
How to Use Type C USB Port: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
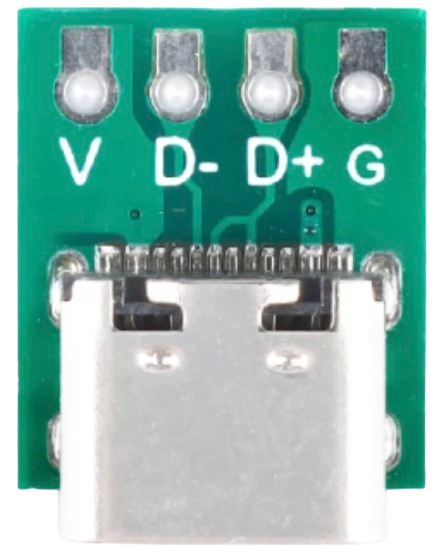

 Design with Type C USB Port in Cirkit Designer
Design with Type C USB Port in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Type C USB Port is a versatile and reversible connector designed for modern electronic devices. It supports faster data transfer rates, higher power delivery, and improved durability compared to its predecessors (USB Type-A and Type-B). Its symmetrical design eliminates orientation issues, making it user-friendly and reliable.
Explore Projects Built with Type C USB Port
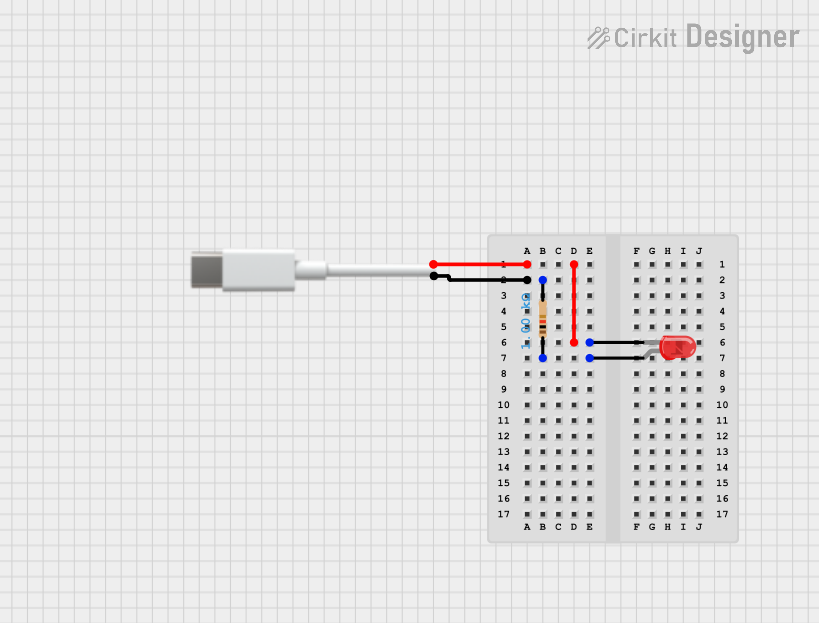
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer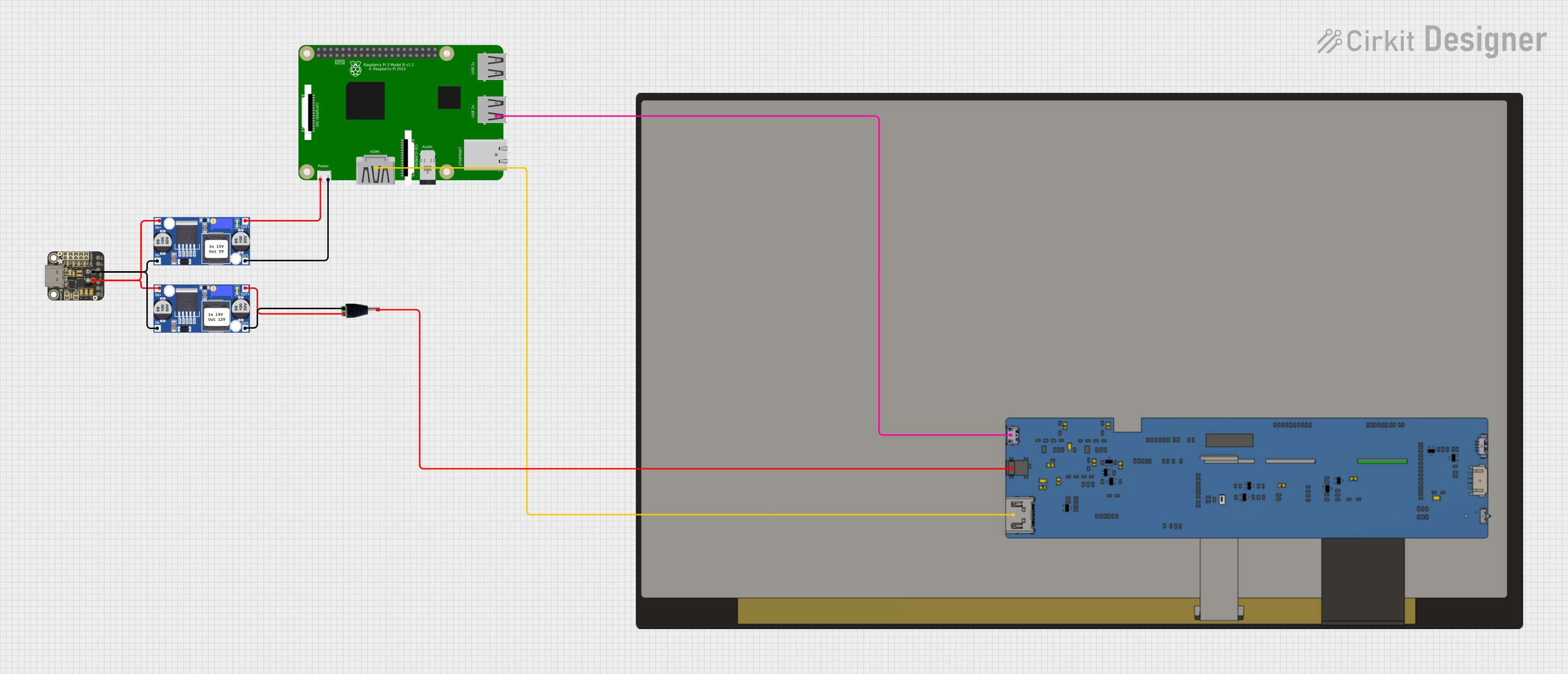
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer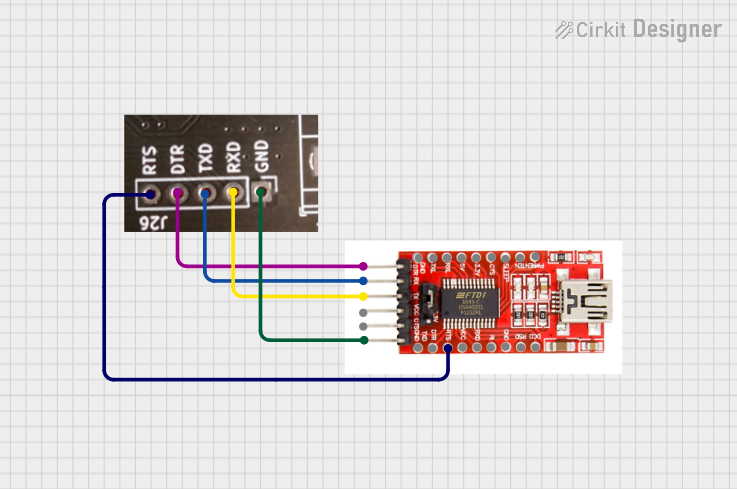
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Type C USB Port

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Smartphones and Tablets: Charging and data transfer.
- Laptops and Desktops: Connecting peripherals, external storage, and displays.
