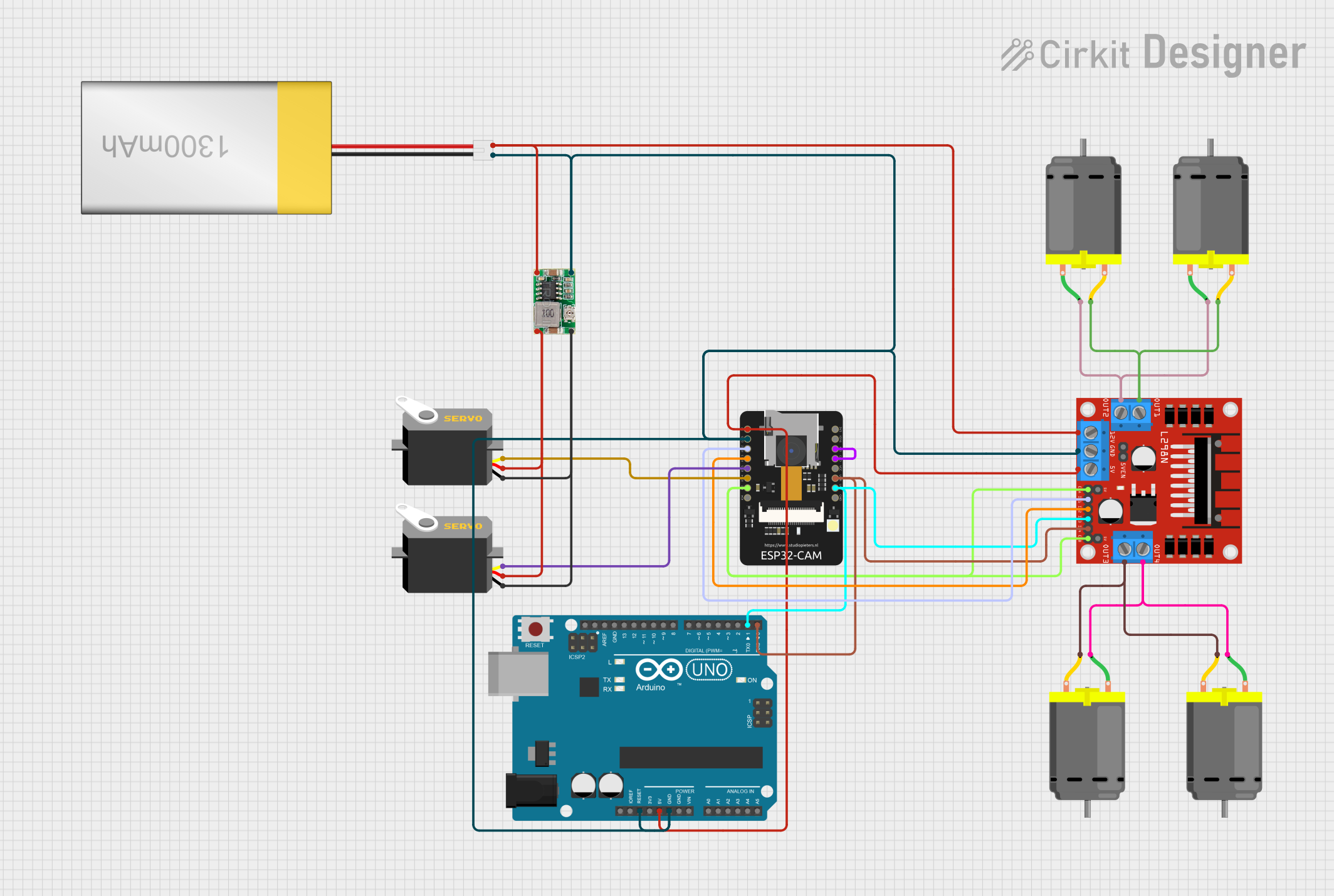
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer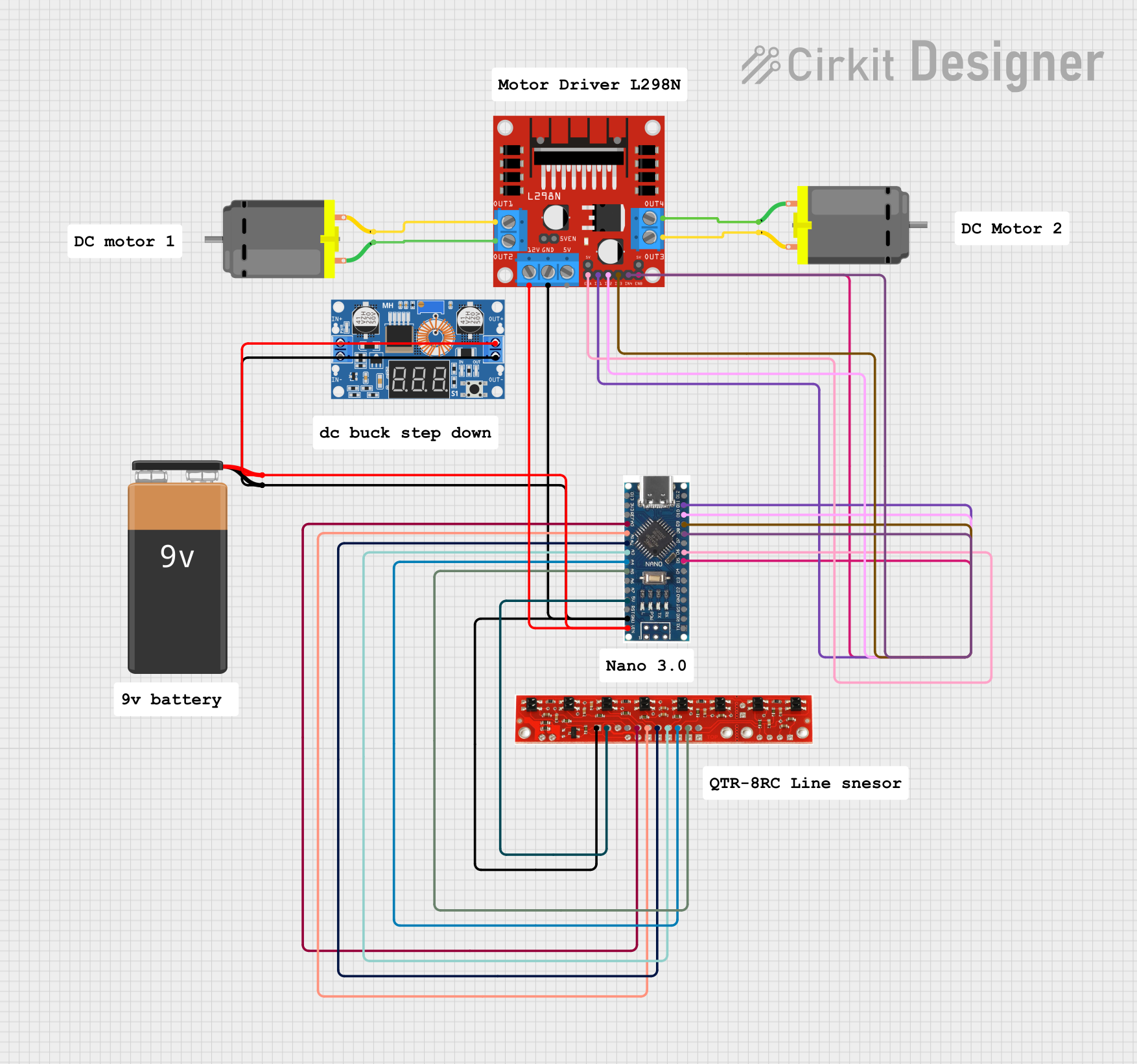
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer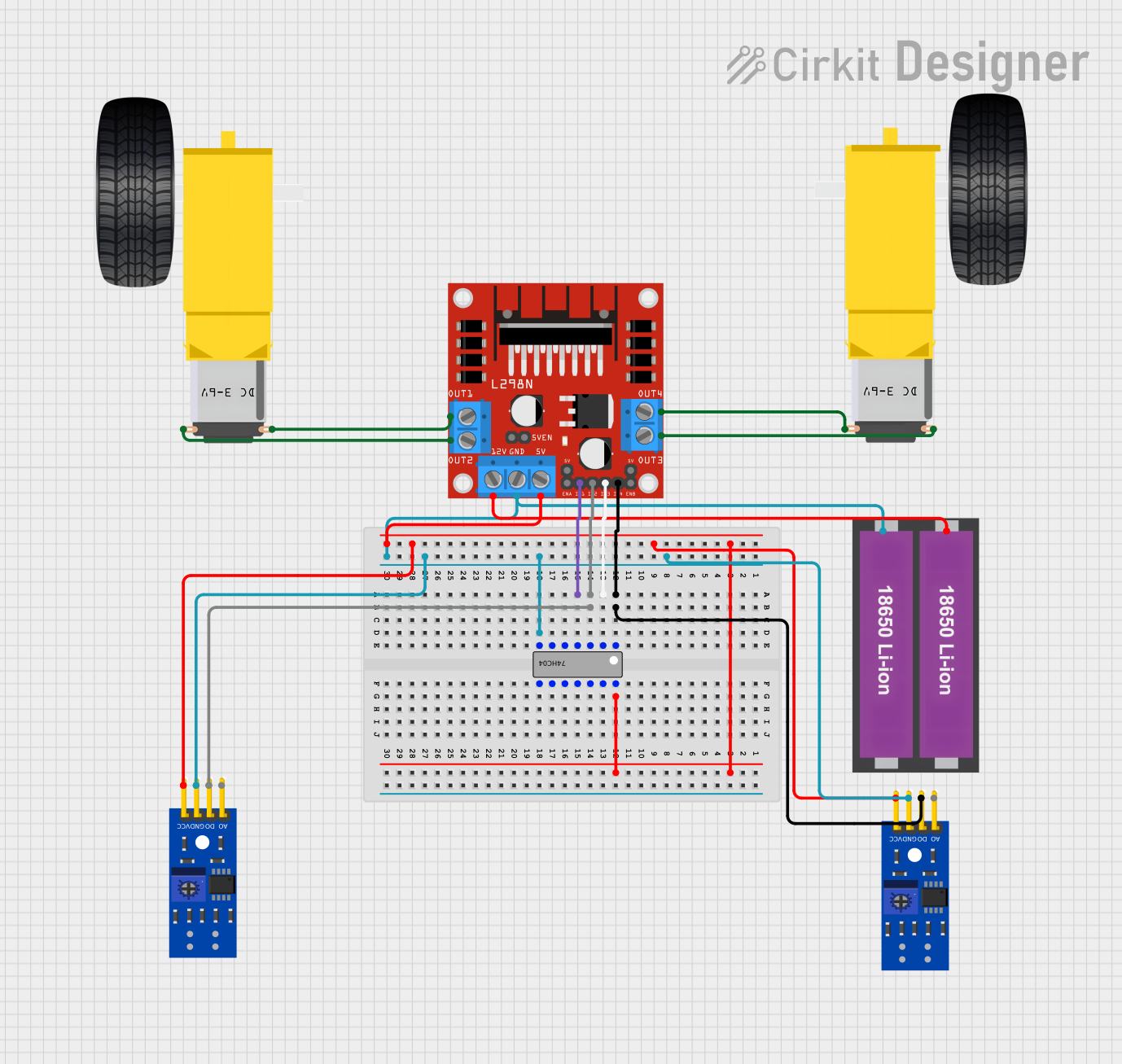
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with L298N

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 5V to 46V
- Output Current: Up to 2A per channel
- Logic Voltage: 5V
- Control Logic Levels: Low (0V to 1.5V), High (2.3V to 5V)
- Power Dissipation: 25W (with proper heat sinking)
- Built-in Protection: Thermal shutdown and overcurrent protection
- Number of Channels: 2 (dual H-bridge)
- Motor Types Supported: DC motors and stepper motors
