
How to Use E220-900T22D LoRa Wireless UART Module RSSI ISM 868MHz 915MHz 22dBm Module LoRa Spread Spectrum UART Interface SMA-K Antenna: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
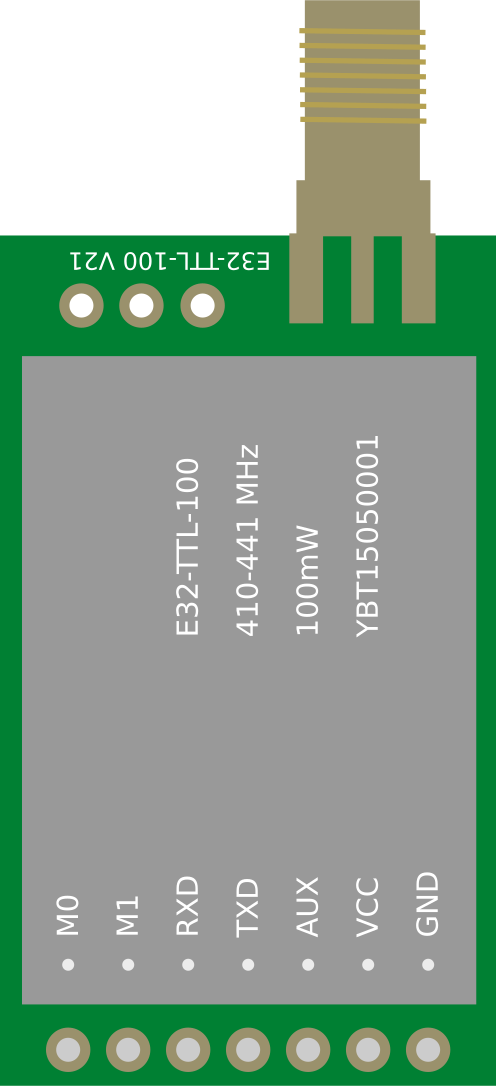
 Design with E220-900T22D LoRa Wireless UART Module RSSI ISM 868MHz 915MHz 22dBm Module LoRa Spread Spectrum UART Interface SMA-K Antenna in Cirkit Designer
Design with E220-900T22D LoRa Wireless UART Module RSSI ISM 868MHz 915MHz 22dBm Module LoRa Spread Spectrum UART Interface SMA-K Antenna in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The E220-900T22D is a high-performance LoRa (Long Range) wireless UART module designed for low-power, long-distance communication. Operating in the ISM frequency bands of 868MHz and 915MHz, this module supports