
How to Use Power Transformer (220V to 24V): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Power Transformer (220V to 24V) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Power Transformer (220V to 24V) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A power transformer is a critical component in electrical engineering, serving as a static device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. The specified power transformer is designed to convert a high-voltage input, typically 220V AC, to a lower-voltage output of 24V AC. This type of transformer is commonly used in industrial control systems, home automation, HVAC systems, and power supply design, providing a safer, lower voltage for devices and circuits.
Explore Projects Built with Power Transformer (220V to 24V)
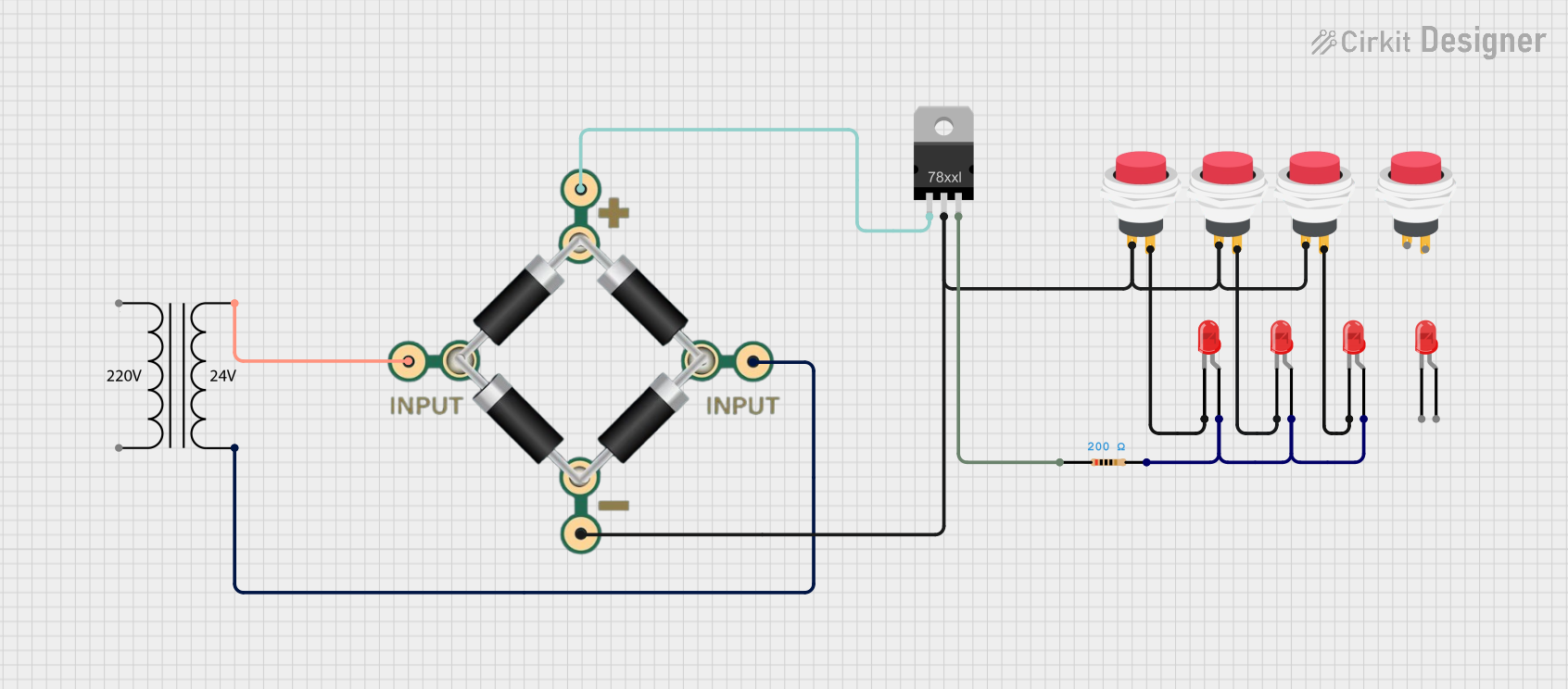
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer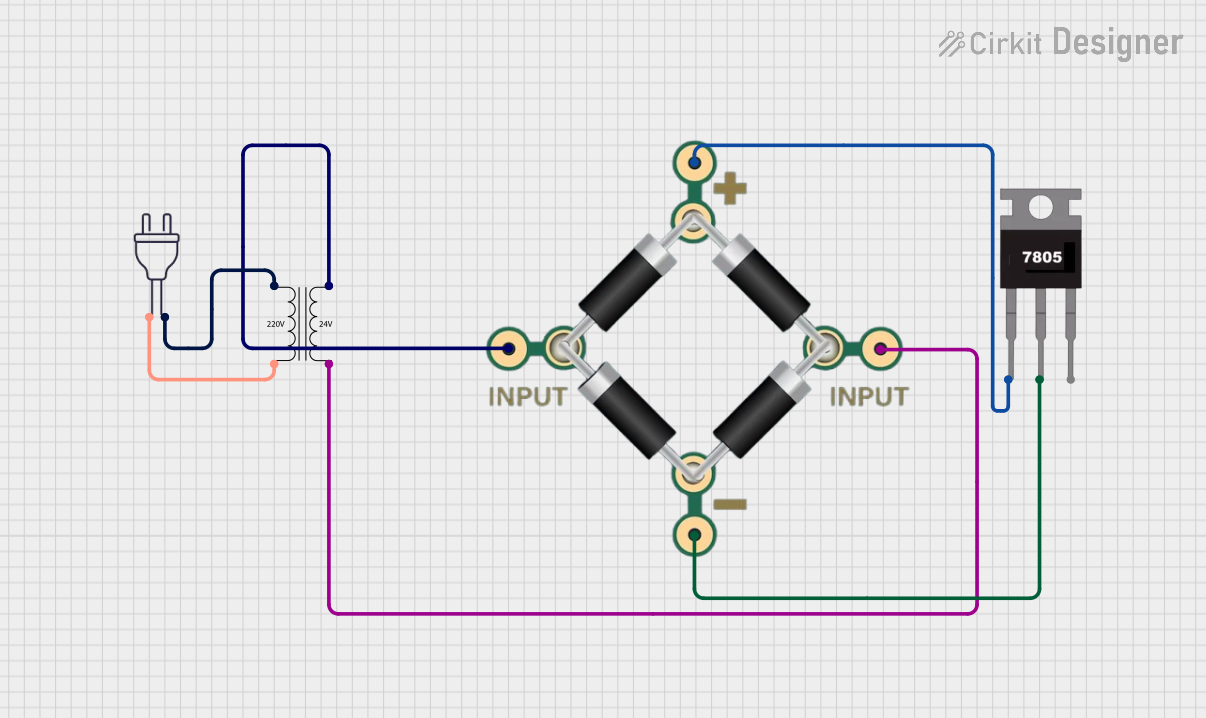
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer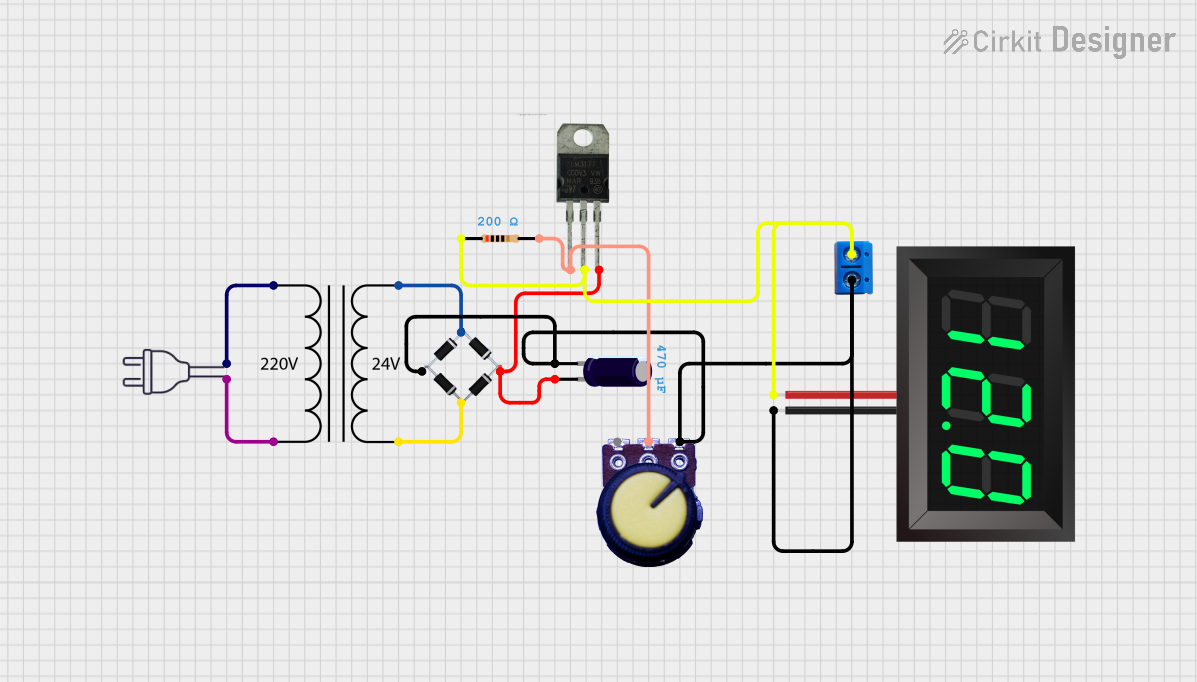
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer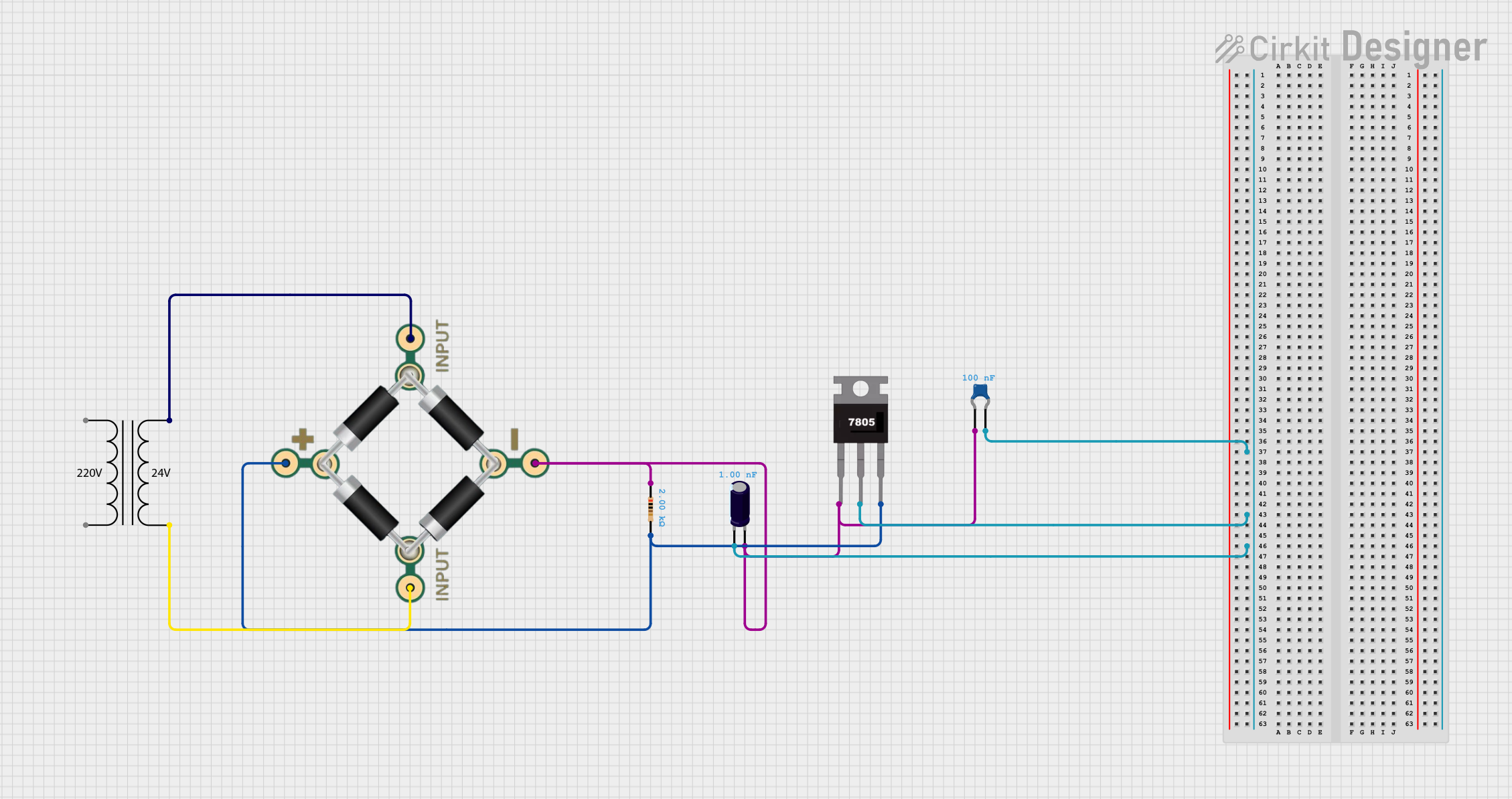
