
How to Use Buzzer: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Buzzer in Cirkit Designer
Design with Buzzer in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A buzzer, also known as a beeper, is an audio signaling device that can convert audio signals into sound waves. The buzzer component BUZZ is commonly used in alarm devices, timers, confirmation of user input like button presses, and other electronic devices that require audible feedback. Buzzers can be found in a variety of applications, from household appliances to industrial equipment.
Explore Projects Built with Buzzer
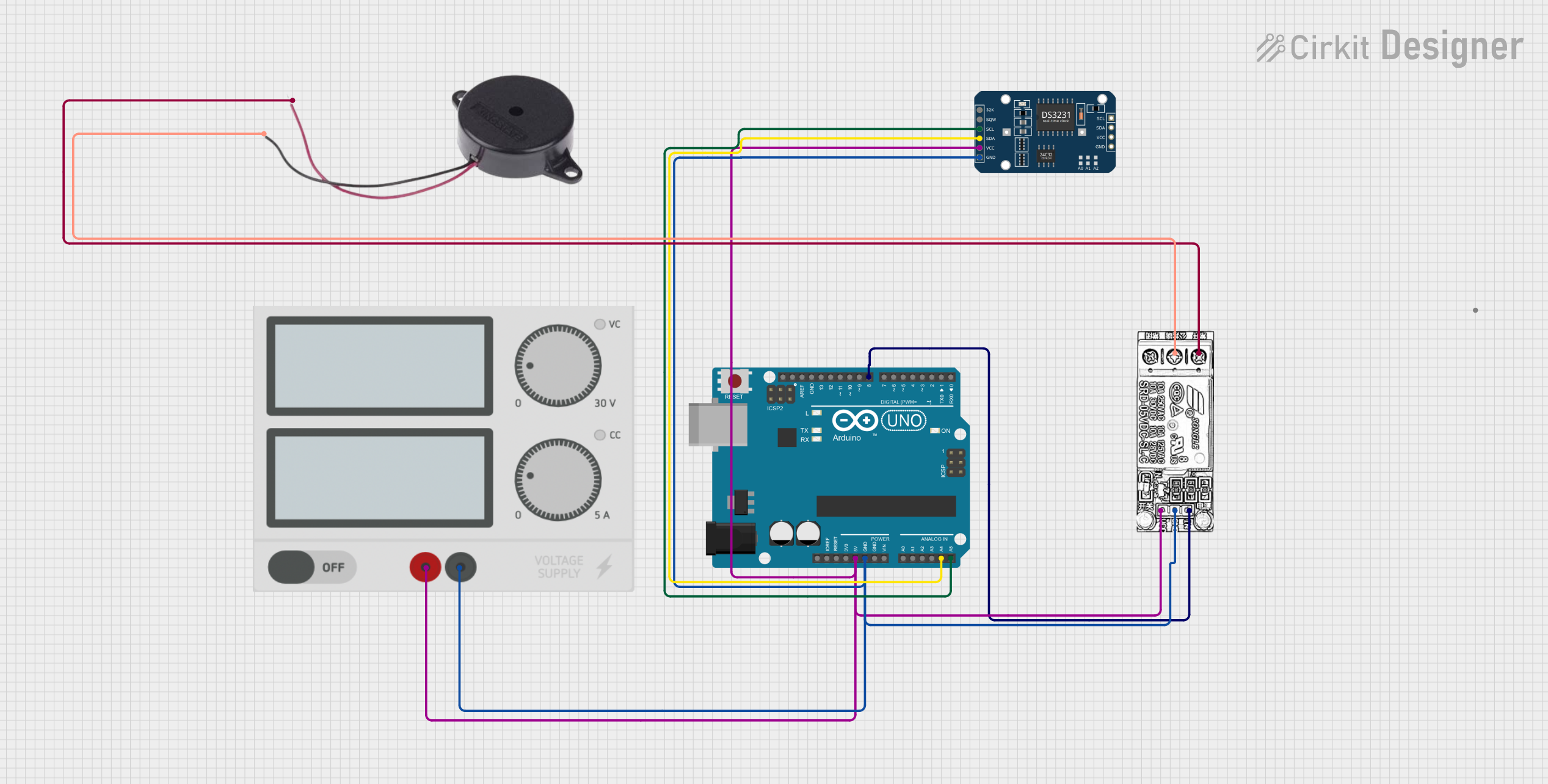
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer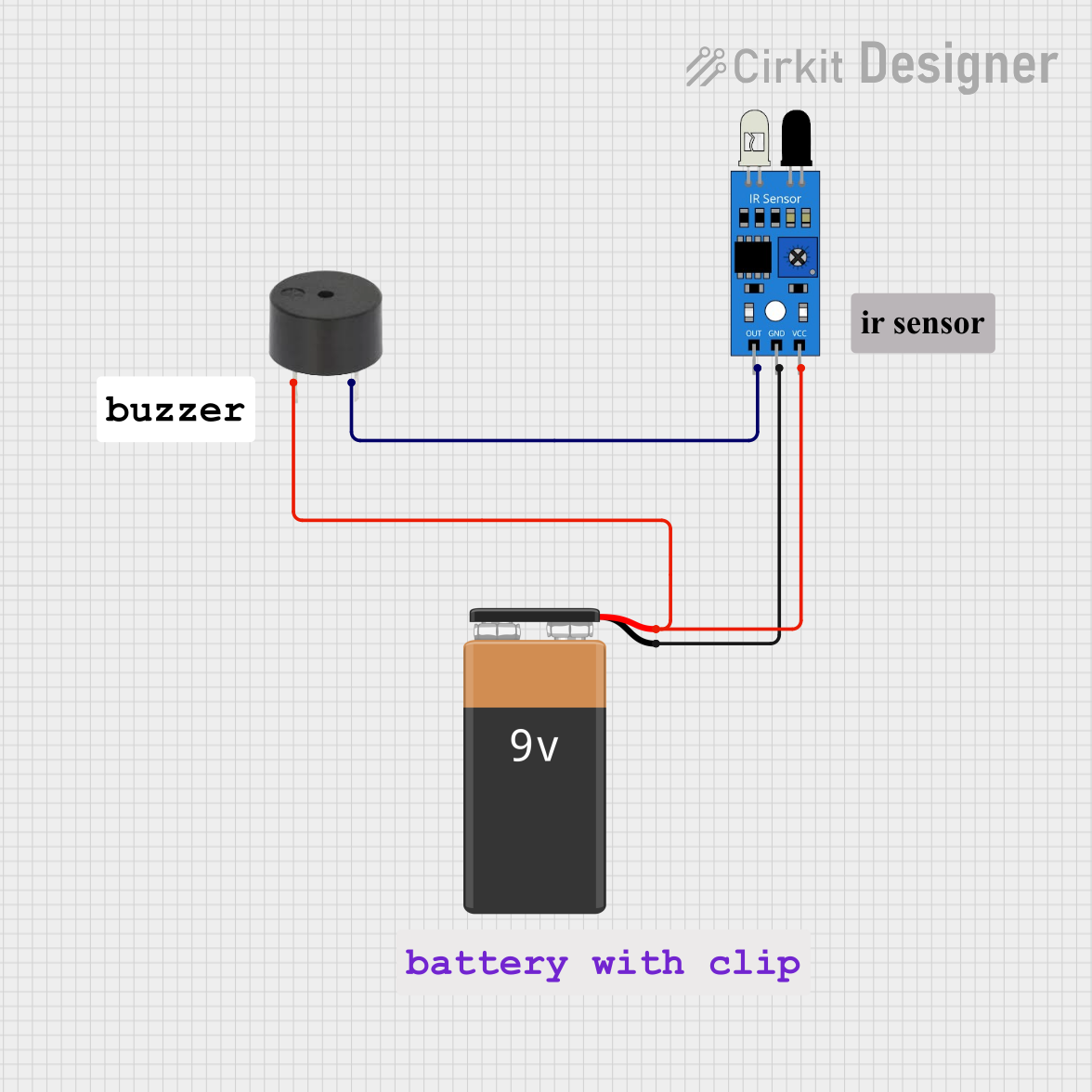
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer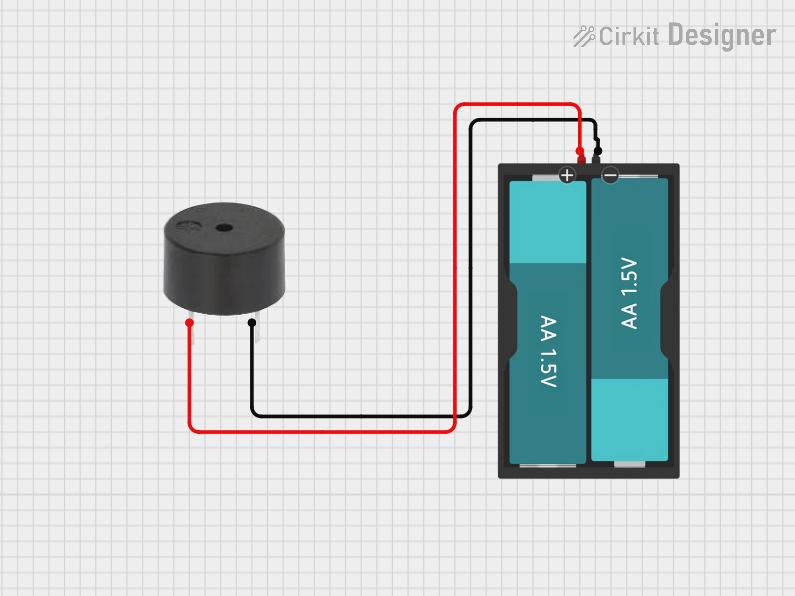
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer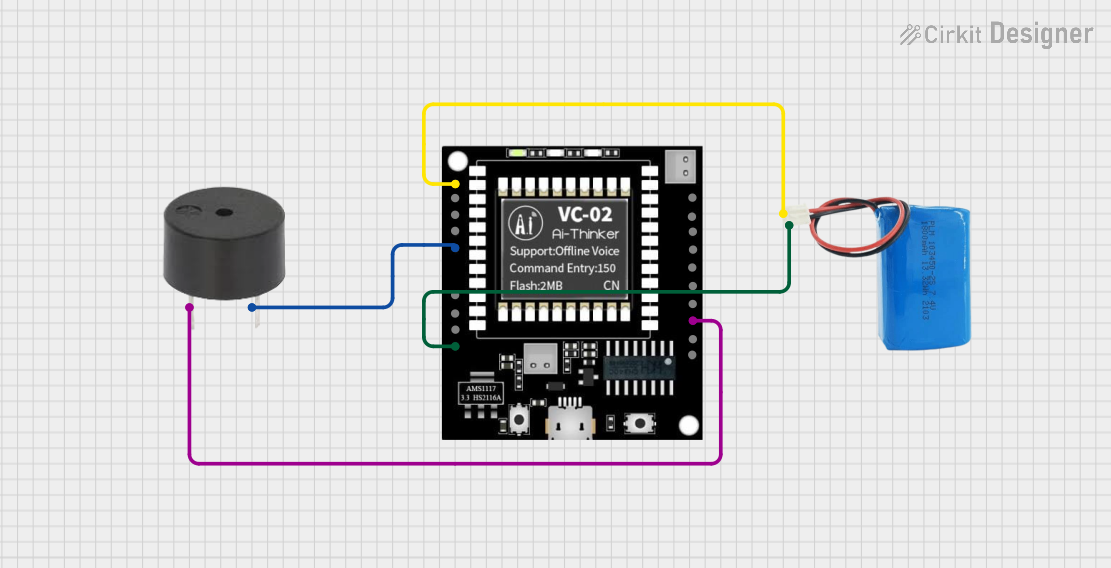
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Buzzer

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
General Characteristics
- Sound Output: Typically >85 dB
- Operating Voltage: 3V to 12V DC
- Rated Current: 5 mA to 30 mA
- Frequency: 2 kHz to 4 kHz
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 70°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vcc | Connect to the positive supply voltage |
