
How to Use 74HC595 Shift Register Breakout 8 Bit Shift Register: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
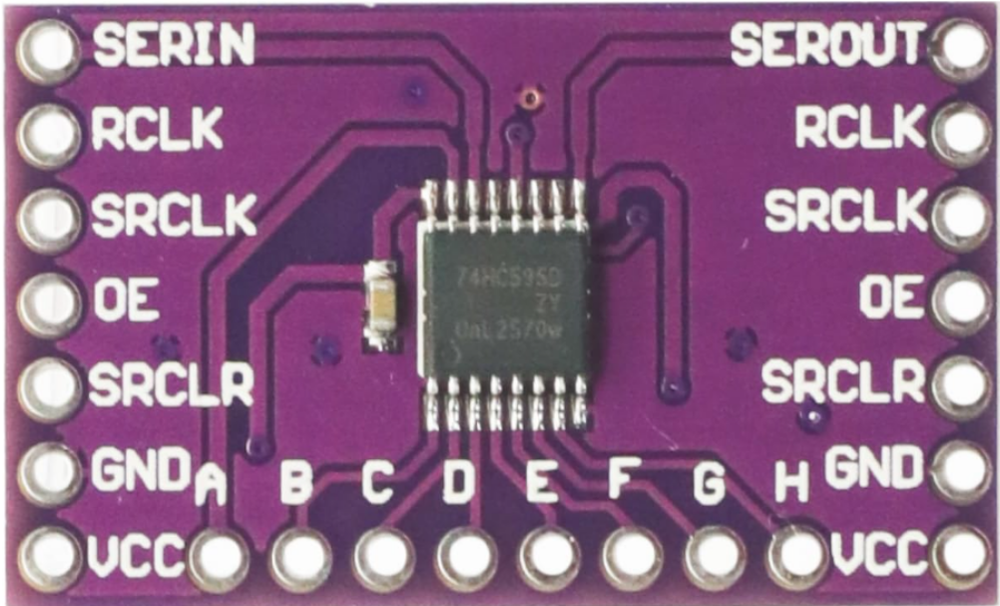
 Design with 74HC595 Shift Register Breakout 8 Bit Shift Register in Cirkit Designer
Design with 74HC595 Shift Register Breakout 8 Bit Shift Register in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 74HC595 Shift Register Breakout (Manufacturer: CJMCU, Part ID: CJMCU-595) is an 8-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift register. It is designed to expand the number of output pins available on microcontrollers, such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or other embedded systems. By using a serial data input, the 74HC595 allows you to control up to 8 output pins with just 3 control pins from your microcontroller. This makes it an ideal solution for applications requiring multiple outputs, such as LED displays, motor drivers, or other digital control systems.
Explore Projects Built with 74HC595 Shift Register Breakout 8 Bit Shift Register
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer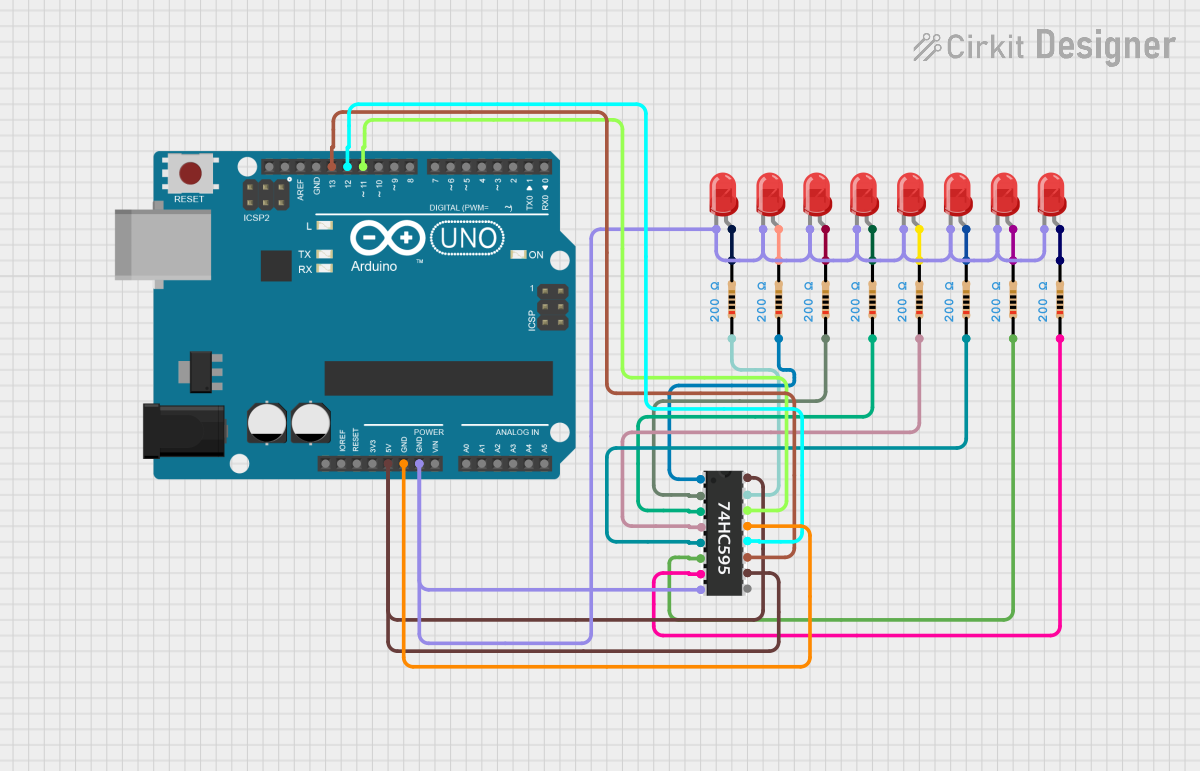
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer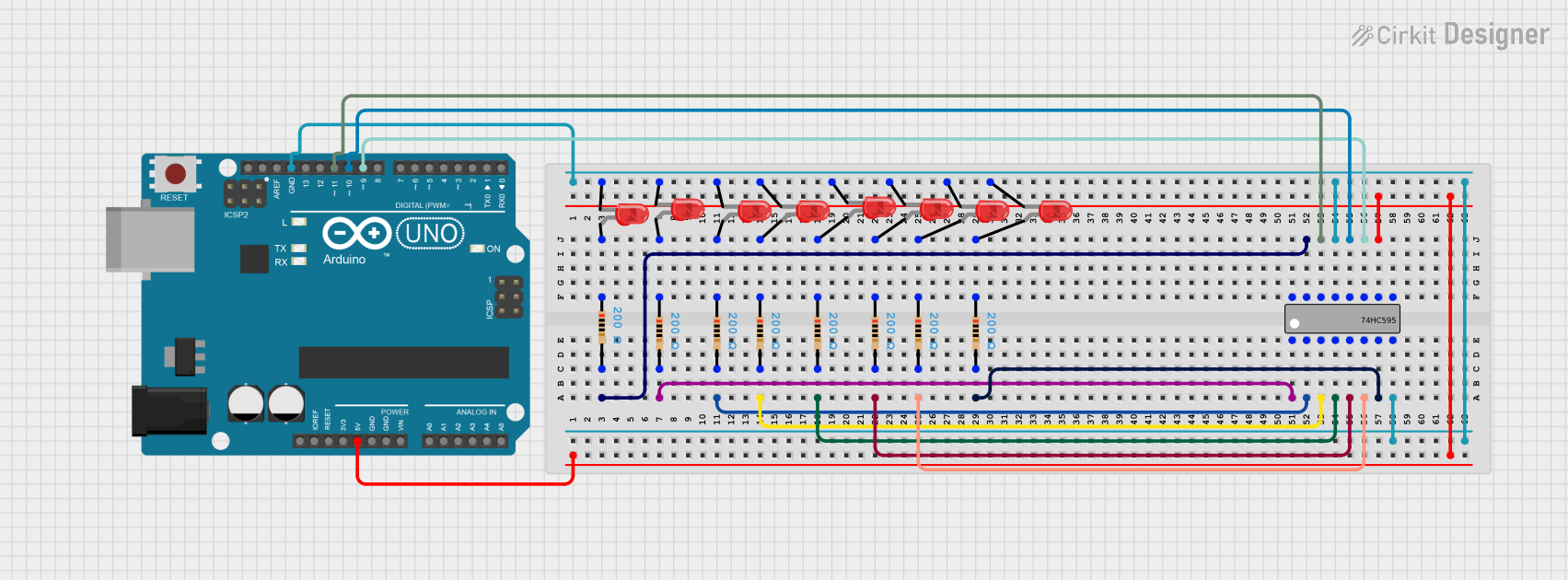
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 74HC595 Shift Register Breakout 8 Bit Shift Register

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Driving LED arrays or 7-segment displays
- Controlling relays or motors
- Expanding GPIO pins on microcontrollers
- Digital signal multiplexing
- Building custom digital logic circuits
Technical Specifications
The following are the key technical details of the CJMCU-595:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 2V to 6V |
| Input Voltage (VI) | 0V to Vcc |
| Output Current (IO) | ±35mA per pin |
| Maximum Clock Frequency | 25 MHz (at 5V supply) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Package Type | Breakout board with 74HC595 IC |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The CJMCU-595 breakout board has the following pinout:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Vcc | 16 | Power supply pin (2V to 6V). Connect to the microcontroller's 5V or 3.3V pin. |