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The L298N module typically comes with a breakout board for easier use. Below is the pin configuration for the module:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IN1 | Input | Controls the direction of Motor A (High/Low). |
| IN2 | Input | Controls the direction of Motor A (High/Low). |
| IN3 | Input | Controls the direction of Motor B (High/Low). |
| IN4 | Input | Controls the direction of Motor B (High/Low). |
| ENA | Input (PWM) | Enables and controls the speed of Motor A (PWM signal). |
| ENB | Input (PWM) | Enables and controls the speed of Motor B (PWM signal). |
| OUT1 | Output | Connects to one terminal of Motor A. |
| OUT2 | Output | Connects to the other terminal of Motor A. |
| OUT3 | Output | Connects to one terminal of Motor B. |
| OUT4 | Output | Connects to the other terminal of Motor B. |
| 12V | Power Input | Connects to the motor power supply (up to 46V). |
| 5V | Power Output | Provides 5V output (used to power logic circuits if no external 5V is supplied). |
| GND | Ground | Common ground for the circuit. |
Note: The onboard 5V regulator is active only if the motor power supply voltage is greater than 7V.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the L298N in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect the motor power supply (e.g., 12V) to the
12Vpin. - Connect the ground of the power supply to the
GNDpin. - If your microcontroller operates at 5V, you can use the
5Vpin to power it (if the motor supply voltage is >7V).
