
How to Use Blade Fuse: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
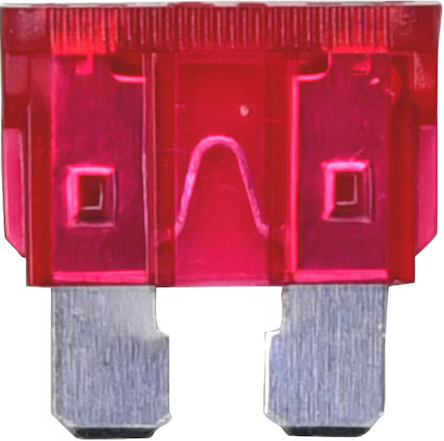

 Design with Blade Fuse in Cirkit Designer
Design with Blade Fuse in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A blade fuse is a type of electrical fuse with a plastic body and two metal prongs. It is designed to protect electrical circuits by breaking the circuit when excessive current flows through it, thereby preventing damage to connected components or wiring. Blade fuses are widely used in automotive, marine, and industrial applications due to their compact size, ease of replacement, and reliable performance.
Explore Projects Built with Blade Fuse

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer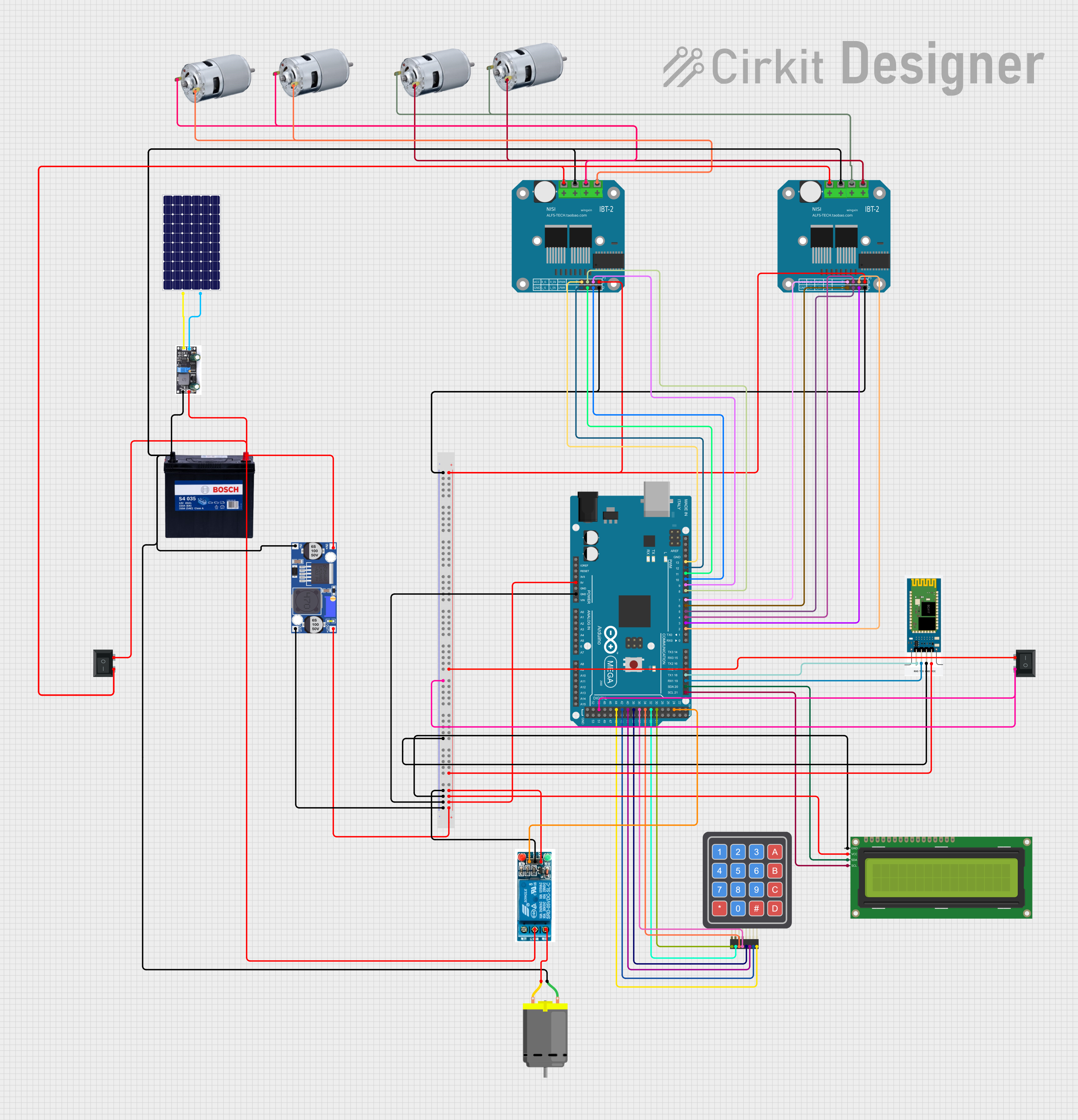
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer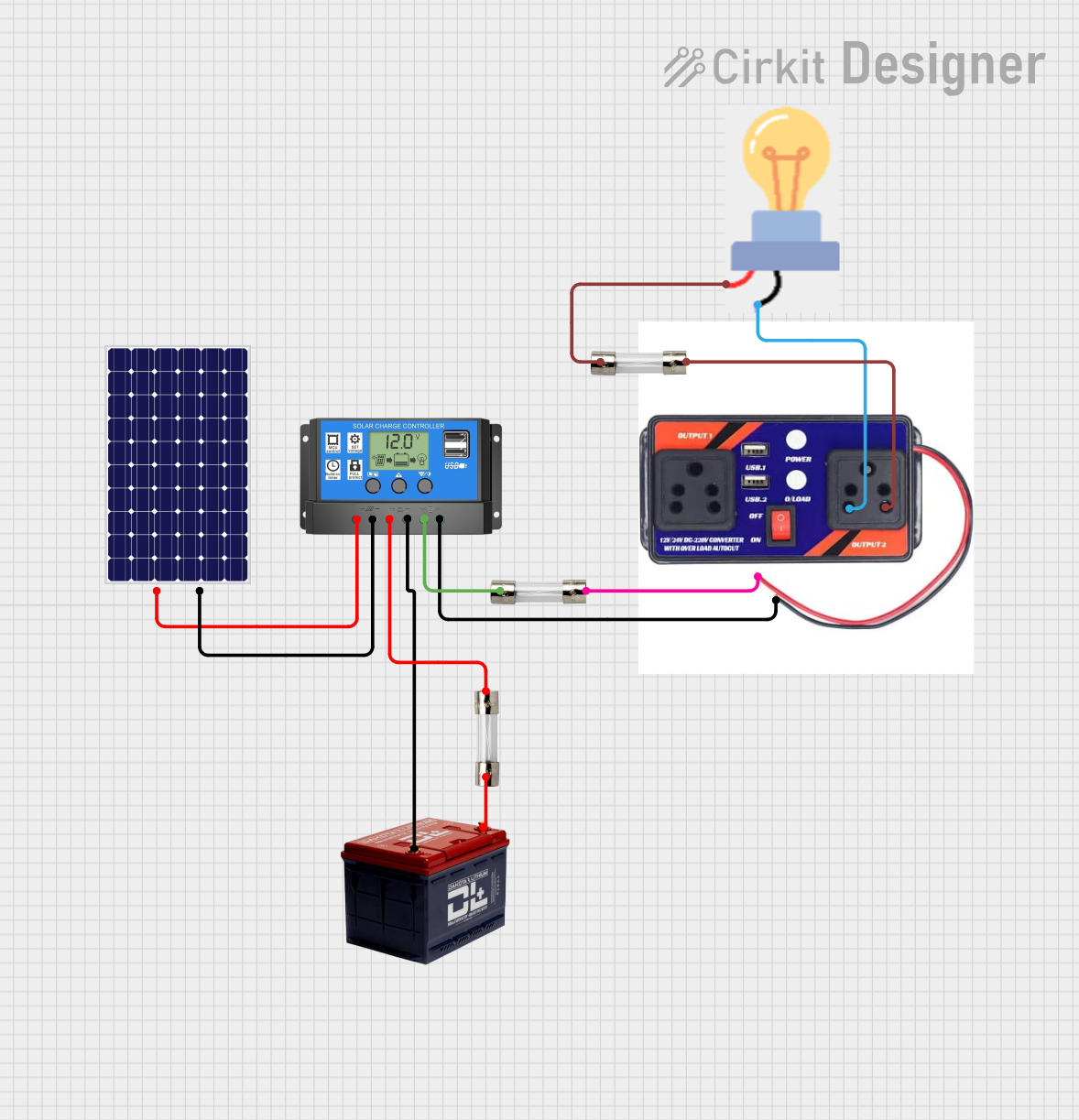
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer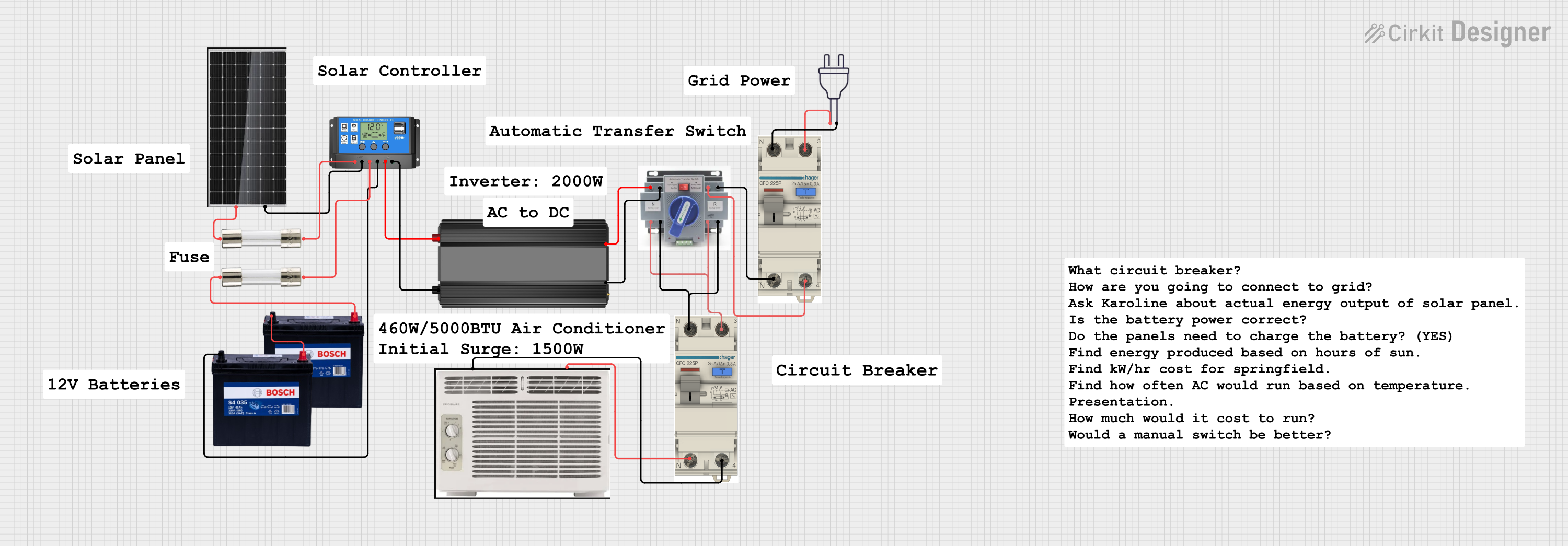
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Blade Fuse

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive electrical systems (e.g., car stereos, headlights, and power windows)
- Marine electrical systems
- Industrial equipment and machinery
- Low-voltage DC circuits
- Consumer electronics and appliances
Technical Specifications
Blade fuses come in various sizes and current ratings to suit different applications. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