| 2 | GND | Connect to the ground of the circuit |
Usage Instructions
Connecting to a Circuit
- Connect the Vcc pin of the buzzer to the positive supply voltage within the specified operating voltage range.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the circuit.
Driving with an Arduino UNO
To use the BUZZ buzzer with an Arduino UNO, you can connect it directly to one of the digital I/O pins. Here is a simple example of how to make the buzzer sound for one second:
// Define the buzzer pin
const int buzzerPin = 8;
void setup() {
// Set the buzzer pin as an output
pinMode(buzzerPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn on the buzzer
digitalWrite(buzzerPin, HIGH);
// Keep it on for 1000 milliseconds (1 second)
delay(1000);
// Turn off the buzzer
digitalWrite(buzzerPin, LOW);
// Pause for 1000 milliseconds (1 second)
delay(1000);
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the buzzer's operating voltage matches the supply voltage to prevent damage.
- Do not exceed the rated current by overdriving the buzzer.
- Use a current-limiting resistor if necessary to protect the buzzer.
- Avoid continuous operation at high volume levels to prolong the buzzer's lifespan.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Buzzer not sounding: Check the connections and ensure the supply voltage is within the specified range.
- Sound is very faint: Ensure the buzzer is receiving enough current and that the voltage is not too low.
- Distorted sound: The operating voltage might be too high, or the buzzer could be damaged.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a different voltage than specified? A: It is recommended to use the buzzer within the specified voltage range to avoid damage and ensure proper operation.
Q: Is it possible to change the tone of the buzzer? A: The tone is typically fixed based on the internal structure of the buzzer. However, you can create different effects by turning the buzzer on and off rapidly.
Q: Can I use the buzzer with a microcontroller other than Arduino? A: Yes, as long as the microcontroller can provide the appropriate voltage and current within the buzzer's specifications.
Q: How do I make the buzzer sound louder? A: Ensure that the buzzer is operating at its optimal voltage and current. Additionally, mounting the buzzer on a solid surface can amplify the sound.
For further assistance, please refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or contact technical support.