
How to Use Wheatstone Bridge Phidget: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Wheatstone Bridge Phidget in Cirkit Designer
Design with Wheatstone Bridge Phidget in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Wheatstone Bridge Phidget (Manufacturer Part ID: Load Cell Amplifier) is a precision device designed to measure resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit. It is widely used in applications requiring accurate detection of small resistance changes, such as strain gauges, load cells, and temperature sensors. This component is ideal for scenarios where precise measurements of physical parameters like force, pressure, or temperature are required.
Explore Projects Built with Wheatstone Bridge Phidget

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer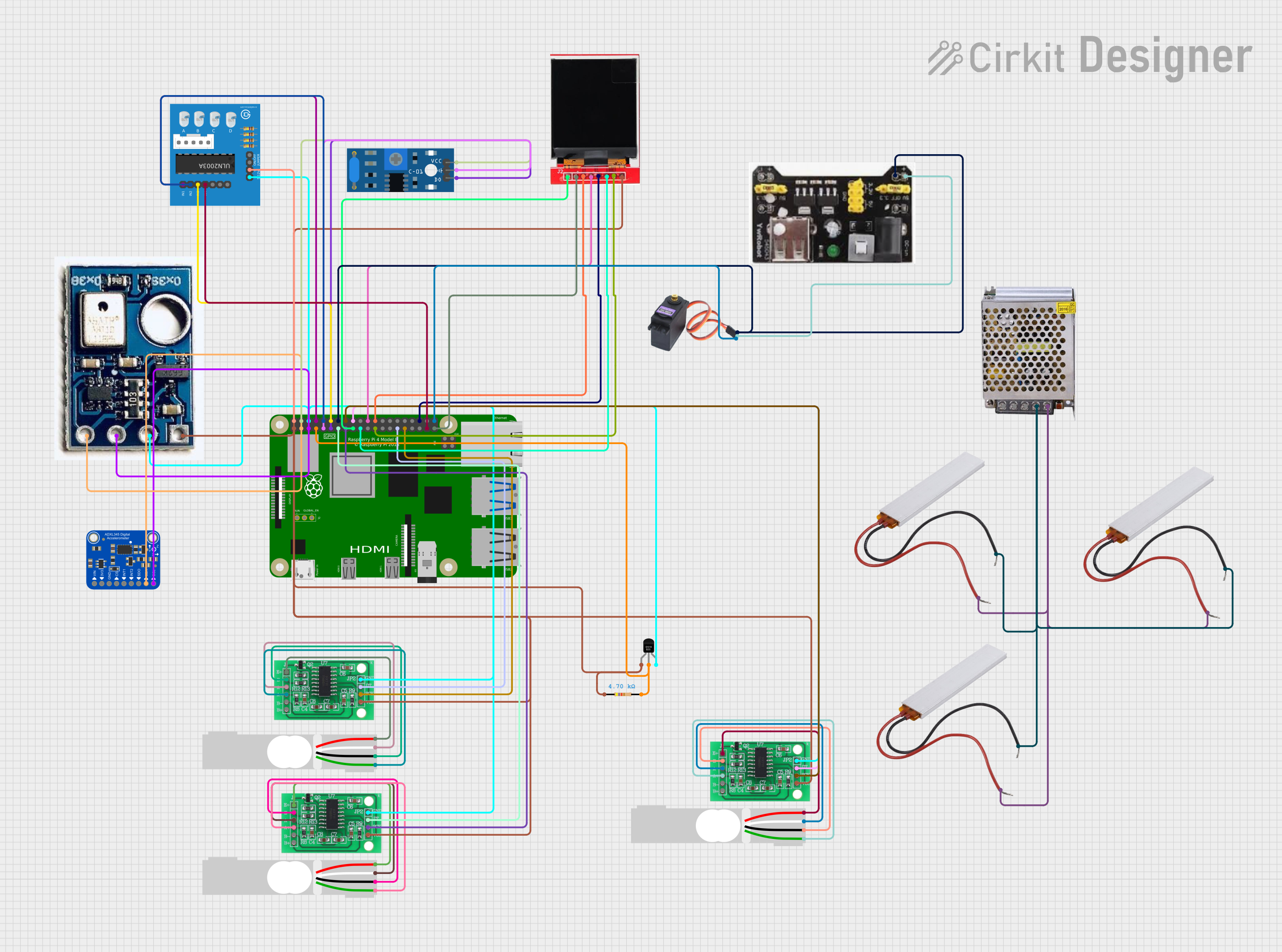