- Voltage Rating: Typically 12V to 32V DC
- Current Ratings: Commonly available in 1A to 40A (varies by size)
- Interrupting Rating: Typically 1,000A at rated voltage
- Body Material: Plastic (usually thermoplastic)
- Prong Material: Tin-plated copper or zinc
Blade Fuse Sizes
Blade fuses are categorized into different sizes, each with specific dimensions and current ratings. The table below outlines the most common types:
| Fuse Type | Dimensions (mm) | Current Ratings (A) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mini (ATM) | 10.9 x 3.6 x 16 | 1A to 30A | Compact automotive circuits |
| Standard (ATO) | 19.1 x 5.1 x 18 | 1A to 40A | General automotive use |
| Maxi | 29.2 x 8.4 x 34 | 20A to 100A | High-current applications |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Blade fuses have two metal prongs that serve as the electrical terminals. The table below describes their function:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Prong 1 | Connects to the power source |
| Prong 2 | Connects to the load (protected side) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Blade Fuse in a Circuit
- Determine the Current Rating: Select a blade fuse with a current rating slightly higher than the normal operating current of the circuit but lower than the maximum current the wiring can handle.
- Insert into Fuse Holder: Place the blade fuse into a compatible fuse holder or fuse box. Ensure the prongs are fully seated for a secure connection.
