
How to Use AD5933 Dev Board: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
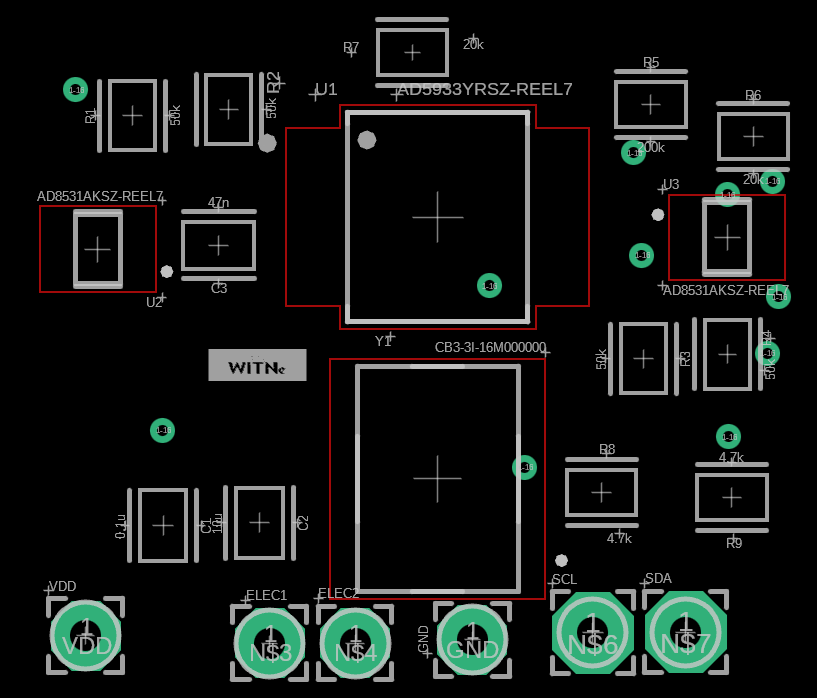
 Design with AD5933 Dev Board in Cirkit Designer
Design with AD5933 Dev Board in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The AD5933 Dev Board, manufactured by WitNe, is a development platform built around the AD5933 integrated circuit. The AD5933 is a high-precision impedance converter that simplifies the process of measuring and analyzing impedance across a wide frequency range. This development board is designed to help users evaluate and prototype applications involving impedance spectroscopy, such as material characterization, bio-impedance analysis, and sensor development.
Explore Projects Built with AD5933 Dev Board
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer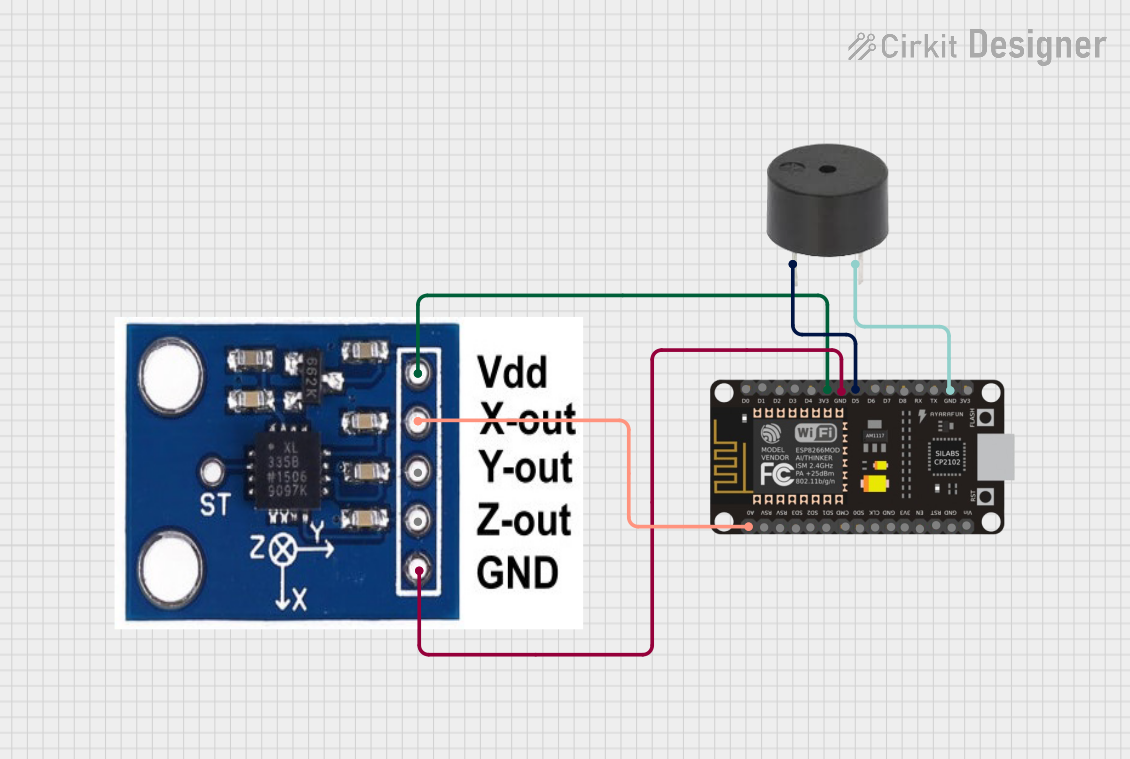
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with AD5933 Dev Board

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Bio-impedance analysis for medical devices
- Material property characterization
- Corrosion monitoring in industrial systems
- Liquid and gas sensor development
- Dielectric spectroscopy
- Research and development in impedance-based systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Integrated Circuit: AD5933 (Impedance Converter with Programmable Frequency Generator)
- Frequency Range: 1 kHz to 100 kHz (programmable)
- Impedance Measurement Range: 1 kΩ to 10 MΩ (depending on external components)
- Power Supply Voltage: 3.3V or 5V (selectable via jumper)
- Communication Interface: I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit)
- Onboard Oscillator: 16 MHz crystal oscillator
- PCB Dimensions: 50 mm x 50 mm
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The AD5933 Dev Board features a set of pins for power, communication, and signal connections. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power Input | Power supply input (3.3V or 5V, depending on jumper configuration). |
| GND | Power Ground | Ground connection. |
| SDA | I²C Data Line | Serial data line for I²C communication. |
| SCL | I²C Clock Line | Serial clock line for I²C communication. |
| VIN | Analog Input | Input for the signal to be measured (connect to the impedance network). |
| VOUT | Analog Output | Output signal generated by the AD5933 for impedance measurement. |
| RESET | Digital Input | Resets the AD5933 IC. |
| INT | Digital Output | Interrupt signal output (optional, for advanced configurations). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source, depending on the jumper configuration.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your power supply.