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Power Transformer (220V to 24V)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
General Characteristics
- Type: Step-down transformer
- Input Voltage: 220V AC
- Output Voltage: 24V AC
- Frequency: 50/60 Hz
- Phase: Single
- Insulation Class: Class B (130°C)
- Cooling Type: Air Natural (AN)
- Mounting Type: Chassis mount
Electrical Ratings
- Rated Power: 100VA (Volt-Ampere)
- Maximum Current: Approximately 4.17A at full load
- Temperature Rise: Typically <85°C under full load
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Primary winding (P1) | Connect to 220V AC phase |
| 2 | Primary winding (P2) | Connect to 220V AC neutral |
| 3 | Secondary winding (S1) | Connect to circuit or load (+) |
| 4 | Secondary winding (S2) | Connect to circuit or load (-) |
Usage Instructions
Integration into a Circuit
- Mounting: Secure the transformer to a chassis or enclosure, ensuring adequate ventilation for cooling.
- Primary Connection: Connect the primary winding pins (P1 and P2) to the 220V AC power source. Ensure that the connections are insulated and comply with local electrical codes.
- Secondary Connection: Connect the secondary winding pins (S1 and S2) to the circuit or load that requires 24V AC. Use appropriate wire gauge to handle the expected current draw.
- Grounding: Properly ground the transformer's core and enclosure to prevent shock hazards and electrical noise.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Safety: Always disconnect power before making connections to the transformer.
- Fuse Protection: Incorporate a fuse on the primary side to protect against overcurrent conditions.
- Isolation: Maintain isolation between the primary and secondary circuits to prevent electrical shock.
- Load Matching: Ensure that the connected load does not exceed the transformer's rated power and current specifications.
- Heat Management: Allow for adequate air circulation around the transformer to dissipate heat.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
- Overheating: Ensure proper ventilation and check for overloading. Reduce the load if necessary.
- No Output Voltage: Verify input connections, check for blown fuses, and ensure that the primary voltage is present.
- Unexpected Voltage Levels: Confirm that the load matches the transformer's specifications. Check for wiring errors or short circuits.
FAQs
Q: Can this transformer be used with a rectifier to provide DC output? A: Yes, the AC output can be rectified to DC using a bridge rectifier followed by a filter capacitor and voltage regulator as needed.
Q: Is it possible to adjust the output voltage of the transformer? A: The output voltage is fixed based on the turns ratio. To adjust the voltage, a variable transformer (variac) on the input side or a buck/boost transformer on the output side is required.
Q: What should I do if the transformer makes a humming noise? A: A slight humming is normal due to magnetostriction. However, if the noise is excessive, check for loose mounting or core laminations, and ensure the load is not exceeding the transformer's rating.
Q: Can this transformer be used for international voltages? A: This specific model is designed for 220V AC input. For other voltages, a transformer with the appropriate input rating should be used.
Please note that this documentation is for informational purposes only and should be adapted to specific applications and local regulations. Always consult a professional electrician or engineer when working with high-voltage equipment.