- Power Delivery: Supporting up to 100W for fast charging of devices.
- Audio and Video Transmission: Compatible with HDMI, DisplayPort, and Thunderbolt standards.
- IoT Devices: Powering and interfacing with smart devices.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Connector Type: USB Type-C
- Data Transfer Rates: Up to 10 Gbps (USB 3.1 Gen 2) or 40 Gbps (Thunderbolt 3/4)
- Power Delivery: Up to 100W (20V, 5A) with USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) protocol
- Reversibility: Symmetrical design for easy insertion
- Durability: Rated for 10,000+ insertion/removal cycles
- Backward Compatibility: Supports USB 2.0, 3.0, and 3.1 standards with appropriate adapters
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Type C USB Port has 24 pins, divided into two symmetrical rows. Below is a simplified pinout:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A1, B1 | GND | Ground |
| A4, B4 | VBUS | Power supply (up to 20V, 5A) |
| A5, B5 | CC1, CC2 | Configuration channel for cable orientation and power |
| A6, B6 | D+ | USB 2.0 differential pair (positive) |
| A7, B7 | D- | USB 2.0 differential pair (negative) |
| A8, B8 | SBU1, SBU2 | Sideband use for alternate modes (e.g., audio/video) |
| A2, A3, B2, B3 | TX+/TX-, RX+/RX- | High-speed differential pairs for USB 3.1/Thunderbolt |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Type C USB Port in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure the VBUS pin is connected to a regulated power source. For USB-PD, use a compatible controller to negotiate power levels.
- Data Lines: Connect the D+ and D- pins for USB 2.0 communication. For USB 3.1 or higher, connect the TX/RX differential pairs.
- Configuration Channel (CC): Use the CC pins to detect cable orientation and negotiate power delivery. A pull-up or pull-down resistor is typically required.
- Alternate Modes: For video or other protocols, configure the SBU pins and high-speed lanes accordingly.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Regulation: Use a USB-PD controller IC to safely manage power delivery.
- Cable Quality: Ensure the cable supports the required data rate and power level.
- Overcurrent Protection: Add fuses or current-limiting ICs to protect the circuit.
- Signal Integrity: Use proper PCB layout techniques to minimize noise and interference on high-speed data lines.
- Reversibility: Design the circuit to handle both orientations of the connector.
Example: Connecting a Type C USB Port to an Arduino UNO
While the Arduino UNO does not natively support USB Type-C, you can use a USB Type-C breakout board for power or data communication. Below is an example of using the Type-C port for power:
// Example: Powering an Arduino UNO via USB Type-C
// Ensure the Type-C breakout board is connected to the Arduino's VIN and GND pins.
// This setup allows the Arduino to be powered by a USB Type-C power source.
void setup() {
// No specific setup required for power-only connections
}
void loop() {
// Your main code here
}
For data communication, additional USB-to-serial converters or USB host shields may be required.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Device Not Recognized:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring of data lines or missing pull-up/pull-down resistors on CC pins.
- Solution: Verify connections and ensure proper resistor values are used.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor thermal management.
- Solution: Check power delivery settings and ensure adequate heat dissipation.
No Power Delivery:
- Cause: Incompatible cable or missing USB-PD controller.
- Solution: Use a certified USB Type-C cable and implement a USB-PD controller IC.
Data Transfer Issues:
- Cause: Signal integrity problems or incompatible devices.
- Solution: Use high-quality cables and ensure proper PCB layout for high-speed signals.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a Type C USB Port for both power and data simultaneously?
A: Yes, the Type C USB Port is designed to handle both power delivery and data transfer simultaneously.Q: Do I need a special cable for USB Power Delivery?
A: Yes, ensure the cable is USB-PD certified to support higher power levels.Q: How do I implement alternate modes like HDMI or DisplayPort?
A: Use a compatible controller IC to configure the SBU and high-speed pins for the desired protocol.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and troubleshoot the Type C USB Port in your projects.