
How to Use Solar Isol: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
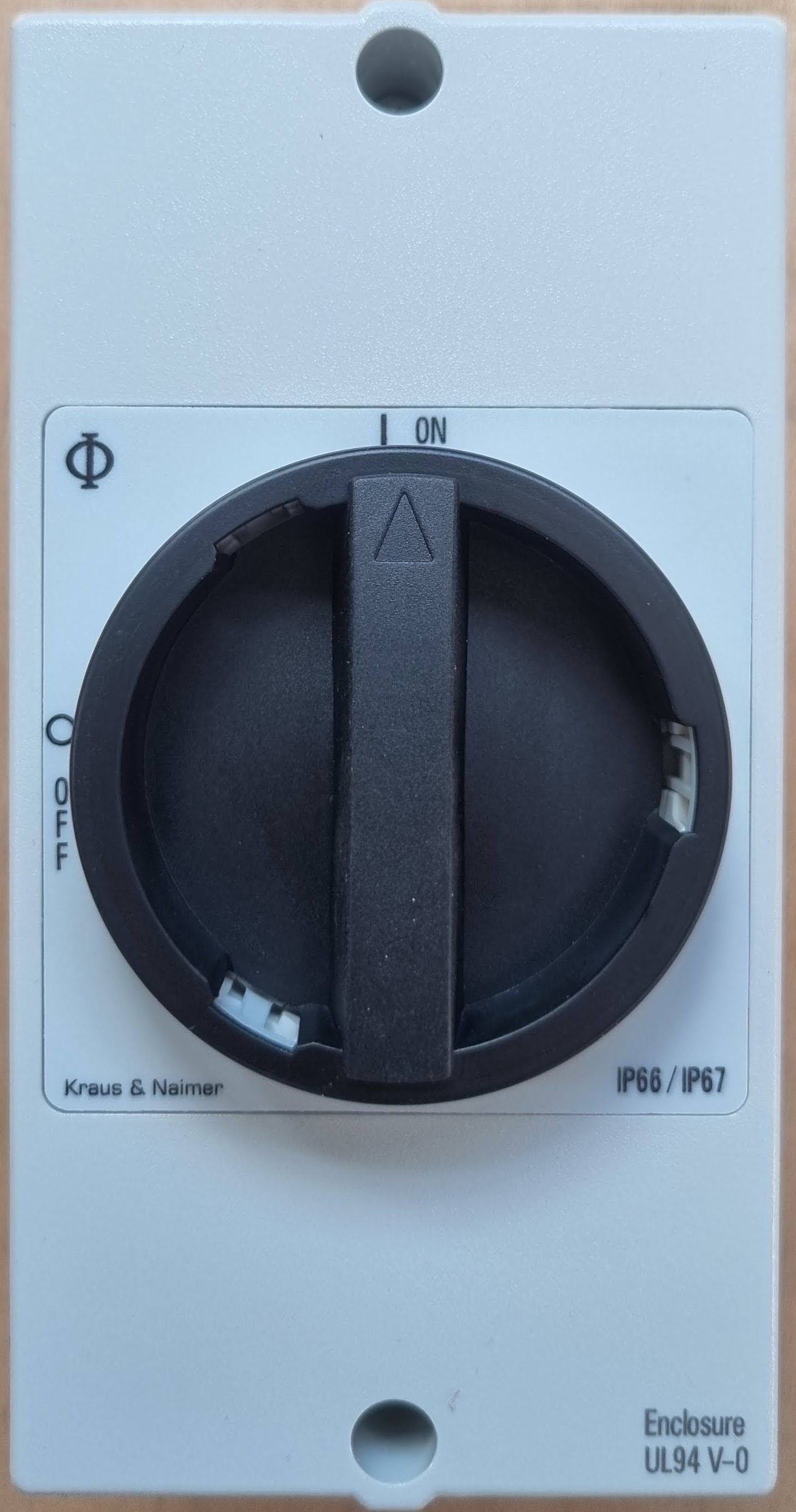

 Design with Solar Isol in Cirkit Designer
Design with Solar Isol in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Solar Isolator, commonly referred to as a solar disconnect switch, is a critical safety device in any photovoltaic (PV) system. It allows for the solar panel array to be isolated from the electrical system, ensuring that maintenance or emergency services can be performed safely without the risk of electric shock or damage to the system. Solar Isolators are typically installed in both the DC side, between the solar panels and the inverter, and the AC side, between the inverter and the grid connection.