- Connect the Fuse Holder: Wire the fuse holder in series with the circuit to ensure the fuse protects the load.
- Test the Circuit: Power on the circuit and verify that it operates correctly. If the fuse blows, check for short circuits or excessive current draw.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always use a fuse with the correct voltage and current rating for your application.
- Avoid bypassing or replacing a blown fuse with one of a higher rating, as this can damage the circuit.
- Inspect the fuse holder for corrosion or damage before installation.
- For automotive applications, ensure the fuse is compatible with the vehicle's fuse box.
Example: Using a Blade Fuse with an Arduino UNO
When connecting an Arduino UNO to a motor or other high-current device, a blade fuse can protect the circuit. Below is an example of how to wire a blade fuse in such a setup:
Circuit Diagram
- Power Source (+) → Fuse Holder → Motor (+)
- Motor (-) → Ground
Arduino Code Example
// Example code for controlling a motor with an Arduino UNO
// Ensure a blade fuse is used to protect the motor circuit
const int motorPin = 9; // Pin connected to motor driver input
void setup() {
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT); // Set motor pin as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(motorPin, HIGH); // Turn motor on
delay(1000); // Run motor for 1 second
digitalWrite(motorPin, LOW); // Turn motor off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Note: Ensure the blade fuse is rated for the motor's current draw to prevent nuisance tripping.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Fuse Blows Repeatedly
- Cause: Excessive current draw or short circuit in the circuit.
- Solution: Check the circuit for faults, such as damaged wiring or overloaded components. Replace the fuse with one of the correct rating.
Fuse Does Not Blow When Expected
- Cause: Incorrect fuse rating or faulty fuse.
- Solution: Verify the fuse rating matches the circuit requirements. Replace the fuse if it is defective.
Corroded Fuse Prongs
- Cause: Exposure to moisture or poor-quality materials.
- Solution: Use a fuse with corrosion-resistant prongs and ensure the fuse holder is sealed or in a dry location.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a blade fuse in an AC circuit?
A: Blade fuses are typically designed for DC circuits. For AC applications, use a fuse specifically rated for AC voltage.
Q: How do I know if a blade fuse is blown?
A: Inspect the fuse visually. A blown fuse will have a broken or melted metal strip inside the plastic body. Alternatively, use a multimeter to check for continuity.
Q: Can I replace a blade fuse with a circuit breaker?
A: Yes, in some cases, a circuit breaker can replace a blade fuse, but ensure the breaker is compatible with the circuit's voltage and current requirements.