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer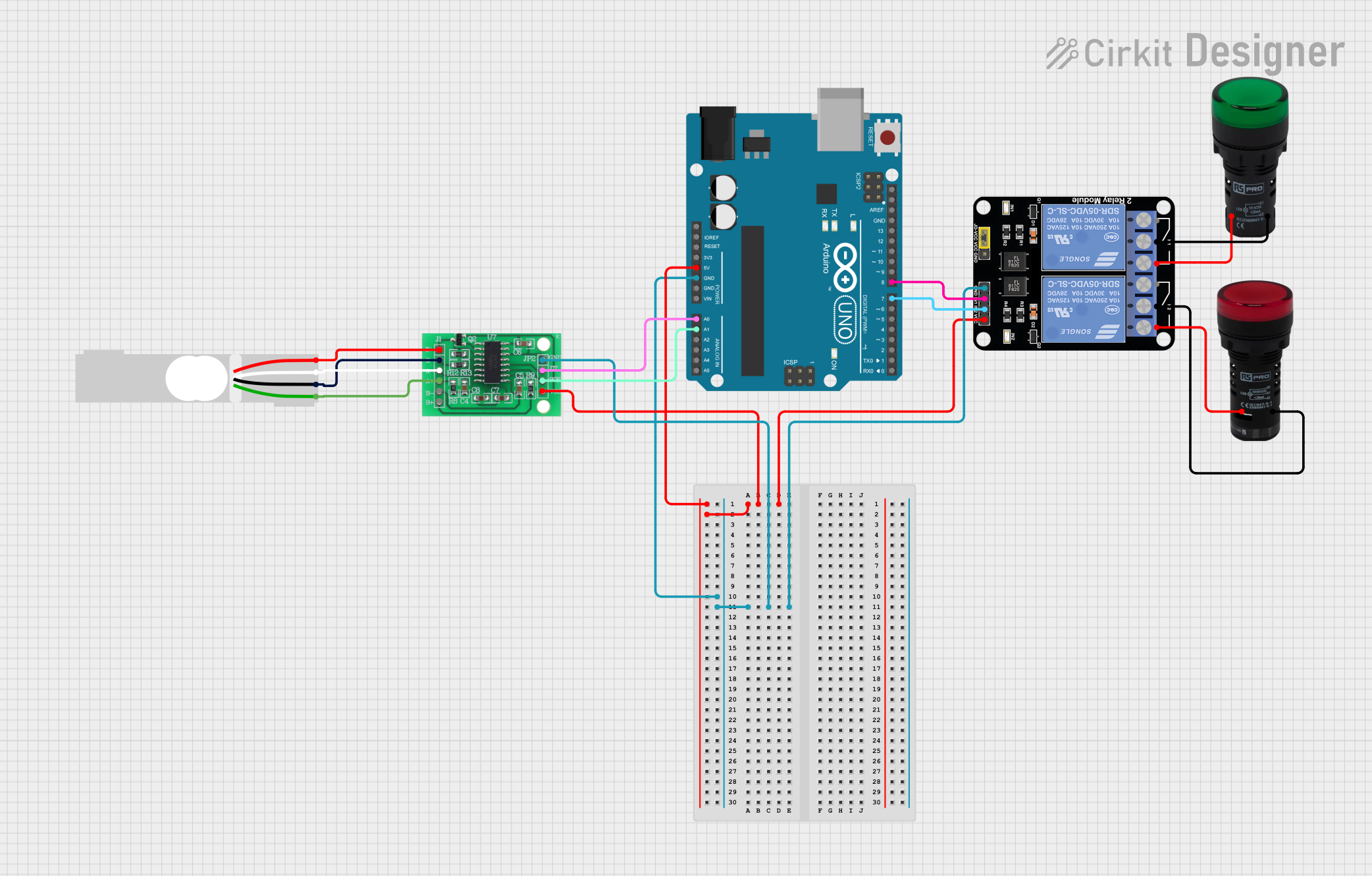
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer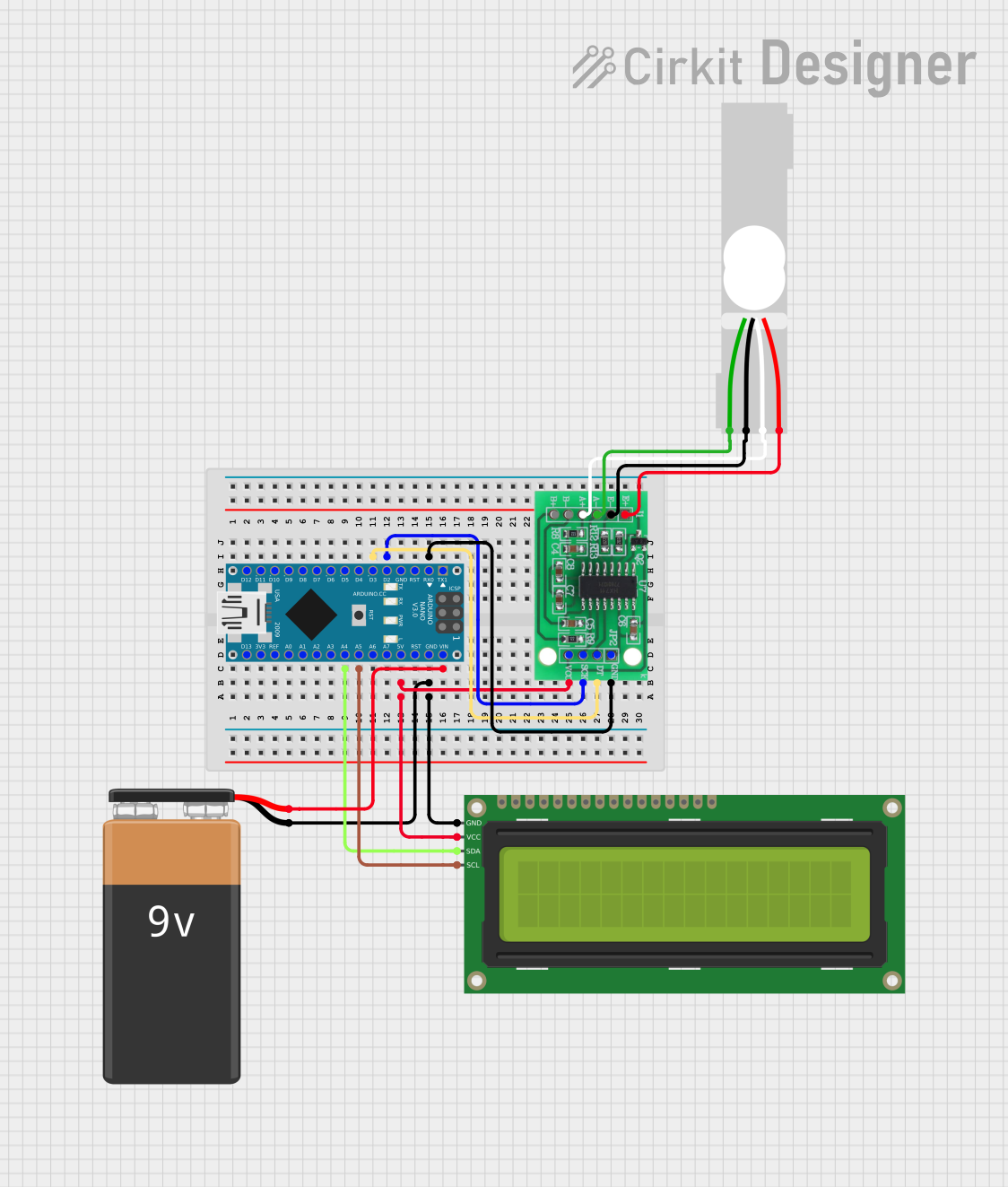
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Wheatstone Bridge Phidget

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Strain Gauges: Measuring deformation or strain in materials.