a maximum transmission power of 22dBm and utilizes LoRa spread spectrum technology to achieve robust and reliable communication over extended distances. It features an SMA-K antenna interface for enhanced signal quality and is ideal for applications requiring low power consumption and long-range connectivity.
Explore Projects Built with E220-900T22D LoRa Wireless UART Module RSSI ISM 868MHz 915MHz 22dBm Module LoRa Spread Spectrum UART Interface SMA-K Antenna
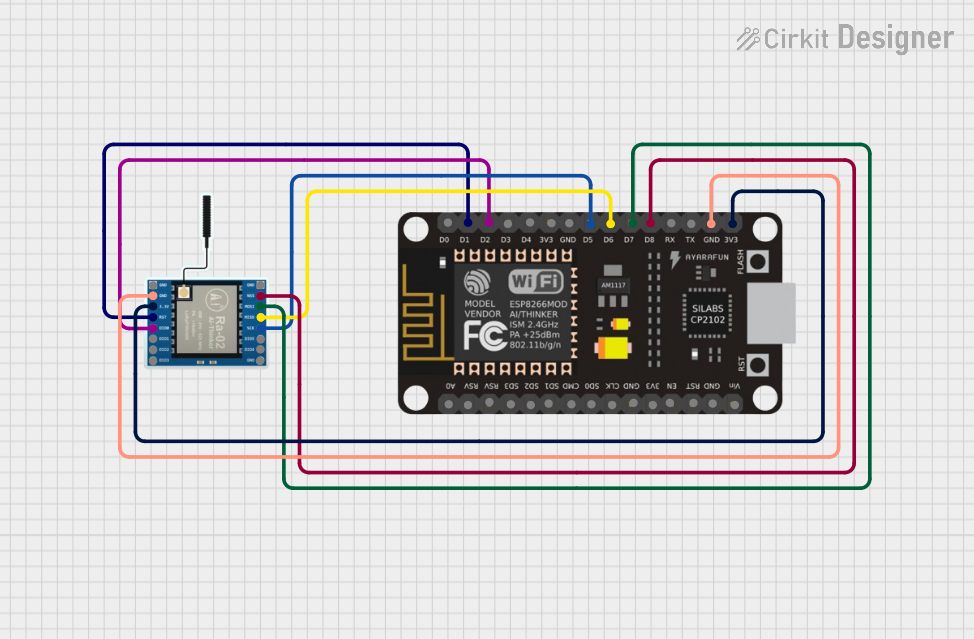
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer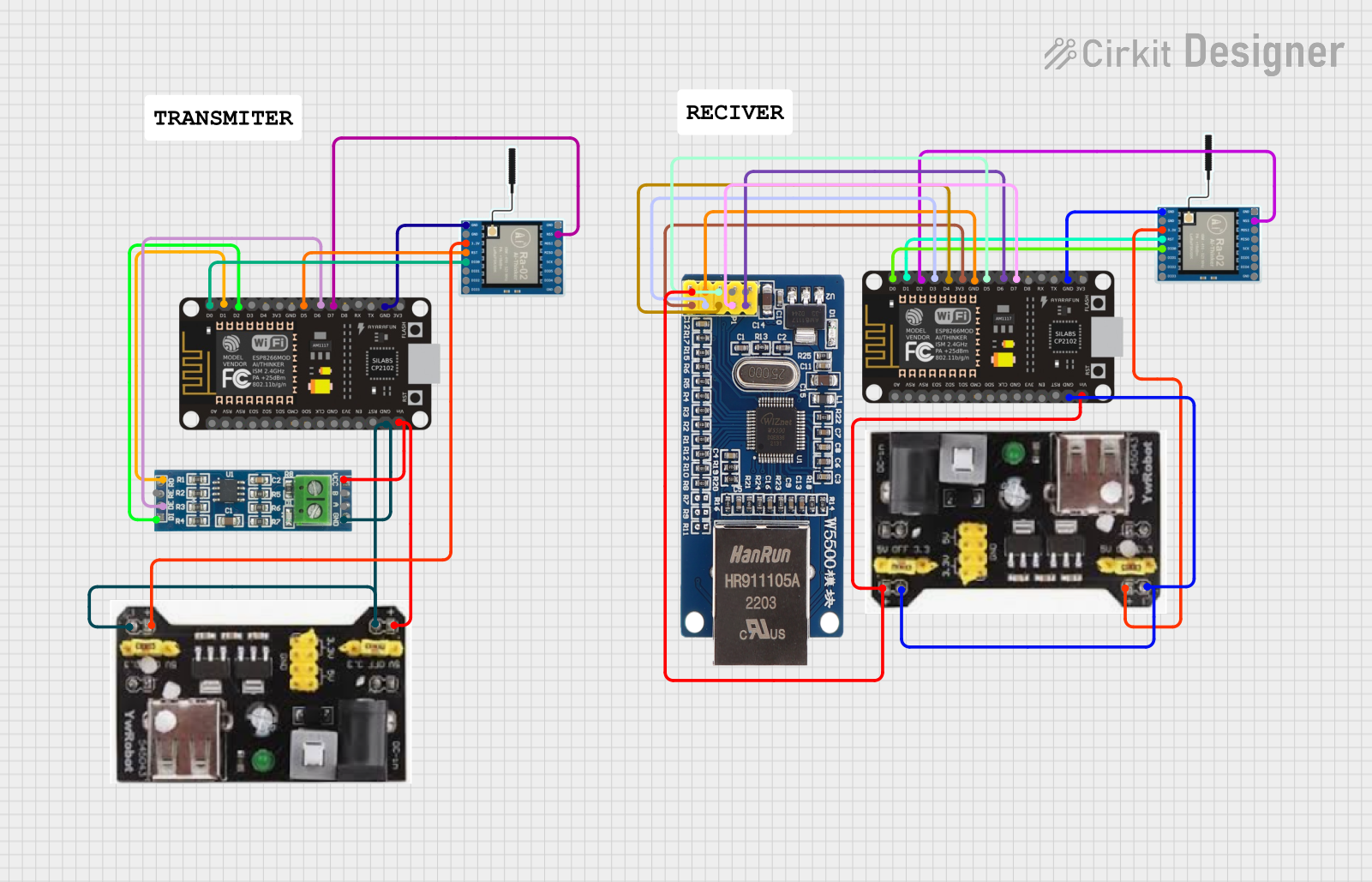
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer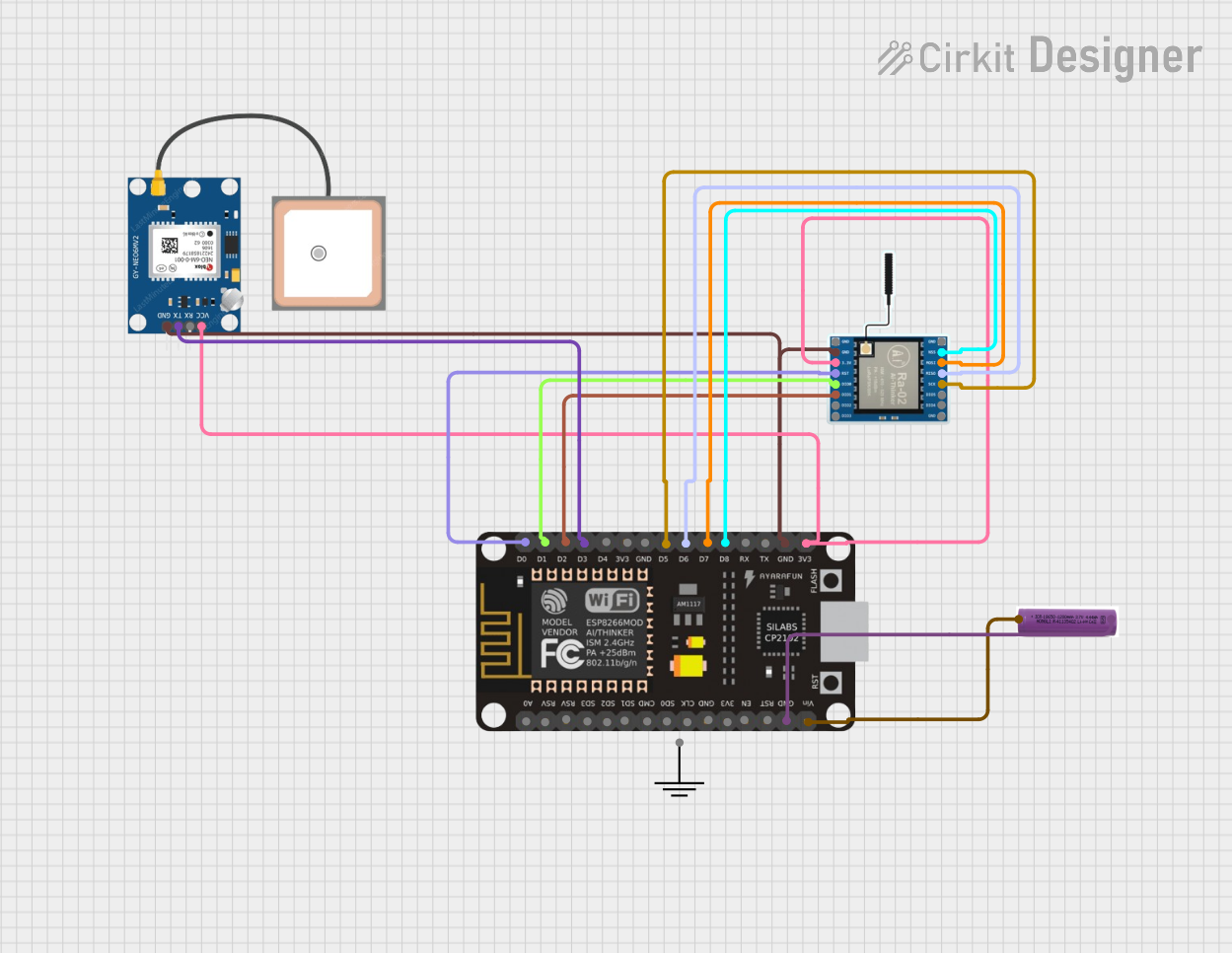
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer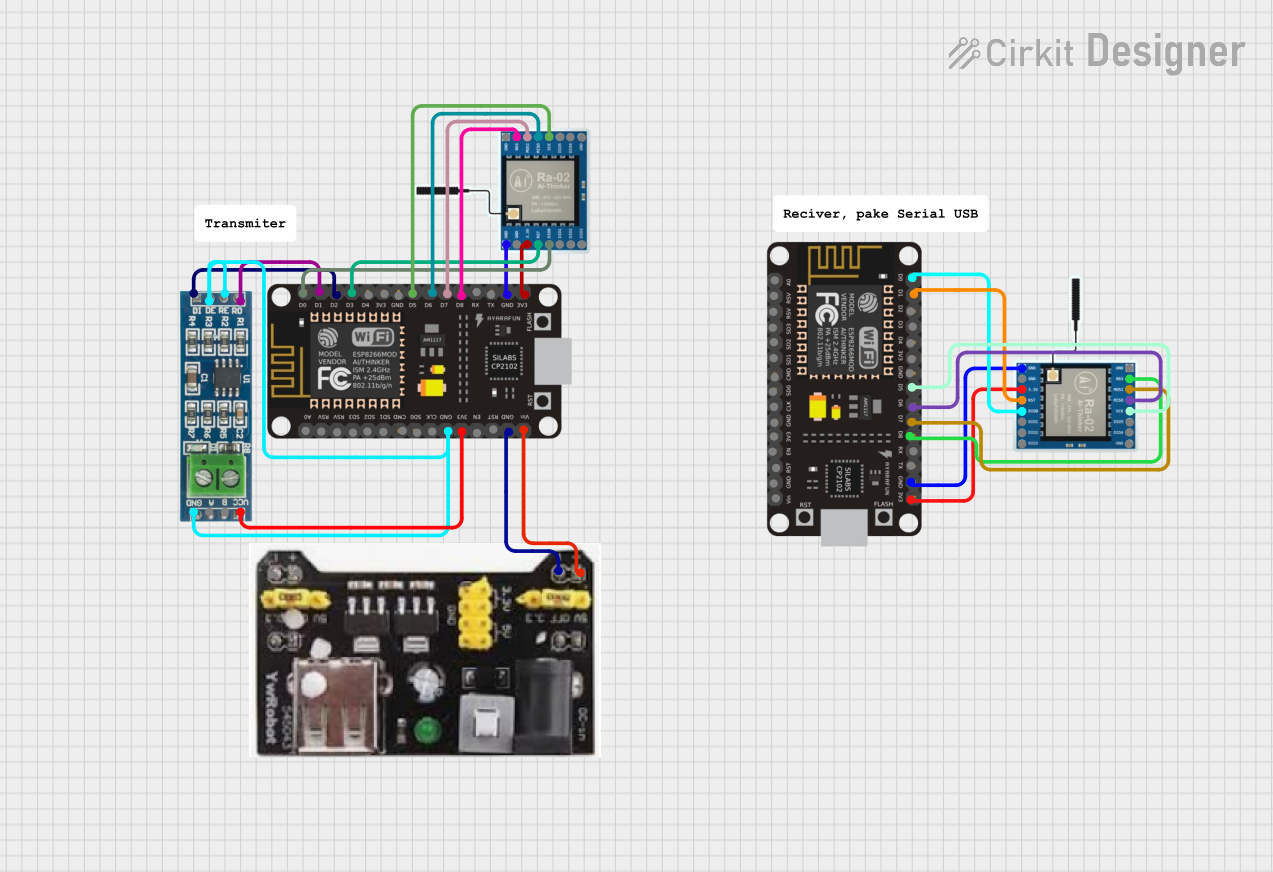