Explore Projects Built with Solar Isol
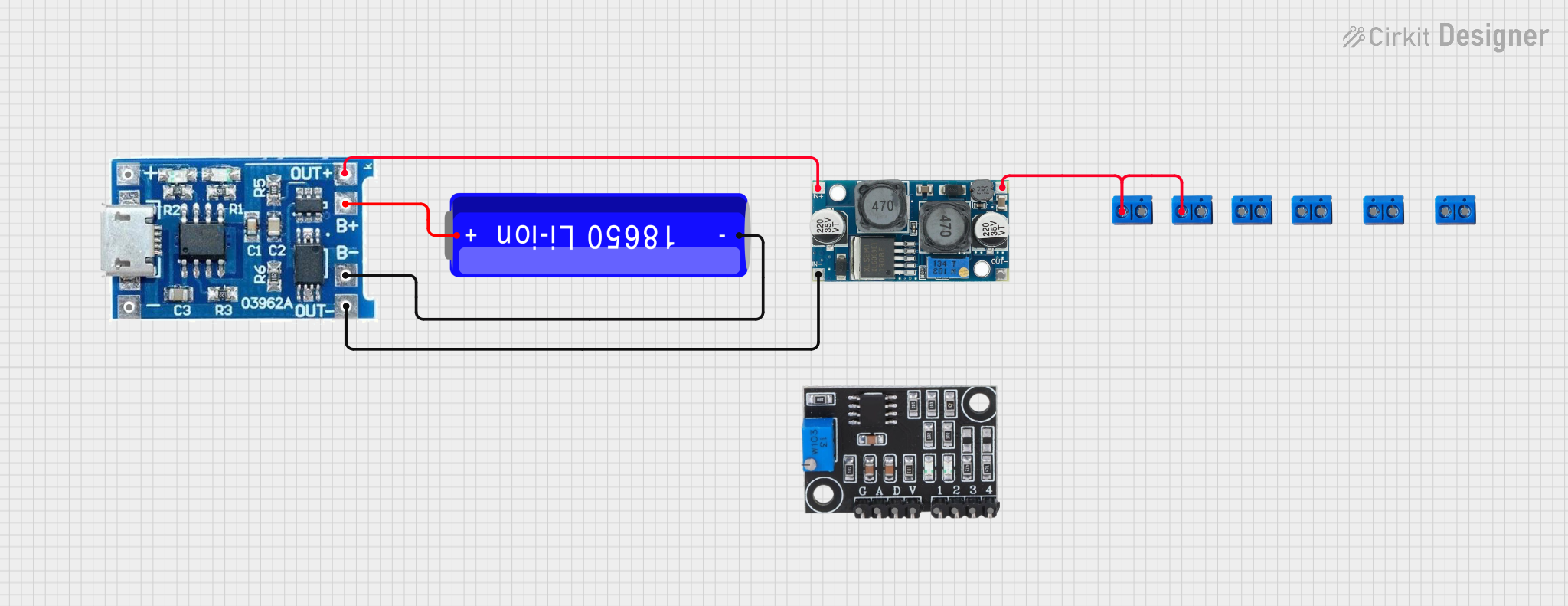
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer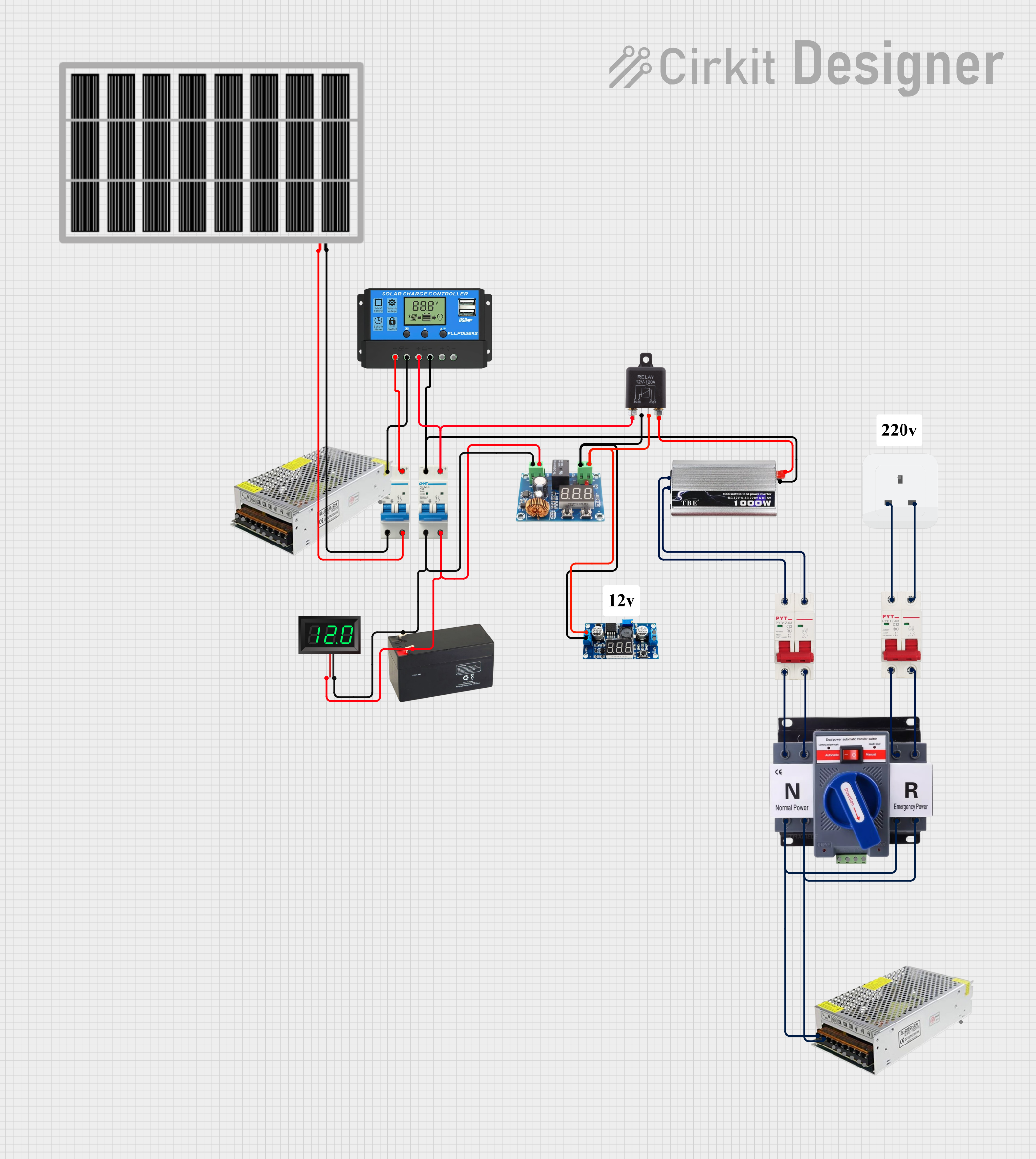
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer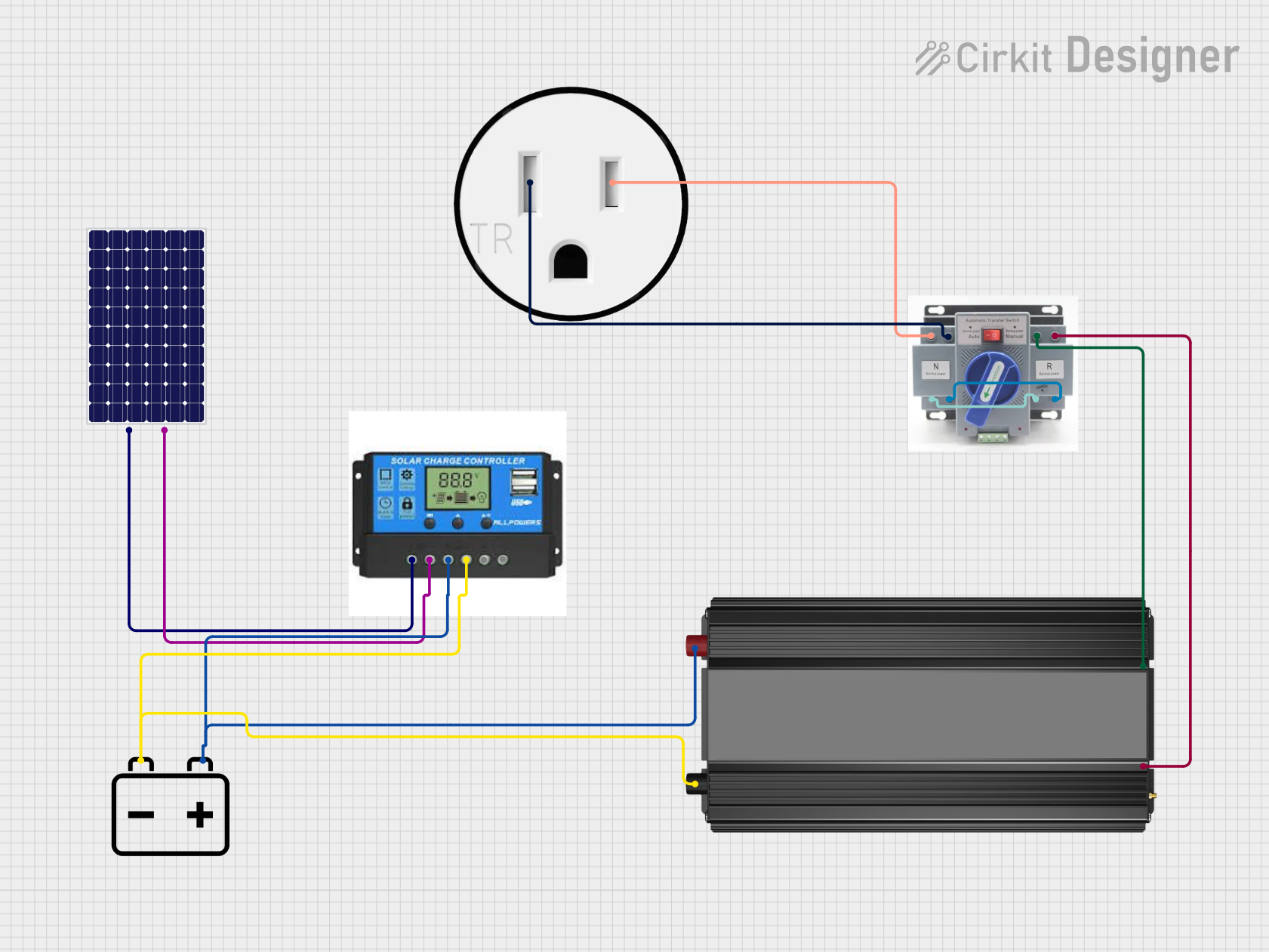
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer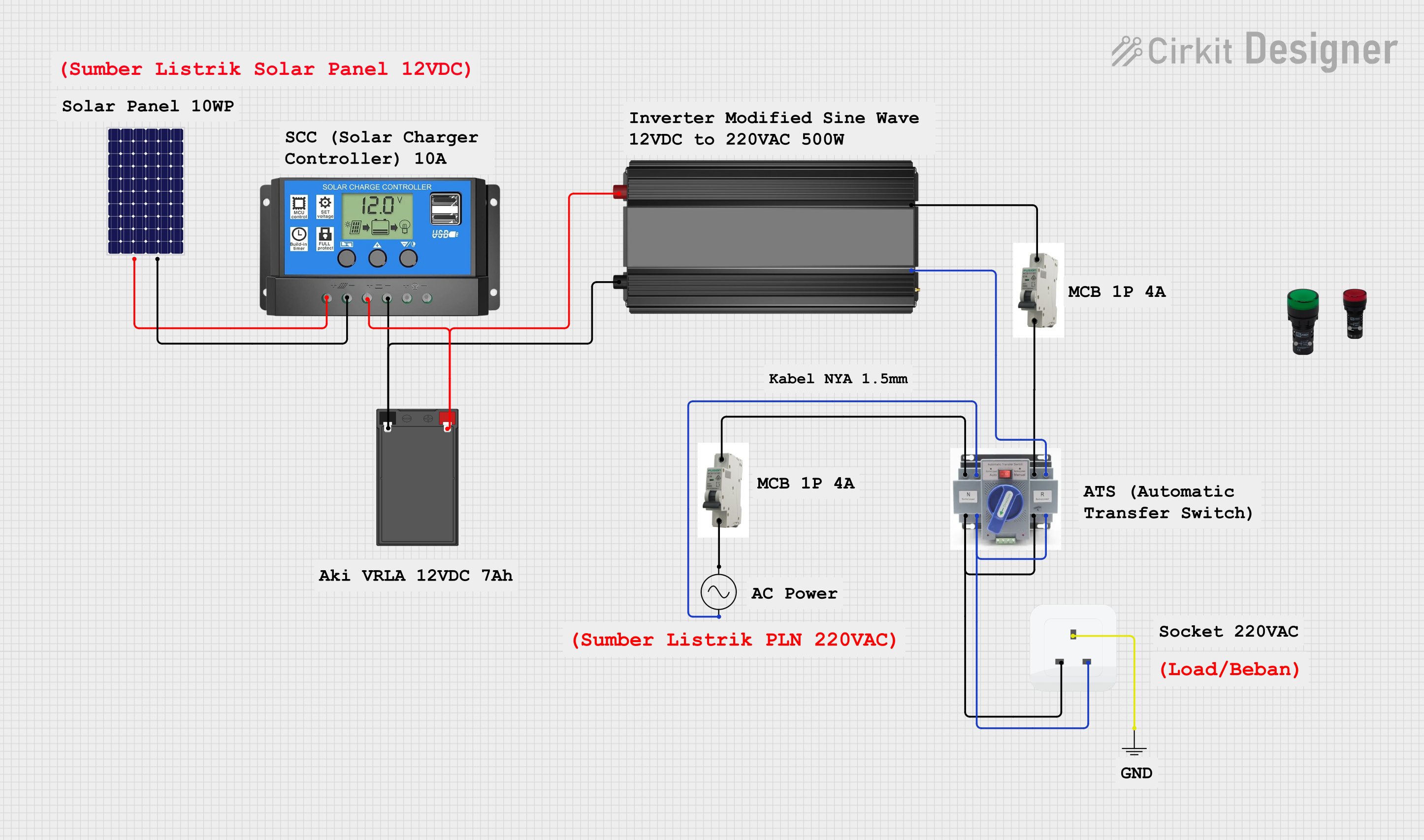
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Solar Isol

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential and commercial solar panel installations
- Off-grid solar power systems
- Grid-tied solar power systems with battery backup
- Maintenance and repair of solar panel systems
- Emergency shutdown of solar panel systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Rated Voltage: The maximum DC voltage the isolator can handle.
- Rated Current: The maximum current that can pass through the isolator.
- Power Ratings: The maximum power capacity of the isolator.
- Temperature Range: The operating temperature range of the isolator.