- Connect the motor power supply (e.g., 12V) to the
Motor Connections:
- Connect the terminals of Motor A to
OUT1andOUT2. - Connect the terminals of Motor B to
OUT3andOUT4.
- Connect the terminals of Motor A to
Control Connections:
- Connect the
ENAandENBpins to PWM-capable pins on your microcontroller to control motor speed. - Connect
IN1,IN2,IN3, andIN4to digital pins on your microcontroller to control motor direction.
- Connect the
Logic Power:
- If your microcontroller has its own 5V power supply, connect it to the
5Vpin on the L298N module.
- If your microcontroller has its own 5V power supply, connect it to the
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example of how to control two DC motors using the L298N and an Arduino UNO:
// Define motor control pins
#define ENA 9 // PWM pin for Motor A speed control
#define IN1 8 // Direction control for Motor A
#define IN2 7 // Direction control for Motor A
#define ENB 10 // PWM pin for Motor B speed control
#define IN3 6 // Direction control for Motor B
#define IN4 5 // Direction control for Motor B
void setup() {
// Set motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Motor A: Forward at 50% speed
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH); // Set IN1 high
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW); // Set IN2 low
analogWrite(ENA, 128); // Set ENA to 50% duty cycle (128/255)
// Motor B: Backward at 75% speed
digitalWrite(IN3, LOW); // Set IN3 low
digitalWrite(IN4, HIGH); // Set IN4 high
analogWrite(ENB, 192); // Set ENB to 75% duty cycle (192/255)
delay(2000); // Run motors for 2 seconds
// Stop both motors
analogWrite(ENA, 0); // Set ENA to 0% duty cycle
analogWrite(ENB, 0); // Set ENB to 0% duty cycle
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use a heat sink with the L298N to prevent overheating, especially when driving motors at high currents.
- Ensure the motor power supply voltage matches the motor's rated voltage.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating (2A per channel) to prevent damage to the IC.
- Use external diodes for additional protection if your motors generate significant back EMF.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motors Not Running:
- Check all power connections and ensure the motor power supply is connected to the
12Vpin. - Verify that the
ENAandENBpins are receiving a valid PWM signal.
- Check all power connections and ensure the motor power supply is connected to the
Motors Running in the Wrong Direction:
- Swap the connections of
IN1andIN2(orIN3andIN4) to reverse the motor direction.
- Swap the connections of
Overheating:
- Attach a heat sink to the L298N IC.
- Reduce the motor load or use motors with lower current requirements.
No Output on the 5V Pin:
- Ensure the motor power supply voltage is greater than 7V for the onboard 5V regulator to function.
FAQs
Can the L298N drive stepper motors? Yes, the L298N can drive bipolar stepper motors by controlling the two H-bridge channels.
What is the maximum voltage the L298N can handle? The L298N can handle up to 46V on the motor power supply pin.
Can I use the L298N with a 3.3V microcontroller? Yes, but you may need level shifters to ensure proper logic level compatibility.
Why is my motor speed inconsistent? Check the PWM signal quality and ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current.