
How to Use OLED: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with OLED in Cirkit Designer
Design with OLED in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Midas MDOB128064BV-WS is a high-quality Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) display module. OLED technology utilizes organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied, eliminating the need for a backlight. This results in displays with exceptional contrast ratios, vibrant colors, and deep blacks. The MDOB128064BV-WS is a 128x64 pixel monochrome display, ideal for applications requiring clear and sharp visuals in a compact form factor.
Explore Projects Built with OLED

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer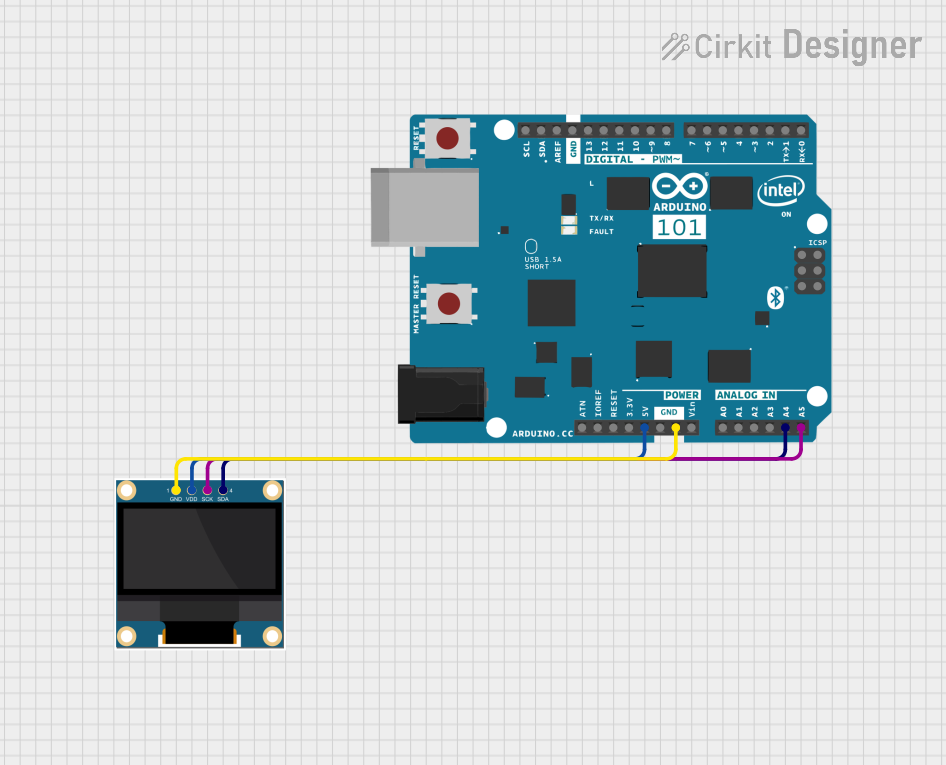
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer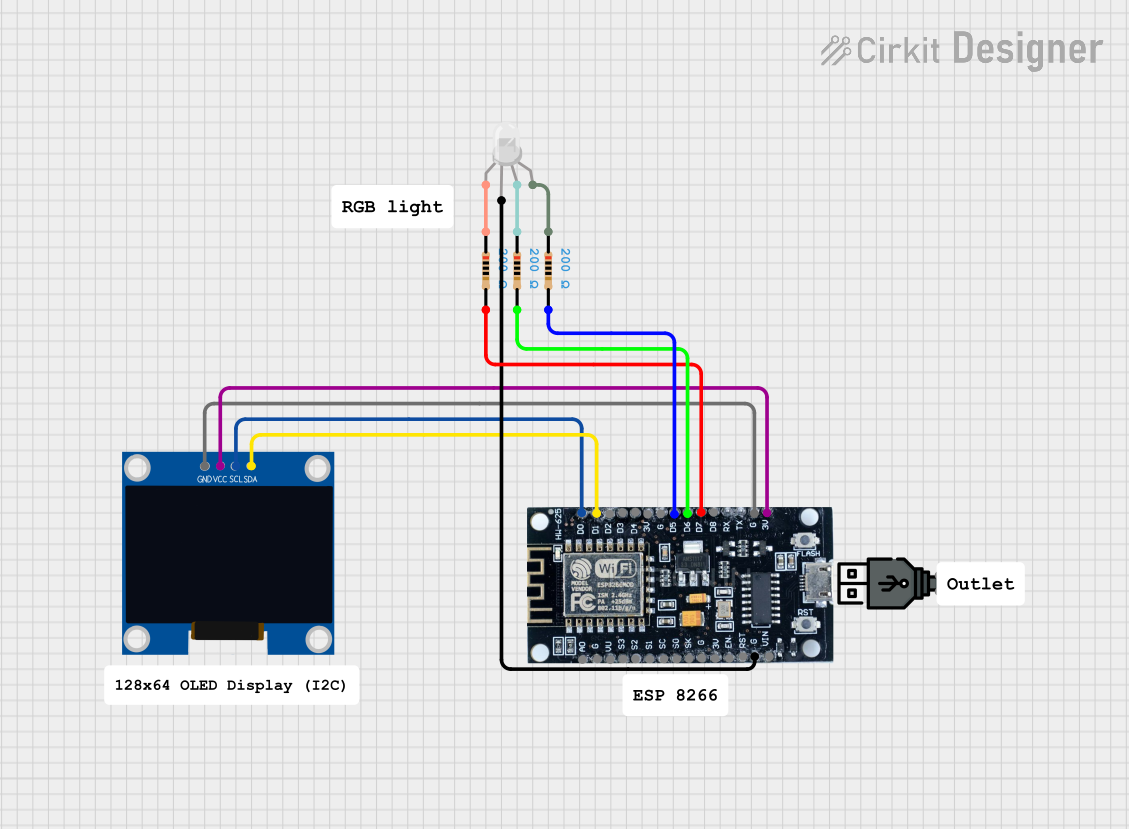
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer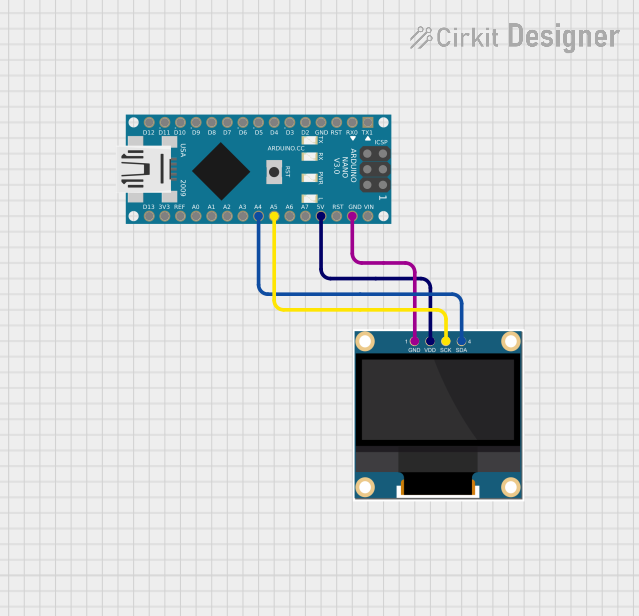
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with OLED

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Wearable devices
- Industrial control panels
- Consumer electronics (e.g., smart home devices)
- Medical equipment
- Prototyping with microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the MDOB128064BV-WS OLED display:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Display Type | Monochrome OLED |
| Resolution | 128 x 64 pixels |
| Active Area | 26.42mm x 14.70mm |
| Interface | SPI / I2C |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +80°C |
| Dimensions | 27.3mm x 27.3mm x 1.65mm |
| Manufacturer Part ID | MDOB128064BV-WS |
Pin Configuration
The MDOB128064BV-WS has a standard pinout for SPI/I2C communication. Below is the pin configuration:
SPI Mode Pinout
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground (0V reference) |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V or 5V) |
| 3 | SCL | Serial Clock Line (SPI Clock) |
| 4 | SDA | Serial Data Line (SPI MOSI) |
| 5 | RES | Reset pin (active low) |
| 6 | DC | Data/Command control pin |
| 7 | CS | Chip Select (active low) |
I2C Mode Pinout
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground (0V reference) |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V or 5V) |
| 3 | SCL | Serial Clock Line (I2C Clock) |
| 4 | SDA | Serial Data Line (I2C Data) |
| 5 | RES | Reset pin (active low) |
| 6 | DC | Data/Command control pin (optional) |
| 7 | NC | Not connected |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the OLED to an Arduino UNO
The MDOB128064BV-WS can be easily interfaced with an Arduino UNO using either SPI or I2C communication. Below is an example of how to connect the OLED in I2C mode:
Wiring Diagram (I2C Mode)
| OLED Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 5V |
| SCL | A5 (SCL) |
| SDA | A4 (SDA) |