Connecting to a Microcontroller:
- Use the SDA and SCL pins to connect the board to the I²C interface of your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO).
- Ensure proper pull-up resistors (typically 4.7 kΩ) are present on the I²C lines if not already included on the board.
Impedance Measurement:
- Connect the impedance network (e.g., resistor, capacitor, or inductor) to the VIN and VOUT pins.
- Configure the AD5933 IC using I²C commands to set the frequency range, gain factor, and other parameters.
Reading Data:
- Use the I²C interface to read the real and imaginary components of the impedance.
- Calculate the impedance magnitude and phase using the formula:
- Magnitude = √(Real² + Imaginary²)
- Phase = arctan(Imaginary / Real)
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Calibration: Always calibrate the AD5933 using a known reference impedance before taking measurements to ensure accuracy.
- Frequency Range: Ensure the selected frequency range is appropriate for the impedance network being measured.
- Signal Integrity: Use short and shielded cables for connections to minimize noise and signal degradation.
- Power Supply: Use a stable and noise-free power supply to avoid interference in measurements.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example Arduino sketch to interface with the AD5933 Dev Board via I²C:
#include <Wire.h>
// AD5933 I²C address
#define AD5933_ADDR 0x0D
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I²C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Initialize AD5933
if (!initializeAD5933()) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize AD5933!");
while (1); // Halt execution if initialization fails
}
Serial.println("AD5933 initialized successfully.");
}
void loop() {
// Example: Read temperature from AD5933
float temperature = readTemperature();
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" °C");
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
// Function to initialize the AD5933
bool initializeAD5933() {
Wire.beginTransmission(AD5933_ADDR);
Wire.write(0x80); // Address of the control register
Wire.write(0x10); // Set to standby mode
return (Wire.endTransmission() == 0); // Return true if successful
}
// Function to read temperature from AD5933
float readTemperature() {
Wire.beginTransmission(AD5933_ADDR);
Wire.write(0x92); // Address of the temperature register
Wire.endTransmission(false); // Send repeated start
Wire.requestFrom(AD5933_ADDR, 2); // Request 2 bytes of data
if (Wire.available() < 2) {
return -273.15; // Return an error value if data is unavailable
}
int16_t rawTemp = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Combine MSB and LSB
return rawTemp / 32.0; // Convert to Celsius
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication with the AD5933:
- Cause: Incorrect I²C wiring or address mismatch.
- Solution: Verify SDA and SCL connections. Ensure the I²C address matches the AD5933's default (0x0D).
Inaccurate Impedance Measurements:
- Cause: Improper calibration or incorrect gain factor.
- Solution: Perform calibration using a known reference impedance and verify the gain factor settings.
High Noise in Measurements:
- Cause: Poor signal integrity or noisy power supply.
- Solution: Use shielded cables and a stable power source. Minimize external interference.
Temperature Readings Seem Incorrect:
- Cause: Faulty I²C communication or incorrect register access.
- Solution: Double-check the I²C commands and ensure proper initialization of the AD5933.
FAQs
Q: Can the AD5933 Dev Board measure DC impedance?
A: No, the AD5933 is designed for AC impedance measurements only.Q: What is the maximum impedance range the board can measure?
A: The range depends on the external components but typically spans from 1 kΩ to 10 MΩ.Q: Is the board compatible with 5V logic microcontrollers?
A: Yes, the board supports both 3.3V and 5V logic levels, configurable via a jumper.Q: Can I use the board for bio-impedance analysis?
A: Yes, the AD5933 is suitable for bio-impedance applications, but ensure proper safety measures are in place.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the AD5933 Dev Board effectively. For further assistance, refer to the AD5933 datasheet or contact WitNe support.