- Enclosure Rating: The environmental protection provided by the isolator's enclosure.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DC Positive Input | From solar panels |
| 2 | DC Negative Input | From solar panels |
| 3 | DC Positive Output | To inverter or load |
| 4 | DC Negative Output | To inverter or load |
| 5 | Grounding Terminal | Safety ground connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Installation: The Solar Isolator should be installed by a qualified electrician, following local electrical codes and standards.
- Wiring: Connect the DC positive and negative inputs from the solar panels to the respective input terminals of the Solar Isolator. Similarly, connect the output terminals to the inverter or load.
- Operation: To engage the Solar Isolator, switch it to the 'ON' position. To isolate the solar panels from the electrical system, switch it to the 'OFF' position.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure that the Solar Isolator's voltage and current ratings match or exceed the solar system's specifications.
- Install the Solar Isolator in an easily accessible location for quick operation in case of an emergency.
- Regularly inspect the Solar Isolator for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Test the Solar Isolator periodically to ensure proper operation.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Isolator Does Not Engage: Check for any obstructions or damage to the switch mechanism.
- Electrical Arcing: Ensure that the connections are tight and secure to prevent arcing.
- System Not Powering On: Verify that the Solar Isolator is in the 'ON' position and that all connections are correct.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- If the isolator does not engage, inspect the mechanism for debris or damage and clean or replace as necessary.
- For electrical arcing, turn off the system and tighten all connections. If arcing persists, consult a professional.
- If the system is not powering on, double-check the Solar Isolator's position and review all wiring connections.
FAQs
Q: Can I install a Solar Isolator myself? A: It is recommended that a qualified electrician install the Solar Isolator to ensure compliance with electrical codes and safety standards.
Q: How often should I test the Solar Isolator? A: Test the Solar Isolator every 6 months to ensure it is functioning correctly.
Q: What should I do if my Solar Isolator is damaged? A: If the Solar Isolator is damaged, it should be replaced immediately to maintain the safety and integrity of the solar system.
Q: Is a Solar Isolator required by law? A: In many regions, a Solar Isolator is required by law for solar installations. Always check local regulations.
Q: Can the Solar Isolator be used for both AC and DC applications? A: Solar Isolators are typically designed for DC applications. For AC isolation, a separate AC disconnect switch should be used.
This documentation provides a comprehensive overview of the Solar Isolator component. For further assistance or information, consult the manufacturer's datasheet or contact a professional.