- Load Cells: Detecting weight or force in industrial and laboratory settings.
- Temperature Sensors: Monitoring temperature changes using resistive temperature devices (RTDs).
- Pressure Sensors: Measuring pressure variations in fluid systems.
- Scientific Research: High-precision resistance measurements in experimental setups.
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Wheatstone Bridge Phidget:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | 5V DC |
| Operating Current | 20 mA (typical) |
| Input Resistance Range | 350 Ω to 10 kΩ |
| Output Signal Range | 0 to 5V |
| Amplification Factor | Configurable (default: 128x) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
| Interface | Analog Output |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Wheatstone Bridge Phidget has a simple pinout for easy integration into circuits. The table below describes each pin:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input (5V DC). |
| GND | Ground connection. |
| SIG+ | Positive signal input from the sensor (e.g., strain gauge). |
| SIG- | Negative signal input from the sensor. |
| OUT | Analog output signal proportional to the resistance imbalance in the bridge. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Device: Connect the VCC pin to a 5V DC power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Connect the Sensor: Attach the resistive sensor (e.g., strain gauge or load cell) to the SIG+ and SIG- pins. Ensure proper polarity and secure connections.
- Read the Output: The OUT pin provides an analog voltage signal proportional to the resistance imbalance in the Wheatstone bridge. This signal can be read using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or a microcontroller like an Arduino.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Calibration: Always calibrate the system with known reference values to ensure accurate measurements.
- Shielding: Use shielded cables for the sensor connections to minimize noise and interference.
- Amplification: Adjust the amplification factor if your application requires a higher or lower sensitivity.
- Temperature Compensation: If using in environments with varying temperatures, consider implementing temperature compensation to maintain accuracy.
- Load Cell Wiring: For load cells, ensure the wiring matches the manufacturer's specifications (e.g., excitation and signal wires).
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the Wheatstone Bridge Phidget to an Arduino UNO and read the output signal:
Circuit Diagram
- VCC → Arduino 5V
- GND → Arduino GND
- OUT → Arduino A0 (Analog Pin)
- SIG+ and SIG- → Connected to the resistive sensor (e.g., strain gauge).
Arduino Code
// Define the analog pin connected to the OUT pin of the Wheatstone Bridge Phidget
const int analogPin = A0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the Wheatstone Bridge Phidget
int sensorValue = analogRead(analogPin);
// Convert the analog value to a voltage (assuming 5V reference)
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, especially the sensor wiring to SIG+ and SIG-.
Fluctuating Readings:
- Cause: Electrical noise or interference.
- Solution: Use shielded cables and ensure proper grounding.
Inaccurate Measurements:
- Cause: Lack of calibration or temperature effects.
- Solution: Calibrate the system with known reference values and implement temperature compensation if necessary.
Output Signal Saturation:
- Cause: Amplification factor too high.
- Solution: Reduce the amplification factor or use a sensor with a higher resistance range.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this component with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but ensure the output signal range (0-5V) is compatible with the ADC input range of your microcontroller. You may need a voltage divider or level shifter.
Q: How do I adjust the amplification factor?
A: The amplification factor can typically be adjusted via onboard jumpers or potentiometers. Refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for specific instructions.
Q: Is this component suitable for dynamic measurements?
A: Yes, but ensure the sampling rate of your ADC is sufficient to capture the changes in the output signal.
Q: Can I use multiple Wheatstone Bridge Phidgets in the same system?
A: Yes, but ensure each device has a dedicated ADC input and proper isolation to avoid interference.
This concludes the documentation for the Wheatstone Bridge Phidget. For further assistance, refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or support resources.