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with E220-900T22D LoRa Wireless UART Module RSSI ISM 868MHz 915MHz 22dBm Module LoRa Spread Spectrum UART Interface SMA-K Antenna

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- Smart agriculture and environmental monitoring
- Industrial automation and control systems
- Wireless sensor networks
- Remote data acquisition and telemetry
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 868MHz / 915MHz (ISM Band) |
| Modulation Technique | LoRa Spread Spectrum |
| Transmission Power | Up to 22dBm (160mW) |
| Communication Interface | UART (TTL Level) |
| Operating Voltage | 2.8V to 5.5V |
| Operating Current | 120mA (max) @ 22dBm |
| Sleep Current | < 2µA |
| Sensitivity | -139dBm @ 0.3kbps |
| Data Rate | 0.3kbps to 19.2kbps |
| Antenna Interface | SMA-K Connector |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 24mm x 43mm x 3mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | M0 | Mode selection pin (used to configure operating modes) |
| 2 | M1 | Mode selection pin (used to configure operating modes) |
| 3 | RXD | UART Receive Data (connect to TXD of the host microcontroller) |
| 4 | TXD | UART Transmit Data (connect to RXD of the host microcontroller) |
| 5 | AUX | Auxiliary pin (indicates module status, e.g., busy or idle) |
| 6 | VCC | Power supply input (2.8V to 5.5V) |
| 7 | GND | Ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the E220-900T22D in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a stable power source (2.8V to 5.5V) and the GND pin to ground.