| GND | 8 | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the microcontroller. |
| SER (DS) | 14 | Serial data input. Used to send data to the shift register. |
| SRCLK | 11 | Shift register clock input. Data is shifted on the rising edge of this clock. |
| RCLK | 12 | Latch clock input. Transfers data from the shift register to the output pins. |
| OE (Output Enable) | 13 | Active-low output enable. Connect to GND to enable outputs. |
| Q0-Q7 | 15, 1-7 | Parallel output pins. These are the 8 output pins controlled by the register. |
| MR (Master Reset) | 10 | Active-low reset. Clears the shift register when pulled low. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Shift Register: Connect the Vcc pin to a 5V or 3.3V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Connect Control Pins:
- Connect the
SERpin to a digital output pin on your microcontroller for serial data input. - Connect the
SRCLKpin to a digital output pin for the shift register clock. - Connect the
RCLKpin to a digital output pin for the latch clock. - Optionally, connect the
OEpin to GND to enable outputs or to a microcontroller pin for dynamic control.
- Connect the
- Connect Outputs: Use the Q0-Q7 pins to drive LEDs, relays, or other devices. Add current-limiting resistors if necessary.
- Write Data: Send serial data to the shift register using the
SERpin, and use theSRCLKandRCLKpins to shift and latch the data.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting: Ensure that the total current drawn by the output pins does not exceed the IC's maximum rating. Use resistors for LEDs or other current-limiting components as needed.
- Decoupling Capacitor: Place a 0.1µF decoupling capacitor between Vcc and GND to stabilize the power supply.
- Daisy-Chaining: Multiple 74HC595 ICs can be daisy-chained to control more outputs. Connect the
Q7S(serial out) pin of one IC to theSERpin of the next IC.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to control the 74HC595 with an Arduino UNO to light up LEDs connected to the output pins.
// Define the control pins for the 74HC595
const int dataPin = 2; // SER pin (Serial Data Input)
const int clockPin = 3; // SRCLK pin (Shift Register Clock)
const int latchPin = 4; // RCLK pin (Latch Clock)