| RES | Digital Pin 8 |
Example Code
The following Arduino sketch demonstrates how to initialize and display text on the OLED using the Adafruit SSD1306 library:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
// Define OLED display dimensions
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 128
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64
// Create an instance of the SSD1306 display object
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, -1);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize the OLED display
if (!display.begin(SSD1306_I2C_ADDRESS, 0x3C)) {
Serial.println(F("SSD1306 allocation failed"));
for (;;); // Halt execution if initialization fails
}
// Clear the display buffer
display.clearDisplay();
// Set text size and color
display.setTextSize(1); // Small text size
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE);
// Display a message
display.setCursor(0, 0); // Set cursor to top-left corner
display.println(F("Hello, OLED!"));
display.display(); // Render the text on the screen
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do here
}
Important Considerations
- Power Supply: Ensure the OLED is powered within its operating voltage range (3.3V to 5V).
- Library Compatibility: Use the Adafruit SSD1306 and GFX libraries for seamless integration.
- Reset Pin: Connect the RES pin to a digital pin on the microcontroller for proper initialization.
- Pull-up Resistors: For I2C communication, ensure pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) are present on the SCL and SDA lines.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Display Not Turning On
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the power supply is stable.
Garbage Data on Screen
- Cause: Incorrect communication protocol or address.
- Solution: Verify the I2C address (default is 0x3C) and ensure the correct protocol is selected.
Flickering Display
- Cause: Insufficient current supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Use a stable power source and secure all connections.
Library Initialization Fails
- Cause: Missing or outdated libraries.
- Solution: Install the latest Adafruit SSD1306 and GFX libraries via the Arduino Library Manager.
FAQs
Can I use the OLED with a 3.3V microcontroller?
- Yes, the MDOB128064BV-WS is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels.
What is the default I2C address of the OLED?
- The default I2C address is
0x3C.
- The default I2C address is
Can I use SPI and I2C simultaneously?
- No, the OLED operates in either SPI or I2C mode, but not both at the same time.
How do I change the I2C address?
- The I2C address is fixed and cannot be changed for this module.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the Midas MDOB128064BV-WS OLED display into their projects for high-quality visual output.