- UART Connection: Connect the RXD pin of the module to the TXD pin of the host microcontroller and the TXD pin of the module to the RXD pin of the host microcontroller.
- Mode Selection: Use the M0 and M1 pins to configure the module's operating mode:
- Mode 0 (Normal Mode): M0 = 0, M1 = 0
- Mode 1 (Wake-up Mode): M0 = 1, M1 = 0
- Mode 2 (Power-saving Mode): M0 = 0, M1 = 1
- Mode 3 (Configuration Mode): M0 = 1, M1 = 1
- Antenna Connection: Attach an SMA-K antenna to the antenna interface for optimal signal transmission and reception.
- Data Transmission: Send and receive data via the UART interface. Ensure the baud rate and other UART settings match between the module and the host device.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use a high-quality SMA antenna to maximize range and signal quality.
- Avoid placing the module near sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI) to ensure stable communication.
- Configure the module's parameters (e.g., frequency, data rate) using AT commands in Configuration Mode.
- Ensure proper decoupling capacitors are placed near the VCC pin to stabilize the power supply.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and use the E220-900T22D with an Arduino UNO:
Wiring Diagram
| E220-900T22D Pin | Arduino UNO Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| RXD | D3 |
| TXD | D2 |
| M0 | D4 |
| M1 | D5 |
| AUX | Not Connected |
Arduino Code Example
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial LoRaSerial(2, 3); // RX = D2, TX = D3
// Define mode control pins
const int M0 = 4;
const int M1 = 5;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600); // For debugging
LoRaSerial.begin(9600); // For communication with E220-900T22D
// Set mode control pins as outputs
pinMode(M0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(M1, OUTPUT);
// Set module to Normal Mode (M0 = 0, M1 = 0)
digitalWrite(M0, LOW);
digitalWrite(M1, LOW);
Serial.println("E220-900T22D Initialized in Normal Mode");
}
void loop() {
// Send data to the module
LoRaSerial.println("Hello, LoRa!");
// Check for incoming data from the module
if (LoRaSerial.available()) {
String receivedData = LoRaSerial.readString();
Serial.print("Received: ");
Serial.println(receivedData);
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before sending the next message
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication Between Devices
- Ensure the RXD and TXD pins are correctly connected to the host microcontroller.
- Verify that the UART baud rate and settings (e.g., parity, stop bits) match between the module and the host.
Short Communication Range
- Check the antenna connection and ensure it is securely attached.
- Avoid obstructions or interference sources in the communication path.
Module Not Responding to AT Commands
- Ensure the module is in Configuration Mode (M0 = 1, M1 = 1).
- Verify the power supply voltage is within the specified range.
High Power Consumption
- Use Power-saving Mode (M0 = 0, M1 = 1) to reduce power consumption during idle periods.
FAQs
Q: Can the module operate at 3.3V?
A: Yes, the module supports a wide operating voltage range of 2.8V to 5.5V.Q: What is the maximum communication distance?
A: The maximum range depends on environmental conditions but can reach up to 5km in open areas with a clear line of sight.Q: How do I reset the module?
A: Toggle the power supply or use the AUX pin to monitor the module's status during reset.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the E220-900T22D module effectively. For further assistance, refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or support resources.