void setup() {
// Set the control pins as outputs
pinMode(dataPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(clockPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(latchPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Example: Light up LEDs in a binary counting pattern
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
digitalWrite(latchPin, LOW); // Disable latch to load data
shiftOut(dataPin, clockPin, MSBFIRST, i); // Send data to shift register
digitalWrite(latchPin, HIGH); // Enable latch to update outputs
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms
}
}
Explanation of the Code
- The
shiftOut()function sends 8 bits of data to the shift register, one bit at a time. - The
latchPinis toggled to transfer the data from the shift register to the output pins. - The loop cycles through values from 0 to 255, lighting up LEDs in a binary counting pattern.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Outputs Not Working:
- Ensure the
OEpin is connected to GND or properly controlled by the microcontroller. - Verify that the
RCLKpin is toggled after sending data to update the outputs.
- Ensure the
Flickering Outputs:
- Check for loose connections or unstable power supply. Add a decoupling capacitor if needed.
- Ensure the
SRCLKandRCLKsignals are not overlapping or noisy.
Incorrect Output States:
- Verify the data being sent to the shift register. Use a logic analyzer or debug the code.
- Ensure the
MRpin is not accidentally pulled low, as this will reset the register.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the 74HC595 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the 74HC595 operates with a supply voltage as low as 2V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems.
Q: How many 74HC595 ICs can I daisy-chain?
A: Theoretically, you can daisy-chain as many as you need, but practical limitations like signal degradation and timing constraints may arise after 8-10 ICs.
Q: Do I need pull-up or pull-down resistors for the control pins?
A: No, the control pins are internally pulled to a defined state. However, you may add resistors for noise immunity in noisy environments.
This concludes the documentation for the CJMCU-595 8-bit shift register.